 +
+[](https://godoc.org/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go)
+[](https://travis-ci.org/lucas-clemente/quic-go)
+[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/lucas-clemente/quic-go/branch/master)
+[](https://codecov.io/gh/lucas-clemente/quic-go/)
+
+quic-go is an implementation of the [QUIC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QUIC) protocol in Go. While we're not far from being feature complete, there's still work to do regarding performance and security. At the moment, we do not recommend use in production systems. We appreciate any feedback :)
+
+## Roadmap
+
+Done:
+
+- Basic protocol with support for QUIC version 34-36
+- HTTP/2 support
+- Crypto (RSA / ECDSA certificates, Curve25519 for key exchange, AES-GCM or Chacha20-Poly1305 as stream cipher)
+- Loss detection and retransmission (currently fast retransmission & RTO)
+- Flow Control
+- Congestion control using cubic
+
+Major TODOs:
+
+- Security, especially DOS protections
+- Performance
+- Better packet loss detection
+- Connection migration
+- QUIC client
+
+## Guides
+
+Installing deps:
+
+ go get -t
+
+Running tests:
+
+ go test ./...
+
+Running the example server:
+
+ go run example/main.go -www /var/www/
+
+Using the `quic_client` from chromium:
+
+ quic_client --quic-version=32 --host=127.0.0.1 --port=6121 --v=1 https://quic.clemente.io
+
+Using Chrome:
+
+ /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome --user-data-dir=/tmp/chrome --no-proxy-server --enable-quic --origin-to-force-quic-on=quic.clemente.io:443 --host-resolver-rules='MAP quic.clemente.io:443 127.0.0.1:6121' https://quic.clemente.io
+
+## Usage
+
+See the [example server](example/main.go) or try out [Caddy](https://github.com/mholt/caddy) (from version 0.9, [instructions here](https://github.com/mholt/caddy/wiki/QUIC)). Starting a QUIC server is very similar to the standard lib http in go:
+
+```go
+http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.Dir(wwwDir)))
+h2quic.ListenAndServeQUIC("localhost:4242", "/path/to/cert/chain.pem", "/path/to/privkey.pem", nil)
+```
+
+## Building on Windows
+
+Due to the low Windows timer resolution (see [StackOverflow question](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/37706834/high-resolution-timers-millisecond-precision-in-go-on-windows)) available with Go 1.6.x, some optimizations might not work when compiled with this version of the compiler. Please use Go 1.7 on Windows.
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/_gen.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/_gen.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..154515b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/_gen.go
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+package main
+
+import (
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/linkedlist"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/slice"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/stringer"
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/interfaces.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/interfaces.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ee7ac59
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/interfaces.go
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// SentPacketHandler handles ACKs received for outgoing packets
+type SentPacketHandler interface {
+ SentPacket(packet *Packet) error
+ ReceivedAck(ackFrame *frames.AckFrame, withPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, recvTime time.Time) error
+
+ GetStopWaitingFrame(force bool) *frames.StopWaitingFrame
+
+ MaybeQueueRTOs()
+ DequeuePacketForRetransmission() (packet *Packet)
+
+ BytesInFlight() protocol.ByteCount
+ GetLeastUnacked() protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ SendingAllowed() bool
+ CheckForError() error
+
+ TimeOfFirstRTO() time.Time
+}
+
+// ReceivedPacketHandler handles ACKs needed to send for incoming packets
+type ReceivedPacketHandler interface {
+ ReceivedPacket(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) error
+ ReceivedStopWaiting(*frames.StopWaitingFrame) error
+
+ GetAckFrame(dequeue bool) (*frames.AckFrame, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6fe567c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet.go
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A Packet is a packet
+// +gen linkedlist
+type Packet struct {
+ PacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ Frames []frames.Frame
+ Length protocol.ByteCount
+
+ MissingReports uint8
+
+ SendTime time.Time
+}
+
+// GetStreamFramesForRetransmission gets all the streamframes for retransmission
+func (p *Packet) GetStreamFramesForRetransmission() []*frames.StreamFrame {
+ var streamFrames []*frames.StreamFrame
+ for _, frame := range p.Frames {
+ if streamFrame, isStreamFrame := frame.(*frames.StreamFrame); isStreamFrame {
+ streamFrames = append(streamFrames, streamFrame)
+ }
+ }
+ return streamFrames
+}
+
+// GetControlFramesForRetransmission gets all the control frames for retransmission
+func (p *Packet) GetControlFramesForRetransmission() []frames.Frame {
+ var controlFrames []frames.Frame
+ for _, frame := range p.Frames {
+ // omit ACKs
+ if _, isStreamFrame := frame.(*frames.StreamFrame); isStreamFrame {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ _, isAck := frame.(*frames.AckFrame)
+ _, isStopWaiting := frame.(*frames.StopWaitingFrame)
+ if !isAck && !isStopWaiting {
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, frame)
+ }
+ }
+ return controlFrames
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a827b21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+// Generated by: main
+// TypeWriter: linkedlist
+// Directive: +gen on Packet
+
+package ackhandler
+
+// List is a modification of http://golang.org/pkg/container/list/
+// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+// PacketElement is an element of a linked list.
+type PacketElement struct {
+ // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
+ // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
+ // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
+ // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
+ // element (l.Front()).
+ next, prev *PacketElement
+
+ // The list to which this element belongs.
+ list *PacketList
+
+ // The value stored with this element.
+ Value Packet
+}
+
+// Next returns the next list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketElement) Next() *PacketElement {
+ if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketElement) Prev() *PacketElement {
+ if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// PacketList represents a doubly linked list.
+// The zero value for PacketList is an empty list ready to use.
+type PacketList struct {
+ root PacketElement // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
+ len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
+}
+
+// Init initializes or clears list l.
+func (l *PacketList) Init() *PacketList {
+ l.root.next = &l.root
+ l.root.prev = &l.root
+ l.len = 0
+ return l
+}
+
+// NewPacketList returns an initialized list.
+func NewPacketList() *PacketList { return new(PacketList).Init() }
+
+// Len returns the number of elements of list l.
+// The complexity is O(1).
+func (l *PacketList) Len() int { return l.len }
+
+// Front returns the first element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketList) Front() *PacketElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.next
+}
+
+// Back returns the last element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketList) Back() *PacketElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.prev
+}
+
+// lazyInit lazily initializes a zero PacketList value.
+func (l *PacketList) lazyInit() {
+ if l.root.next == nil {
+ l.Init()
+ }
+}
+
+// insert inserts e after at, increments l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) insert(e, at *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ n := at.next
+ at.next = e
+ e.prev = at
+ e.next = n
+ n.prev = e
+ e.list = l
+ l.len++
+ return e
+}
+
+// insertValue is a convenience wrapper for insert(&PacketElement{Value: v}, at).
+func (l *PacketList) insertValue(v Packet, at *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ return l.insert(&PacketElement{Value: v}, at)
+}
+
+// remove removes e from its list, decrements l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) remove(e *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ e.prev.next = e.next
+ e.next.prev = e.prev
+ e.next = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.prev = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.list = nil
+ l.len--
+ return e
+}
+
+// Remove removes e from l if e is an element of list l.
+// It returns the element value e.Value.
+func (l *PacketList) Remove(e *PacketElement) Packet {
+ if e.list == l {
+ // if e.list == l, l must have been initialized when e was inserted
+ // in l or l == nil (e is a zero PacketElement) and l.remove will crash
+ l.remove(e)
+ }
+ return e.Value
+}
+
+// PushFront inserts a new element e with value v at the front of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) PushFront(v Packet) *PacketElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, &l.root)
+}
+
+// PushBack inserts a new element e with value v at the back of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) PushBack(v Packet) *PacketElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertBefore inserts a new element e with value v immediately before mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) InsertBefore(v Packet, mark *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertAfter inserts a new element e with value v immediately after mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) InsertAfter(v Packet, mark *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark)
+}
+
+// MoveToFront moves element e to the front of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveToFront(e *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.next == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), &l.root)
+}
+
+// MoveToBack moves element e to the back of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveToBack(e *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.prev == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveBefore moves element e to its new position before mark.
+// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveBefore(e, mark *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveAfter moves element e to its new position after mark.
+// If e is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveAfter(e, mark *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark)
+}
+
+// PushBackList inserts a copy of an other list at the back of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketList) PushBackList(other *PacketList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Front(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Next() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, l.root.prev)
+ }
+}
+
+// PushFrontList inserts a copy of an other list at the front of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketList) PushFrontList(other *PacketList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Back(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Prev() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, &l.root)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_handler.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_handler.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dcc1b30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_handler.go
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+)
+
+var (
+ // ErrDuplicatePacket occurres when a duplicate packet is received
+ ErrDuplicatePacket = errors.New("ReceivedPacketHandler: Duplicate Packet")
+ // ErrMapAccess occurs when a NACK contains invalid NACK ranges
+ ErrMapAccess = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, "Packet does not exist in PacketHistory")
+ // ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting occurs when a packet arrives with a packet number smaller than the largest LeastUnacked of a StopWaitingFrame. If this error occurs, the packet should be ignored
+ ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting = errors.New("ReceivedPacketHandler: Packet number smaller than highest StopWaiting")
+)
+
+var (
+ errInvalidPacketNumber = errors.New("ReceivedPacketHandler: Invalid packet number")
+ errTooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets = qerr.Error(qerr.TooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets, "")
+)
+
+type receivedPacketHandler struct {
+ largestInOrderObserved protocol.PacketNumber
+ largestObserved protocol.PacketNumber
+ ignorePacketsBelow protocol.PacketNumber
+ currentAckFrame *frames.AckFrame
+ stateChanged bool // has an ACK for this state already been sent? Will be set to false every time a new packet arrives, and to false every time an ACK is sent
+
+ packetHistory *receivedPacketHistory
+
+ receivedTimes map[protocol.PacketNumber]time.Time
+ lowestInReceivedTimes protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+// NewReceivedPacketHandler creates a new receivedPacketHandler
+func NewReceivedPacketHandler() ReceivedPacketHandler {
+ return &receivedPacketHandler{
+ receivedTimes: make(map[protocol.PacketNumber]time.Time),
+ packetHistory: newReceivedPacketHistory(),
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) ReceivedPacket(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) error {
+ if packetNumber == 0 {
+ return errInvalidPacketNumber
+ }
+
+ // if the packet number is smaller than the largest LeastUnacked value of a StopWaiting we received, we cannot detect if this packet has a duplicate number
+ // the packet has to be ignored anyway
+ if packetNumber <= h.ignorePacketsBelow {
+ return ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting
+ }
+
+ _, ok := h.receivedTimes[packetNumber]
+ if packetNumber <= h.largestInOrderObserved || ok {
+ return ErrDuplicatePacket
+ }
+
+ h.packetHistory.ReceivedPacket(packetNumber)
+
+ h.stateChanged = true
+ h.currentAckFrame = nil
+
+ if packetNumber > h.largestObserved {
+ h.largestObserved = packetNumber
+ }
+
+ if packetNumber == h.largestInOrderObserved+1 {
+ h.largestInOrderObserved = packetNumber
+ }
+
+ h.receivedTimes[packetNumber] = time.Now()
+
+ if protocol.PacketNumber(len(h.receivedTimes)) > protocol.MaxTrackedReceivedPackets {
+ return errTooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) ReceivedStopWaiting(f *frames.StopWaitingFrame) error {
+ // ignore if StopWaiting is unneeded, because we already received a StopWaiting with a higher LeastUnacked
+ if h.ignorePacketsBelow >= f.LeastUnacked {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ h.ignorePacketsBelow = f.LeastUnacked - 1
+ h.garbageCollectReceivedTimes()
+
+ // the LeastUnacked is the smallest packet number of any packet for which the sender is still awaiting an ack. So the largestInOrderObserved is one less than that
+ if f.LeastUnacked > h.largestInOrderObserved {
+ h.largestInOrderObserved = f.LeastUnacked - 1
+ }
+
+ h.packetHistory.DeleteBelow(f.LeastUnacked)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) GetAckFrame(dequeue bool) (*frames.AckFrame, error) {
+ if !h.stateChanged {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+
+ if dequeue {
+ h.stateChanged = false
+ }
+
+ if h.currentAckFrame != nil {
+ return h.currentAckFrame, nil
+ }
+
+ packetReceivedTime, ok := h.receivedTimes[h.largestObserved]
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, ErrMapAccess
+ }
+
+ ackRanges := h.packetHistory.GetAckRanges()
+ h.currentAckFrame = &frames.AckFrame{
+ LargestAcked: h.largestObserved,
+ LowestAcked: ackRanges[len(ackRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber,
+ PacketReceivedTime: packetReceivedTime,
+ }
+
+ if len(ackRanges) > 1 {
+ h.currentAckFrame.AckRanges = ackRanges
+ }
+
+ return h.currentAckFrame, nil
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) garbageCollectReceivedTimes() {
+ for i := h.lowestInReceivedTimes; i <= h.ignorePacketsBelow; i++ {
+ delete(h.receivedTimes, i)
+ }
+ if h.ignorePacketsBelow > h.lowestInReceivedTimes {
+ h.lowestInReceivedTimes = h.ignorePacketsBelow + 1
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_history.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_history.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..14bb08f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_history.go
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type receivedPacketHistory struct {
+ ranges *utils.PacketIntervalList
+
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+}
+
+// newReceivedPacketHistory creates a new received packet history
+func newReceivedPacketHistory() *receivedPacketHistory {
+ return &receivedPacketHistory{
+ ranges: utils.NewPacketIntervalList(),
+ }
+}
+
+// ReceivedPacket registers a packet with PacketNumber p and updates the ranges
+func (h *receivedPacketHistory) ReceivedPacket(p protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ if h.ranges.Len() == 0 {
+ h.ranges.PushBack(utils.PacketInterval{Start: p, End: p})
+ return
+ }
+
+ for el := h.ranges.Back(); el != nil; el = el.Prev() {
+ // p already included in an existing range. Nothing to do here
+ if p >= el.Value.Start && p <= el.Value.End {
+ return
+ }
+
+ var rangeExtended bool
+ if el.Value.End == p-1 { // extend a range at the end
+ rangeExtended = true
+ el.Value.End = p
+ } else if el.Value.Start == p+1 { // extend a range at the beginning
+ rangeExtended = true
+ el.Value.Start = p
+ }
+
+ // if a range was extended (either at the beginning or at the end, maybe it is possible to merge two ranges into one)
+ if rangeExtended {
+ prev := el.Prev()
+ if prev != nil && prev.Value.End+1 == el.Value.Start { // merge two ranges
+ prev.Value.End = el.Value.End
+ h.ranges.Remove(el)
+ return
+ }
+ return // if the two ranges were not merge, we're done here
+ }
+
+ // create a new range at the end
+ if p > el.Value.End {
+ h.ranges.InsertAfter(utils.PacketInterval{Start: p, End: p}, el)
+ return
+ }
+ }
+
+ // create a new range at the beginning
+ h.ranges.InsertBefore(utils.PacketInterval{Start: p, End: p}, h.ranges.Front())
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHistory) DeleteBelow(leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ nextEl := h.ranges.Front()
+ for el := h.ranges.Front(); nextEl != nil; el = nextEl {
+ nextEl = el.Next()
+
+ if leastUnacked > el.Value.Start && leastUnacked <= el.Value.End {
+ el.Value.Start = leastUnacked
+ }
+ if el.Value.End < leastUnacked { // delete a whole range
+ h.ranges.Remove(el)
+ } else {
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// GetAckRanges gets a slice of all AckRanges that can be used in an AckFrame
+func (h *receivedPacketHistory) GetAckRanges() []frames.AckRange {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if h.ranges.Len() == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ var ackRanges []frames.AckRange
+
+ for el := h.ranges.Back(); el != nil; el = el.Prev() {
+ ackRanges = append(ackRanges, frames.AckRange{FirstPacketNumber: el.Value.Start, LastPacketNumber: el.Value.End})
+ }
+
+ return ackRanges
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/sent_packet_handler.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/sent_packet_handler.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..531a99a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/sent_packet_handler.go
@@ -0,0 +1,350 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ // ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck occurs when a duplicate or an out-of-order ACK is received
+ ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck = errors.New("SentPacketHandler: Duplicate or out-of-order ACK")
+ // ErrTooManyTrackedSentPackets occurs when the sentPacketHandler has to keep track of too many packets
+ ErrTooManyTrackedSentPackets = errors.New("Too many outstanding non-acked and non-retransmitted packets")
+ // ErrAckForSkippedPacket occurs when the client sent an ACK for a packet number that we intentionally skipped
+ ErrAckForSkippedPacket = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, "Received an ACK for a skipped packet number")
+ errAckForUnsentPacket = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, "Received ACK for an unsent package")
+)
+
+var errPacketNumberNotIncreasing = errors.New("Already sent a packet with a higher packet number.")
+
+type sentPacketHandler struct {
+ lastSentPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ lastSentPacketTime time.Time
+ skippedPackets []protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ LargestAcked protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ largestReceivedPacketWithAck protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ packetHistory *PacketList
+ stopWaitingManager stopWaitingManager
+
+ retransmissionQueue []*Packet
+
+ bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount
+
+ rttStats *congestion.RTTStats
+ congestion congestion.SendAlgorithm
+
+ consecutiveRTOCount uint32
+}
+
+// NewSentPacketHandler creates a new sentPacketHandler
+func NewSentPacketHandler() SentPacketHandler {
+ rttStats := &congestion.RTTStats{}
+
+ congestion := congestion.NewCubicSender(
+ congestion.DefaultClock{},
+ rttStats,
+ false, /* don't use reno since chromium doesn't (why?) */
+ protocol.InitialCongestionWindow,
+ protocol.DefaultMaxCongestionWindow,
+ )
+
+ return &sentPacketHandler{
+ packetHistory: NewPacketList(),
+ stopWaitingManager: stopWaitingManager{},
+ rttStats: rttStats,
+ congestion: congestion,
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) ackPacket(packetElement *PacketElement) {
+ packet := &packetElement.Value
+ h.bytesInFlight -= packet.Length
+ h.packetHistory.Remove(packetElement)
+}
+
+// nackPacket NACKs a packet
+// it returns true if a FastRetransmissions was triggered
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) nackPacket(packetElement *PacketElement) bool {
+ packet := &packetElement.Value
+
+ packet.MissingReports++
+
+ if packet.MissingReports > protocol.RetransmissionThreshold {
+ utils.Debugf("\tQueueing packet 0x%x for retransmission (fast)", packet.PacketNumber)
+ h.queuePacketForRetransmission(packetElement)
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+// does NOT set packet.Retransmitted. This variable is not needed anymore
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) queuePacketForRetransmission(packetElement *PacketElement) {
+ packet := &packetElement.Value
+ h.bytesInFlight -= packet.Length
+ h.retransmissionQueue = append(h.retransmissionQueue, packet)
+
+ h.packetHistory.Remove(packetElement)
+
+ // strictly speaking, this is only necessary for RTO retransmissions
+ // this is because FastRetransmissions are triggered by missing ranges in ACKs, and then the LargestAcked will already be higher than the packet number of the retransmitted packet
+ h.stopWaitingManager.QueuedRetransmissionForPacketNumber(packet.PacketNumber)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) largestInOrderAcked() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if f := h.packetHistory.Front(); f != nil {
+ return f.Value.PacketNumber - 1
+ }
+ return h.LargestAcked
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) SentPacket(packet *Packet) error {
+ if packet.PacketNumber <= h.lastSentPacketNumber {
+ return errPacketNumberNotIncreasing
+ }
+
+ for p := h.lastSentPacketNumber + 1; p < packet.PacketNumber; p++ {
+ h.skippedPackets = append(h.skippedPackets, p)
+
+ if len(h.skippedPackets) > protocol.MaxTrackedSkippedPackets {
+ h.skippedPackets = h.skippedPackets[1:]
+ }
+ }
+
+ now := time.Now()
+ h.lastSentPacketTime = now
+ packet.SendTime = now
+ if packet.Length == 0 {
+ return errors.New("SentPacketHandler: packet cannot be empty")
+ }
+ h.bytesInFlight += packet.Length
+
+ h.lastSentPacketNumber = packet.PacketNumber
+ h.packetHistory.PushBack(*packet)
+
+ h.congestion.OnPacketSent(
+ now,
+ h.BytesInFlight(),
+ packet.PacketNumber,
+ packet.Length,
+ true, /* TODO: is retransmittable */
+ )
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) ReceivedAck(ackFrame *frames.AckFrame, withPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, rcvTime time.Time) error {
+ if ackFrame.LargestAcked > h.lastSentPacketNumber {
+ return errAckForUnsentPacket
+ }
+
+ // duplicate or out-of-order ACK
+ if withPacketNumber <= h.largestReceivedPacketWithAck {
+ return ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck
+ }
+
+ h.largestReceivedPacketWithAck = withPacketNumber
+
+ // ignore repeated ACK (ACKs that don't have a higher LargestAcked than the last ACK)
+ if ackFrame.LargestAcked <= h.largestInOrderAcked() {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // check if it acks any packets that were skipped
+ for _, p := range h.skippedPackets {
+ if ackFrame.AcksPacket(p) {
+ return ErrAckForSkippedPacket
+ }
+ }
+
+ h.LargestAcked = ackFrame.LargestAcked
+
+ var ackedPackets congestion.PacketVector
+ var lostPackets congestion.PacketVector
+ ackRangeIndex := 0
+ rttUpdated := false
+
+ var el, elNext *PacketElement
+ for el = h.packetHistory.Front(); el != nil; el = elNext {
+ // determine the next list element right at the beginning, because el.Next() is not avaible anymore, when the list element is deleted (i.e. when the packet is ACKed)
+ elNext = el.Next()
+ packet := el.Value
+ packetNumber := packet.PacketNumber
+
+ // NACK packets below the LowestAcked
+ if packetNumber < ackFrame.LowestAcked {
+ retransmitted := h.nackPacket(el)
+ if retransmitted {
+ lostPackets = append(lostPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ }
+ continue
+ }
+
+ // Update the RTT
+ if packetNumber == h.LargestAcked {
+ rttUpdated = true
+ timeDelta := rcvTime.Sub(packet.SendTime)
+ h.rttStats.UpdateRTT(timeDelta, ackFrame.DelayTime, rcvTime)
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Debugf("\tEstimated RTT: %dms", h.rttStats.SmoothedRTT()/time.Millisecond)
+ }
+ }
+
+ if packetNumber > ackFrame.LargestAcked {
+ break
+ }
+
+ if ackFrame.HasMissingRanges() {
+ ackRange := ackFrame.AckRanges[len(ackFrame.AckRanges)-1-ackRangeIndex]
+
+ for packetNumber > ackRange.LastPacketNumber && ackRangeIndex < len(ackFrame.AckRanges)-1 {
+ ackRangeIndex++
+ ackRange = ackFrame.AckRanges[len(ackFrame.AckRanges)-1-ackRangeIndex]
+ }
+
+ if packetNumber >= ackRange.FirstPacketNumber { // packet i contained in ACK range
+ if packetNumber > ackRange.LastPacketNumber {
+ return fmt.Errorf("BUG: ackhandler would have acked wrong packet 0x%x, while evaluating range 0x%x -> 0x%x", packetNumber, ackRange.FirstPacketNumber, ackRange.LastPacketNumber)
+ }
+ h.ackPacket(el)
+ ackedPackets = append(ackedPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ } else {
+ retransmitted := h.nackPacket(el)
+ if retransmitted {
+ lostPackets = append(lostPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ h.ackPacket(el)
+ ackedPackets = append(ackedPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ }
+ }
+
+ if rttUpdated {
+ // Reset counter if a new packet was acked
+ h.consecutiveRTOCount = 0
+ }
+
+ h.garbageCollectSkippedPackets()
+
+ h.stopWaitingManager.ReceivedAck(ackFrame)
+
+ h.congestion.OnCongestionEvent(
+ rttUpdated,
+ h.BytesInFlight(),
+ ackedPackets,
+ lostPackets,
+ )
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) DequeuePacketForRetransmission() *Packet {
+ if len(h.retransmissionQueue) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if len(h.retransmissionQueue) > 0 {
+ queueLen := len(h.retransmissionQueue)
+ // packets are usually NACKed in descending order. So use the slice as a stack
+ packet := h.retransmissionQueue[queueLen-1]
+ h.retransmissionQueue = h.retransmissionQueue[:queueLen-1]
+ return packet
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) BytesInFlight() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return h.bytesInFlight
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) GetLeastUnacked() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ return h.largestInOrderAcked() + 1
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) GetStopWaitingFrame(force bool) *frames.StopWaitingFrame {
+ return h.stopWaitingManager.GetStopWaitingFrame(force)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) SendingAllowed() bool {
+ congestionLimited := h.BytesInFlight() > h.congestion.GetCongestionWindow()
+ maxTrackedLimited := protocol.PacketNumber(len(h.retransmissionQueue)+h.packetHistory.Len()) >= protocol.MaxTrackedSentPackets
+ return !(congestionLimited || maxTrackedLimited)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) CheckForError() error {
+ length := len(h.retransmissionQueue) + h.packetHistory.Len()
+ if protocol.PacketNumber(length) > protocol.MaxTrackedSentPackets {
+ return ErrTooManyTrackedSentPackets
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) MaybeQueueRTOs() {
+ if time.Now().Before(h.TimeOfFirstRTO()) {
+ return
+ }
+
+ // Always queue the two oldest packets
+ if h.packetHistory.Front() != nil {
+ h.queueRTO(h.packetHistory.Front())
+ }
+ if h.packetHistory.Front() != nil {
+ h.queueRTO(h.packetHistory.Front())
+ }
+
+ // Reset the RTO timer here, since it's not clear that this packet contained any retransmittable frames
+ h.lastSentPacketTime = time.Now()
+ h.consecutiveRTOCount++
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) queueRTO(el *PacketElement) {
+ packet := &el.Value
+ packetsLost := congestion.PacketVector{congestion.PacketInfo{
+ Number: packet.PacketNumber,
+ Length: packet.Length,
+ }}
+ h.congestion.OnCongestionEvent(false, h.BytesInFlight(), nil, packetsLost)
+ h.congestion.OnRetransmissionTimeout(true)
+ utils.Debugf("\tQueueing packet 0x%x for retransmission (RTO)", packet.PacketNumber)
+ h.queuePacketForRetransmission(el)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) getRTO() time.Duration {
+ rto := h.congestion.RetransmissionDelay()
+ if rto == 0 {
+ rto = protocol.DefaultRetransmissionTime
+ }
+ rto = utils.MaxDuration(rto, protocol.MinRetransmissionTime)
+ // Exponential backoff
+ rto *= 1 << h.consecutiveRTOCount
+ return utils.MinDuration(rto, protocol.MaxRetransmissionTime)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) TimeOfFirstRTO() time.Time {
+ if h.lastSentPacketTime.IsZero() {
+ return time.Time{}
+ }
+ return h.lastSentPacketTime.Add(h.getRTO())
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) garbageCollectSkippedPackets() {
+ lioa := h.largestInOrderAcked()
+ deleteIndex := 0
+ for i, p := range h.skippedPackets {
+ if p <= lioa {
+ deleteIndex = i + 1
+ }
+ }
+ h.skippedPackets = h.skippedPackets[deleteIndex:]
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/stop_waiting_manager.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/stop_waiting_manager.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dfd79ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/stop_waiting_manager.go
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// This stopWaitingManager is not supposed to satisfy the StopWaitingManager interface, which is a remnant of the legacy AckHandler, and should be remove once we drop support for QUIC 33
+type stopWaitingManager struct {
+ largestLeastUnackedSent protocol.PacketNumber
+ nextLeastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ lastStopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame
+}
+
+func (s *stopWaitingManager) GetStopWaitingFrame(force bool) *frames.StopWaitingFrame {
+ if s.nextLeastUnacked <= s.largestLeastUnackedSent {
+ if force {
+ return s.lastStopWaitingFrame
+ }
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ s.largestLeastUnackedSent = s.nextLeastUnacked
+ swf := &frames.StopWaitingFrame{
+ LeastUnacked: s.nextLeastUnacked,
+ }
+ s.lastStopWaitingFrame = swf
+ return swf
+}
+
+func (s *stopWaitingManager) ReceivedAck(ack *frames.AckFrame) {
+ if ack.LargestAcked >= s.nextLeastUnacked {
+ s.nextLeastUnacked = ack.LargestAcked + 1
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *stopWaitingManager) QueuedRetransmissionForPacketNumber(p protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ if p >= s.nextLeastUnacked {
+ s.nextLeastUnacked = p + 1
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/appveyor.yml b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/appveyor.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..837facc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/appveyor.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+version: "{build}"
+
+os: Windows Server 2012 R2
+
+environment:
+ GOPATH: c:\gopath
+ CGO_ENABLED: 0
+ matrix:
+ - GOARCH: 386
+ - GOARCH: amd64
+
+clone_folder: c:\gopath\src\github.com\lucas-clemente\quic-go
+
+install:
+ - rmdir c:\go /s /q
+ - appveyor DownloadFile https://storage.googleapis.com/golang/go1.7.1.windows-amd64.zip
+ - 7z x go1.7.1.windows-amd64.zip -y -oC:\ > NUL
+ - set PATH=%PATH%;%GOPATH%\bin\windows_%GOARCH%;%GOPATH%\bin
+ - echo %PATH%
+ - echo %GOPATH%
+ - git submodule update --init --recursive
+ - go get github.com/onsi/ginkgo/ginkgo
+ - go get github.com/onsi/gomega
+ - go version
+ - go env
+ - go get -v -t ./...
