| cmd/gost | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| chain.go | ||
| conn.go | ||
| forward.go | ||
| gost.go | ||
| http.go | ||
| kcp.go | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| node.go | ||
| quic.go | ||
| README_en.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| server.go | ||
| socks.go | ||
| ss.go | ||
| ws.go | ||
gost - GO Simple Tunnel
A simple security tunnel written in Golang
Features
- Listening on multiple ports
- Multi-level forward proxy - proxy chain
- Standard HTTP/HTTPS/SOCKS5 proxy protocols support
- TLS encryption via negotiation support for SOCKS5 proxy
- Tunnel UDP over TCP
- Shadowsocks protocol support (OTA: 2.2+)
- Local/remote port forwarding (2.1+)
- HTTP 2.0 support (2.2+)
- Experimental QUIC support (2.3+)
- KCP protocol support (2.3+)
Binary file download:https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases
Google group: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/go-gost
Gost and other proxy services are considered to be proxy nodes, gost can handle the request itself, or forward the request to any one or more proxy nodes.
Parameter Description
Proxy and proxy chain
Effective for the -L and -F parameters
[scheme://][user:pass@host]:port
scheme can be divided into two parts: protocol+transport
protocol: proxy protocol types (http, socks5, shadowsocks), transport: data transmission mode (ws, wss, tls, http2, quic, kcp), may be used in any combination or individually:
http - standard HTTP proxy: http://:8080
http+tls - standard HTTPS proxy (may need to provide a trusted certificate): http+tls://:443
http2 - HTTP2 proxy and backwards-compatible with HTTPS proxy: http2://:443
socks - standard SOCKS5 proxy: socks://:1080
socks+wss - SOCKS5 over websocket: socks+wss://:1080
tls - HTTPS/SOCKS5 over tls: tls://:443
ss - standard shadowsocks proxy, ss://aes-256-cfb:123456@:8338
quic - standard QUIC proxy, quic://:6121
kcp - standard KCP tunnel,kcp://:8388 or kcp://aes:123456@:8388
Port forwarding
Effective for the -L parameter
scheme://[bind_address]:port/[host]:hostport
scheme - forward mode, local: tcp, udp; remote: rtcp, rudp
bind_address:port - local/remote binding address
host:hostport - target address
Logging
-logtostderr : log to console
-v=3 : log level (1-5),The higher the level, the more detailed the log (level 5 will enable HTTP2 debug)
-log_dir=/log/dir/path : log to directory /log/dir/path
Usage
No forward proxy
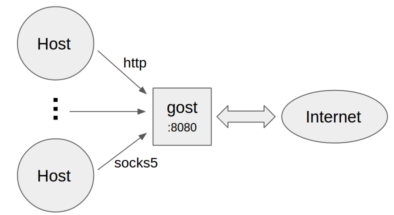
- Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
gost -L=:8080
- Proxy authentication
gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
- Listen on multiple ports
gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
Forward proxy
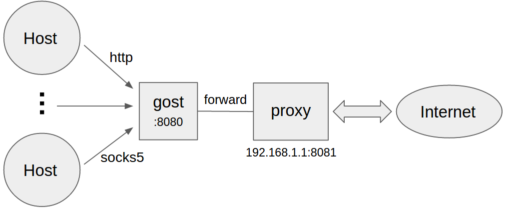 ```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
```
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
```
- Forward proxy authentication
gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
Multi-level forward proxy
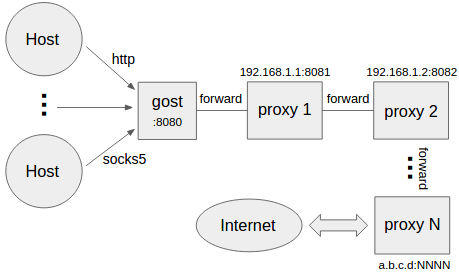 ```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
```
Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
```
Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
Local TCP port forwarding
gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=...
The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
Local UDP port forwarding
gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
NOTE: When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
Remote TCP port forwarding
gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
Remote UDP port forwarding
gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
NOTE: To use the remote port forwarding feature, the proxy chain can not be empty (at least one -F parameter is set) and the end of the chain (last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
HTTP2
Gost HTTP2 supports two modes and self-adapting:
- As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
- As transport (similar to wss), tunnel other protocol.