+
+build_script:
+ - rm -r integrationtests
+ - ginkgo -r --randomizeAllSpecs --randomizeSuites --trace --progress
+
+test: off
+
+deploy: off
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/buffer_pool.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/buffer_pool.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..bb4feb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/buffer_pool.go
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+var bufferPool sync.Pool
+
+func getPacketBuffer() []byte {
+ return bufferPool.Get().([]byte)
+}
+
+func putPacketBuffer(buf []byte) {
+ if cap(buf) != int(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ panic("putPacketBuffer called with packet of wrong size!")
+ }
+ bufferPool.Put(buf[:0])
+}
+
+func init() {
+ bufferPool.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, 0, protocol.MaxPacketSize)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/codecov.yml b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/codecov.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4e4e039
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/codecov.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+coverage:
+ round: nearest
+ ignore:
+ - ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go
+ - utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go
+ - utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go
+ status:
+ project:
+ default:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ patch: false
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/bandwidth.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/bandwidth.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2c7ff23
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/bandwidth.go
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// Bandwidth of a connection
+type Bandwidth uint64
+
+const (
+ // BitsPerSecond is 1 bit per second
+ BitsPerSecond Bandwidth = 1
+ // KBitsPerSecond is 1000 bits per second
+ KBitsPerSecond = 1000 * BitsPerSecond
+ // BytesPerSecond is 1 byte per second
+ BytesPerSecond = 8 * BitsPerSecond
+ // KBytesPerSecond is 1000 bytes per second
+ KBytesPerSecond = 1000 * BytesPerSecond
+)
+
+// BandwidthFromDelta calculates the bandwidth from a number of bytes and a time delta
+func BandwidthFromDelta(bytes protocol.ByteCount, delta time.Duration) Bandwidth {
+ return Bandwidth(bytes) * Bandwidth(time.Second) / Bandwidth(delta) * BytesPerSecond
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/clock.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/clock.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..405fae7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/clock.go
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package congestion
+
+import "time"
+
+// A Clock returns the current time
+type Clock interface {
+ Now() time.Time
+}
+
+// DefaultClock implements the Clock interface using the Go stdlib clock.
+type DefaultClock struct{}
+
+var _ Clock = DefaultClock{}
+
+// Now gets the current time
+func (DefaultClock) Now() time.Time {
+ return time.Now()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/congestion_vector.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/congestion_vector.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9c6ebb4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/congestion_vector.go
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+package congestion
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// PacketInfo combines packet number and length of a packet for congestion calculation
+type PacketInfo struct {
+ Number protocol.PacketNumber
+ Length protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// PacketVector is passed to the congestion algorithm
+type PacketVector []PacketInfo
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e6e8bf6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic.go
@@ -0,0 +1,218 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "math"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// This cubic implementation is based on the one found in Chromiums's QUIC
+// implementation, in the files net/quic/congestion_control/cubic.{hh,cc}.
+
+// Constants based on TCP defaults.
+// The following constants are in 2^10 fractions of a second instead of ms to
+// allow a 10 shift right to divide.
+
+// 1024*1024^3 (first 1024 is from 0.100^3)
+// where 0.100 is 100 ms which is the scaling
+// round trip time.
+const cubeScale = 40
+const cubeCongestionWindowScale = 410
+const cubeFactor protocol.PacketNumber = 1 << cubeScale / cubeCongestionWindowScale
+
+const defaultNumConnections = 2
+
+// Default Cubic backoff factor
+const beta float32 = 0.7
+
+// Additional backoff factor when loss occurs in the concave part of the Cubic
+// curve. This additional backoff factor is expected to give up bandwidth to
+// new concurrent flows and speed up convergence.
+const betaLastMax float32 = 0.85
+
+// If true, Cubic's epoch is shifted when the sender is application-limited.
+const shiftQuicCubicEpochWhenAppLimited = true
+
+const maxCubicTimeInterval = 30 * time.Millisecond
+
+// Cubic implements the cubic algorithm from TCP
+type Cubic struct {
+ clock Clock
+ // Number of connections to simulate.
+ numConnections int
+ // Time when this cycle started, after last loss event.
+ epoch time.Time
+ // Time when sender went into application-limited period. Zero if not in
+ // application-limited period.
+ appLimitedStartTime time.Time
+ // Time when we updated last_congestion_window.
+ lastUpdateTime time.Time
+ // Last congestion window (in packets) used.
+ lastCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Max congestion window (in packets) used just before last loss event.
+ // Note: to improve fairness to other streams an additional back off is
+ // applied to this value if the new value is below our latest value.
+ lastMaxCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Number of acked packets since the cycle started (epoch).
+ ackedPacketsCount protocol.PacketNumber
+ // TCP Reno equivalent congestion window in packets.
+ estimatedTCPcongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Origin point of cubic function.
+ originPointCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Time to origin point of cubic function in 2^10 fractions of a second.
+ timeToOriginPoint uint32
+ // Last congestion window in packets computed by cubic function.
+ lastTargetCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+// NewCubic returns a new Cubic instance
+func NewCubic(clock Clock) *Cubic {
+ c := &Cubic{
+ clock: clock,
+ numConnections: defaultNumConnections,
+ }
+ c.Reset()
+ return c
+}
+
+// Reset is called after a timeout to reset the cubic state
+func (c *Cubic) Reset() {
+ c.epoch = time.Time{}
+ c.appLimitedStartTime = time.Time{}
+ c.lastUpdateTime = time.Time{}
+ c.lastCongestionWindow = 0
+ c.lastMaxCongestionWindow = 0
+ c.ackedPacketsCount = 0
+ c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow = 0
+ c.originPointCongestionWindow = 0
+ c.timeToOriginPoint = 0
+ c.lastTargetCongestionWindow = 0
+}
+
+func (c *Cubic) alpha() float32 {
+ // TCPFriendly alpha is described in Section 3.3 of the CUBIC paper. Note that
+ // beta here is a cwnd multiplier, and is equal to 1-beta from the paper.
+ // We derive the equivalent alpha for an N-connection emulation as:
+ b := c.beta()
+ return 3 * float32(c.numConnections) * float32(c.numConnections) * (1 - b) / (1 + b)
+}
+
+func (c *Cubic) beta() float32 {
+ // kNConnectionBeta is the backoff factor after loss for our N-connection
+ // emulation, which emulates the effective backoff of an ensemble of N
+ // TCP-Reno connections on a single loss event. The effective multiplier is
+ // computed as:
+ return (float32(c.numConnections) - 1 + beta) / float32(c.numConnections)
+}
+
+// OnApplicationLimited is called on ack arrival when sender is unable to use
+// the available congestion window. Resets Cubic state during quiescence.
+func (c *Cubic) OnApplicationLimited() {
+ if shiftQuicCubicEpochWhenAppLimited {
+ // When sender is not using the available congestion window, Cubic's epoch
+ // should not continue growing. Record the time when sender goes into an
+ // app-limited period here, to compensate later when cwnd growth happens.
+ if c.appLimitedStartTime.IsZero() {
+ c.appLimitedStartTime = c.clock.Now()
+ }
+ } else {
+ // When sender is not using the available congestion window, Cubic's epoch
+ // should not continue growing. Reset the epoch when in such a period.
+ c.epoch = time.Time{}
+ }
+}
+
+// CongestionWindowAfterPacketLoss computes a new congestion window to use after
+// a loss event. Returns the new congestion window in packets. The new
+// congestion window is a multiplicative decrease of our current window.
+func (c *Cubic) CongestionWindowAfterPacketLoss(currentCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if currentCongestionWindow < c.lastMaxCongestionWindow {
+ // We never reached the old max, so assume we are competing with another
+ // flow. Use our extra back off factor to allow the other flow to go up.
+ c.lastMaxCongestionWindow = protocol.PacketNumber(betaLastMax * float32(currentCongestionWindow))
+ } else {
+ c.lastMaxCongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ }
+ c.epoch = time.Time{} // Reset time.
+ return protocol.PacketNumber(float32(currentCongestionWindow) * c.beta())
+}
+
+// CongestionWindowAfterAck computes a new congestion window to use after a received ACK.
+// Returns the new congestion window in packets. The new congestion window
+// follows a cubic function that depends on the time passed since last
+// packet loss.
+func (c *Cubic) CongestionWindowAfterAck(currentCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber, delayMin time.Duration) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ c.ackedPacketsCount++ // Packets acked.
+ currentTime := c.clock.Now()
+
+ // Cubic is "independent" of RTT, the update is limited by the time elapsed.
+ if c.lastCongestionWindow == currentCongestionWindow && (currentTime.Sub(c.lastUpdateTime) <= maxCubicTimeInterval) {
+ return utils.MaxPacketNumber(c.lastTargetCongestionWindow, c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow)
+ }
+ c.lastCongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ c.lastUpdateTime = currentTime
+
+ if c.epoch.IsZero() {
+ // First ACK after a loss event.
+ c.epoch = currentTime // Start of epoch.
+ c.ackedPacketsCount = 1 // Reset count.
+ // Reset estimated_tcp_congestion_window_ to be in sync with cubic.
+ c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ if c.lastMaxCongestionWindow <= currentCongestionWindow {
+ c.timeToOriginPoint = 0
+ c.originPointCongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ } else {
+ c.timeToOriginPoint = uint32(math.Cbrt(float64(cubeFactor * (c.lastMaxCongestionWindow - currentCongestionWindow))))
+ c.originPointCongestionWindow = c.lastMaxCongestionWindow
+ }
+ } else {
+ // If sender was app-limited, then freeze congestion window growth during
+ // app-limited period. Continue growth now by shifting the epoch-start
+ // through the app-limited period.
+ if shiftQuicCubicEpochWhenAppLimited && !c.appLimitedStartTime.IsZero() {
+ shift := currentTime.Sub(c.appLimitedStartTime)
+ c.epoch = c.epoch.Add(shift)
+ c.appLimitedStartTime = time.Time{}
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Change the time unit from microseconds to 2^10 fractions per second. Take
+ // the round trip time in account. This is done to allow us to use shift as a
+ // divide operator.
+ elapsedTime := int64((currentTime.Add(delayMin).Sub(c.epoch)/time.Microsecond)<<10) / 1000000
+
+ offset := int64(c.timeToOriginPoint) - elapsedTime
+ deltaCongestionWindow := protocol.PacketNumber((cubeCongestionWindowScale * offset * offset * offset) >> cubeScale)
+ targetCongestionWindow := c.originPointCongestionWindow - deltaCongestionWindow
+
+ // With dynamic beta/alpha based on number of active streams, it is possible
+ // for the required_ack_count to become much lower than acked_packets_count_
+ // suddenly, leading to more than one iteration through the following loop.
+ for {
+ // Update estimated TCP congestion_window.
+ requiredAckCount := protocol.PacketNumber(float32(c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow) / c.alpha())
+ if c.ackedPacketsCount < requiredAckCount {
+ break
+ }
+ c.ackedPacketsCount -= requiredAckCount
+ c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow++
+ }
+
+ // We have a new cubic congestion window.
+ c.lastTargetCongestionWindow = targetCongestionWindow
+
+ // Compute target congestion_window based on cubic target and estimated TCP
+ // congestion_window, use highest (fastest).
+ if targetCongestionWindow < c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow {
+ targetCongestionWindow = c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow
+ }
+
+ return targetCongestionWindow
+}
+
+// SetNumConnections sets the number of emulated connections
+func (c *Cubic) SetNumConnections(n int) {
+ c.numConnections = n
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic_sender.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic_sender.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a34a69d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic_sender.go
@@ -0,0 +1,309 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+const (
+ maxBurstBytes = 3 * protocol.DefaultTCPMSS
+ defaultMinimumCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber = 2
+ renoBeta float32 = 0.7 // Reno backoff factor.
+)
+
+type cubicSender struct {
+ hybridSlowStart HybridSlowStart
+ prr PrrSender
+ rttStats *RTTStats
+ stats connectionStats
+ cubic *Cubic
+
+ reno bool
+
+ // Track the largest packet that has been sent.
+ largestSentPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Track the largest packet that has been acked.
+ largestAckedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Track the largest packet number outstanding when a CWND cutback occurs.
+ largestSentAtLastCutback protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Congestion window in packets.
+ congestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Slow start congestion window in packets, aka ssthresh.
+ slowstartThreshold protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Whether the last loss event caused us to exit slowstart.
+ // Used for stats collection of slowstartPacketsLost
+ lastCutbackExitedSlowstart bool
+
+ // When true, exit slow start with large cutback of congestion window.
+ slowStartLargeReduction bool
+
+ // Minimum congestion window in packets.
+ minCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Maximum number of outstanding packets for tcp.
+ maxTCPCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Number of connections to simulate.
+ numConnections int
+
+ // ACK counter for the Reno implementation.
+ congestionWindowCount protocol.ByteCount
+
+ initialCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ initialMaxCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+// NewCubicSender makes a new cubic sender
+func NewCubicSender(clock Clock, rttStats *RTTStats, reno bool, initialCongestionWindow, initialMaxCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber) SendAlgorithmWithDebugInfo {
+ return &cubicSender{
+ rttStats: rttStats,
+ initialCongestionWindow: initialCongestionWindow,
+ initialMaxCongestionWindow: initialMaxCongestionWindow,
+ congestionWindow: initialCongestionWindow,
+ minCongestionWindow: defaultMinimumCongestionWindow,
+ slowstartThreshold: initialMaxCongestionWindow,
+ maxTCPCongestionWindow: initialMaxCongestionWindow,
+ numConnections: defaultNumConnections,
+ cubic: NewCubic(clock),
+ reno: reno,
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) TimeUntilSend(now time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) time.Duration {
+ if c.InRecovery() {
+ // PRR is used when in recovery.
+ return c.prr.TimeUntilSend(c.GetCongestionWindow(), bytesInFlight, c.GetSlowStartThreshold())
+ }
+ if c.GetCongestionWindow() > bytesInFlight {
+ return 0
+ }
+ return utils.InfDuration
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) OnPacketSent(sentTime time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, bytes protocol.ByteCount, isRetransmittable bool) bool {
+ // Only update bytesInFlight for data packets.
+ if !isRetransmittable {
+ return false
+ }
+ if c.InRecovery() {
+ // PRR is used when in recovery.
+ c.prr.OnPacketSent(bytes)
+ }
+ c.largestSentPacketNumber = packetNumber
+ c.hybridSlowStart.OnPacketSent(packetNumber)
+ return true
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) InRecovery() bool {
+ return c.largestAckedPacketNumber <= c.largestSentAtLastCutback && c.largestAckedPacketNumber != 0
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) InSlowStart() bool {
+ return c.GetCongestionWindow() < c.GetSlowStartThreshold()
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) GetCongestionWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(c.congestionWindow) * protocol.DefaultTCPMSS
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) GetSlowStartThreshold() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(c.slowstartThreshold) * protocol.DefaultTCPMSS
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) ExitSlowstart() {
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) SlowstartThreshold() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ return c.slowstartThreshold
+}
+
+// OnCongestionEvent indicates an update to the congestion state, caused either by an incoming
+// ack or loss event timeout. |rttUpdated| indicates whether a new
+// latest_rtt sample has been taken, |byte_in_flight| the bytes in flight
+// prior to the congestion event. |ackedPackets| and |lostPackets| are
+// any packets considered acked or lost as a result of the congestion event.
+func (c *cubicSender) OnCongestionEvent(rttUpdated bool, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, ackedPackets PacketVector, lostPackets PacketVector) {
+ if rttUpdated && c.InSlowStart() && c.hybridSlowStart.ShouldExitSlowStart(c.rttStats.LatestRTT(), c.rttStats.MinRTT(), c.GetCongestionWindow()/protocol.DefaultTCPMSS) {
+ c.ExitSlowstart()
+ }
+ for _, i := range lostPackets {
+ c.onPacketLost(i.Number, i.Length, bytesInFlight)
+ }
+ for _, i := range ackedPackets {
+ c.onPacketAcked(i.Number, i.Length, bytesInFlight)
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) onPacketAcked(ackedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, ackedBytes protocol.ByteCount, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.largestAckedPacketNumber = utils.MaxPacketNumber(ackedPacketNumber, c.largestAckedPacketNumber)
+ if c.InRecovery() {
+ // PRR is used when in recovery.
+ c.prr.OnPacketAcked(ackedBytes)
+ return
+ }
+ c.maybeIncreaseCwnd(ackedPacketNumber, ackedBytes, bytesInFlight)
+ if c.InSlowStart() {
+ c.hybridSlowStart.OnPacketAcked(ackedPacketNumber)
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) onPacketLost(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, lostBytes protocol.ByteCount, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ // TCP NewReno (RFC6582) says that once a loss occurs, any losses in packets
+ // already sent should be treated as a single loss event, since it's expected.
+ if packetNumber <= c.largestSentAtLastCutback {
+ if c.lastCutbackExitedSlowstart {
+ c.stats.slowstartPacketsLost++
+ c.stats.slowstartBytesLost += lostBytes
+ if c.slowStartLargeReduction {
+ if c.stats.slowstartPacketsLost == 1 || (c.stats.slowstartBytesLost/protocol.DefaultTCPMSS) > (c.stats.slowstartBytesLost-lostBytes)/protocol.DefaultTCPMSS {
+ // Reduce congestion window by 1 for every mss of bytes lost.
+ c.congestionWindow = utils.MaxPacketNumber(c.congestionWindow-1, c.minCongestionWindow)
+ }
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow
+ }
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ c.lastCutbackExitedSlowstart = c.InSlowStart()
+ if c.InSlowStart() {
+ c.stats.slowstartPacketsLost++
+ }
+
+ c.prr.OnPacketLost(bytesInFlight)
+
+ // TODO(chromium): Separate out all of slow start into a separate class.
+ if c.slowStartLargeReduction && c.InSlowStart() {
+ c.congestionWindow = c.congestionWindow - 1
+ } else if c.reno {
+ c.congestionWindow = protocol.PacketNumber(float32(c.congestionWindow) * c.RenoBeta())
+ } else {
+ c.congestionWindow = c.cubic.CongestionWindowAfterPacketLoss(c.congestionWindow)
+ }
+ // Enforce a minimum congestion window.
+ if c.congestionWindow < c.minCongestionWindow {
+ c.congestionWindow = c.minCongestionWindow
+ }
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow
+ c.largestSentAtLastCutback = c.largestSentPacketNumber
+ // reset packet count from congestion avoidance mode. We start
+ // counting again when we're out of recovery.
+ c.congestionWindowCount = 0
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) RenoBeta() float32 {
+ // kNConnectionBeta is the backoff factor after loss for our N-connection
+ // emulation, which emulates the effective backoff of an ensemble of N
+ // TCP-Reno connections on a single loss event. The effective multiplier is
+ // computed as:
+ return (float32(c.numConnections) - 1. + renoBeta) / float32(c.numConnections)
+}
+
+// Called when we receive an ack. Normal TCP tracks how many packets one ack
+// represents, but quic has a separate ack for each packet.
+func (c *cubicSender) maybeIncreaseCwnd(ackedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, ackedBytes protocol.ByteCount, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ // Do not increase the congestion window unless the sender is close to using
+ // the current window.
+ if !c.isCwndLimited(bytesInFlight) {
+ c.cubic.OnApplicationLimited()
+ return
+ }
+ if c.congestionWindow >= c.maxTCPCongestionWindow {
+ return
+ }
+ if c.InSlowStart() {
+ // TCP slow start, exponential growth, increase by one for each ACK.
+ c.congestionWindow++
+ return
+ }
+ if c.reno {
+ // Classic Reno congestion avoidance.
+ c.congestionWindowCount++
+ // Divide by num_connections to smoothly increase the CWND at a faster
+ // rate than conventional Reno.
+ if protocol.PacketNumber(c.congestionWindowCount*protocol.ByteCount(c.numConnections)) >= c.congestionWindow {
+ c.congestionWindow++
+ c.congestionWindowCount = 0
+ }
+ } else {
+ c.congestionWindow = utils.MinPacketNumber(c.maxTCPCongestionWindow, c.cubic.CongestionWindowAfterAck(c.congestionWindow, c.rttStats.MinRTT()))
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) isCwndLimited(bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) bool {
+ congestionWindow := c.GetCongestionWindow()
+ if bytesInFlight >= congestionWindow {
+ return true
+ }
+ availableBytes := congestionWindow - bytesInFlight
+ slowStartLimited := c.InSlowStart() && bytesInFlight > congestionWindow/2
+ return slowStartLimited || availableBytes <= maxBurstBytes
+}
+
+// BandwidthEstimate returns the current bandwidth estimate
+func (c *cubicSender) BandwidthEstimate() Bandwidth {
+ srtt := c.rttStats.SmoothedRTT()
+ if srtt == 0 {
+ // If we haven't measured an rtt, the bandwidth estimate is unknown.
+ return 0
+ }
+ return BandwidthFromDelta(c.GetCongestionWindow(), srtt)
+}
+
+// HybridSlowStart returns the hybrid slow start instance for testing
+func (c *cubicSender) HybridSlowStart() *HybridSlowStart {
+ return &c.hybridSlowStart
+}
+
+// SetNumEmulatedConnections sets the number of emulated connections
+func (c *cubicSender) SetNumEmulatedConnections(n int) {
+ c.numConnections = utils.Max(n, 1)
+ c.cubic.SetNumConnections(c.numConnections)
+}
+
+// OnRetransmissionTimeout is called on an retransmission timeout
+func (c *cubicSender) OnRetransmissionTimeout(packetsRetransmitted bool) {
+ c.largestSentAtLastCutback = 0
+ if !packetsRetransmitted {
+ return
+ }
+ c.hybridSlowStart.Restart()
+ c.cubic.Reset()
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow / 2
+ c.congestionWindow = c.minCongestionWindow
+}
+
+// OnConnectionMigration is called when the connection is migrated (?)
+func (c *cubicSender) OnConnectionMigration() {
+ c.hybridSlowStart.Restart()
+ c.prr = PrrSender{}
+ c.largestSentPacketNumber = 0
+ c.largestAckedPacketNumber = 0
+ c.largestSentAtLastCutback = 0
+ c.lastCutbackExitedSlowstart = false
+ c.cubic.Reset()
+ c.congestionWindowCount = 0
+ c.congestionWindow = c.initialCongestionWindow
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.initialMaxCongestionWindow
+ c.maxTCPCongestionWindow = c.initialMaxCongestionWindow
+}
+
+// SetSlowStartLargeReduction allows enabling the SSLR experiment
+func (c *cubicSender) SetSlowStartLargeReduction(enabled bool) {
+ c.slowStartLargeReduction = enabled
+}
+
+// RetransmissionDelay gives the time to retransmission
+func (c *cubicSender) RetransmissionDelay() time.Duration {
+ if c.rttStats.SmoothedRTT() == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ return c.rttStats.SmoothedRTT() + c.rttStats.MeanDeviation()*4
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/hybrid_slow_start.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/hybrid_slow_start.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..29204ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/hybrid_slow_start.go
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// Note(pwestin): the magic clamping numbers come from the original code in
+// tcp_cubic.c.
+const hybridStartLowWindow = protocol.ByteCount(16)
+
+// Number of delay samples for detecting the increase of delay.
+const hybridStartMinSamples = uint32(8)
+
+// Exit slow start if the min rtt has increased by more than 1/8th.
+const hybridStartDelayFactorExp = 3 // 2^3 = 8
+// The original paper specifies 2 and 8ms, but those have changed over time.
+const hybridStartDelayMinThresholdUs = int64(4000)
+const hybridStartDelayMaxThresholdUs = int64(16000)
+
+// HybridSlowStart implements the TCP hybrid slow start algorithm
+type HybridSlowStart struct {
+ endPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ lastSentPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ started bool
+ currentMinRTT time.Duration
+ rttSampleCount uint32
+ hystartFound bool
+}
+
+// StartReceiveRound is called for the start of each receive round (burst) in the slow start phase.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) StartReceiveRound(lastSent protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ s.endPacketNumber = lastSent
+ s.currentMinRTT = 0
+ s.rttSampleCount = 0
+ s.started = true
+}
+
+// IsEndOfRound returns true if this ack is the last packet number of our current slow start round.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) IsEndOfRound(ack protocol.PacketNumber) bool {
+ return s.endPacketNumber < ack
+}
+
+// ShouldExitSlowStart should be called on every new ack frame, since a new
+// RTT measurement can be made then.
+// rtt: the RTT for this ack packet.
+// minRTT: is the lowest delay (RTT) we have seen during the session.
+// congestionWindow: the congestion window in packets.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) ShouldExitSlowStart(latestRTT time.Duration, minRTT time.Duration, congestionWindow protocol.ByteCount) bool {
+ if !s.started {
+ // Time to start the hybrid slow start.
+ s.StartReceiveRound(s.lastSentPacketNumber)
+ }
+ if s.hystartFound {
+ return true
+ }
+ // Second detection parameter - delay increase detection.
+ // Compare the minimum delay (s.currentMinRTT) of the current
+ // burst of packets relative to the minimum delay during the session.
+ // Note: we only look at the first few(8) packets in each burst, since we
+ // only want to compare the lowest RTT of the burst relative to previous
+ // bursts.
+ s.rttSampleCount++
+ if s.rttSampleCount <= hybridStartMinSamples {
+ if s.currentMinRTT == 0 || s.currentMinRTT > latestRTT {
+ s.currentMinRTT = latestRTT
+ }
+ }
+ // We only need to check this once per round.
+ if s.rttSampleCount == hybridStartMinSamples {
+ // Divide minRTT by 8 to get a rtt increase threshold for exiting.
+ minRTTincreaseThresholdUs := int64(minRTT / time.Microsecond >> hybridStartDelayFactorExp)
+ // Ensure the rtt threshold is never less than 2ms or more than 16ms.
+ minRTTincreaseThresholdUs = utils.MinInt64(minRTTincreaseThresholdUs, hybridStartDelayMaxThresholdUs)
+ minRTTincreaseThreshold := time.Duration(utils.MaxInt64(minRTTincreaseThresholdUs, hybridStartDelayMinThresholdUs)) * time.Microsecond
+
+ if s.currentMinRTT > (minRTT + minRTTincreaseThreshold) {
+ s.hystartFound = true
+ }
+ }
+ // Exit from slow start if the cwnd is greater than 16 and
+ // increasing delay is found.
+ return congestionWindow >= hybridStartLowWindow && s.hystartFound
+}
+
+// OnPacketSent is called when a packet was sent
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) OnPacketSent(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ s.lastSentPacketNumber = packetNumber
+}
+
+// OnPacketAcked gets invoked after ShouldExitSlowStart, so it's best to end
+// the round when the final packet of the burst is received and start it on
+// the next incoming ack.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) OnPacketAcked(ackedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ if s.IsEndOfRound(ackedPacketNumber) {
+ s.started = false
+ }
+}
+
+// Started returns true if started
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) Started() bool {
+ return s.started
+}
+
+// Restart the slow start phase
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) Restart() {
+ s.started = false
+ s.hystartFound = false
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/interface.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/interface.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..593c09e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/interface.go
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A SendAlgorithm performs congestion control and calculates the congestion window
+type SendAlgorithm interface {
+ TimeUntilSend(now time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) time.Duration
+ OnPacketSent(sentTime time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, bytes protocol.ByteCount, isRetransmittable bool) bool
+ GetCongestionWindow() protocol.ByteCount
+ OnCongestionEvent(rttUpdated bool, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, ackedPackets PacketVector, lostPackets PacketVector)
+ SetNumEmulatedConnections(n int)
+ OnRetransmissionTimeout(packetsRetransmitted bool)
+ OnConnectionMigration()
+ RetransmissionDelay() time.Duration
+
+ // Experiments
+ SetSlowStartLargeReduction(enabled bool)
+}
+
+// SendAlgorithmWithDebugInfo adds some debug functions to SendAlgorithm
+type SendAlgorithmWithDebugInfo interface {
+ SendAlgorithm
+ BandwidthEstimate() Bandwidth
+
+ // Stuff only used in testing
+
+ HybridSlowStart() *HybridSlowStart
+ SlowstartThreshold() protocol.PacketNumber
+ RenoBeta() float32
+ InRecovery() bool
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/prr_sender.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/prr_sender.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f8e6d59
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/prr_sender.go
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// PrrSender implements the Proportional Rate Reduction (PRR) per RFC 6937
+type PrrSender struct {
+ bytesSentSinceLoss protocol.ByteCount
+ bytesDeliveredSinceLoss protocol.ByteCount
+ ackCountSinceLoss protocol.ByteCount
+ bytesInFlightBeforeLoss protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// OnPacketSent should be called after a packet was sent
+func (p *PrrSender) OnPacketSent(sentBytes protocol.ByteCount) {
+ p.bytesSentSinceLoss += sentBytes
+}
+
+// OnPacketLost should be called on the first loss that triggers a recovery
+// period and all other methods in this class should only be called when in
+// recovery.
+func (p *PrrSender) OnPacketLost(bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ p.bytesSentSinceLoss = 0
+ p.bytesInFlightBeforeLoss = bytesInFlight
+ p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss = 0
+ p.ackCountSinceLoss = 0
+}
+
+// OnPacketAcked should be called after a packet was acked
+func (p *PrrSender) OnPacketAcked(ackedBytes protocol.ByteCount) {
+ p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss += ackedBytes
+ p.ackCountSinceLoss++
+}
+
+// TimeUntilSend calculates the time until a packet can be sent
+func (p *PrrSender) TimeUntilSend(congestionWindow, bytesInFlight, slowstartThreshold protocol.ByteCount) time.Duration {
+ // Return QuicTime::Zero In order to ensure limited transmit always works.
+ if p.bytesSentSinceLoss == 0 || bytesInFlight < protocol.DefaultTCPMSS {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if congestionWindow > bytesInFlight {
+ // During PRR-SSRB, limit outgoing packets to 1 extra MSS per ack, instead
+ // of sending the entire available window. This prevents burst retransmits
+ // when more packets are lost than the CWND reduction.
+ // limit = MAX(prr_delivered - prr_out, DeliveredData) + MSS
+ if p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss+p.ackCountSinceLoss*protocol.DefaultTCPMSS <= p.bytesSentSinceLoss {
+ return utils.InfDuration
+ }
+ return 0
+ }
+ // Implement Proportional Rate Reduction (RFC6937).
+ // Checks a simplified version of the PRR formula that doesn't use division:
+ // AvailableSendWindow =
+ // CEIL(prr_delivered * ssthresh / BytesInFlightAtLoss) - prr_sent
+ if p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss*slowstartThreshold > p.bytesSentSinceLoss*p.bytesInFlightBeforeLoss {
+ return 0
+ }
+ return utils.InfDuration
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/rtt_stats.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/rtt_stats.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0bf7b05
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/rtt_stats.go
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+const (
+ initialRTTus = 100 * 1000
+ rttAlpha float32 = 0.125
+ oneMinusAlpha float32 = (1 - rttAlpha)
+ rttBeta float32 = 0.25
+ oneMinusBeta float32 = (1 - rttBeta)
+ halfWindow float32 = 0.5
+ quarterWindow float32 = 0.25
+)
+
+type rttSample struct {
+ rtt time.Duration
+ time time.Time
+}
+
+// RTTStats provides round-trip statistics
+type RTTStats struct {
+ initialRTTus int64
+
+ recentMinRTTwindow time.Duration
+ minRTT time.Duration
+ latestRTT time.Duration
+ smoothedRTT time.Duration
+ meanDeviation time.Duration
+
+ numMinRTTsamplesRemaining uint32
+
+ newMinRTT rttSample
+ recentMinRTT rttSample
+ halfWindowRTT rttSample
+ quarterWindowRTT rttSample
+}
+
+// NewRTTStats makes a properly initialized RTTStats object
+func NewRTTStats() *RTTStats {
+ return &RTTStats{
+ initialRTTus: initialRTTus,
+ recentMinRTTwindow: utils.InfDuration,
+ }
+}
+
+// InitialRTTus is the initial RTT in us
+func (r *RTTStats) InitialRTTus() int64 { return r.initialRTTus }
+
+// MinRTT Returns the minRTT for the entire connection.
+// May return Zero if no valid updates have occurred.
+func (r *RTTStats) MinRTT() time.Duration { return r.minRTT }
+
+// LatestRTT returns the most recent rtt measurement.
+// May return Zero if no valid updates have occurred.
+func (r *RTTStats) LatestRTT() time.Duration { return r.latestRTT }
+
+// RecentMinRTT the minRTT since SampleNewRecentMinRtt has been called, or the
+// minRTT for the entire connection if SampleNewMinRtt was never called.
+func (r *RTTStats) RecentMinRTT() time.Duration { return r.recentMinRTT.rtt }
+
+// SmoothedRTT returns the EWMA smoothed RTT for the connection.
+// May return Zero if no valid updates have occurred.
+func (r *RTTStats) SmoothedRTT() time.Duration { return r.smoothedRTT }
+
+// GetQuarterWindowRTT gets the quarter window RTT
+func (r *RTTStats) GetQuarterWindowRTT() time.Duration { return r.quarterWindowRTT.rtt }
+
+// GetHalfWindowRTT gets the half window RTT
+func (r *RTTStats) GetHalfWindowRTT() time.Duration { return r.halfWindowRTT.rtt }
+
+// MeanDeviation gets the mean deviation
+func (r *RTTStats) MeanDeviation() time.Duration { return r.meanDeviation }
+
+// SetRecentMinRTTwindow sets how old a recent min rtt sample can be.
+func (r *RTTStats) SetRecentMinRTTwindow(recentMinRTTwindow time.Duration) {
+ r.recentMinRTTwindow = recentMinRTTwindow
+}
+
+// UpdateRTT updates the RTT based on a new sample.
+func (r *RTTStats) UpdateRTT(sendDelta, ackDelay time.Duration, now time.Time) {
+ if sendDelta == utils.InfDuration || sendDelta <= 0 {
+ utils.Debugf("Ignoring measured sendDelta, because it's is either infinite, zero, or negative: %d", sendDelta/time.Microsecond)
+ return
+ }
+
+ // Update r.minRTT first. r.minRTT does not use an rttSample corrected for
+ // ackDelay but the raw observed sendDelta, since poor clock granularity at
+ // the client may cause a high ackDelay to result in underestimation of the
+ // r.minRTT.
+ if r.minRTT == 0 || r.minRTT > sendDelta {
+ r.minRTT = sendDelta
+ }
+ r.updateRecentMinRTT(sendDelta, now)
+
+ // Correct for ackDelay if information received from the peer results in a
+ // positive RTT sample. Otherwise, we use the sendDelta as a reasonable
+ // measure for smoothedRTT.
+ sample := sendDelta
+ if sample > ackDelay {
+ sample -= ackDelay
+ }
+ r.latestRTT = sample
+ // First time call.
+ if r.smoothedRTT == 0 {
+ r.smoothedRTT = sample
+ r.meanDeviation = sample / 2
+ } else {
+ r.meanDeviation = time.Duration(oneMinusBeta*float32(r.meanDeviation/time.Microsecond)+rttBeta*float32(utils.AbsDuration(r.smoothedRTT-sample)/time.Microsecond)) * time.Microsecond
+ r.smoothedRTT = time.Duration((float32(r.smoothedRTT/time.Microsecond)*oneMinusAlpha)+(float32(sample/time.Microsecond)*rttAlpha)) * time.Microsecond
+ }
+}
+
+func (r *RTTStats) updateRecentMinRTT(sample time.Duration, now time.Time) { // Recent minRTT update.
+ if r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining > 0 {
+ r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining--
+ if r.newMinRTT.rtt == 0 || sample <= r.newMinRTT.rtt {
+ r.newMinRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ }
+ if r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining == 0 {
+ r.recentMinRTT = r.newMinRTT
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.newMinRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = r.newMinRTT
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Update the three recent rtt samples.
+ if r.recentMinRTT.rtt == 0 || sample <= r.recentMinRTT.rtt {
+ r.recentMinRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.recentMinRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = r.recentMinRTT
+ } else if sample <= r.halfWindowRTT.rtt {
+ r.halfWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = r.halfWindowRTT
+ } else if sample <= r.quarterWindowRTT.rtt {
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ }
+
+ // Expire old min rtt samples.
+ if r.recentMinRTT.time.Before(now.Add(-r.recentMinRTTwindow)) {
+ r.recentMinRTT = r.halfWindowRTT
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.quarterWindowRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ } else if r.halfWindowRTT.time.Before(now.Add(-time.Duration(float32(r.recentMinRTTwindow/time.Microsecond)*halfWindow) * time.Microsecond)) {
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.quarterWindowRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ } else if r.quarterWindowRTT.time.Before(now.Add(-time.Duration(float32(r.recentMinRTTwindow/time.Microsecond)*quarterWindow) * time.Microsecond)) {
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ }
+}
+
+// SampleNewRecentMinRTT forces RttStats to sample a new recent min rtt within the next
+// |numSamples| UpdateRTT calls.
+func (r *RTTStats) SampleNewRecentMinRTT(numSamples uint32) {
+ r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining = numSamples
+ r.newMinRTT = rttSample{}
+}
+
+// OnConnectionMigration is called when connection migrates and rtt measurement needs to be reset.
+func (r *RTTStats) OnConnectionMigration() {
+ r.latestRTT = 0
+ r.minRTT = 0
+ r.smoothedRTT = 0
+ r.meanDeviation = 0
+ r.initialRTTus = initialRTTus
+ r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining = 0
+ r.recentMinRTTwindow = utils.InfDuration
+ r.recentMinRTT = rttSample{}
+ r.halfWindowRTT = rttSample{}
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{}
+}
+
+// ExpireSmoothedMetrics causes the smoothed_rtt to be increased to the latest_rtt if the latest_rtt
+// is larger. The mean deviation is increased to the most recent deviation if
+// it's larger.
+func (r *RTTStats) ExpireSmoothedMetrics() {
+ r.meanDeviation = utils.MaxDuration(r.meanDeviation, utils.AbsDuration(r.smoothedRTT-r.latestRTT))
+ r.smoothedRTT = utils.MaxDuration(r.smoothedRTT, r.latestRTT)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/stats.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/stats.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8f272b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/stats.go
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+package congestion
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+type connectionStats struct {
+ slowstartPacketsLost protocol.PacketNumber
+ slowstartBytesLost protocol.ByteCount
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/AEAD.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/AEAD.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a59ce6e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/AEAD.go
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+package crypto
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// An AEAD implements QUIC's authenticated encryption and associated data
+type AEAD interface {
+ Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error)
+ Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/aesgcm_aead.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/aesgcm_aead.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a738cc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/aesgcm_aead.go
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/aes12"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type aeadAESGCM struct {
+ otherIV []byte
+ myIV []byte
+ encrypter cipher.AEAD
+ decrypter cipher.AEAD
+}
+
+// NewAEADAESGCM creates a AEAD using AES-GCM with 12 bytes tag size
+//
+// AES-GCM support is a bit hacky, since the go stdlib does not support 12 byte
+// tag size, and couples the cipher and aes packages closely.
+// See https://github.com/lucas-clemente/aes12.
+func NewAEADAESGCM(otherKey []byte, myKey []byte, otherIV []byte, myIV []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+ if len(myKey) != 16 || len(otherKey) != 16 || len(myIV) != 4 || len(otherIV) != 4 {
+ return nil, errors.New("AES-GCM: expected 16-byte keys and 4-byte IVs")
+ }
+ encrypterCipher, err := aes12.NewCipher(myKey)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ encrypter, err := aes12.NewGCM(encrypterCipher)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ decrypterCipher, err := aes12.NewCipher(otherKey)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ decrypter, err := aes12.NewGCM(decrypterCipher)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return &aeadAESGCM{
+ otherIV: otherIV,
+ myIV: myIV,
+ encrypter: encrypter,
+ decrypter: decrypter,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadAESGCM) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return aead.decrypter.Open(dst, makeNonce(aead.otherIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadAESGCM) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ return aead.encrypter.Seal(dst, makeNonce(aead.myIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_cache.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_cache.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3ebdc1a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_cache.go
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "hash/fnv"
+
+ "github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+var (
+ compressedCertsCache *lru.Cache
+)
+
+func getCompressedCert(chain [][]byte, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ // Hash all inputs
+ hasher := fnv.New64a()
+ for _, v := range chain {
+ hasher.Write(v)
+ }
+ hasher.Write(pCommonSetHashes)
+ hasher.Write(pCachedHashes)
+ hash := hasher.Sum64()
+
+ var result []byte
+
+ resultI, isCached := compressedCertsCache.Get(hash)
+ if isCached {
+ result = resultI.([]byte)
+ } else {
+ var err error
+ result, err = compressChain(chain, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ compressedCertsCache.Add(hash, result)
+ }
+
+ return result, nil
+}
+
+func init() {
+ var err error
+ compressedCertsCache, err = lru.New(protocol.NumCachedCertificates)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(fmt.Sprintf("fatal error in quic-go: could not create lru cache: %s", err.Error()))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_compression.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_compression.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8fdb257
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_compression.go
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "compress/flate"
+ "compress/zlib"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "hash/fnv"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type entryType uint8
+
+const (
+ entryCompressed entryType = 1
+ entryCached entryType = 2
+ entryCommon entryType = 3
+)
+
+type entry struct {
+ t entryType
+ h uint64
+ i uint32
+}
+
+func compressChain(chain [][]byte, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ res := &bytes.Buffer{}
+
+ cachedHashes, err := splitHashes(pCachedHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ setHashes, err := splitHashes(pCommonSetHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ chainHashes := make([]uint64, len(chain))
+ for i := range chain {
+ chainHashes[i] = hashCert(chain[i])
+ }
+
+ entries := buildEntries(chain, chainHashes, cachedHashes, setHashes)
+
+ totalUncompressedLen := 0
+ for i, e := range entries {
+ res.WriteByte(uint8(e.t))
+ switch e.t {
+ case entryCached:
+ utils.WriteUint64(res, e.h)
+ case entryCommon:
+ utils.WriteUint64(res, e.h)
+ utils.WriteUint32(res, e.i)
+ case entryCompressed:
+ totalUncompressedLen += 4 + len(chain[i])
+ }
+ }
+ res.WriteByte(0) // end of list
+
+ if totalUncompressedLen > 0 {
+ gz, err := zlib.NewWriterLevelDict(res, flate.BestCompression, buildZlibDictForEntries(entries, chain))
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, fmt.Errorf("cert compression failed: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+
+ utils.WriteUint32(res, uint32(totalUncompressedLen))
+
+ for i, e := range entries {
+ if e.t != entryCompressed {
+ continue
+ }
+ lenCert := len(chain[i])
+ gz.Write([]byte{
+ byte(lenCert & 0xff),
+ byte((lenCert >> 8) & 0xff),
+ byte((lenCert >> 16) & 0xff),
+ byte((lenCert >> 24) & 0xff),
+ })
+ gz.Write(chain[i])
+ }
+
+ gz.Close()
+ }
+
+ return res.Bytes(), nil
+}
+
+func buildEntries(chain [][]byte, chainHashes, cachedHashes, setHashes []uint64) []entry {
+ res := make([]entry, len(chain))
+chainLoop:
+ for i := range chain {
+ // Check if hash is in cachedHashes
+ for j := range cachedHashes {
+ if chainHashes[i] == cachedHashes[j] {
+ res[i] = entry{t: entryCached, h: chainHashes[i]}
+ continue chainLoop
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Go through common sets and check if it's in there
+ for _, setHash := range setHashes {
+ set, ok := certSets[setHash]
+ if !ok {
+ // We don't have this set
+ continue
+ }
+ // We have this set, check if chain[i] is in the set
+ pos := set.findCertInSet(chain[i])
+ if pos >= 0 {
+ // Found
+ res[i] = entry{t: entryCommon, h: setHash, i: uint32(pos)}
+ continue chainLoop
+ }
+ }
+
+ res[i] = entry{t: entryCompressed}
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func buildZlibDictForEntries(entries []entry, chain [][]byte) []byte {
+ var dict bytes.Buffer
+
+ // First the cached and common in reverse order
+ for i := len(entries) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
+ if entries[i].t == entryCompressed {
+ continue
+ }
+ dict.Write(chain[i])
+ }
+
+ dict.Write(certDictZlib)
+ return dict.Bytes()
+}
+
+func splitHashes(hashes []byte) ([]uint64, error) {
+ if len(hashes)%8 != 0 {
+ return nil, errors.New("expected a multiple of 8 bytes for CCS / CCRT hashes")
+ }
+ n := len(hashes) / 8
+ res := make([]uint64, n)
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ res[i] = binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(hashes[i*8 : (i+1)*8])
+ }
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+func hashCert(cert []byte) uint64 {
+ h := fnv.New64()
+ h.Write(cert)
+ return h.Sum64()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_dict.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_dict.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..300ec71
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_dict.go
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+package crypto
+
+var certDictZlib = []byte{
+ 0x04, 0x02, 0x30, 0x00, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x25, 0x04,
+ 0x16, 0x30, 0x14, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x03,
+ 0x01, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x03, 0x02, 0x30,
+ 0x5f, 0x06, 0x09, 0x60, 0x86, 0x48, 0x01, 0x86, 0xf8, 0x42, 0x04, 0x01,
+ 0x06, 0x06, 0x0b, 0x60, 0x86, 0x48, 0x01, 0x86, 0xfd, 0x6d, 0x01, 0x07,
+ 0x17, 0x01, 0x30, 0x33, 0x20, 0x45, 0x78, 0x74, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x64, 0x65,
+ 0x64, 0x20, 0x56, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x69, 0x64, 0x61, 0x74, 0x69, 0x6f, 0x6e,
+ 0x20, 0x53, 0x20, 0x4c, 0x69, 0x6d, 0x69, 0x74, 0x65, 0x64, 0x31, 0x34,
+ 0x20, 0x53, 0x53, 0x4c, 0x20, 0x43, 0x41, 0x30, 0x1e, 0x17, 0x0d, 0x31,
+ 0x32, 0x20, 0x53, 0x65, 0x63, 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x20, 0x53, 0x65, 0x72,
+ 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x20, 0x43, 0x41, 0x30, 0x2d, 0x61, 0x69, 0x61, 0x2e,
+ 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d,
+ 0x2f, 0x45, 0x2d, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x2e, 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73,
+ 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x45, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x65,
+ 0x72, 0x30, 0x0d, 0x06, 0x09, 0x2a, 0x86, 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01,
+ 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x00, 0x03, 0x82, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0x4a, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x73, 0x6f, 0x75, 0x72, 0x63, 0x65, 0x73,
+ 0x2f, 0x63, 0x70, 0x73, 0x20, 0x28, 0x63, 0x29, 0x30, 0x30, 0x09, 0x06,
+ 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x13, 0x04, 0x02, 0x30, 0x00, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x30, 0x0d,
+ 0x06, 0x09, 0x2a, 0x86, 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05,
+ 0x00, 0x03, 0x82, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0x7b, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55,
+ 0x1d, 0x0e, 0x30, 0x82, 0x01, 0x22, 0x30, 0x0d, 0x06, 0x09, 0x2a, 0x86,
+ 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01, 0x01, 0x01, 0x05, 0x00, 0x03, 0x82, 0x01,
+ 0x0f, 0x00, 0x30, 0x82, 0x01, 0x0a, 0x02, 0x82, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0xd2,
+ 0x6f, 0x64, 0x6f, 0x63, 0x61, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x43, 0x2e,
+ 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x0e, 0x04, 0x16,
+ 0x04, 0x14, 0xb4, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x62, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x73, 0x69,
+ 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x30, 0x0b, 0x06, 0x03,
+ 0x55, 0x1d, 0x0f, 0x04, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x01, 0x30, 0x0d, 0x06, 0x09,
+ 0x2a, 0x86, 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x00, 0x30,
+ 0x81, 0xca, 0x31, 0x0b, 0x30, 0x09, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x06, 0x13,
+ 0x02, 0x55, 0x53, 0x31, 0x10, 0x30, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x08,
+ 0x13, 0x07, 0x41, 0x72, 0x69, 0x7a, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x61, 0x31, 0x13, 0x30,
+ 0x11, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x07, 0x13, 0x0a, 0x53, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x74,
+ 0x74, 0x73, 0x64, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x65, 0x31, 0x1a, 0x30, 0x18, 0x06, 0x03,
+ 0x55, 0x04, 0x0a, 0x13, 0x11, 0x47, 0x6f, 0x44, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79,
+ 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2c, 0x20, 0x49, 0x6e, 0x63, 0x2e, 0x31, 0x33,
+ 0x30, 0x31, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x2a, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74,
+ 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x65, 0x72, 0x74, 0x69, 0x66, 0x69, 0x63,
+ 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x73, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79,
+ 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6f, 0x73, 0x69, 0x74,
+ 0x6f, 0x72, 0x79, 0x31, 0x30, 0x30, 0x2e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x03,
+ 0x13, 0x27, 0x47, 0x6f, 0x20, 0x44, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x20, 0x53,
+ 0x65, 0x63, 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x20, 0x43, 0x65, 0x72, 0x74, 0x69, 0x66,
+ 0x69, 0x63, 0x61, 0x74, 0x69, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x41, 0x75, 0x74, 0x68,
+ 0x6f, 0x72, 0x69, 0x74, 0x79, 0x31, 0x11, 0x30, 0x0f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55,
+ 0x04, 0x05, 0x13, 0x08, 0x30, 0x37, 0x39, 0x36, 0x39, 0x32, 0x38, 0x37,
+ 0x30, 0x1e, 0x17, 0x0d, 0x31, 0x31, 0x30, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d,
+ 0x0f, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff, 0x04, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x05, 0xa0, 0x30, 0x0c,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x13, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff, 0x04, 0x02, 0x30, 0x00,
+ 0x30, 0x1d, 0x30, 0x0f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x13, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff,
+ 0x04, 0x05, 0x30, 0x03, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55,
+ 0x1d, 0x25, 0x04, 0x16, 0x30, 0x14, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05,
+ 0x05, 0x07, 0x03, 0x01, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07,
+ 0x03, 0x02, 0x30, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x0f, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff,
+ 0x04, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x05, 0xa0, 0x30, 0x33, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d,
+ 0x1f, 0x04, 0x2c, 0x30, 0x2a, 0x30, 0x28, 0xa0, 0x26, 0xa0, 0x24, 0x86,
+ 0x22, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x2e,
+ 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f,
+ 0x67, 0x64, 0x73, 0x31, 0x2d, 0x32, 0x30, 0x2a, 0x30, 0x28, 0x06, 0x08,
+ 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x02, 0x01, 0x16, 0x1c, 0x68, 0x74,
+ 0x74, 0x70, 0x73, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x76, 0x65,
+ 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x63,
+ 0x70, 0x73, 0x30, 0x34, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x5a, 0x17,
+ 0x0d, 0x31, 0x33, 0x30, 0x35, 0x30, 0x39, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01,
+ 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x30, 0x02, 0x86, 0x2d, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a,
+ 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x73, 0x30, 0x39, 0x30, 0x37, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01,
+ 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x02, 0x30, 0x44, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x20, 0x04,
+ 0x3d, 0x30, 0x3b, 0x30, 0x39, 0x06, 0x0b, 0x60, 0x86, 0x48, 0x01, 0x86,
+ 0xf8, 0x45, 0x01, 0x07, 0x17, 0x06, 0x31, 0x0b, 0x30, 0x09, 0x06, 0x03,
+ 0x55, 0x04, 0x06, 0x13, 0x02, 0x47, 0x42, 0x31, 0x1b, 0x53, 0x31, 0x17,
+ 0x30, 0x15, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0a, 0x13, 0x0e, 0x56, 0x65, 0x72,
+ 0x69, 0x53, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2c, 0x20, 0x49, 0x6e, 0x63, 0x2e, 0x31,
+ 0x1f, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x16, 0x56, 0x65,
+ 0x72, 0x69, 0x53, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x54, 0x72, 0x75, 0x73, 0x74,
+ 0x20, 0x4e, 0x65, 0x74, 0x77, 0x6f, 0x72, 0x6b, 0x31, 0x3b, 0x30, 0x39,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x32, 0x54, 0x65, 0x72, 0x6d, 0x73,
+ 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x20, 0x75, 0x73, 0x65, 0x20, 0x61, 0x74, 0x20, 0x68,
+ 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x73, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x76,
+ 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f,
+ 0x72, 0x70, 0x61, 0x20, 0x28, 0x63, 0x29, 0x30, 0x31, 0x10, 0x30, 0x0e,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x07, 0x13, 0x07, 0x53, 0x31, 0x13, 0x30, 0x11,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x0a, 0x47, 0x31, 0x13, 0x30, 0x11,
+ 0x06, 0x0b, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x04, 0x01, 0x82, 0x37, 0x3c, 0x02, 0x01,
+ 0x03, 0x13, 0x02, 0x55, 0x31, 0x16, 0x30, 0x14, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04,
+ 0x03, 0x14, 0x31, 0x19, 0x30, 0x17, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x03, 0x13,
+ 0x31, 0x1d, 0x30, 0x1b, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0f, 0x13, 0x14, 0x50,
+ 0x72, 0x69, 0x76, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x20, 0x4f, 0x72, 0x67, 0x61, 0x6e,
+ 0x69, 0x7a, 0x61, 0x74, 0x69, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x31, 0x12, 0x31, 0x21, 0x30,
+ 0x1f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x18, 0x44, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x61,
+ 0x69, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x43, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x74, 0x72, 0x6f, 0x6c, 0x20, 0x56,
+ 0x61, 0x6c, 0x69, 0x64, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x64, 0x31, 0x14, 0x31, 0x31,
+ 0x30, 0x2f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x28, 0x53, 0x65, 0x65,
+ 0x20, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x72, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x73, 0x65, 0x63,
+ 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x47, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x62, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x53,
+ 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x31, 0x53, 0x65, 0x72, 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x43, 0x41,
+ 0x2e, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x56, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x53, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e,
+ 0x20, 0x43, 0x6c, 0x61, 0x73, 0x73, 0x20, 0x33, 0x20, 0x45, 0x63, 0x72,
+ 0x6c, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x65, 0x6f, 0x74, 0x72, 0x75, 0x73, 0x74, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x73, 0x2f, 0x73, 0x64, 0x31, 0x1a,
+ 0x30, 0x18, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0a, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a,
+ 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x45, 0x56, 0x49, 0x6e, 0x74, 0x6c, 0x2d, 0x63, 0x63, 0x72,
+ 0x74, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x69, 0x63, 0x65, 0x72,
+ 0x74, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x31, 0x6f, 0x63, 0x73, 0x70, 0x2e,
+ 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d,
+ 0x30, 0x39, 0x72, 0x61, 0x70, 0x69, 0x64, 0x73, 0x73, 0x6c, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x73, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6f, 0x73, 0x69, 0x74, 0x6f, 0x72,
+ 0x79, 0x2f, 0x30, 0x81, 0x80, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05,
+ 0x07, 0x01, 0x01, 0x04, 0x74, 0x30, 0x72, 0x30, 0x24, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b,
+ 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x30, 0x01, 0x86, 0x18, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74,
+ 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x6f, 0x63, 0x73, 0x70, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64,
+ 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x30, 0x4a, 0x06,
+ 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x30, 0x02, 0x86, 0x3e, 0x68,
+ 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x65, 0x72, 0x74, 0x69, 0x66,
+ 0x69, 0x63, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x73, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64,
+ 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6f, 0x73,
+ 0x69, 0x74, 0x6f, 0x72, 0x79, 0x2f, 0x67, 0x64, 0x5f, 0x69, 0x6e, 0x74,
+ 0x65, 0x72, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x64, 0x69, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x72,
+ 0x74, 0x30, 0x1f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x23, 0x04, 0x18, 0x30, 0x16,
+ 0x80, 0x14, 0xfd, 0xac, 0x61, 0x32, 0x93, 0x6c, 0x45, 0xd6, 0xe2, 0xee,
+ 0x85, 0x5f, 0x9a, 0xba, 0xe7, 0x76, 0x99, 0x68, 0xcc, 0xe7, 0x30, 0x27,
+ 0x86, 0x29, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x86, 0x30,
+ 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x73,
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_sets.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_sets.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1552668
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_sets.go
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go-certificates"
+)
+
+type certSet [][]byte
+
+var certSets = map[uint64]certSet{
+ certsets.CertSet2Hash: certsets.CertSet2,
+ certsets.CertSet3Hash: certsets.CertSet3,
+}
+
+// findCertInSet searches for the cert in the set. Negative return value means not found.