NOTE: The proxy chain of gost supports only one HTTP2 proxy node and the nearest rule applies, the first HTTP2 proxy node is treated as an HTTP2 proxy, and the other HTTP2 proxy nodes are treated as HTTPS proxies.
QUIC
Support for QUIC is based on library quic-go.
Server:
gost -L=quic://:6121
Client(Chrome):
chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
NOTE: Due to Chrome's limitations, it is currently only possible to access the HTTP (but not HTTPS) site through QUIC.
KCP
Support for KCP is based on libraries kcp-go and kcptun.
Server:
gost -L=kcp://:8388
Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388
Or manually specify the encryption method and password (Manually specifying the encryption method and password overwrites the corresponding value in the configuration file)
Server:
gost -L=kcp://aes:123456@:8388
Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://aes:123456@server_ip:8388
Gost will automatically load kcp.json configuration file from current working directory if exists, or you can use the parameter to specify the path to the file.
gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
NOTE: KCP will be enabled if and only if the proxy chain is not empty and the first proxy node (the first -F parameter) is of type KCP. When KCP is enabled, other proxy nodes are ignored.
Encryption Mechanism
HTTP
For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
Server:
gost -L=http+tls://:443
Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
HTTP2
Gost supports only the HTTP2 protocol that uses TLS encryption (h2) and does not support plaintext HTTP2 (h2c) transport.
Server:
gost -L=http2://:443
Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443
SOCKS5
Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02), and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80) and tls-auth(0x82).
Server:
gost -L=socks://:1080
Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
If both ends are gosts (as example above), the data transfer will be encrypted (using tls or tls-auth). Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
NOTE: If transport already supports encryption (wss, tls, http2), SOCKS5 will no longer use the encryption method to prevent unnecessary double encryption.
Shadowsocks
Support for shadowsocks is based on library shadowsocks-go.
Server (The OTA mode can be enabled by the ota parameter):
gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338?ota=1
Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
TLS
There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
- Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
- Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
No forward proxy
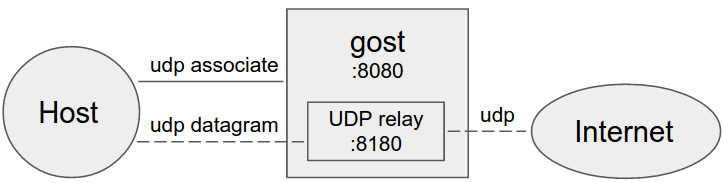
Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
Forward proxy
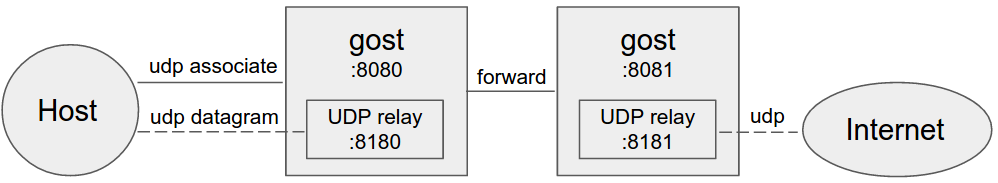
Multi-level forward proxy
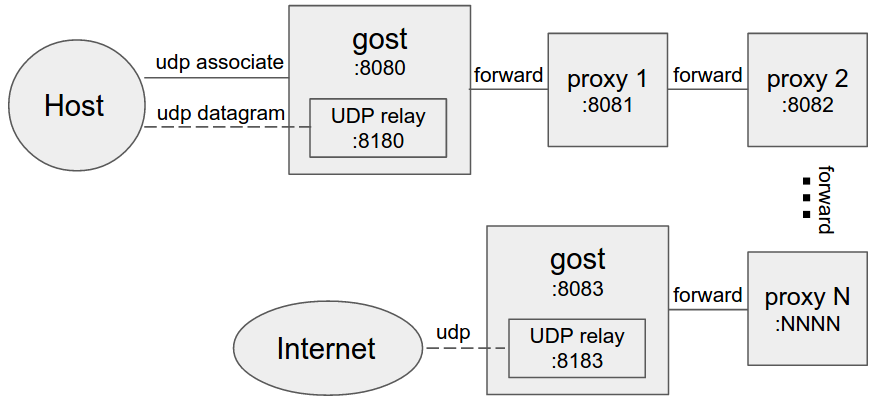
When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
Limitation
The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.