+func (s *certSet) findCertInSet(cert []byte) int {
+ for i, c := range *s {
+ if bytes.Equal(c, cert) {
+ return i
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5c58c4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead.go
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+// +build ignore
+
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/aead/chacha20"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type aeadChacha20Poly1305 struct {
+ otherIV []byte
+ myIV []byte
+ encrypter cipher.AEAD
+ decrypter cipher.AEAD
+}
+
+// NewAEADChacha20Poly1305 creates a AEAD using chacha20poly1305
+func NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(otherKey []byte, myKey []byte, otherIV []byte, myIV []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+ if len(myKey) != 32 || len(otherKey) != 32 || len(myIV) != 4 || len(otherIV) != 4 {
+ return nil, errors.New("chacha20poly1305: expected 32-byte keys and 4-byte IVs")
+ }
+ // copy because ChaCha20Poly1305 expects array pointers
+ var MyKey, OtherKey [32]byte
+ copy(MyKey[:], myKey)
+ copy(OtherKey[:], otherKey)
+
+ encrypter, err := chacha20.NewChaCha20Poly1305WithTagSize(&MyKey, 12)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ decrypter, err := chacha20.NewChaCha20Poly1305WithTagSize(&OtherKey, 12)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return &aeadChacha20Poly1305{
+ otherIV: otherIV,
+ myIV: myIV,
+ encrypter: encrypter,
+ decrypter: decrypter,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadChacha20Poly1305) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return aead.decrypter.Open(dst, makeNonce(aead.otherIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadChacha20Poly1305) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ return aead.encrypter.Seal(dst, makeNonce(aead.myIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead_test.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead_test.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9d5197b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead_test.go
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+// +build ignore
+
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+
+ . "github.com/onsi/ginkgo"
+ . "github.com/onsi/gomega"
+)
+
+var _ = Describe("Chacha20poly1305", func() {
+ var (
+ alice, bob AEAD
+ keyAlice, keyBob, ivAlice, ivBob []byte
+ )
+
+ BeforeEach(func() {
+ keyAlice = make([]byte, 32)
+ keyBob = make([]byte, 32)
+ ivAlice = make([]byte, 4)
+ ivBob = make([]byte, 4)
+ rand.Reader.Read(keyAlice)
+ rand.Reader.Read(keyBob)
+ rand.Reader.Read(ivAlice)
+ rand.Reader.Read(ivBob)
+ var err error
+ alice, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice, ivBob, ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ bob, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyAlice, keyBob, ivAlice, ivBob)
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ })
+
+ It("seals and opens", func() {
+ b := alice.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ text, err := bob.Open(nil, b, 42, []byte("aad"))
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ Expect(text).To(Equal([]byte("foobar")))
+ })
+
+ It("seals and opens reverse", func() {
+ b := bob.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ text, err := alice.Open(nil, b, 42, []byte("aad"))
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ Expect(text).To(Equal([]byte("foobar")))
+ })
+
+ It("has the proper length", func() {
+ b := bob.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ Expect(b).To(HaveLen(6 + 12))
+ })
+
+ It("fails with wrong aad", func() {
+ b := alice.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ _, err := bob.Open(nil, b, 42, []byte("aad2"))
+ Expect(err).To(HaveOccurred())
+ })
+
+ It("rejects wrong key and iv sizes", func() {
+ var err error
+ e := "chacha20poly1305: expected 32-byte keys and 4-byte IVs"
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob[1:], keyAlice, ivBob, ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice[1:], ivBob, ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice, ivBob[1:], ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice, ivBob, ivAlice[1:])
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ })
+})
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/curve_25519.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/curve_25519.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a570d6b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/curve_25519.go
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "errors"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/curve25519"
+)
+
+// KeyExchange manages the exchange of keys
+type curve25519KEX struct {
+ secret [32]byte
+ public [32]byte
+}
+
+var _ KeyExchange = &curve25519KEX{}
+
+// NewCurve25519KEX creates a new KeyExchange using Curve25519, see https://cr.yp.to/ecdh.html
+func NewCurve25519KEX() (KeyExchange, error) {
+ c := &curve25519KEX{}
+ if _, err := rand.Read(c.secret[:]); err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.New("Curve25519: could not create private key")
+ }
+ // See https://cr.yp.to/ecdh.html
+ c.secret[0] &= 248
+ c.secret[31] &= 127
+ c.secret[31] |= 64
+ curve25519.ScalarBaseMult(&c.public, &c.secret)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+func (c *curve25519KEX) PublicKey() []byte {
+ return c.public[:]
+}
+
+func (c *curve25519KEX) CalculateSharedKey(otherPublic []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ if len(otherPublic) != 32 {
+ return nil, errors.New("Curve25519: expected public key of 32 byte")
+ }
+ var res [32]byte
+ var otherPublicArray [32]byte
+ copy(otherPublicArray[:], otherPublic)
+ curve25519.ScalarMult(&res, &c.secret, &otherPublicArray)
+ return res[:], nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_derivation.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_derivation.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..60648d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_derivation.go
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/sha256"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/hkdf"
+)
+
+// DeriveKeysChacha20 derives the client and server keys and creates a matching chacha20poly1305 AEAD instance
+// func DeriveKeysChacha20(version protocol.VersionNumber, forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo []byte, scfg []byte, cert []byte, divNonce []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+// otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV, err := deriveKeys(version, forwardSecure, sharedSecret, nonces, connID, chlo, scfg, cert, divNonce, 32)
+// if err != nil {
+// return nil, err
+// }
+// return NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV)
+// }
+
+// DeriveKeysAESGCM derives the client and server keys and creates a matching AES-GCM AEAD instance
+func DeriveKeysAESGCM(forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo []byte, scfg []byte, cert []byte, divNonce []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+ otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV, err := deriveKeys(forwardSecure, sharedSecret, nonces, connID, chlo, scfg, cert, divNonce, 16)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return NewAEADAESGCM(otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV)
+}
+
+func deriveKeys(forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo, scfg, cert, divNonce []byte, keyLen int) ([]byte, []byte, []byte, []byte, error) {
+ var info bytes.Buffer
+ if forwardSecure {
+ info.Write([]byte("QUIC forward secure key expansion\x00"))
+ } else {
+ info.Write([]byte("QUIC key expansion\x00"))
+ }
+ utils.WriteUint64(&info, uint64(connID))
+ info.Write(chlo)
+ info.Write(scfg)
+ info.Write(cert)
+
+ r := hkdf.New(sha256.New, sharedSecret, nonces, info.Bytes())
+
+ s := make([]byte, 2*keyLen+2*4)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, s); err != nil {
+ return nil, nil, nil, nil, err
+ }
+ otherKey := s[:keyLen]
+ myKey := s[keyLen : 2*keyLen]
+ otherIV := s[2*keyLen : 2*keyLen+4]
+ myIV := s[2*keyLen+4:]
+
+ if !forwardSecure {
+ if err := diversify(myKey, myIV, divNonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, nil, nil, nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ return otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV, nil
+}
+
+func diversify(key, iv, divNonce []byte) error {
+ secret := make([]byte, len(key)+len(iv))
+ copy(secret, key)
+ copy(secret[len(key):], iv)
+
+ r := hkdf.New(sha256.New, secret, divNonce, []byte("QUIC key diversification"))
+
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, key); err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, iv); err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_exchange.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_exchange.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d240b9c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_exchange.go
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+package crypto
+
+// KeyExchange manages the exchange of keys
+type KeyExchange interface {
+ PublicKey() []byte
+ CalculateSharedKey(otherPublic []byte) ([]byte, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/nonce.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/nonce.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9b6d416
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/nonce.go
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+func makeNonce(iv []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) []byte {
+ res := make([]byte, 12)
+ copy(res[0:4], iv)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(res[4:12], uint64(packetNumber))
+ return res
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/null_aead.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/null_aead.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5aa198c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/null_aead.go
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/fnv128a"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// NullAEAD handles not-yet encrypted packets
+type NullAEAD struct{}
+
+var _ AEAD = &NullAEAD{}
+
+// Open and verify the ciphertext
+func (NullAEAD) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ if len(src) < 12 {
+ return nil, errors.New("NullAEAD: ciphertext cannot be less than 12 bytes long")
+ }
+
+ hash := fnv128a.New()
+ hash.Write(associatedData)
+ hash.Write(src[12:])
+ testHigh, testLow := hash.Sum128()
+
+ low := binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(src)
+ high := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(src[8:])
+
+ if uint32(testHigh&0xffffffff) != high || testLow != low {
+ return nil, errors.New("NullAEAD: failed to authenticate received data")
+ }
+ return src[12:], nil
+}
+
+// Seal writes hash and ciphertext to the buffer
+func (NullAEAD) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ if cap(dst) < 12+len(src) {
+ dst = make([]byte, 12+len(src))
+ } else {
+ dst = dst[:12+len(src)]
+ }
+
+ hash := fnv128a.New()
+ hash.Write(associatedData)
+ hash.Write(src)
+ high, low := hash.Sum128()
+
+ copy(dst[12:], src)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(dst, low)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(dst[8:], uint32(high))
+ return dst
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/proof_source.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/proof_source.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6af8072
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/proof_source.go
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto"
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "crypto/rsa"
+ "crypto/sha256"
+ "crypto/tls"
+ "errors"
+ "strings"
+)
+
+// proofSource stores a key and a certificate for the server proof
+type proofSource struct {
+ config *tls.Config
+}
+
+// NewProofSource loads the key and cert from files
+func NewProofSource(tlsConfig *tls.Config) (Signer, error) {
+ return &proofSource{config: tlsConfig}, nil
+}
+
+// SignServerProof signs CHLO and server config for use in the server proof
+func (ps *proofSource) SignServerProof(sni string, chlo []byte, serverConfigData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ cert, err := ps.getCertForSNI(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ hash := sha256.New()
+ hash.Write([]byte("QUIC CHLO and server config signature\x00"))
+ chloHash := sha256.Sum256(chlo)
+ hash.Write([]byte{32, 0, 0, 0})
+ hash.Write(chloHash[:])
+ hash.Write(serverConfigData)
+
+ key, ok := cert.PrivateKey.(crypto.Signer)
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, errors.New("expected PrivateKey to implement crypto.Signer")
+ }
+
+ opts := crypto.SignerOpts(crypto.SHA256)
+
+ if _, ok = key.(*rsa.PrivateKey); ok {
+ opts = &rsa.PSSOptions{SaltLength: 32, Hash: crypto.SHA256}
+ }
+
+ return key.Sign(rand.Reader, hash.Sum(nil), opts)
+}
+
+// GetCertsCompressed gets the certificate in the format described by the QUIC crypto doc
+func (ps *proofSource) GetCertsCompressed(sni string, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ cert, err := ps.getCertForSNI(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return getCompressedCert(cert.Certificate, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes)
+}
+
+// GetLeafCert gets the leaf certificate
+func (ps *proofSource) GetLeafCert(sni string) ([]byte, error) {
+ cert, err := ps.getCertForSNI(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return cert.Certificate[0], nil
+}
+
+func (ps *proofSource) getCertForSNI(sni string) (*tls.Certificate, error) {
+ if ps.config.GetCertificate != nil {
+ cert, err := ps.config.GetCertificate(&tls.ClientHelloInfo{ServerName: sni})
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ if cert != nil {
+ return cert, nil
+ }
+ }
+ if len(ps.config.NameToCertificate) != 0 {
+ if cert, ok := ps.config.NameToCertificate[sni]; ok {
+ return cert, nil
+ }
+ wildcardSNI := "*" + strings.TrimLeftFunc(sni, func(r rune) bool { return r != '.' })
+ if cert, ok := ps.config.NameToCertificate[wildcardSNI]; ok {
+ return cert, nil
+ }
+ }
+ if len(ps.config.Certificates) != 0 {
+ return &ps.config.Certificates[0], nil
+ }
+ return nil, errors.New("no matching certificate found")
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/signer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/signer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0d9ba4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/signer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+package crypto
+
+// A Signer holds a certificate and a private key
+type Signer interface {
+ SignServerProof(sni string, chlo []byte, serverConfigData []byte) ([]byte, error)
+ GetCertsCompressed(sni string, commonSetHashes, cachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error)
+ GetLeafCert(sni string) ([]byte, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/source_address_token.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/source_address_token.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6afdacd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/source_address_token.go
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/aes"
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "crypto/sha256"
+ "crypto/subtle"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "net"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/hkdf"
+)
+
+// StkSource is used to create and verify source address tokens
+type StkSource interface {
+ // NewToken creates a new token for a given IP address
+ NewToken(ip net.IP) ([]byte, error)
+ // VerifyToken verifies if a token matches a given IP address and is not outdated
+ VerifyToken(ip net.IP, data []byte) error
+}
+
+type sourceAddressToken struct {
+ ip net.IP
+ // unix timestamp in seconds
+ timestamp uint64
+}
+
+func (t *sourceAddressToken) serialize() []byte {
+ res := make([]byte, 8+len(t.ip))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(res, t.timestamp)
+ copy(res[8:], t.ip)
+ return res
+}
+
+func parseToken(data []byte) (*sourceAddressToken, error) {
+ if len(data) != 8+4 && len(data) != 8+16 {
+ return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid STK length: %d", len(data))
+ }
+ return &sourceAddressToken{
+ ip: data[8:],
+ timestamp: binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(data),
+ }, nil
+}
+
+type stkSource struct {
+ aead cipher.AEAD
+}
+
+const stkKeySize = 16
+
+// Chrome currently sets this to 12, but discusses changing it to 16. We start
+// at 16 :)
+const stkNonceSize = 16
+
+// NewStkSource creates a source for source address tokens
+func NewStkSource(secret []byte) (StkSource, error) {
+ key, err := deriveKey(secret)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ aead, err := cipher.NewGCMWithNonceSize(c, stkNonceSize)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return &stkSource{aead: aead}, nil
+}
+
+func (s *stkSource) NewToken(ip net.IP) ([]byte, error) {
+ return encryptToken(s.aead, &sourceAddressToken{
+ ip: ip,
+ timestamp: uint64(time.Now().Unix()),
+ })
+}
+
+func (s *stkSource) VerifyToken(ip net.IP, data []byte) error {
+ if len(data) < stkNonceSize {
+ return errors.New("STK too short")
+ }
+ nonce := data[:stkNonceSize]
+
+ res, err := s.aead.Open(nil, nonce, data[stkNonceSize:], nil)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ token, err := parseToken(res)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ if subtle.ConstantTimeCompare(token.ip, ip) != 1 {
+ return errors.New("invalid ip in STK")
+ }
+
+ if time.Now().Unix() > int64(token.timestamp)+protocol.STKExpiryTimeSec {
+ return errors.New("STK expired")
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func deriveKey(secret []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ r := hkdf.New(sha256.New, secret, nil, []byte("QUIC source address token key"))
+ key := make([]byte, stkKeySize)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, key); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return key, nil
+}
+
+func encryptToken(aead cipher.AEAD, token *sourceAddressToken) ([]byte, error) {
+ nonce := make([]byte, stkNonceSize)
+ if _, err := rand.Read(nonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return aead.Seal(nonce, nonce, token.serialize(), nil), nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_control_manager.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_control_manager.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0ab6363
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_control_manager.go
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
+package flowcontrol
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type flowControlManager struct {
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+ streamFlowController map[protocol.StreamID]*flowController
+ contributesToConnectionFlowControl map[protocol.StreamID]bool
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+}
+
+var (
+ // ErrStreamFlowControlViolation is a stream flow control violation
+ ErrStreamFlowControlViolation = errors.New("Stream level flow control violation")
+ // ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation is a connection level flow control violation
+ ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation = errors.New("Connection level flow control violation")
+)
+
+var errMapAccess = errors.New("Error accessing the flowController map.")
+
+// NewFlowControlManager creates a new flow control manager
+func NewFlowControlManager(connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager) FlowControlManager {
+ fcm := flowControlManager{
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ streamFlowController: make(map[protocol.StreamID]*flowController),
+ contributesToConnectionFlowControl: make(map[protocol.StreamID]bool),
+ }
+ // initialize connection level flow controller
+ fcm.streamFlowController[0] = newFlowController(0, connectionParametersManager)
+ fcm.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[0] = false
+ return &fcm
+}
+
+// NewStream creates new flow controllers for a stream
+func (f *flowControlManager) NewStream(streamID protocol.StreamID, contributesToConnectionFlow bool) {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ if _, ok := f.streamFlowController[streamID]; ok {
+ return
+ }
+
+ f.streamFlowController[streamID] = newFlowController(streamID, f.connectionParametersManager)
+ f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] = contributesToConnectionFlow
+}
+
+// RemoveStream removes a closed stream from flow control
+func (f *flowControlManager) RemoveStream(streamID protocol.StreamID) {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ delete(f.streamFlowController, streamID)
+ delete(f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl, streamID)
+ f.mutex.Unlock()
+}
+
+// UpdateHighestReceived updates the highest received byte offset for a stream
+// it adds the number of additional bytes to connection level flow control
+// streamID must not be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) UpdateHighestReceived(streamID protocol.StreamID, byteOffset protocol.ByteCount) error {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ increment := streamFlowController.UpdateHighestReceived(byteOffset)
+
+ if streamFlowController.CheckFlowControlViolation() {
+ return ErrStreamFlowControlViolation
+ }
+
+ if f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] {
+ connectionFlowController := f.streamFlowController[0]
+ connectionFlowController.IncrementHighestReceived(increment)
+ if connectionFlowController.CheckFlowControlViolation() {
+ return ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation
+ }
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// streamID must not be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) AddBytesRead(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ streamFlowController.AddBytesRead(n)
+
+ if f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] {
+ f.streamFlowController[0].AddBytesRead(n)
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (f *flowControlManager) GetWindowUpdates() (res []WindowUpdate) {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+ for id, fc := range f.streamFlowController {
+ if necessary, offset := fc.MaybeTriggerWindowUpdate(); necessary {
+ res = append(res, WindowUpdate{StreamID: id, Offset: offset})
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+// streamID must not be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) AddBytesSent(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ f.mutex.Unlock()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ streamFlowController.AddBytesSent(n)
+
+ if f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] {
+ f.streamFlowController[0].AddBytesSent(n)
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// must not be called with StreamID 0
+func (f *flowControlManager) SendWindowSize(streamID protocol.StreamID) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.RLock()
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ f.mutex.RUnlock()
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ res := streamFlowController.SendWindowSize()
+
+ contributes, ok := f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID]
+ if !ok {
+ return 0, errMapAccess
+ }
+ if contributes {
+ res = utils.MinByteCount(res, f.streamFlowController[0].SendWindowSize())
+ }
+
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+func (f *flowControlManager) RemainingConnectionWindowSize() protocol.ByteCount {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.RLock()
+ res := f.streamFlowController[0].SendWindowSize()
+ f.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return res
+}
+
+// streamID may be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) UpdateWindow(streamID protocol.StreamID, offset protocol.ByteCount) (bool, error) {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ f.mutex.Unlock()
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+
+ return streamFlowController.UpdateSendWindow(offset), nil
+}
+
+func (f *flowControlManager) getFlowController(streamID protocol.StreamID) (*flowController, error) {
+ streamFlowController, ok := f.streamFlowController[streamID]
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, errMapAccess
+ }
+ return streamFlowController, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_controller.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_controller.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..21020ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_controller.go
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+package flowcontrol
+
+import (
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type flowController struct {
+ streamID protocol.StreamID
+
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ bytesSent protocol.ByteCount
+ sendFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+
+ bytesRead protocol.ByteCount
+ highestReceived protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// newFlowController gets a new flow controller
+func newFlowController(streamID protocol.StreamID, connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager) *flowController {
+ fc := flowController{
+ streamID: streamID,
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ }
+
+ if streamID == 0 {
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindow = connectionParametersManager.GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow()
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement = fc.receiveFlowControlWindow
+ } else {
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindow = connectionParametersManager.GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow()
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement = fc.receiveFlowControlWindow
+ }
+
+ return &fc
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) getSendFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ if c.sendFlowControlWindow == 0 {
+ if c.streamID == 0 {
+ return c.connectionParametersManager.GetSendConnectionFlowControlWindow()
+ }
+ return c.connectionParametersManager.GetSendStreamFlowControlWindow()
+ }
+ return c.sendFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) AddBytesSent(n protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.bytesSent += n
+}
+
+// UpdateSendWindow should be called after receiving a WindowUpdateFrame
+// it returns true if the window was actually updated
+func (c *flowController) UpdateSendWindow(newOffset protocol.ByteCount) bool {
+ if newOffset > c.sendFlowControlWindow {
+ c.sendFlowControlWindow = newOffset
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) SendWindowSize() protocol.ByteCount {
+ sendFlowControlWindow := c.getSendFlowControlWindow()
+
+ if c.bytesSent > sendFlowControlWindow { // should never happen, but make sure we don't do an underflow here
+ return 0
+ }
+ return sendFlowControlWindow - c.bytesSent
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) SendWindowOffset() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return c.getSendFlowControlWindow()
+}
+
+// UpdateHighestReceived updates the highestReceived value, if the byteOffset is higher
+// Should **only** be used for the stream-level FlowController
+func (c *flowController) UpdateHighestReceived(byteOffset protocol.ByteCount) protocol.ByteCount {
+ if byteOffset > c.highestReceived {
+ increment := byteOffset - c.highestReceived
+ c.highestReceived = byteOffset
+ return increment
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// IncrementHighestReceived adds an increment to the highestReceived value
+// Should **only** be used for the connection-level FlowController
+func (c *flowController) IncrementHighestReceived(increment protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.highestReceived += increment
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) AddBytesRead(n protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.bytesRead += n
+}
+
+// MaybeTriggerWindowUpdate determines if it is necessary to send a WindowUpdate
+// if so, it returns true and the offset of the window
+func (c *flowController) MaybeTriggerWindowUpdate() (bool, protocol.ByteCount) {
+ diff := c.receiveFlowControlWindow - c.bytesRead
+ // Chromium implements the same threshold
+ if diff < (c.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement / 2) {
+ c.receiveFlowControlWindow = c.bytesRead + c.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement
+ return true, c.receiveFlowControlWindow
+ }
+ return false, 0
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) CheckFlowControlViolation() bool {
+ if c.highestReceived > c.receiveFlowControlWindow {
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/interface.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/interface.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3f4b089
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/interface.go
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package flowcontrol
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// WindowUpdate provides the data for WindowUpdateFrames.
+type WindowUpdate struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ Offset protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// A FlowControlManager manages the flow control
+type FlowControlManager interface {
+ NewStream(streamID protocol.StreamID, contributesToConnectionFlow bool)
+ RemoveStream(streamID protocol.StreamID)
+ // methods needed for receiving data
+ UpdateHighestReceived(streamID protocol.StreamID, byteOffset protocol.ByteCount) error
+ AddBytesRead(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error
+ GetWindowUpdates() []WindowUpdate
+ // methods needed for sending data
+ AddBytesSent(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error
+ SendWindowSize(streamID protocol.StreamID) (protocol.ByteCount, error)
+ RemainingConnectionWindowSize() protocol.ByteCount
+ UpdateWindow(streamID protocol.StreamID, offset protocol.ByteCount) (bool, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b68b448
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,466 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ // ErrInvalidAckRanges occurs when a client sends inconsistent ACK ranges
+ ErrInvalidAckRanges = errors.New("AckFrame: ACK frame contains invalid ACK ranges")
+ // ErrInvalidFirstAckRange occurs when the first ACK range contains no packets
+ ErrInvalidFirstAckRange = errors.New("AckFrame: ACK frame has invalid first ACK range")
+)
+
+var (
+ errInconsistentAckLargestAcked = errors.New("internal inconsistency: LargestAcked does not match ACK ranges")
+ errInconsistentAckLowestAcked = errors.New("internal inconsistency: LowestAcked does not match ACK ranges")
+)
+
+// An AckFrame is an ACK frame in QUIC
+type AckFrame struct {
+ LargestAcked protocol.PacketNumber
+ LowestAcked protocol.PacketNumber
+ AckRanges []AckRange // has to be ordered. The ACK range with the highest FirstPacketNumber goes first, the ACK range with the lowest FirstPacketNumber goes last
+
+ DelayTime time.Duration
+ PacketReceivedTime time.Time // only for received packets. Will not be modified for received ACKs frames
+}
+
+// ParseAckFrame reads an ACK frame
+func ParseAckFrame(r *bytes.Reader, version protocol.VersionNumber) (*AckFrame, error) {
+ frame := &AckFrame{}
+
+ typeByte, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ hasMissingRanges := false
+ if typeByte&0x20 == 0x20 {
+ hasMissingRanges = true
+ }
+
+ largestAckedLen := 2 * ((typeByte & 0x0C) >> 2)
+ if largestAckedLen == 0 {
+ largestAckedLen = 1
+ }
+
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen := 2 * (typeByte & 0x03)
+ if missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen == 0 {
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen = 1
+ }
+
+ largestAcked, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, largestAckedLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.LargestAcked = protocol.PacketNumber(largestAcked)
+
+ delay, err := utils.ReadUfloat16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.DelayTime = time.Duration(delay) * time.Microsecond
+
+ var numAckBlocks uint8
+ if hasMissingRanges {
+ numAckBlocks, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if hasMissingRanges && numAckBlocks == 0 {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidAckRanges
+ }
+
+ ackBlockLength, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ if ackBlockLength < 1 {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidFirstAckRange
+ }
+
+ if ackBlockLength > largestAcked {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidAckRanges
+ }
+
+ if hasMissingRanges {
+ ackRange := AckRange{
+ FirstPacketNumber: protocol.PacketNumber(largestAcked-ackBlockLength) + 1,
+ LastPacketNumber: frame.LargestAcked,
+ }
+ frame.AckRanges = append(frame.AckRanges, ackRange)
+
+ var inLongBlock bool
+ var lastRangeComplete bool
+ for i := uint8(0); i < numAckBlocks; i++ {
+ var gap uint8
+ gap, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ ackBlockLength, err = utils.ReadUintN(r, missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ length := protocol.PacketNumber(ackBlockLength)
+
+ if inLongBlock {
+ frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber -= protocol.PacketNumber(gap) + length
+ frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].LastPacketNumber -= protocol.PacketNumber(gap)
+ } else {
+ lastRangeComplete = false
+ ackRange := AckRange{
+ LastPacketNumber: frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber - protocol.PacketNumber(gap) - 1,
+ }
+ ackRange.FirstPacketNumber = ackRange.LastPacketNumber - length + 1
+ frame.AckRanges = append(frame.AckRanges, ackRange)
+ }
+
+ if length > 0 {
+ lastRangeComplete = true
+ }
+
+ inLongBlock = (ackBlockLength == 0)
+ }
+
+ // if the last range was not complete, FirstPacketNumber and LastPacketNumber make no sense
+ // remove the range from frame.AckRanges
+ if !lastRangeComplete {
+ frame.AckRanges = frame.AckRanges[:len(frame.AckRanges)-1]
+ }
+
+ frame.LowestAcked = frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber
+ } else {
+ frame.LowestAcked = protocol.PacketNumber(largestAcked + 1 - ackBlockLength)
+ }
+
+ if !frame.validateAckRanges() {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidAckRanges
+ }
+
+ var numTimestamp byte
+ numTimestamp, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if numTimestamp > 0 {
+ // Delta Largest acked
+ _, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ // First Timestamp
+ _, err = utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ for i := 0; i < int(numTimestamp)-1; i++ {
+ // Delta Largest acked
+ _, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ // Time Since Previous Timestamp
+ _, err = utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+// Write writes an ACK frame.
+func (f *AckFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ largestAckedLen := protocol.GetPacketNumberLength(f.LargestAcked)
+
+ typeByte := uint8(0x40)
+
+ if largestAckedLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen1 {
+ typeByte ^= (uint8(largestAckedLen / 2)) << 2
+ }
+
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen := f.getMissingSequenceNumberDeltaLen()
+ if missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen1 {
+ typeByte ^= (uint8(missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen / 2))
+ }
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ typeByte |= 0x20
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ switch largestAckedLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(f.LargestAcked))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(f.LargestAcked))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.LargestAcked))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(f.LargestAcked))
+ }
+
+ f.DelayTime = time.Now().Sub(f.PacketReceivedTime)
+ utils.WriteUfloat16(b, uint64(f.DelayTime/time.Microsecond))
+
+ var numRanges uint64
+ var numRangesWritten uint64
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ numRanges = f.numWritableNackRanges()
+ if numRanges > 0xFF {
+ panic("AckFrame: Too many ACK ranges")
+ }
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(numRanges - 1))
+ }
+
+ var firstAckBlockLength protocol.PacketNumber
+ if !f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ firstAckBlockLength = f.LargestAcked - f.LowestAcked + 1
+ } else {
+ if f.LargestAcked != f.AckRanges[0].LastPacketNumber {
+ return errInconsistentAckLargestAcked
+ }
+ if f.LowestAcked != f.AckRanges[len(f.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber {
+ return errInconsistentAckLowestAcked
+ }
+ firstAckBlockLength = f.LargestAcked - f.AckRanges[0].FirstPacketNumber + 1
+ numRangesWritten++
+ }
+
+ switch missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(firstAckBlockLength))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(firstAckBlockLength))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(firstAckBlockLength))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(firstAckBlockLength))
+ }
+
+ for i, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if i == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ length := ackRange.LastPacketNumber - ackRange.FirstPacketNumber + 1
+ gap := f.AckRanges[i-1].FirstPacketNumber - ackRange.LastPacketNumber - 1
+
+ num := gap/0xFF + 1
+ if gap%0xFF == 0 {
+ num--
+ }
+
+ if num == 1 {
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(gap))
+ switch missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(length))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(length))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(length))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(length))
+ }
+ numRangesWritten++
+ } else {
+ for i := 0; i < int(num); i++ {
+ var lengthWritten uint64
+ var gapWritten uint8
+
+ if i == int(num)-1 { // last block
+ lengthWritten = uint64(length)
+ gapWritten = uint8(1 + ((gap - 1) % 255))
+ } else {
+ lengthWritten = 0
+ gapWritten = 0xFF
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(gapWritten)
+ switch missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(lengthWritten))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(lengthWritten))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(lengthWritten))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, lengthWritten)
+ }
+
+ numRangesWritten++
+ }
+ }
+
+ // this is needed if not all AckRanges can be written to the ACK frame (if there are more than 0xFF)
+ if numRangesWritten >= numRanges {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if numRanges != numRangesWritten {
+ return errors.New("BUG: Inconsistent number of ACK ranges written")
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(0) // no timestamps
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *AckFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ var length protocol.ByteCount
+ length = 1 + 2 + 1 // 1 TypeByte, 2 ACK delay time, 1 Num Timestamp
+ length += protocol.ByteCount(protocol.GetPacketNumberLength(f.LargestAcked))
+
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen := protocol.ByteCount(f.getMissingSequenceNumberDeltaLen())
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ length += (1 + missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen) * protocol.ByteCount(f.numWritableNackRanges())
+ } else {
+ length += missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen
+ }
+
+ length += (1 + 2) * 0 /* TODO: num_timestamps */
+
+ return length, nil
+}
+
+// HasMissingRanges returns if this frame reports any missing packets
+func (f *AckFrame) HasMissingRanges() bool {
+ if len(f.AckRanges) > 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func (f *AckFrame) validateAckRanges() bool {
+ if len(f.AckRanges) == 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+
+ // if there are missing packets, there will always be at least 2 ACK ranges
+ if len(f.AckRanges) == 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+
+ if f.AckRanges[0].LastPacketNumber != f.LargestAcked {
+ return false
+ }
+
+ // check the validity of every single ACK range
+ for _, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if ackRange.FirstPacketNumber > ackRange.LastPacketNumber {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+
+ // check the consistency for ACK with multiple NACK ranges
+ for i, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if i == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+ lastAckRange := f.AckRanges[i-1]
+ if lastAckRange.FirstPacketNumber <= ackRange.FirstPacketNumber {
+ return false
+ }
+ if lastAckRange.FirstPacketNumber <= ackRange.LastPacketNumber+1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+
+ return true
+}
+
+// numWritableNackRanges calculates the number of ACK blocks that are about to be written
+// this number is different from len(f.AckRanges) for the case of long gaps (> 255 packets)
+func (f *AckFrame) numWritableNackRanges() uint64 {
+ if len(f.AckRanges) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+
+ var numRanges uint64
+ for i, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if i == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ lastAckRange := f.AckRanges[i-1]
+ gap := lastAckRange.FirstPacketNumber - ackRange.LastPacketNumber - 1
+ rangeLength := 1 + uint64(gap)/0xFF
+ if uint64(gap)%0xFF == 0 {
+ rangeLength--
+ }
+
+ if numRanges+rangeLength < 0xFF {
+ numRanges += rangeLength
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ return numRanges + 1
+}
+
+func (f *AckFrame) getMissingSequenceNumberDeltaLen() protocol.PacketNumberLen {
+ var maxRangeLength protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ for _, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ rangeLength := ackRange.LastPacketNumber - ackRange.FirstPacketNumber + 1
+ if rangeLength > maxRangeLength {
+ maxRangeLength = rangeLength
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ maxRangeLength = f.LargestAcked - f.LowestAcked + 1
+ }
+
+ if maxRangeLength <= 0xFF {
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen1
+ }
+ if maxRangeLength <= 0xFFFF {
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen2
+ }
+ if maxRangeLength <= 0xFFFFFFFF {
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen4
+ }
+
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen6
+}
+
+// AcksPacket determines if this ACK frame acks a certain packet number
+func (f *AckFrame) AcksPacket(p protocol.PacketNumber) bool {
+ if p < f.LowestAcked || p > f.LargestAcked { // this is just a performance optimization
+ return false
+ }
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ // TODO: this could be implemented as a binary search
+ for _, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if p >= ackRange.FirstPacketNumber && p <= ackRange.LastPacketNumber {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+ // if packet doesn't have missing ranges
+ return (p >= f.LowestAcked && p <= f.LargestAcked)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_range.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_range.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ac65d33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_range.go
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+package frames
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// AckRange is an ACK range
+type AckRange struct {
+ FirstPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ LastPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/blocked_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/blocked_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b7e640c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/blocked_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A BlockedFrame in QUIC
+type BlockedFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+}
+
+//Write writes a BlockedFrame frame
+func (f *BlockedFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ b.WriteByte(0x05)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *BlockedFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4, nil
+}
+
+// ParseBlockedFrame parses a BLOCKED frame
+func ParseBlockedFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*BlockedFrame, error) {
+ frame := &BlockedFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/connection_close_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/connection_close_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5681414
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/connection_close_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "io"
+ "math"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A ConnectionCloseFrame in QUIC
+type ConnectionCloseFrame struct {
+ ErrorCode qerr.ErrorCode
+ ReasonPhrase string
+}
+
+// ParseConnectionCloseFrame reads a CONNECTION_CLOSE frame
+func ParseConnectionCloseFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*ConnectionCloseFrame, error) {
+ frame := &ConnectionCloseFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ errorCode, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ErrorCode = qerr.ErrorCode(errorCode)
+
+ reasonPhraseLen, err := utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if reasonPhraseLen > uint16(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidConnectionCloseData, "reason phrase too long")
+ }
+
+ reasonPhrase := make([]byte, reasonPhraseLen)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, reasonPhrase); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ReasonPhrase = string(reasonPhrase)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *ConnectionCloseFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4 + 2 + protocol.ByteCount(len(f.ReasonPhrase)), nil
+}
+
+// Write writes an CONNECTION_CLOSE frame.
+func (f *ConnectionCloseFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ b.WriteByte(0x02)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.ErrorCode))
+
+ if len(f.ReasonPhrase) > math.MaxUint16 {
+ return errors.New("ConnectionFrame: ReasonPhrase too long")
+ }
+
+ reasonPhraseLen := uint16(len(f.ReasonPhrase))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, reasonPhraseLen)
+ b.WriteString(f.ReasonPhrase)
+
+ return nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..464e669
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A Frame in QUIC
+type Frame interface {
+ Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error
+ MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/goaway_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/goaway_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7d452d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/goaway_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A GoawayFrame is a GOAWAY frame
+type GoawayFrame struct {
+ ErrorCode qerr.ErrorCode
+ LastGoodStream protocol.StreamID
+ ReasonPhrase string
+}
+
+// ParseGoawayFrame parses a GOAWAY frame
+func ParseGoawayFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*GoawayFrame, error) {
+ frame := &GoawayFrame{}
+
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ errorCode, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ErrorCode = qerr.ErrorCode(errorCode)
+
+ lastGoodStream, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.LastGoodStream = protocol.StreamID(lastGoodStream)
+
+ reasonPhraseLen, err := utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if reasonPhraseLen > uint16(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidGoawayData, "reason phrase too long")
+ }
+
+ reasonPhrase := make([]byte, reasonPhraseLen)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, reasonPhrase); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ReasonPhrase = string(reasonPhrase)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+func (f *GoawayFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ typeByte := uint8(0x03)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.ErrorCode))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.LastGoodStream))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(len(f.ReasonPhrase)))
+ b.WriteString(f.ReasonPhrase)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *GoawayFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(1 + 4 + 4 + 2 + len(f.ReasonPhrase)), nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/log.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/log.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ac548c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/log.go
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package frames
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+
+// LogFrame logs a frame, either sent or received
+func LogFrame(frame Frame, sent bool) {
+ if !utils.Debug() {
+ return
+ }
+ dir := "<-"
+ if sent {
+ dir = "->"
+ }
+ if sf, ok := frame.(*StreamFrame); ok {
+ utils.Debugf("\t%s &frames.StreamFrame{StreamID: %d, FinBit: %t, Offset: 0x%x, Data length: 0x%x, Offset + Data length: 0x%x}", dir, sf.StreamID, sf.FinBit, sf.Offset, sf.DataLen(), sf.Offset+sf.DataLen())
+ return
+ }
+ utils.Debugf("\t%s %#v", dir, frame)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ping_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ping_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8486af5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ping_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A PingFrame is a ping frame
+type PingFrame struct{}
+
+// ParsePingFrame parses a Ping frame
+func ParsePingFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*PingFrame, error) {
+ frame := &PingFrame{}
+
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+func (f *PingFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ typeByte := uint8(0x07)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *PingFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/rst_stream_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/rst_stream_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8777875
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/rst_stream_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A RstStreamFrame in QUIC
+type RstStreamFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ ErrorCode uint32
+ ByteOffset protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+//Write writes a RST_STREAM frame
+func (f *RstStreamFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ b.WriteByte(0x01)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(f.ByteOffset))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, f.ErrorCode)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *RstStreamFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4 + 8 + 4, nil
+}
+
+// ParseRstStreamFrame parses a RST_STREAM frame
+func ParseRstStreamFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*RstStreamFrame, error) {
+ frame := &RstStreamFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ byteOffset, err := utils.ReadUint64(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ByteOffset = protocol.ByteCount(byteOffset)
+
+ frame.ErrorCode, err = utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stop_waiting_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stop_waiting_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8267825
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stop_waiting_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A StopWaitingFrame in QUIC
+type StopWaitingFrame struct {
+ LeastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber
+ PacketNumberLen protocol.PacketNumberLen
+ PacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+var (
+ errLeastUnackedHigherThanPacketNumber = errors.New("StopWaitingFrame: LeastUnacked can't be greater than the packet number")
+ errPacketNumberNotSet = errors.New("StopWaitingFrame: PacketNumber not set")
+ errPacketNumberLenNotSet = errors.New("StopWaitingFrame: PacketNumberLen not set")
+)
+
+func (f *StopWaitingFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ // packetNumber is the packet number of the packet that this StopWaitingFrame will be sent with
+ typeByte := uint8(0x06)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ // make sure the PacketNumber was set
+ if f.PacketNumber == protocol.PacketNumber(0) {
+ return errPacketNumberNotSet
+ }
+
+ if f.LeastUnacked > f.PacketNumber {
+ return errLeastUnackedHigherThanPacketNumber
+ }
+
+ leastUnackedDelta := uint64(f.PacketNumber - f.LeastUnacked)
+
+ switch f.PacketNumberLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(leastUnackedDelta))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(leastUnackedDelta))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(leastUnackedDelta))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, leastUnackedDelta)
+ default:
+ return errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *StopWaitingFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ var minLength protocol.ByteCount
+ minLength = 1 // typeByte
+
+ if f.PacketNumberLen == protocol.PacketNumberLenInvalid {
+ return 0, errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+ minLength += protocol.ByteCount(f.PacketNumberLen)
+
+ return minLength, nil
+}
+
+// ParseStopWaitingFrame parses a StopWaiting frame
+func ParseStopWaitingFrame(r *bytes.Reader, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, packetNumberLen protocol.PacketNumberLen, version protocol.VersionNumber) (*StopWaitingFrame, error) {
+ frame := &StopWaitingFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ leastUnackedDelta, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, uint8(packetNumberLen))
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if leastUnackedDelta > uint64(packetNumber) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStopWaitingData, "invalid LeastUnackedDelta")
+ }
+
+ frame.LeastUnacked = protocol.PacketNumber(uint64(packetNumber) - leastUnackedDelta)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stream_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stream_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fa833f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stream_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A StreamFrame of QUIC
+type StreamFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ FinBit bool
+ DataLenPresent bool
+ Offset protocol.ByteCount
+ Data []byte
+}
+
+var (
+ errInvalidStreamIDLen = errors.New("StreamFrame: Invalid StreamID length")
+ errInvalidOffsetLen = errors.New("StreamFrame: Invalid offset length")
+)
+
+// ParseStreamFrame reads a stream frame. The type byte must not have been read yet.
+func ParseStreamFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*StreamFrame, error) {
+ frame := &StreamFrame{}
+
+ typeByte, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ frame.FinBit = typeByte&0x40 > 0
+ frame.DataLenPresent = typeByte&0x20 > 0
+ offsetLen := typeByte & 0x1C >> 2
+ if offsetLen != 0 {
+ offsetLen++
+ }
+ streamIDLen := typeByte&0x03 + 1
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, streamIDLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ offset, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, offsetLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.Offset = protocol.ByteCount(offset)
+
+ var dataLen uint16
+ if frame.DataLenPresent {
+ dataLen, err = utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if dataLen > uint16(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamData, "data len too large")
+ }
+
+ if dataLen == 0 {
+ // The rest of the packet is data
+ dataLen = uint16(r.Len())
+ }
+ if dataLen != 0 {
+ frame.Data = make([]byte, dataLen)
+ n, err := r.Read(frame.Data)
+ if n != int(dataLen) {
+ return nil, errors.New("BUG: StreamFrame could not read dataLen bytes")
+ }
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if !frame.FinBit && len(frame.Data) == 0 {
+ return nil, qerr.EmptyStreamFrameNoFin
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+// WriteStreamFrame writes a stream frame.
+func (f *StreamFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ if len(f.Data) == 0 && !f.FinBit {
+ return errors.New("StreamFrame: attempting to write empty frame without FIN")
+ }
+
+ typeByte := uint8(0x80) // sets the leftmost bit to 1
+
+ if f.FinBit {
+ typeByte ^= 0x40
+ }
+
+ if f.DataLenPresent {
+ typeByte ^= 0x20
+ }
+
+ offsetLength := f.getOffsetLength()
+
+ if offsetLength > 0 {
+ typeByte ^= (uint8(offsetLength) - 1) << 2
+ }
+
+ streamIDLen := f.calculateStreamIDLength()
+ typeByte ^= streamIDLen - 1
+
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ switch streamIDLen {
+ case 1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(f.StreamID))
+ case 2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(f.StreamID))
+ case 3:
+ utils.WriteUint24(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ case 4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ default:
+ return errInvalidStreamIDLen
+ }
+
+ switch offsetLength {
+ case 0:
+ case 2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(f.Offset))
+ case 3:
+ utils.WriteUint24(b, uint32(f.Offset))
+ case 4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.Offset))
+ case 5:
+ utils.WriteUint40(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ case 6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ case 7:
+ utils.WriteUint56(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ case 8:
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ default:
+ return errInvalidOffsetLen
+ }
+
+ if f.DataLenPresent {
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(len(f.Data)))
+ }
+
+ b.Write(f.Data)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (f *StreamFrame) calculateStreamIDLength() uint8 {
+ if f.StreamID < (1 << 8) {
+ return 1
+ } else if f.StreamID < (1 << 16) {
+ return 2
+ } else if f.StreamID < (1 << 24) {
+ return 3
+ }
+ return 4
+}
+
+func (f *StreamFrame) getOffsetLength() protocol.ByteCount {
+ if f.Offset == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 16) {
+ return 2
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 24) {
+ return 3
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 32) {
+ return 4
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 40) {
+ return 5
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 48) {
+ return 6
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 56) {
+ return 7
+ }
+ return 8
+}
+
+// MinLength returns the length of the header of a StreamFrame
+// the total length of the StreamFrame is frame.MinLength() + frame.DataLen()
+func (f *StreamFrame) MinLength(protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ length := protocol.ByteCount(1) + protocol.ByteCount(f.calculateStreamIDLength()) + f.getOffsetLength()
+ if f.DataLenPresent {
+ length += 2
+ }
+
+ return length, nil
+}
+
+// DataLen gives the length of data in bytes
+func (f *StreamFrame) DataLen() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(len(f.Data))
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/window_update_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/window_update_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..93e7f8c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/window_update_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A WindowUpdateFrame in QUIC
+type WindowUpdateFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ ByteOffset protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+//Write writes a RST_STREAM frame
+func (f *WindowUpdateFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ typeByte := uint8(0x04)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(f.ByteOffset))
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *WindowUpdateFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4 + 8, nil
+}
+
+// ParseWindowUpdateFrame parses a RST_STREAM frame
+func ParseWindowUpdateFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*WindowUpdateFrame, error) {
+ frame := &WindowUpdateFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ byteOffset, err := utils.ReadUint64(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ByteOffset = protocol.ByteCount(byteOffset)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/request.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/request.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f2e0fa5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/request.go
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+package h2quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "net/http"
+ "net/url"
+
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack"
+)
+
+func requestFromHeaders(headers []hpack.HeaderField) (*http.Request, error) {
+ var path, authority, method string
+ httpHeaders := http.Header{}
+
+ for _, h := range headers {
+ switch h.Name {
+ case ":path":
+ path = h.Value
+ case ":method":
+ method = h.Value
+ case ":authority":
+ authority = h.Value
+ default:
+ if !h.IsPseudo() {
+ httpHeaders.Add(h.Name, h.Value)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ if len(path) == 0 || len(authority) == 0 || len(method) == 0 {
+ return nil, errors.New(":path, :authority and :method must not be empty")
+ }
+
+ u, err := url.Parse(path)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return &http.Request{
+ Method: method,
+ URL: u,
+ Proto: "HTTP/2.0",
+ ProtoMajor: 2,
+ ProtoMinor: 0,
+ Header: httpHeaders,
+ Body: nil,
+ // ContentLength: -1,
+ Host: authority,
+ RequestURI: path,
+ }, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/response_writer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/response_writer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0b5e930
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/response_writer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+package h2quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "net/http"
+ "strconv"
+ "strings"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack"
+)
+
+type responseWriter struct {
+ dataStreamID protocol.StreamID
+ dataStream utils.Stream
+
+ headerStream utils.Stream
+ headerStreamMutex *sync.Mutex
+
+ header http.Header
+ headerWritten bool
+}
+
+func newResponseWriter(headerStream utils.Stream, headerStreamMutex *sync.Mutex, dataStream utils.Stream, dataStreamID protocol.StreamID) *responseWriter {
+ return &responseWriter{
+ header: http.Header{},
+ headerStream: headerStream,
+ headerStreamMutex: headerStreamMutex,
+ dataStream: dataStream,
+ dataStreamID: dataStreamID,
+ }
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) Header() http.Header {
+ return w.header
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) WriteHeader(status int) {
+ if w.headerWritten {
+ return
+ }
+ w.headerWritten = true
+
+ var headers bytes.Buffer
+ enc := hpack.NewEncoder(&headers)
+ enc.WriteField(hpack.HeaderField{Name: ":status", Value: strconv.Itoa(status)})
+
+ for k, v := range w.header {
+ for index := range v {
+ enc.WriteField(hpack.HeaderField{Name: strings.ToLower(k), Value: v[index]})
+ }
+ }
+
+ utils.Infof("Responding with %d", status)
+ w.headerStreamMutex.Lock()
+ defer w.headerStreamMutex.Unlock()
+ h2framer := http2.NewFramer(w.headerStream, nil)
+ err := h2framer.WriteHeaders(http2.HeadersFrameParam{
+ StreamID: uint32(w.dataStreamID),
+ EndHeaders: true,
+ BlockFragment: headers.Bytes(),
+ })
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("could not write h2 header: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) Write(p []byte) (int, error) {
+ if !w.headerWritten {
+ w.WriteHeader(200)
+ }
+ return w.dataStream.Write(p)
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) Flush() {}
+
+// test that we implement http.Flusher
+var _ http.Flusher = &responseWriter{}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/server.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/server.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4e301b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/server.go
@@ -0,0 +1,335 @@
+package h2quic
+
+import (
+ "crypto/tls"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "io/ioutil"
+ "net"
+ "net/http"
+ "runtime"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack"
+)
+
+type streamCreator interface {
+ GetOrOpenStream(protocol.StreamID) (utils.Stream, error)
+ Close(error) error
+ RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr
+}
+
+// Server is a HTTP2 server listening for QUIC connections.
+type Server struct {
+ *http.Server
+
+ // Private flag for demo, do not use
+ CloseAfterFirstRequest bool
+
+ port uint32 // used atomically
+
+ server *quic.Server
+ serverMutex sync.Mutex
+}
+
+// ListenAndServe listens on the UDP address s.Addr and calls s.Handler to handle HTTP/2 requests on incoming connections.
+func (s *Server) ListenAndServe() error {
+ if s.Server == nil {
+ return errors.New("use of h2quic.Server without http.Server")
+ }
+ return s.serveImpl(s.TLSConfig, nil)
+}
+
+// ListenAndServeTLS listens on the UDP address s.Addr and calls s.Handler to handle HTTP/2 requests on incoming connections.
+func (s *Server) ListenAndServeTLS(certFile, keyFile string) error {
+ var err error
+ certs := make([]tls.Certificate, 1)
+ certs[0], err = tls.LoadX509KeyPair(certFile, keyFile)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ // We currently only use the cert-related stuff from tls.Config,
+ // so we don't need to make a full copy.
+ config := &tls.Config{
+ Certificates: certs,
+ }
+ return s.serveImpl(config, nil)
+}
+
+// Serve an existing UDP connection.
+func (s *Server) Serve(conn *net.UDPConn) error {
+ return s.serveImpl(s.TLSConfig, conn)
+}
+
+func (s *Server) serveImpl(tlsConfig *tls.Config, conn *net.UDPConn) error {
+ if s.Server == nil {
+ return errors.New("use of h2quic.Server without http.Server")
+ }
+ s.serverMutex.Lock()
+ if s.server != nil {
+ s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ return errors.New("ListenAndServe may only be called once")
+ }
+ var err error
+ server, err := quic.NewServer(s.Addr, tlsConfig, s.handleStreamCb)
+ if err != nil {
+ s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ return err
+ }
+ s.server = server
+ s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ if conn == nil {
+ return server.ListenAndServe()
+ }
+ return server.Serve(conn)
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handleStreamCb(session *quic.Session, stream utils.Stream) {
+ s.handleStream(session, stream)
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handleStream(session streamCreator, stream utils.Stream) {
+ if stream.StreamID() != 3 {
+ return
+ }
+
+ hpackDecoder := hpack.NewDecoder(4096, nil)
+ h2framer := http2.NewFramer(nil, stream)
+
+ go func() {
+ var headerStreamMutex sync.Mutex // Protects concurrent calls to Write()
+ for {
+ if err := s.handleRequest(session, stream, &headerStreamMutex, hpackDecoder, h2framer); err != nil {
+ // QuicErrors must originate from stream.Read() returning an error.
+ // In this case, the session has already logged the error, so we don't
+ // need to log it again.
+ if _, ok := err.(*qerr.QuicError); !ok {
+ utils.Errorf("error handling h2 request: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ }
+ }()
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handleRequest(session streamCreator, headerStream utils.Stream, headerStreamMutex *sync.Mutex, hpackDecoder *hpack.Decoder, h2framer *http2.Framer) error {
+ h2frame, err := h2framer.ReadFrame()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ h2headersFrame := h2frame.(*http2.HeadersFrame)
+ if !h2headersFrame.HeadersEnded() {
+ return errors.New("http2 header continuation not implemented")
+ }
+ headers, err := hpackDecoder.DecodeFull(h2headersFrame.HeaderBlockFragment())
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("invalid http2 headers encoding: %s", err.Error())
+ return err
+ }
+
+ req, err := requestFromHeaders(headers)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ req.RemoteAddr = session.RemoteAddr().String()
+
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Infof("%s %s%s, on data stream %d", req.Method, req.Host, req.RequestURI, h2headersFrame.StreamID)
+ } else {
+ utils.Infof("%s %s%s", req.Method, req.Host, req.RequestURI)
+ }
+
+ dataStream, err := session.GetOrOpenStream(protocol.StreamID(h2headersFrame.StreamID))
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ if h2headersFrame.StreamEnded() {
+ dataStream.CloseRemote(0)
+ _, _ = dataStream.Read([]byte{0}) // read the eof
+ }
+
+ // stream's Close() closes the write side, not the read side
+ req.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(dataStream)
+
+ responseWriter := newResponseWriter(headerStream, headerStreamMutex, dataStream, protocol.StreamID(h2headersFrame.StreamID))
+
+ go func() {
+ handler := s.Handler
+ if handler == nil {
+ handler = http.DefaultServeMux
+ }
+ panicked := false
+ func() {
+ defer func() {
+ if p := recover(); p != nil {
+ // Copied from net/http/server.go
+ const size = 64 << 10
+ buf := make([]byte, size)
+ buf = buf[:runtime.Stack(buf, false)]
+ utils.Errorf("http: panic serving: %v\n%s", p, buf)
+ panicked = true
+ }
+ }()
+ handler.ServeHTTP(responseWriter, req)
+ }()
+ if panicked {
+ responseWriter.WriteHeader(500)
+ } else {
+ responseWriter.WriteHeader(200)
+ }
+ if responseWriter.dataStream != nil {
+ responseWriter.dataStream.Close()
+ }
+ if s.CloseAfterFirstRequest {
+ time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
+ session.Close(nil)
+ }
+ }()
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Close the server immediately, aborting requests and sending CONNECTION_CLOSE frames to connected clients.
+// Close in combination with ListenAndServe() (instead of Serve()) may race if it is called before a UDP socket is established.
+func (s *Server) Close() error {
+ s.serverMutex.Lock()
+ defer s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ if s.server != nil {
+ err := s.server.Close()
+ s.server = nil
+ return err
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// CloseGracefully shuts down the server gracefully. The server sends a GOAWAY frame first, then waits for either timeout to trigger, or for all running requests to complete.
+// CloseGracefully in combination with ListenAndServe() (instead of Serve()) may race if it is called before a UDP socket is established.
+func (s *Server) CloseGracefully(timeout time.Duration) error {
+ // TODO: implement
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetQuicHeaders can be used to set the proper headers that announce that this server supports QUIC.
+// The values that are set depend on the port information from s.Server.Addr, and currently look like this (if Addr has port 443):
+// Alternate-Protocol: 443:quic
+// Alt-Svc: quic=":443"; ma=2592000; v="33,32,31,30"
+func (s *Server) SetQuicHeaders(hdr http.Header) error {
+ port := atomic.LoadUint32(&s.port)
+
+ if port == 0 {
+ // Extract port from s.Server.Addr
+ _, portStr, err := net.SplitHostPort(s.Server.Addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ portInt, err := net.LookupPort("tcp", portStr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ port = uint32(portInt)
+ atomic.StoreUint32(&s.port, port)
+ }
+
+ hdr.Add("Alternate-Protocol", fmt.Sprintf("%d:quic", port))
+ hdr.Add("Alt-Svc", fmt.Sprintf(`quic=":%d"; ma=2592000; v="%s"`, port, protocol.SupportedVersionsAsString))
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// ListenAndServeQUIC listens on the UDP network address addr and calls the
+// handler for HTTP/2 requests on incoming connections. http.DefaultServeMux is
+// used when handler is nil.
+func ListenAndServeQUIC(addr, certFile, keyFile string, handler http.Handler) error {
+ server := &Server{
+ Server: &http.Server{
+ Addr: addr,
+ Handler: handler,
+ },
+ }
+ return server.ListenAndServeTLS(certFile, keyFile)
+}
+
+// ListenAndServe listens on the given network address for both, TLS and QUIC
+// connetions in parallel. It returns if one of the two returns an error.
+// http.DefaultServeMux is used when handler is nil.
+// The correct Alt-Svc headers for QUIC are set.
+func ListenAndServe(addr, certFile, keyFile string, handler http.Handler) error {
+ // Load certs
+ var err error
+ certs := make([]tls.Certificate, 1)
+ certs[0], err = tls.LoadX509KeyPair(certFile, keyFile)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ // We currently only use the cert-related stuff from tls.Config,
+ // so we don't need to make a full copy.
+ config := &tls.Config{
+ Certificates: certs,
+ }
+
+ // Open the listeners
+ udpAddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ udpConn, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", udpAddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ defer udpConn.Close()
+
+ tcpAddr, err := net.ResolveTCPAddr("tcp", addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ tcpConn, err := net.ListenTCP("tcp", tcpAddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ defer tcpConn.Close()
+
+ // Start the servers
+ httpServer := &http.Server{
+ Addr: addr,
+ TLSConfig: config,
+ }
+
+ quicServer := &Server{
+ Server: httpServer,
+ }
+
+ if handler == nil {
+ handler = http.DefaultServeMux
+ }
+ httpServer.Handler = http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
+ quicServer.SetQuicHeaders(w.Header())
+ handler.ServeHTTP(w, r)
+ })
+
+ hErr := make(chan error)
+ qErr := make(chan error)
+ go func() {
+ hErr <- httpServer.Serve(tcpConn)
+ }()
+ go func() {
+ qErr <- quicServer.Serve(udpConn)
+ }()
+
+ select {
+ case err := <-hErr:
+ quicServer.Close()
+ return err
+ case err := <-qErr:
+ // Cannot close the HTTP server or wait for requests to complete properly :/
+ return err
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/connection_parameters_manager.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/connection_parameters_manager.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..df26119
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/connection_parameters_manager.go
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+ "sync"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// ConnectionParametersManager stores the connection parameters
+// Warning: Writes may only be done from the crypto stream, see the comment
+// in GetSHLOMap().
+type ConnectionParametersManager struct {
+ params map[Tag][]byte
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+
+ flowControlNegotiated bool // have the flow control parameters for sending already been negotiated
+
+ maxStreamsPerConnection uint32
+ idleConnectionStateLifetime time.Duration
+ sendStreamFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ sendConnectionFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveStreamFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveConnectionFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+var errTagNotInConnectionParameterMap = errors.New("ConnectionParametersManager: Tag not found in ConnectionsParameter map")
+
+// ErrMalformedTag is returned when the tag value cannot be read
+var (
+ ErrMalformedTag = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidCryptoMessageParameter, "malformed Tag value")
+ ErrFlowControlRenegotiationNotSupported = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidCryptoMessageParameter, "renegotiation of flow control parameters not supported")
+)
+
+// NewConnectionParamatersManager creates a new connection parameters manager
+func NewConnectionParamatersManager() *ConnectionParametersManager {
+ return &ConnectionParametersManager{
+ params: make(map[Tag][]byte),
+ idleConnectionStateLifetime: protocol.DefaultIdleTimeout,
+ sendStreamFlowControlWindow: protocol.InitialStreamFlowControlWindow, // can only be changed by the client
+ sendConnectionFlowControlWindow: protocol.InitialConnectionFlowControlWindow, // can only be changed by the client
+ receiveStreamFlowControlWindow: protocol.ReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow,
+ receiveConnectionFlowControlWindow: protocol.ReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow,
+ maxStreamsPerConnection: protocol.MaxStreamsPerConnection,
+ }
+}
+
+// SetFromMap reads all params
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) SetFromMap(params map[Tag][]byte) error {
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ for key, value := range params {
+ switch key {
+ case TagTCID:
+ h.params[key] = value
+ case TagMSPC:
+ clientValue, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.maxStreamsPerConnection = h.negotiateMaxStreamsPerConnection(clientValue)
+ case TagICSL:
+ clientValue, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.idleConnectionStateLifetime = h.negotiateIdleConnectionStateLifetime(time.Duration(clientValue) * time.Second)
+ case TagSFCW:
+ if h.flowControlNegotiated {
+ return ErrFlowControlRenegotiationNotSupported
+ }
+ sendStreamFlowControlWindow, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.sendStreamFlowControlWindow = protocol.ByteCount(sendStreamFlowControlWindow)
+ case TagCFCW:
+ if h.flowControlNegotiated {
+ return ErrFlowControlRenegotiationNotSupported
+ }
+ sendConnectionFlowControlWindow, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.sendConnectionFlowControlWindow = protocol.ByteCount(sendConnectionFlowControlWindow)
+ }
+ }
+
+ _, containsSFCW := params[TagSFCW]
+ _, containsCFCW := params[TagCFCW]
+ if containsCFCW || containsSFCW {
+ h.flowControlNegotiated = true
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) negotiateMaxStreamsPerConnection(clientValue uint32) uint32 {
+ return utils.MinUint32(clientValue, protocol.MaxStreamsPerConnection)
+}
+
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) negotiateIdleConnectionStateLifetime(clientValue time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ return utils.MinDuration(clientValue, protocol.MaxIdleTimeout)
+}
+
+// getRawValue gets the byte-slice for a tag
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) getRawValue(tag Tag) ([]byte, error) {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ rawValue, ok := h.params[tag]
+ h.mutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, errTagNotInConnectionParameterMap
+ }
+ return rawValue, nil
+}
+
+// GetSHLOMap gets all values (except crypto values) needed for the SHLO
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetSHLOMap() map[Tag][]byte {
+ sfcw := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(sfcw, uint32(h.GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow()))
+ cfcw := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(cfcw, uint32(h.GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow()))
+ mspc := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(mspc, h.GetMaxStreamsPerConnection())
+ mids := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(mids, protocol.MaxIncomingDynamicStreams)
+ icsl := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(icsl, uint32(h.GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime()/time.Second))
+
+ return map[Tag][]byte{
+ TagICSL: icsl.Bytes(),
+ TagMSPC: mspc.Bytes(),
+ TagMIDS: mids.Bytes(),
+ TagCFCW: cfcw.Bytes(),
+ TagSFCW: sfcw.Bytes(),
+ }
+}
+
+// GetSendStreamFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for sending data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetSendStreamFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.sendStreamFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetSendConnectionFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for sending data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetSendConnectionFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.sendConnectionFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.receiveStreamFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.receiveConnectionFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetMaxStreamsPerConnection gets the maximum number of streams per connection
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetMaxStreamsPerConnection() uint32 {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.maxStreamsPerConnection
+}
+
+// GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime gets the idle timeout
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime() time.Duration {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.idleConnectionStateLifetime
+}
+
+// TruncateConnectionID determines if the client requests truncated ConnectionIDs
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) TruncateConnectionID() bool {
+ rawValue, err := h.getRawValue(TagTCID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false
+ }
+ if len(rawValue) != 4 {
+ return false
+ }
+ value := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(rawValue)
+ if value == 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/crypto_setup.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/crypto_setup.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..56e9764
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/crypto_setup.go
@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "io"
+ "net"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// KeyDerivationFunction is used for key derivation
+type KeyDerivationFunction func(forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo []byte, scfg []byte, cert []byte, divNonce []byte) (crypto.AEAD, error)
+
+// KeyExchangeFunction is used to make a new KEX
+type KeyExchangeFunction func() crypto.KeyExchange
+
+// The CryptoSetup handles all things crypto for the Session
+type CryptoSetup struct {
+ connID protocol.ConnectionID
+ ip net.IP
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+ scfg *ServerConfig
+ diversificationNonce []byte
+
+ secureAEAD crypto.AEAD
+ forwardSecureAEAD crypto.AEAD
+ receivedForwardSecurePacket bool
+ receivedSecurePacket bool
+ aeadChanged chan struct{}
+
+ keyDerivation KeyDerivationFunction
+ keyExchange KeyExchangeFunction
+
+ cryptoStream utils.Stream
+
+ connectionParametersManager *ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+}
+
+var _ crypto.AEAD = &CryptoSetup{}
+
+// NewCryptoSetup creates a new CryptoSetup instance
+func NewCryptoSetup(
+ connID protocol.ConnectionID,
+ ip net.IP,
+ version protocol.VersionNumber,
+ scfg *ServerConfig,
+ cryptoStream utils.Stream,
+ connectionParametersManager *ConnectionParametersManager,
+ aeadChanged chan struct{},
+) (*CryptoSetup, error) {
+ return &CryptoSetup{
+ connID: connID,
+ ip: ip,
+ version: version,
+ scfg: scfg,
+ keyDerivation: crypto.DeriveKeysAESGCM,
+ keyExchange: getEphermalKEX,
+ cryptoStream: cryptoStream,
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ aeadChanged: aeadChanged,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+// HandleCryptoStream reads and writes messages on the crypto stream
+func (h *CryptoSetup) HandleCryptoStream() error {
+ for {
+ var chloData bytes.Buffer
+ messageTag, cryptoData, err := ParseHandshakeMessage(io.TeeReader(h.cryptoStream, &chloData))
+ if err != nil {
+ return qerr.HandshakeFailed
+ }
+ if messageTag != TagCHLO {
+ return qerr.InvalidCryptoMessageType
+ }
+
+ utils.Debugf("Got CHLO:\n%s", printHandshakeMessage(cryptoData))
+
+ done, err := h.handleMessage(chloData.Bytes(), cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if done {
+ return nil
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) handleMessage(chloData []byte, cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) (bool, error) {
+ sniSlice, ok := cryptoData[TagSNI]
+ if !ok {
+ return false, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoMessageParameterNotFound, "SNI required")
+ }
+ sni := string(sniSlice)
+ if sni == "" {
+ return false, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoMessageParameterNotFound, "SNI required")
+ }
+
+ var reply []byte
+ var err error
+ if !h.isInchoateCHLO(cryptoData) {
+ // We have a CHLO with a proper server config ID, do a 0-RTT handshake
+ reply, err = h.handleCHLO(sni, chloData, cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ _, err = h.cryptoStream.Write(reply)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ // We have an inchoate or non-matching CHLO, we now send a rejection
+ reply, err = h.handleInchoateCHLO(sni, chloData, cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ _, err = h.cryptoStream.Write(reply)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ return false, nil
+}
+
+// Open a message
+func (h *CryptoSetup) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if h.forwardSecureAEAD != nil {
+ res, err := h.forwardSecureAEAD.Open(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ if err == nil {
+ h.receivedForwardSecurePacket = true
+ return res, nil
+ }
+ if h.receivedForwardSecurePacket {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+ if h.secureAEAD != nil {
+ res, err := h.secureAEAD.Open(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ if err == nil {
+ h.receivedSecurePacket = true
+ return res, nil
+ }
+ if h.receivedSecurePacket {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+ return (&crypto.NullAEAD{}).Open(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+}
+
+// Seal a message, call LockForSealing() before!
+func (h *CryptoSetup) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ if h.receivedForwardSecurePacket {
+ return h.forwardSecureAEAD.Seal(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ } else if h.secureAEAD != nil {
+ return h.secureAEAD.Seal(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ } else {
+ return (&crypto.NullAEAD{}).Seal(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) isInchoateCHLO(cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) bool {
+ scid, ok := cryptoData[TagSCID]
+ if !ok || !bytes.Equal(h.scfg.ID, scid) {
+ return true
+ }
+ if _, ok := cryptoData[TagPUBS]; !ok {
+ return true
+ }
+ if err := h.scfg.stkSource.VerifyToken(h.ip, cryptoData[TagSTK]); err != nil {
+ utils.Infof("STK invalid: %s", err.Error())
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) handleInchoateCHLO(sni string, chlo []byte, cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ if len(chlo) < protocol.ClientHelloMinimumSize {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoInvalidValueLength, "CHLO too small")
+ }
+
+ token, err := h.scfg.stkSource.NewToken(h.ip)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ replyMap := map[Tag][]byte{
+ TagSCFG: h.scfg.Get(),
+ TagSTK: token,
+ TagSVID: []byte("quic-go"),
+ }
+
+ if h.scfg.stkSource.VerifyToken(h.ip, cryptoData[TagSTK]) == nil {
+ proof, err := h.scfg.Sign(sni, chlo)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ commonSetHashes := cryptoData[TagCCS]
+ cachedCertsHashes := cryptoData[TagCCRT]
+
+ certCompressed, err := h.scfg.GetCertsCompressed(sni, commonSetHashes, cachedCertsHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ // Token was valid, send more details
+ replyMap[TagPROF] = proof
+ replyMap[TagCERT] = certCompressed
+ }
+
+ var serverReply bytes.Buffer
+ WriteHandshakeMessage(&serverReply, TagREJ, replyMap)
+ return serverReply.Bytes(), nil
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) handleCHLO(sni string, data []byte, cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ // We have a CHLO matching our server config, we can continue with the 0-RTT handshake
+ sharedSecret, err := h.scfg.kex.CalculateSharedKey(cryptoData[TagPUBS])
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ certUncompressed, err := h.scfg.signer.GetLeafCert(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ nonce := make([]byte, 32)
+ if _, err = rand.Read(nonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ h.diversificationNonce = make([]byte, 32)
+ if _, err = rand.Read(h.diversificationNonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ h.secureAEAD, err = h.keyDerivation(
+ false,
+ sharedSecret,
+ cryptoData[TagNONC],
+ h.connID,
+ data,
+ h.scfg.Get(),
+ certUncompressed,
+ h.diversificationNonce,
+ )
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ // Generate a new curve instance to derive the forward secure key
+ var fsNonce bytes.Buffer
+ fsNonce.Write(cryptoData[TagNONC])
+ fsNonce.Write(nonce)
+ ephermalKex := h.keyExchange()
+ ephermalSharedSecret, err := ephermalKex.CalculateSharedKey(cryptoData[TagPUBS])
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ h.forwardSecureAEAD, err = h.keyDerivation(
+ true,
+ ephermalSharedSecret,
+ fsNonce.Bytes(),
+ h.connID,
+ data,
+ h.scfg.Get(),
+ certUncompressed,
+ nil,
+ )
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ err = h.connectionParametersManager.SetFromMap(cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ replyMap := h.connectionParametersManager.GetSHLOMap()
+ // add crypto parameters
+ replyMap[TagPUBS] = ephermalKex.PublicKey()
+ replyMap[TagSNO] = nonce
+ replyMap[TagVER] = protocol.SupportedVersionsAsTags
+
+ var reply bytes.Buffer
+ WriteHandshakeMessage(&reply, TagSHLO, replyMap)
+
+ h.aeadChanged <- struct{}{}
+
+ return reply.Bytes(), nil
+}
+
+// DiversificationNonce returns a diversification nonce if required in the next packet to be Seal'ed. See LockForSealing()!
+func (h *CryptoSetup) DiversificationNonce() []byte {
+ if h.receivedForwardSecurePacket || h.secureAEAD == nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return h.diversificationNonce
+}
+
+// LockForSealing should be called before Seal(). It is needed so that diversification nonces can be obtained before packets are sealed, and the AEADs are not changed in the meantime.
+func (h *CryptoSetup) LockForSealing() {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+}
+
+// UnlockForSealing should be called after Seal() is complete, see LockForSealing().
+func (h *CryptoSetup) UnlockForSealing() {
+ h.mutex.RUnlock()
+}
+
+// HandshakeComplete returns true after the first forward secure packet was received form the client.
+func (h *CryptoSetup) HandshakeComplete() bool {
+ return h.receivedForwardSecurePacket
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/ephermal_cache.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/ephermal_cache.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..794bcbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/ephermal_cache.go
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "sync"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ kexLifetime = protocol.EphermalKeyLifetime
+ kexCurrent crypto.KeyExchange
+ kexCurrentTime time.Time
+ kexMutex sync.RWMutex
+)
+
+// getEphermalKEX returns the currently active KEX, which changes every protocol.EphermalKeyLifetime
+// See the explanation from the QUIC crypto doc:
+//
+// A single connection is the usual scope for forward security, but the security
+// difference between an ephemeral key used for a single connection, and one
+// used for all connections for 60 seconds is negligible. Thus we can amortise
+// the Diffie-Hellman key generation at the server over all the connections in a
+// small time span.
+func getEphermalKEX() (res crypto.KeyExchange) {
+ kexMutex.RLock()
+ res = kexCurrent
+ t := kexCurrentTime
+ kexMutex.RUnlock()
+ if res != nil && time.Now().Sub(t) < kexLifetime {
+ return res
+ }
+
+ kexMutex.Lock()
+ defer kexMutex.Unlock()
+ // Check if still unfulfilled
+ if kexCurrent == nil || time.Now().Sub(kexCurrentTime) > kexLifetime {
+ kex, err := crypto.NewCurve25519KEX()
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("could not set KEX: %s", err.Error())
+ return kexCurrent
+ }
+ kexCurrent = kex
+ kexCurrentTime = time.Now()
+ return kexCurrent
+ }
+ return kexCurrent
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/handshake_message.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/handshake_message.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..013c44b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/handshake_message.go
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "sort"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// ParseHandshakeMessage reads a crypto message
+func ParseHandshakeMessage(r io.Reader) (Tag, map[Tag][]byte, error) {
+ slice4 := make([]byte, 4)
+
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, slice4); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+ messageTag := Tag(binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(slice4))
+
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, slice4); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+ nPairs := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(slice4)
+
+ if nPairs > protocol.CryptoMaxParams {
+ return 0, nil, qerr.CryptoTooManyEntries
+ }
+
+ index := make([]byte, nPairs*8)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, index); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+
+ resultMap := map[Tag][]byte{}
+
+ var dataStart uint32
+ for indexPos := 0; indexPos < int(nPairs)*8; indexPos += 8 {
+ tag := Tag(binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(index[indexPos : indexPos+4]))
+ dataEnd := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(index[indexPos+4 : indexPos+8])
+
+ dataLen := dataEnd - dataStart
+ if dataLen > protocol.CryptoParameterMaxLength {
+ return 0, nil, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoInvalidValueLength, "value too long")
+ }
+
+ data := make([]byte, dataLen)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, data); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+
+ resultMap[tag] = data
+ dataStart = dataEnd
+ }
+
+ return messageTag, resultMap, nil
+}
+
+// WriteHandshakeMessage writes a crypto message
+func WriteHandshakeMessage(b *bytes.Buffer, messageTag Tag, data map[Tag][]byte) {
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(messageTag))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(len(data)))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, 0)
+
+ // Save current position in the buffer, so that we can update the index in-place later
+ indexStart := b.Len()
+
+ indexData := make([]byte, 8*len(data))
+ b.Write(indexData) // Will be updated later
+
+ // Sort the tags
+ tags := make([]uint32, len(data))
+ i := 0
+ for t := range data {
+ tags[i] = uint32(t)
+ i++
+ }
+ sort.Sort(utils.Uint32Slice(tags))
+
+ offset := uint32(0)
+ for i, t := range tags {
+ v := data[Tag(t)]
+ b.Write(v)
+ offset += uint32(len(v))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(indexData[i*8:], t)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(indexData[i*8+4:], offset)
+ }
+
+ // Now we write the index data for real
+ copy(b.Bytes()[indexStart:], indexData)
+}
+
+func printHandshakeMessage(data map[Tag][]byte) string {
+ var res string
+ for k, v := range data {
+ if k == TagPAD {
+ continue
+ }
+ res += fmt.Sprintf("\t%s: %#v\n", tagToString(k), string(v))
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func tagToString(tag Tag) string {
+ b := make([]byte, 4)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(b, uint32(tag))
+ for i := range b {
+ if b[i] == 0 {
+ b[i] = ' '
+ }
+ }
+ return string(b)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/server_config.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/server_config.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dc33e97
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/server_config.go
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/rand"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+)
+
+// ServerConfig is a server config
+type ServerConfig struct {
+ kex crypto.KeyExchange
+ signer crypto.Signer
+ ID []byte
+ stkSource crypto.StkSource
+}
+
+// NewServerConfig creates a new server config
+func NewServerConfig(kex crypto.KeyExchange, signer crypto.Signer) (*ServerConfig, error) {
+ id := make([]byte, 16)
+ _, err := rand.Read(id)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ stkSecret := make([]byte, 32)
+ if _, err = rand.Read(stkSecret); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ stkSource, err := crypto.NewStkSource(stkSecret)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return &ServerConfig{
+ kex: kex,
+ signer: signer,
+ ID: id,
+ stkSource: stkSource,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+// Get the server config binary representation
+func (s *ServerConfig) Get() []byte {
+ var serverConfig bytes.Buffer
+ WriteHandshakeMessage(&serverConfig, TagSCFG, map[Tag][]byte{
+ TagSCID: s.ID,
+ TagKEXS: []byte("C255"),
+ TagAEAD: []byte("AESG"),
+ TagPUBS: append([]byte{0x20, 0x00, 0x00}, s.kex.PublicKey()...),
+ TagOBIT: {0x0, 0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4, 0x5, 0x6, 0x7},
+ TagEXPY: {0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff},
+ })
+ return serverConfig.Bytes()
+}
+
+// Sign the server config and CHLO with the server's keyData
+func (s *ServerConfig) Sign(sni string, chlo []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return s.signer.SignServerProof(sni, chlo, s.Get())
+}
+
+// GetCertsCompressed returns the certificate data
+func (s *ServerConfig) GetCertsCompressed(sni string, commonSetHashes, compressedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return s.signer.GetCertsCompressed(sni, commonSetHashes, compressedHashes)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/tags.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/tags.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..92d4d84
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/tags.go
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+package handshake
+
+// A Tag in the QUIC crypto
+type Tag uint32
+
+const (
+ // TagCHLO is a client hello
+ TagCHLO Tag = 'C' + 'H'<<8 + 'L'<<16 + 'O'<<24
+ // TagREJ is a server hello rejection
+ TagREJ Tag = 'R' + 'E'<<8 + 'J'<<16
+ // TagSCFG is a server config
+ TagSCFG Tag = 'S' + 'C'<<8 + 'F'<<16 + 'G'<<24
+
+ // TagPAD is padding
+ TagPAD Tag = 'P' + 'A'<<8 + 'D'<<16
+ // TagSNI is the server name indication
+ TagSNI Tag = 'S' + 'N'<<8 + 'I'<<16
+ // TagVER is the QUIC version
+ TagVER Tag = 'V' + 'E'<<8 + 'R'<<16
+ // TagCCS are the hashes of the common certificate sets
+ TagCCS Tag = 'C' + 'C'<<8 + 'S'<<16
+ // TagCCRT are the hashes of the cached certificates
+ TagCCRT Tag = 'C' + 'C'<<8 + 'R'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagMSPC is max streams per connection
+ TagMSPC Tag = 'M' + 'S'<<8 + 'P'<<16 + 'C'<<24
+ // TagMIDS is max incoming dyanamic streams
+ TagMIDS Tag = 'M' + 'I'<<8 + 'D'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagUAID is the user agent ID
+ TagUAID Tag = 'U' + 'A'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagSVID is the server ID (unofficial tag by us :)
+ TagSVID Tag = 'S' + 'V'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagTCID is truncation of the connection ID
+ TagTCID Tag = 'T' + 'C'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagPDMD is the proof demand
+ TagPDMD Tag = 'P' + 'D'<<8 + 'M'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagSRBF is the socket receive buffer
+ TagSRBF Tag = 'S' + 'R'<<8 + 'B'<<16 + 'F'<<24
+ // TagICSL is the idle connection state lifetime
+ TagICSL Tag = 'I' + 'C'<<8 + 'S'<<16 + 'L'<<24
+ // TagNONP is the client proof nonce
+ TagNONP Tag = 'N' + 'O'<<8 + 'N'<<16 + 'P'<<24
+ // TagSCLS is the silently close timeout
+ TagSCLS Tag = 'S' + 'C'<<8 + 'L'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagCSCT is the signed cert timestamp (RFC6962) of leaf cert
+ TagCSCT Tag = 'C' + 'S'<<8 + 'C'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagCOPT are the connection options
+ TagCOPT Tag = 'C' + 'O'<<8 + 'P'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagCFCW is the initial session/connection flow control receive window
+ TagCFCW Tag = 'C' + 'F'<<8 + 'C'<<16 + 'W'<<24
+ // TagSFCW is the initial stream flow control receive window.
+ TagSFCW Tag = 'S' + 'F'<<8 + 'C'<<16 + 'W'<<24
+
+ // TagSTK is the source-address token
+ TagSTK Tag = 'S' + 'T'<<8 + 'K'<<16
+ // TagSNO is the server nonce
+ TagSNO Tag = 'S' + 'N'<<8 + 'O'<<16
+ // TagPROF is the server proof
+ TagPROF Tag = 'P' + 'R'<<8 + 'O'<<16 + 'F'<<24
+
+ // TagNONC is the client nonce
+ TagNONC Tag = 'N' + 'O'<<8 + 'N'<<16 + 'C'<<24
+
+ // TagSCID is the server config ID
+ TagSCID Tag = 'S' + 'C'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagKEXS is the list of key exchange algos
+ TagKEXS Tag = 'K' + 'E'<<8 + 'X'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagAEAD is the list of AEAD algos
+ TagAEAD Tag = 'A' + 'E'<<8 + 'A'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagPUBS is the public value for the KEX
+ TagPUBS Tag = 'P' + 'U'<<8 + 'B'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagOBIT is the client orbit
+ TagOBIT Tag = 'O' + 'B'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagEXPY is the server config expiry
+ TagEXPY Tag = 'E' + 'X'<<8 + 'P'<<16 + 'Y'<<24
+ // TagCERT is the CERT data
+ TagCERT Tag = 0xff545243
+
+ // TagSHLO is the server hello
+ TagSHLO Tag = 'S' + 'H'<<8 + 'L'<<16 + 'O'<<24
+
+ // TagPRST is the public reset tag
+ TagPRST Tag = 'P' + 'R'<<8 + 'S'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagRSEQ is the public reset rejected packet number
+ TagRSEQ Tag = 'R' + 'S'<<8 + 'E'<<16 + 'Q'<<24
+ // TagRNON is the public reset nonce
+ TagRNON Tag = 'R' + 'N'<<8 + 'O'<<16 + 'N'<<24
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_number_generator.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_number_generator.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..71ca9a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_number_generator.go
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "math"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// The packetNumberGenerator generates the packet number for the next packet
+// it randomly skips a packet number every averagePeriod packets (on average)
+// it is guarantued to never skip two consecutive packet numbers
+type packetNumberGenerator struct {
+ averagePeriod protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ next protocol.PacketNumber
+ nextToSkip protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+func newPacketNumberGenerator(averagePeriod protocol.PacketNumber) *packetNumberGenerator {
+ return &packetNumberGenerator{
+ next: 1,
+ averagePeriod: averagePeriod,
+ }
+}
+
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) Peek() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ return p.next
+}
+
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) Pop() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ next := p.next
+
+ // generate a new packet number for the next packet
+ p.next++
+
+ if p.next == p.nextToSkip {
+ p.next++
+ p.generateNewSkip()
+ }
+
+ return next
+}
+
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) generateNewSkip() error {
+ num, err := p.getRandomNumber()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ skip := protocol.PacketNumber(num) * (p.averagePeriod - 1) / (math.MaxUint16 / 2)
+ // make sure that there are never two consecutive packet numbers that are skipped
+ p.nextToSkip = p.next + 2 + skip
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// getRandomNumber() generates a cryptographically secure random number between 0 and MaxUint16 (= 65535)
+// The expectation value is 65535/2
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) getRandomNumber() (uint16, error) {
+ b := make([]byte, 2)
+ _, err := rand.Read(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+
+ num := uint16(b[0])<<8 + uint16(b[1])
+ return num, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_packer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_packer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..359fa73
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_packer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,203 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type packedPacket struct {
+ number protocol.PacketNumber
+ raw []byte
+ frames []frames.Frame
+}
+
+type packetPacker struct {
+ connectionID protocol.ConnectionID
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+ cryptoSetup *handshake.CryptoSetup
+
+ packetNumberGenerator *packetNumberGenerator
+
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ streamFramer *streamFramer
+ controlFrames []frames.Frame
+}
+
+func newPacketPacker(connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, cryptoSetup *handshake.CryptoSetup, connectionParametersHandler *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager, streamFramer *streamFramer, version protocol.VersionNumber) *packetPacker {
+ return &packetPacker{
+ cryptoSetup: cryptoSetup,
+ connectionID: connectionID,
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersHandler,
+ version: version,
+ streamFramer: streamFramer,
+ packetNumberGenerator: newPacketNumberGenerator(protocol.SkipPacketAveragePeriodLength),
+ }
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) PackConnectionClose(frame *frames.ConnectionCloseFrame, leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber) (*packedPacket, error) {
+ return p.packPacket(nil, []frames.Frame{frame}, leastUnacked, true, false)
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) PackPacket(stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame, controlFrames []frames.Frame, leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber, maySendOnlyAck bool) (*packedPacket, error) {
+ return p.packPacket(stopWaitingFrame, controlFrames, leastUnacked, false, maySendOnlyAck)
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) packPacket(stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame, controlFrames []frames.Frame, leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber, onlySendOneControlFrame, maySendOnlyAck bool) (*packedPacket, error) {
+ if len(controlFrames) > 0 {
+ p.controlFrames = append(p.controlFrames, controlFrames...)
+ }
+
+ currentPacketNumber := p.packetNumberGenerator.Peek()
+
+ // cryptoSetup needs to be locked here, so that the AEADs are not changed between
+ // calling DiversificationNonce() and Seal().
+ p.cryptoSetup.LockForSealing()
+ defer p.cryptoSetup.UnlockForSealing()
+
+ packetNumberLen := protocol.GetPacketNumberLengthForPublicHeader(currentPacketNumber, leastUnacked)
+ responsePublicHeader := &PublicHeader{
+ ConnectionID: p.connectionID,
+ PacketNumber: currentPacketNumber,
+ PacketNumberLen: packetNumberLen,
+ TruncateConnectionID: p.connectionParametersManager.TruncateConnectionID(),
+ DiversificationNonce: p.cryptoSetup.DiversificationNonce(),
+ }
+
+ publicHeaderLength, err := responsePublicHeader.GetLength()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ stopWaitingFrame.PacketNumber = currentPacketNumber
+ stopWaitingFrame.PacketNumberLen = packetNumberLen
+ }
+
+ var payloadFrames []frames.Frame
+ if onlySendOneControlFrame {
+ payloadFrames = []frames.Frame{controlFrames[0]}
+ } else {
+ payloadFrames, err = p.composeNextPacket(stopWaitingFrame, publicHeaderLength)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Check if we have enough frames to send
+ if len(payloadFrames) == 0 {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ // Don't send out packets that only contain a StopWaitingFrame
+ if !onlySendOneControlFrame && len(payloadFrames) == 1 && stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ // Don't send out packets that only contain an ACK (plus optional STOP_WAITING), if requested
+ if !maySendOnlyAck {
+ if len(payloadFrames) == 1 {
+ if _, ok := payloadFrames[0].(*frames.AckFrame); ok {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ } else if len(payloadFrames) == 2 && stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ if _, ok := payloadFrames[1].(*frames.AckFrame); ok {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ raw := getPacketBuffer()
+ buffer := bytes.NewBuffer(raw)
+
+ if err = responsePublicHeader.WritePublicHeader(buffer, p.version); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ payloadStartIndex := buffer.Len()
+
+ for _, frame := range payloadFrames {
+ err := frame.Write(buffer, p.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if protocol.ByteCount(buffer.Len()+12) > protocol.MaxPacketSize {
+ return nil, errors.New("PacketPacker BUG: packet too large")
+ }
+
+ raw = raw[0:buffer.Len()]
+ p.cryptoSetup.Seal(raw[payloadStartIndex:payloadStartIndex], raw[payloadStartIndex:], currentPacketNumber, raw[:payloadStartIndex])
+ raw = raw[0 : buffer.Len()+12]
+
+ num := p.packetNumberGenerator.Pop()
+ if num != currentPacketNumber {
+ return nil, errors.New("PacketPacker BUG: Peeked and Popped packet numbers do not match.")
+ }
+
+ return &packedPacket{
+ number: currentPacketNumber,
+ raw: raw,
+ frames: payloadFrames,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) composeNextPacket(stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame, publicHeaderLength protocol.ByteCount) ([]frames.Frame, error) {
+ var payloadLength protocol.ByteCount
+ var payloadFrames []frames.Frame
+
+ maxFrameSize := protocol.MaxFrameAndPublicHeaderSize - publicHeaderLength
+
+ if stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ payloadFrames = append(payloadFrames, stopWaitingFrame)
+ minLength, err := stopWaitingFrame.MinLength(p.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ payloadLength += minLength
+ }
+
+ for len(p.controlFrames) > 0 {
+ frame := p.controlFrames[len(p.controlFrames)-1]
+ minLength, _ := frame.MinLength(p.version) // controlFrames does not contain any StopWaitingFrames. So it will *never* return an error
+ if payloadLength+minLength > maxFrameSize {
+ break
+ }
+ payloadFrames = append(payloadFrames, frame)
+ payloadLength += minLength
+ p.controlFrames = p.controlFrames[:len(p.controlFrames)-1]
+ }
+
+ if payloadLength > maxFrameSize {
+ return nil, fmt.Errorf("Packet Packer BUG: packet payload (%d) too large (%d)", payloadLength, maxFrameSize)
+ }
+
+ // temporarily increase the maxFrameSize by 2 bytes
+ // this leads to a properly sized packet in all cases, since we do all the packet length calculations with StreamFrames that have the DataLen set
+ // however, for the last StreamFrame in the packet, we can omit the DataLen, thus saving 2 bytes and yielding a packet of exactly the correct size
+ maxFrameSize += 2
+
+ fs := p.streamFramer.PopStreamFrames(maxFrameSize - payloadLength)
+ if len(fs) != 0 {
+ fs[len(fs)-1].DataLenPresent = false
+ }
+
+ // TODO: Simplify
+ for _, f := range fs {
+ payloadFrames = append(payloadFrames, f)
+ }
+
+ for b := p.streamFramer.PopBlockedFrame(); b != nil; b = p.streamFramer.PopBlockedFrame() {
+ p.controlFrames = append(p.controlFrames, b)
+ }
+
+ return payloadFrames, nil
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) QueueControlFrameForNextPacket(f frames.Frame) {
+ p.controlFrames = append(p.controlFrames, f)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_unpacker.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_unpacker.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3434751
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_unpacker.go
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+)
+
+type unpackedPacket struct {
+ frames []frames.Frame
+}
+
+type packetUnpacker struct {
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+ aead crypto.AEAD
+}
+
+func (u *packetUnpacker) Unpack(publicHeaderBinary []byte, hdr *PublicHeader, data []byte) (*unpackedPacket, error) {
+ buf := getPacketBuffer()
+ defer putPacketBuffer(buf)
+ decrypted, err := u.aead.Open(buf, data, hdr.PacketNumber, publicHeaderBinary)
+ if err != nil {
+ // Wrap err in quicError so that public reset is sent by session
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.DecryptionFailure, err.Error())
+ }
+ r := bytes.NewReader(decrypted)
+
+ if r.Len() == 0 {
+ return nil, qerr.MissingPayload
+ }
+
+ fs := make([]frames.Frame, 0, 2)
+
+ // Read all frames in the packet
+ReadLoop:
+ for r.Len() > 0 {
+ typeByte, _ := r.ReadByte()
+ r.UnreadByte()
+
+ var frame frames.Frame
+ if typeByte&0x80 == 0x80 {
+ frame, err = frames.ParseStreamFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamData, err.Error())
+ }
+ } else if typeByte&0xc0 == 0x40 {
+ frame, err = frames.ParseAckFrame(r, u.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, err.Error())
+ }
+ } else if typeByte&0xe0 == 0x20 {
+ err = errors.New("unimplemented: CONGESTION_FEEDBACK")
+ } else {
+ switch typeByte {
+ case 0x0: // PAD, end of frames
+ break ReadLoop
+ case 0x01:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseRstStreamFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidRstStreamData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x02:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseConnectionCloseFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidConnectionCloseData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x03:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseGoawayFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidGoawayData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x04:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseWindowUpdateFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidWindowUpdateData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x05:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseBlockedFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidBlockedData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x06:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseStopWaitingFrame(r, hdr.PacketNumber, hdr.PacketNumberLen, u.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStopWaitingData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x07:
+ frame, err = frames.ParsePingFrame(r)
+ default:
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidFrameData, fmt.Sprintf("unknown type byte 0x%x", typeByte))
+ }
+ }
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ if frame != nil {
+ fs = append(fs, frame)
+ }
+ }
+
+ return &unpackedPacket{
+ frames: fs,
+ }, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/packet_number.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/packet_number.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c4f468a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/packet_number.go
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+package protocol
+
+// InferPacketNumber calculates the packet number based on the received packet number, its length and the last seen packet number
+func InferPacketNumber(packetNumberLength PacketNumberLen, lastPacketNumber PacketNumber, wirePacketNumber PacketNumber) PacketNumber {
+ epochDelta := PacketNumber(1) << (uint8(packetNumberLength) * 8)
+ epoch := lastPacketNumber & ^(epochDelta - 1)
+ prevEpochBegin := epoch - epochDelta
+ nextEpochBegin := epoch + epochDelta
+ return closestTo(
+ lastPacketNumber+1,
+ epoch+wirePacketNumber,
+ closestTo(lastPacketNumber+1, prevEpochBegin+wirePacketNumber, nextEpochBegin+wirePacketNumber),
+ )
+}
+
+func closestTo(target, a, b PacketNumber) PacketNumber {
+ if delta(target, a) < delta(target, b) {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+func delta(a, b PacketNumber) PacketNumber {
+ if a < b {
+ return b - a
+ }
+ return a - b
+}
+
+// GetPacketNumberLengthForPublicHeader gets the length of the packet number for the public header
+// it never chooses a PacketNumberLen of 1 byte, since this is too short under certain circumstances
+func GetPacketNumberLengthForPublicHeader(packetNumber PacketNumber, leastUnacked PacketNumber) PacketNumberLen {
+ diff := uint64(packetNumber - leastUnacked)
+ if diff < (2 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen2)*8 - 2)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen2
+ }
+ if diff < (2 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen4)*8 - 2)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen4
+ }
+ // we do not check if there are less than 2^46 packets in flight, since flow control and congestion control will limit this number *a lot* sooner
+ return PacketNumberLen6
+}
+
+// GetPacketNumberLength gets the minimum length needed to fully represent the packet number
+func GetPacketNumberLength(packetNumber PacketNumber) PacketNumberLen {
+ if packetNumber < (1 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen1) * 8)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen1
+ }
+ if packetNumber < (1 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen2) * 8)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen2
+ }
+ if packetNumber < (1 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen4) * 8)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen4
+ }
+ return PacketNumberLen6
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/protocol.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/protocol.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aae2e0a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/protocol.go
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+package protocol
+
+import (
+ "math"
+ "time"
+)
+
+// A PacketNumber in QUIC
+type PacketNumber uint64
+
+// PacketNumberLen is the length of the packet number in bytes
+type PacketNumberLen uint8
+
+const (
+ // PacketNumberLenInvalid is the default value and not a valid length for a packet number
+ PacketNumberLenInvalid PacketNumberLen = 0
+ // PacketNumberLen1 is a packet number length of 1 byte
+ PacketNumberLen1 PacketNumberLen = 1
+ // PacketNumberLen2 is a packet number length of 2 bytes
+ PacketNumberLen2 PacketNumberLen = 2
+ // PacketNumberLen4 is a packet number length of 4 bytes
+ PacketNumberLen4 PacketNumberLen = 4
+ // PacketNumberLen6 is a packet number length of 6 bytes
+ PacketNumberLen6 PacketNumberLen = 6
+)
+
+// A ConnectionID in QUIC
+type ConnectionID uint64
+
+// A StreamID in QUIC
+type StreamID uint32
+
+// A ByteCount in QUIC
+type ByteCount uint64
+
+// MaxByteCount is the maximum value of a ByteCount
+const MaxByteCount = math.MaxUint64
+
+// MaxPacketSize is the maximum packet size, including the public header
+// This is the value used by Chromium for a QUIC packet sent using IPv6 (for IPv4 it would be 1370)
+const MaxPacketSize ByteCount = 1350
+
+// MaxFrameAndPublicHeaderSize is the maximum size of a QUIC frame plus PublicHeader
+const MaxFrameAndPublicHeaderSize = MaxPacketSize - 12 /*crypto signature*/
+
+// DefaultTCPMSS is the default maximum packet size used in the Linux TCP implementation.
+// Used in QUIC for congestion window computations in bytes.
+const DefaultTCPMSS ByteCount = 1460
+
+// InitialStreamFlowControlWindow is the initial stream-level flow control window for sending
+const InitialStreamFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 14) // 16 kB
+
+// InitialConnectionFlowControlWindow is the initial connection-level flow control window for sending
+const InitialConnectionFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 14) // 16 kB
+
+// DefaultRetransmissionTime is the RTO time on new connections
+const DefaultRetransmissionTime = 500 * time.Millisecond
+
+// MinRetransmissionTime is the minimum RTO time
+const MinRetransmissionTime = 200 * time.Millisecond
+
+// MaxRetransmissionTime is the maximum RTO time
+const MaxRetransmissionTime = 60 * time.Second
+
+// ClientHelloMinimumSize is the minimum size the server expects an inchoate CHLO to have.
+const ClientHelloMinimumSize = 1024
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/server_parameters.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/server_parameters.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..99894a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/server_parameters.go
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+package protocol
+
+import "time"
+
+// DefaultMaxCongestionWindow is the default for the max congestion window
+const DefaultMaxCongestionWindow PacketNumber = 1000
+
+// InitialCongestionWindow is the initial congestion window in QUIC packets
+const InitialCongestionWindow PacketNumber = 32
+
+// MaxUndecryptablePackets limits the number of undecryptable packets that a
+// session queues for later until it sends a public reset.
+const MaxUndecryptablePackets = 10
+
+// AckSendDelay is the maximal time delay applied to packets containing only ACKs
+const AckSendDelay = 5 * time.Millisecond
+
+// ReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow is the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+// This is the value that Google servers are using
+const ReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 20) // 1 MB
+
+// ReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow is the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+// This is the value that Google servers are using
+const ReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 20) * 1.5 // 1.5 MB
+
+// MaxStreamsPerConnection is the maximum value accepted for the number of streams per connection
+const MaxStreamsPerConnection = 100
+
+// MaxIncomingDynamicStreams is the maximum value accepted for the incoming number of dynamic streams per connection
+const MaxIncomingDynamicStreams = 100
+
+// MaxStreamsMultiplier is the slack the client is allowed for the maximum number of streams per connection, needed e.g. when packets are out of order or dropped. The minimum of this procentual increase and the absolute increment specified by MaxStreamsMinimumIncrement is used.
+const MaxStreamsMultiplier = 1.1
+
+// MaxStreamsMinimumIncrement is the slack the client is allowed for the maximum number of streams per connection, needed e.g. when packets are out of order or dropped. The minimum of this absolute increment and the procentual increase specified by MaxStreamsMultiplier is used.
+const MaxStreamsMinimumIncrement = 10
+
+// MaxNewStreamIDDelta is the maximum difference between and a newly opened Stream and the highest StreamID that a client has ever opened
+// note that the number of streams is half this value, since the client can only open streams with open StreamID
+const MaxNewStreamIDDelta = 4 * MaxStreamsPerConnection
+
+// MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets is the max number of packets stored in each session that are not yet processed.
+const MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets = DefaultMaxCongestionWindow
+
+// RetransmissionThreshold + 1 is the number of times a packet has to be NACKed so that it gets retransmitted
+const RetransmissionThreshold = 3
+
+// SkipPacketAveragePeriodLength is the average period length in which one packet number is skipped to prevent an Optimistic ACK attack
+const SkipPacketAveragePeriodLength PacketNumber = 500
+
+// MaxTrackedSkippedPackets is the maximum number of skipped packet numbers the SentPacketHandler keep track of for Optimistic ACK attack mitigation
+const MaxTrackedSkippedPackets = 10
+
+// STKExpiryTimeSec is the valid time of a source address token in seconds
+const STKExpiryTimeSec = 24 * 60 * 60
+
+// MaxTrackedSentPackets is maximum number of sent packets saved for either later retransmission or entropy calculation
+const MaxTrackedSentPackets = 2 * DefaultMaxCongestionWindow
+
+// MaxTrackedReceivedPackets is the maximum number of received packets saved for doing the entropy calculations
+const MaxTrackedReceivedPackets = 2 * DefaultMaxCongestionWindow
+
+// MaxStreamFrameSorterGaps is the maximum number of gaps between received StreamFrames
+// prevents DOS attacks against the streamFrameSorter
+const MaxStreamFrameSorterGaps = 1000
+
+// CryptoMaxParams is the upper limit for the number of parameters in a crypto message.
+// Value taken from Chrome.
+const CryptoMaxParams = 128
+
+// CryptoParameterMaxLength is the upper limit for the length of a parameter in a crypto message.
+const CryptoParameterMaxLength = 2000
+
+// EphermalKeyLifetime is the lifetime of the ephermal key during the handshake, see handshake.getEphermalKEX.
+const EphermalKeyLifetime = time.Minute
+
+// InitialIdleTimeout is the timeout before the handshake succeeds.
+const InitialIdleTimeout = 5 * time.Second
+
+// DefaultIdleTimeout is the default idle timeout.
+const DefaultIdleTimeout = 30 * time.Second
+
+// MaxIdleTimeout is the maximum idle timeout that can be negotiated.
+const MaxIdleTimeout = 1 * time.Minute
+
+// MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake is the default timeout for a connection until the crypto handshake succeeds.
+const MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake = 10 * time.Second
+
+// NumCachedCertificates is the number of cached compressed certificate chains, each taking ~1K space
+const NumCachedCertificates = 128
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/version.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/version.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cd0cd47
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/version.go
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+package protocol
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "strconv"
+)
+
+// VersionNumber is a version number as int
+type VersionNumber int
+
+// The version numbers, making grepping easier
+const (
+ Version34 VersionNumber = 34 + iota
+ Version35
+ Version36
+ VersionWhatever = 0 // for when the version doesn't matter
+)
+
+// SupportedVersions lists the versions that the server supports
+var SupportedVersions = []VersionNumber{
+ Version34, Version35, Version36,
+}
+
+// SupportedVersionsAsTags is needed for the SHLO crypto message
+var SupportedVersionsAsTags []byte
+
+// SupportedVersionsAsString is needed for the Alt-Scv HTTP header
+var SupportedVersionsAsString string
+
+// VersionNumberToTag maps version numbers ('32') to tags ('Q032')
+func VersionNumberToTag(vn VersionNumber) uint32 {
+ v := uint32(vn)
+ return 'Q' + ((v/100%10)+'0')<<8 + ((v/10%10)+'0')<<16 + ((v%10)+'0')<<24
+}
+
+// VersionTagToNumber is built from VersionNumberToTag in init()
+func VersionTagToNumber(v uint32) VersionNumber {
+ return VersionNumber(((v>>8)&0xff-'0')*100 + ((v>>16)&0xff-'0')*10 + ((v>>24)&0xff - '0'))
+}
+
+// IsSupportedVersion returns true if the server supports this version
+func IsSupportedVersion(v VersionNumber) bool {
+ for _, t := range SupportedVersions {
+ if t == v {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func init() {
+ var b bytes.Buffer
+ for _, v := range SupportedVersions {
+ s := make([]byte, 4)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(s, VersionNumberToTag(v))
+ b.Write(s)
+ }
+ SupportedVersionsAsTags = b.Bytes()
+
+ for i := len(SupportedVersions) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
+ SupportedVersionsAsString += strconv.Itoa(int(SupportedVersions[i]))
+ if i != 0 {
+ SupportedVersionsAsString += ","
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_header.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_header.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..475c1b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_header.go
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ errPacketNumberLenNotSet = errors.New("PublicHeader: PacketNumberLen not set")
+ errResetAndVersionFlagSet = errors.New("PublicHeader: Reset Flag and Version Flag should not be set at the same time")
+ errReceivedTruncatedConnectionID = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidPacketHeader, "receiving packets with truncated ConnectionID is not supported")
+ errInvalidConnectionID = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidPacketHeader, "connection ID cannot be 0")
+ errGetLengthOnlyForRegularPackets = errors.New("PublicHeader: GetLength can only be called for regular packets")
+)
+
+// The PublicHeader of a QUIC packet
+type PublicHeader struct {
+ Raw []byte
+ ConnectionID protocol.ConnectionID
+ VersionFlag bool
+ ResetFlag bool
+ TruncateConnectionID bool
+ PacketNumberLen protocol.PacketNumberLen
+ PacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ VersionNumber protocol.VersionNumber
+ DiversificationNonce []byte
+}
+
+// WritePublicHeader writes a public header
+func (h *PublicHeader) WritePublicHeader(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ publicFlagByte := uint8(0x00)
+ if h.VersionFlag && h.ResetFlag {
+ return errResetAndVersionFlagSet
+ }
+ if h.VersionFlag {
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x01
+ }
+ if h.ResetFlag {
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x02
+ }
+ if !h.TruncateConnectionID {
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x08
+ }
+
+ if len(h.DiversificationNonce) > 0 {
+ if len(h.DiversificationNonce) != 32 {
+ return errors.New("invalid diversification nonce length")
+ }
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x04
+ }
+
+ if !h.ResetFlag && !h.VersionFlag {
+ switch h.PacketNumberLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x00
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x10
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x20
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x30
+ }
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(publicFlagByte)
+
+ if !h.TruncateConnectionID {
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(h.ConnectionID))
+ }
+
+ if len(h.DiversificationNonce) > 0 {
+ b.Write(h.DiversificationNonce)
+ }
+
+ if !h.ResetFlag && !h.VersionFlag {
+ switch h.PacketNumberLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(h.PacketNumber))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(h.PacketNumber))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(h.PacketNumber))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(h.PacketNumber))
+ default:
+ return errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// ParsePublicHeader parses a QUIC packet's public header
+func ParsePublicHeader(b io.ByteReader) (*PublicHeader, error) {
+ header := &PublicHeader{}
+
+ // First byte
+ publicFlagByte, err := b.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.VersionFlag = publicFlagByte&0x01 > 0
+ header.ResetFlag = publicFlagByte&0x02 > 0
+
+ // TODO: activate this check once Chrome sends the correct value
+ // see https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/issues/232
+ // if publicFlagByte&0x04 > 0 {
+ // return nil, errors.New("diversification nonces should only be sent by servers")
+ // }
+
+ if publicFlagByte&0x08 == 0 {
+ return nil, errReceivedTruncatedConnectionID
+ }
+
+ switch publicFlagByte & 0x30 {
+ case 0x30:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen6
+ case 0x20:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen4
+ case 0x10:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen2
+ case 0x00:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen1
+ }
+
+ // Connection ID
+ connID, err := utils.ReadUint64(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.ConnectionID = protocol.ConnectionID(connID)
+ if header.ConnectionID == 0 {
+ return nil, errInvalidConnectionID
+ }
+
+ // Version (optional)
+ if header.VersionFlag {
+ var versionTag uint32
+ versionTag, err = utils.ReadUint32(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.VersionNumber = protocol.VersionTagToNumber(versionTag)
+ }
+
+ // Packet number
+ packetNumber, err := utils.ReadUintN(b, uint8(header.PacketNumberLen))
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.PacketNumber = protocol.PacketNumber(packetNumber)
+
+ return header, nil
+}
+
+// GetLength gets the length of the publicHeader in bytes
+// can only be called for regular packets
+func (h *PublicHeader) GetLength() (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ if h.VersionFlag || h.ResetFlag {
+ return 0, errGetLengthOnlyForRegularPackets
+ }
+
+ length := protocol.ByteCount(1) // 1 byte for public flags
+ if h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen1 && h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen2 && h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen4 && h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen6 {
+ return 0, errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+ if !h.TruncateConnectionID {
+ length += 8 // 8 bytes for the connection ID
+ }
+ length += protocol.ByteCount(len(h.DiversificationNonce))
+ length += protocol.ByteCount(h.PacketNumberLen)
+ return length, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_reset.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_reset.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7cceb2e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_reset.go
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+func writePublicReset(connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, rejectedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, nonceProof uint64) []byte {
+ b := &bytes.Buffer{}
+ b.WriteByte(0x0a)
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(connectionID))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(handshake.TagPRST))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, 2)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(handshake.TagRNON))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, 8)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(handshake.TagRSEQ))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, 16)
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, nonceProof)
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(rejectedPacketNumber))
+ return b.Bytes()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/error_codes.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/error_codes.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4797530
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/error_codes.go
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+package qerr
+
+// The error codes defined by QUIC
+// Remember to run `go generate ./...` whenever the error codes change.
+//go:generate stringer -type=ErrorCode
+const (
+ InternalError ErrorCode = 1
+ // There were data frames after the a fin or reset.
+ StreamDataAfterTermination ErrorCode = 2
+ // Control frame is malformed.
+ InvalidPacketHeader ErrorCode = 3
+ // Frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidFrameData ErrorCode = 4
+ // The packet contained no payload.
+ MissingPayload ErrorCode = 48
+ // FEC data is malformed.
+ InvalidFecData ErrorCode = 5
+ // STREAM frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidStreamData ErrorCode = 46
+ // STREAM frame data overlaps with buffered data.
+ OverlappingStreamData ErrorCode = 87
+ // Received STREAM frame data is not encrypted.
+ UnencryptedStreamData ErrorCode = 61
+ // Attempt to send unencrypted STREAM frame.
+ AttemptToSendUnencryptedStreamData ErrorCode = 88
+ // FEC frame data is not encrypted.
+ UnencryptedFecData ErrorCode = 77
+ // RST_STREAM frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidRstStreamData ErrorCode = 6
+ // CONNECTION_CLOSE frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidConnectionCloseData ErrorCode = 7
+ // GOAWAY frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidGoawayData ErrorCode = 8
+ // WINDOW_UPDATE frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidWindowUpdateData ErrorCode = 57
+ // BLOCKED frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidBlockedData ErrorCode = 58
+ // STOP_WAITING frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidStopWaitingData ErrorCode = 60
+ // PATH_CLOSE frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidPathCloseData ErrorCode = 78
+ // ACK frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidAckData ErrorCode = 9
+
+ // Version negotiation packet is malformed.
+ InvalidVersionNegotiationPacket ErrorCode = 10
+ // Public RST packet is malformed.
+ InvalidPublicRstPacket ErrorCode = 11
+ // There was an error decrypting.
+ DecryptionFailure ErrorCode = 12
+ // There was an error encrypting.
+ EncryptionFailure ErrorCode = 13
+ // The packet exceeded kMaxPacketSize.
+ PacketTooLarge ErrorCode = 14
+ // The peer is going away. May be a client or server.
+ PeerGoingAway ErrorCode = 16
+ // A stream ID was invalid.
+ InvalidStreamID ErrorCode = 17
+ // A priority was invalid.
+ InvalidPriority ErrorCode = 49
+ // Too many streams already open.
+ TooManyOpenStreams ErrorCode = 18
+ // The peer created too many available streams.
+ TooManyAvailableStreams ErrorCode = 76
+ // Received public reset for this connection.
+ PublicReset ErrorCode = 19
+ // Invalid protocol version.
+ InvalidVersion ErrorCode = 20
+
+ // The Header ID for a stream was too far from the previous.
+ InvalidHeaderID ErrorCode = 22
+ // Negotiable parameter received during handshake had invalid value.
+ InvalidNegotiatedValue ErrorCode = 23
+ // There was an error decompressing data.
+ DecompressionFailure ErrorCode = 24
+ // The connection timed out due to no network activity.
+ NetworkIdleTimeout ErrorCode = 25
+ // The connection timed out waiting for the handshake to complete.
+ HandshakeTimeout ErrorCode = 67
+ // There was an error encountered migrating addresses.
+ ErrorMigratingAddress ErrorCode = 26
+ // There was an error encountered migrating port only.
+ ErrorMigratingPort ErrorCode = 86
+ // There was an error while writing to the socket.
+ PacketWriteError ErrorCode = 27
+ // There was an error while reading from the socket.
+ PacketReadError ErrorCode = 51
+ // We received a STREAM_FRAME with no data and no fin flag set.
+ EmptyStreamFrameNoFin ErrorCode = 50
+ // We received invalid data on the headers stream.
+ InvalidHeadersStreamData ErrorCode = 56
+ // The peer received too much data, violating flow control.
+ FlowControlReceivedTooMuchData ErrorCode = 59
+ // The peer sent too much data, violating flow control.
+ FlowControlSentTooMuchData ErrorCode = 63
+ // The peer received an invalid flow control window.
+ FlowControlInvalidWindow ErrorCode = 64
+ // The connection has been IP pooled into an existing connection.
+ ConnectionIPPooled ErrorCode = 62
+ // The connection has too many outstanding sent packets.
+ TooManyOutstandingSentPackets ErrorCode = 68
+ // The connection has too many outstanding received packets.
+ TooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets ErrorCode = 69
+ // The quic connection has been cancelled.
+ ConnectionCancelled ErrorCode = 70
+ // Disabled QUIC because of high packet loss rate.
+ BadPacketLossRate ErrorCode = 71
+ // Disabled QUIC because of too many PUBLIC_RESETs post handshake.
+ PublicResetsPostHandshake ErrorCode = 73
+ // Disabled QUIC because of too many timeouts with streams open.
+ TimeoutsWithOpenStreams ErrorCode = 74
+ // Closed because we failed to serialize a packet.
+ FailedToSerializePacket ErrorCode = 75
+ // QUIC timed out after too many RTOs.
+ TooManyRtos ErrorCode = 85
+
+ // Crypto errors.
+
+ // Hanshake failed.
+ HandshakeFailed ErrorCode = 28
+ // Handshake message contained out of order tags.
+ CryptoTagsOutOfOrder ErrorCode = 29
+ // Handshake message contained too many entries.
+ CryptoTooManyEntries ErrorCode = 30
+ // Handshake message contained an invalid value length.
+ CryptoInvalidValueLength ErrorCode = 31
+ // A crypto message was received after the handshake was complete.
+ CryptoMessageAfterHandshakeComplete ErrorCode = 32
+ // A crypto message was received with an illegal message tag.
+ InvalidCryptoMessageType ErrorCode = 33
+ // A crypto message was received with an illegal parameter.
+ InvalidCryptoMessageParameter ErrorCode = 34
+ // An invalid channel id signature was supplied.
+ InvalidChannelIDSignature ErrorCode = 52
+ // A crypto message was received with a mandatory parameter missing.
+ CryptoMessageParameterNotFound ErrorCode = 35
+ // A crypto message was received with a parameter that has no overlap
+ // with the local parameter.
+ CryptoMessageParameterNoOverlap ErrorCode = 36
+ // A crypto message was received that contained a parameter with too few
+ // values.
+ CryptoMessageIndexNotFound ErrorCode = 37
+ // An internal error occurred in crypto processing.
+ CryptoInternalError ErrorCode = 38
+ // A crypto handshake message specified an unsupported version.
+ CryptoVersionNotSupported ErrorCode = 39
+ // A crypto handshake message resulted in a stateless reject.
+ CryptoHandshakeStatelessReject ErrorCode = 72
+ // There was no intersection between the crypto primitives supported by the
+ // peer and ourselves.
+ CryptoNoSupport ErrorCode = 40
+ // The server rejected our client hello messages too many times.
+ CryptoTooManyRejects ErrorCode = 41
+ // The client rejected the server's certificate chain or signature.
+ ProofInvalid ErrorCode = 42
+ // A crypto message was received with a duplicate tag.
+ CryptoDuplicateTag ErrorCode = 43
+ // A crypto message was received with the wrong encryption level (i.e. it
+ // should have been encrypted but was not.)
+ CryptoEncryptionLevelIncorrect ErrorCode = 44
+ // The server config for a server has expired.
+ CryptoServerConfigExpired ErrorCode = 45
+ // We failed to setup the symmetric keys for a connection.
+ CryptoSymmetricKeySetupFailed ErrorCode = 53
+ // A handshake message arrived, but we are still validating the
+ // previous handshake message.
+ CryptoMessageWhileValidatingClientHello ErrorCode = 54
+ // A server config update arrived before the handshake is complete.
+ CryptoUpdateBeforeHandshakeComplete ErrorCode = 65
+ // This connection involved a version negotiation which appears to have been
+ // tampered with.
+ VersionNegotiationMismatch ErrorCode = 55
+
+ // Multipath is not enabled, but a packet with multipath flag on is received.
+ BadMultipathFlag ErrorCode = 79
+
+ // IP address changed causing connection close.
+ IPAddressChanged ErrorCode = 80
+
+ // Connection migration errors.
+ // Network changed, but connection had no migratable streams.
+ ConnectionMigrationNoMigratableStreams ErrorCode = 81
+ // Connection changed networks too many times.
+ ConnectionMigrationTooManyChanges ErrorCode = 82
+ // Connection migration was attempted, but there was no new network to
+ // migrate to.
+ ConnectionMigrationNoNewNetwork ErrorCode = 83
+ // Network changed, but connection had one or more non-migratable streams.
+ ConnectionMigrationNonMigratableStream ErrorCode = 84
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/errorcode_string.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/errorcode_string.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aadd657
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/errorcode_string.go
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+// Code generated by "stringer -type=ErrorCode"; DO NOT EDIT
+
+package qerr
+
+import "fmt"
+
+const (
+ _ErrorCode_name_0 = "InternalErrorStreamDataAfterTerminationInvalidPacketHeaderInvalidFrameDataInvalidFecDataInvalidRstStreamDataInvalidConnectionCloseDataInvalidGoawayDataInvalidAckDataInvalidVersionNegotiationPacketInvalidPublicRstPacketDecryptionFailureEncryptionFailurePacketTooLarge"
+ _ErrorCode_name_1 = "PeerGoingAwayInvalidStreamIDTooManyOpenStreamsPublicResetInvalidVersion"
+ _ErrorCode_name_2 = "InvalidHeaderIDInvalidNegotiatedValueDecompressionFailureNetworkIdleTimeoutErrorMigratingAddressPacketWriteErrorHandshakeFailedCryptoTagsOutOfOrderCryptoTooManyEntriesCryptoInvalidValueLengthCryptoMessageAfterHandshakeCompleteInvalidCryptoMessageTypeInvalidCryptoMessageParameterCryptoMessageParameterNotFoundCryptoMessageParameterNoOverlapCryptoMessageIndexNotFoundCryptoInternalErrorCryptoVersionNotSupportedCryptoNoSupportCryptoTooManyRejectsProofInvalidCryptoDuplicateTagCryptoEncryptionLevelIncorrectCryptoServerConfigExpiredInvalidStreamData"
+ _ErrorCode_name_3 = "MissingPayloadInvalidPriorityEmptyStreamFrameNoFinPacketReadErrorInvalidChannelIDSignatureCryptoSymmetricKeySetupFailedCryptoMessageWhileValidatingClientHelloVersionNegotiationMismatchInvalidHeadersStreamDataInvalidWindowUpdateDataInvalidBlockedDataFlowControlReceivedTooMuchDataInvalidStopWaitingDataUnencryptedStreamDataConnectionIPPooledFlowControlSentTooMuchDataFlowControlInvalidWindowCryptoUpdateBeforeHandshakeComplete"
+ _ErrorCode_name_4 = "HandshakeTimeoutTooManyOutstandingSentPacketsTooManyOutstandingReceivedPacketsConnectionCancelledBadPacketLossRateCryptoHandshakeStatelessRejectPublicResetsPostHandshakeTimeoutsWithOpenStreamsFailedToSerializePacketTooManyAvailableStreamsUnencryptedFecDataInvalidPathCloseDataBadMultipathFlagIPAddressChangedConnectionMigrationNoMigratableStreamsConnectionMigrationTooManyChangesConnectionMigrationNoNewNetworkConnectionMigrationNonMigratableStreamTooManyRtosErrorMigratingPortOverlappingStreamDataAttemptToSendUnencryptedStreamData"
+)
+
+var (
+ _ErrorCode_index_0 = [...]uint16{0, 13, 39, 58, 74, 88, 108, 134, 151, 165, 196, 218, 235, 252, 266}
+ _ErrorCode_index_1 = [...]uint8{0, 13, 28, 46, 57, 71}
+ _ErrorCode_index_2 = [...]uint16{0, 15, 37, 57, 75, 96, 112, 127, 147, 167, 191, 226, 250, 279, 309, 340, 366, 385, 410, 425, 445, 457, 475, 505, 530, 547}
+ _ErrorCode_index_3 = [...]uint16{0, 14, 29, 50, 65, 90, 119, 158, 184, 208, 231, 249, 279, 301, 322, 340, 366, 390, 425}
+ _ErrorCode_index_4 = [...]uint16{0, 16, 45, 78, 97, 114, 144, 169, 192, 215, 238, 256, 276, 292, 308, 346, 379, 410, 448, 459, 477, 498, 532}
+)
+
+func (i ErrorCode) String() string {
+ switch {
+ case 1 <= i && i <= 14:
+ i--
+ return _ErrorCode_name_0[_ErrorCode_index_0[i]:_ErrorCode_index_0[i+1]]
+ case 16 <= i && i <= 20:
+ i -= 16
+ return _ErrorCode_name_1[_ErrorCode_index_1[i]:_ErrorCode_index_1[i+1]]
+ case 22 <= i && i <= 46:
+ i -= 22
+ return _ErrorCode_name_2[_ErrorCode_index_2[i]:_ErrorCode_index_2[i+1]]
+ case 48 <= i && i <= 65:
+ i -= 48
+ return _ErrorCode_name_3[_ErrorCode_index_3[i]:_ErrorCode_index_3[i+1]]
+ case 67 <= i && i <= 88:
+ i -= 67
+ return _ErrorCode_name_4[_ErrorCode_index_4[i]:_ErrorCode_index_4[i+1]]
+ default:
+ return fmt.Sprintf("ErrorCode(%d)", i)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/quic_error.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/quic_error.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6259476
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/quic_error.go
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+package qerr
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// ErrorCode can be used as a normal error without reason.
+type ErrorCode uint32
+
+func (e ErrorCode) Error() string {
+ return e.String()
+}
+
+// A QuicError consists of an error code plus a error reason
+type QuicError struct {
+ ErrorCode ErrorCode
+ ErrorMessage string
+}
+
+// Error creates a new QuicError instance
+func Error(errorCode ErrorCode, errorMessage string) *QuicError {
+ return &QuicError{
+ ErrorCode: errorCode,
+ ErrorMessage: errorMessage,
+ }
+}
+
+func (e *QuicError) Error() string {
+ return fmt.Sprintf("%s: %s", e.ErrorCode.String(), e.ErrorMessage)
+}
+
+// ToQuicError converts an arbitrary error to a QuicError. It leaves QuicErrors
+// unchanged, and properly handles `ErrorCode`s.
+func ToQuicError(err error) *QuicError {
+ switch e := err.(type) {
+ case *QuicError:
+ return e
+ case ErrorCode:
+ return Error(e, "")
+ }
+ utils.Errorf("Internal error: %v", err)
+ return Error(InternalError, err.Error())
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/server.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/server.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..54ccc6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/server.go
@@ -0,0 +1,205 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/tls"
+ "net"
+ "strings"
+ "sync"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// packetHandler handles packets
+type packetHandler interface {
+ handlePacket(*receivedPacket)
+ run()
+ Close(error) error
+}
+
+// A Server of QUIC
+type Server struct {
+ addr *net.UDPAddr
+
+ conn *net.UDPConn
+ connMutex sync.Mutex
+
+ signer crypto.Signer
+ scfg *handshake.ServerConfig
+
+ sessions map[protocol.ConnectionID]packetHandler
+ sessionsMutex sync.RWMutex
+
+ streamCallback StreamCallback
+
+ newSession func(conn connection, v protocol.VersionNumber, connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, sCfg *handshake.ServerConfig, streamCallback StreamCallback, closeCallback closeCallback) (packetHandler, error)
+}
+
+// NewServer makes a new server
+func NewServer(addr string, tlsConfig *tls.Config, cb StreamCallback) (*Server, error) {
+ signer, err := crypto.NewProofSource(tlsConfig)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ kex, err := crypto.NewCurve25519KEX()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ scfg, err := handshake.NewServerConfig(kex, signer)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ udpAddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return &Server{
+ addr: udpAddr,
+ signer: signer,
+ scfg: scfg,
+ streamCallback: cb,
+ sessions: map[protocol.ConnectionID]packetHandler{},
+ newSession: newSession,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+// ListenAndServe listens and serves a connection
+func (s *Server) ListenAndServe() error {
+ conn, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", s.addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ return s.Serve(conn)
+}
+
+// Serve on an existing UDP connection.
+func (s *Server) Serve(conn *net.UDPConn) error {
+ s.connMutex.Lock()
+ s.conn = conn
+ s.connMutex.Unlock()
+
+ for {
+ data := getPacketBuffer()
+ data = data[:protocol.MaxPacketSize]
+ n, remoteAddr, err := conn.ReadFromUDP(data)
+ if err != nil {
+ if strings.HasSuffix(err.Error(), "use of closed network connection") {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return err
+ }
+ data = data[:n]
+ if err := s.handlePacket(conn, remoteAddr, data); err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("error handling packet: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// Close the server
+func (s *Server) Close() error {
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ for _, session := range s.sessions {
+ if session != nil {
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+ _ = session.Close(nil)
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ }
+ }
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+
+ s.connMutex.Lock()
+ conn := s.conn
+ s.conn = nil
+ s.connMutex.Unlock()
+
+ if conn == nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return conn.Close()
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handlePacket(conn *net.UDPConn, remoteAddr *net.UDPAddr, packet []byte) error {
+ if protocol.ByteCount(len(packet)) > protocol.MaxPacketSize {
+ return qerr.PacketTooLarge
+ }
+
+ rcvTime := time.Now()
+
+ r := bytes.NewReader(packet)
+
+ hdr, err := ParsePublicHeader(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidPacketHeader, err.Error())
+ }
+ hdr.Raw = packet[:len(packet)-r.Len()]
+
+ // Send Version Negotiation Packet if the client is speaking a different protocol version
+ if hdr.VersionFlag && !protocol.IsSupportedVersion(hdr.VersionNumber) {
+ utils.Infof("Client offered version %d, sending VersionNegotiationPacket", hdr.VersionNumber)
+ _, err = conn.WriteToUDP(composeVersionNegotiation(hdr.ConnectionID), remoteAddr)
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.sessionsMutex.RLock()
+ session, ok := s.sessions[hdr.ConnectionID]
+ s.sessionsMutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if !ok {
+ utils.Infof("Serving new connection: %x, version %d from %v", hdr.ConnectionID, hdr.VersionNumber, remoteAddr)
+ session, err = s.newSession(
+ &udpConn{conn: conn, currentAddr: remoteAddr},
+ hdr.VersionNumber,
+ hdr.ConnectionID,
+ s.scfg,
+ s.streamCallback,
+ s.closeCallback,
+ )
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ go session.run()
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ s.sessions[hdr.ConnectionID] = session
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+ }
+ if session == nil {
+ // Late packet for closed session
+ return nil
+ }
+ session.handlePacket(&receivedPacket{
+ remoteAddr: remoteAddr,
+ publicHeader: hdr,
+ data: packet[len(packet)-r.Len():],
+ rcvTime: rcvTime,
+ })
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Server) closeCallback(id protocol.ConnectionID) {
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ s.sessions[id] = nil
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+}
+
+func composeVersionNegotiation(connectionID protocol.ConnectionID) []byte {
+ fullReply := &bytes.Buffer{}
+ responsePublicHeader := PublicHeader{
+ ConnectionID: connectionID,
+ PacketNumber: 1,
+ VersionFlag: true,
+ }
+ err := responsePublicHeader.WritePublicHeader(fullReply, protocol.Version35)
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("error composing version negotiation packet: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+ fullReply.Write(protocol.SupportedVersionsAsTags)
+ return fullReply.Bytes()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/session.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/session.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2f75299
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/session.go
@@ -0,0 +1,673 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "net"
+ "runtime"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type unpacker interface {
+ Unpack(publicHeaderBinary []byte, hdr *PublicHeader, data []byte) (*unpackedPacket, error)
+}
+
+type receivedPacket struct {
+ remoteAddr interface{}
+ publicHeader *PublicHeader
+ data []byte
+ rcvTime time.Time
+}
+
+var (
+ errRstStreamOnInvalidStream = errors.New("RST_STREAM received for unknown stream")
+ errWindowUpdateOnClosedStream = errors.New("WINDOW_UPDATE received for an already closed stream")
+)
+
+// StreamCallback gets a stream frame and returns a reply frame
+type StreamCallback func(*Session, utils.Stream)
+
+// closeCallback is called when a session is closed
+type closeCallback func(id protocol.ConnectionID)
+
+// A Session is a QUIC session
+type Session struct {
+ connectionID protocol.ConnectionID
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+
+ streamCallback StreamCallback
+ closeCallback closeCallback
+
+ conn connection
+
+ streamsMap *streamsMap
+
+ sentPacketHandler ackhandler.SentPacketHandler
+ receivedPacketHandler ackhandler.ReceivedPacketHandler
+ streamFramer *streamFramer
+
+ flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager
+
+ unpacker unpacker
+ packer *packetPacker
+
+ cryptoSetup *handshake.CryptoSetup
+
+ receivedPackets chan *receivedPacket
+ sendingScheduled chan struct{}
+ // closeChan is used to notify the run loop that it should terminate.
+ // If the value is not nil, the error is sent as a CONNECTION_CLOSE.
+ closeChan chan *qerr.QuicError
+ closed uint32 // atomic bool
+
+ undecryptablePackets []*receivedPacket
+ aeadChanged chan struct{}
+
+ delayedAckOriginTime time.Time
+
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ lastRcvdPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Used to calculate the next packet number from the truncated wire
+ // representation, and sent back in public reset packets
+ largestRcvdPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ sessionCreationTime time.Time
+ lastNetworkActivityTime time.Time
+
+ timer *time.Timer
+ currentDeadline time.Time
+ timerRead bool
+}
+
+// newSession makes a new session
+func newSession(conn connection, v protocol.VersionNumber, connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, sCfg *handshake.ServerConfig, streamCallback StreamCallback, closeCallback closeCallback) (packetHandler, error) {
+ connectionParametersManager := handshake.NewConnectionParamatersManager()
+ flowControlManager := flowcontrol.NewFlowControlManager(connectionParametersManager)
+
+ var sentPacketHandler ackhandler.SentPacketHandler
+ var receivedPacketHandler ackhandler.ReceivedPacketHandler
+
+ sentPacketHandler = ackhandler.NewSentPacketHandler()
+ receivedPacketHandler = ackhandler.NewReceivedPacketHandler()
+
+ now := time.Now()
+ session := &Session{
+ conn: conn,
+ connectionID: connectionID,
+ version: v,
+
+ streamCallback: streamCallback,
+ closeCallback: closeCallback,
+
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ sentPacketHandler: sentPacketHandler,
+ receivedPacketHandler: receivedPacketHandler,
+ flowControlManager: flowControlManager,
+
+ receivedPackets: make(chan *receivedPacket, protocol.MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets),
+ closeChan: make(chan *qerr.QuicError, 1),
+ sendingScheduled: make(chan struct{}, 1),
+ undecryptablePackets: make([]*receivedPacket, 0, protocol.MaxUndecryptablePackets),
+ aeadChanged: make(chan struct{}, 1),
+
+ timer: time.NewTimer(0),
+ lastNetworkActivityTime: now,
+ sessionCreationTime: now,
+ }
+
+ session.streamsMap = newStreamsMap(session.newStream)
+
+ cryptoStream, _ := session.GetOrOpenStream(1)
+ var err error
+ session.cryptoSetup, err = handshake.NewCryptoSetup(connectionID, conn.RemoteAddr().IP, v, sCfg, cryptoStream, session.connectionParametersManager, session.aeadChanged)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ session.streamFramer = newStreamFramer(session.streamsMap, flowControlManager)
+ session.packer = newPacketPacker(connectionID, session.cryptoSetup, session.connectionParametersManager, session.streamFramer, v)
+ session.unpacker = &packetUnpacker{aead: session.cryptoSetup, version: v}
+
+ return session, err
+}
+
+// run the session main loop
+func (s *Session) run() {
+ // Start the crypto stream handler
+ go func() {
+ if err := s.cryptoSetup.HandleCryptoStream(); err != nil {
+ s.Close(err)
+ }
+ }()
+
+ for {
+ // Close immediately if requested
+ select {
+ case errForConnClose := <-s.closeChan:
+ if errForConnClose != nil {
+ s.sendConnectionClose(errForConnClose)
+ }
+ return
+ default:
+ }
+
+ s.maybeResetTimer()
+
+ var err error
+ select {
+ case errForConnClose := <-s.closeChan:
+ if errForConnClose != nil {
+ s.sendConnectionClose(errForConnClose)
+ }
+ return
+ case <-s.timer.C:
+ s.timerRead = true
+ // We do all the interesting stuff after the switch statement, so
+ // nothing to see here.
+ case <-s.sendingScheduled:
+ // We do all the interesting stuff after the switch statement, so
+ // nothing to see here.
+ case p := <-s.receivedPackets:
+ err = s.handlePacketImpl(p)
+ if qErr, ok := err.(*qerr.QuicError); ok && qErr.ErrorCode == qerr.DecryptionFailure {
+ s.tryQueueingUndecryptablePacket(p)
+ continue
+ }
+ // This is a bit unclean, but works properly, since the packet always
+ // begins with the public header and we never copy it.
+ putPacketBuffer(p.publicHeader.Raw)
+ if s.delayedAckOriginTime.IsZero() {
+ s.delayedAckOriginTime = p.rcvTime
+ }
+ case <-s.aeadChanged:
+ s.tryDecryptingQueuedPackets()
+ }
+
+ if err != nil {
+ s.Close(err)
+ }
+
+ if err := s.sendPacket(); err != nil {
+ s.Close(err)
+ }
+ if time.Now().Sub(s.lastNetworkActivityTime) >= s.idleTimeout() {
+ s.Close(qerr.Error(qerr.NetworkIdleTimeout, "No recent network activity."))
+ }
+ if !s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() && time.Now().Sub(s.sessionCreationTime) >= protocol.MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake {
+ s.Close(qerr.Error(qerr.NetworkIdleTimeout, "Crypto handshake did not complete in time."))
+ }
+ s.garbageCollectStreams()
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) maybeResetTimer() {
+ nextDeadline := s.lastNetworkActivityTime.Add(s.idleTimeout())
+
+ if !s.delayedAckOriginTime.IsZero() {
+ nextDeadline = utils.MinTime(nextDeadline, s.delayedAckOriginTime.Add(protocol.AckSendDelay))
+ }
+ if rtoTime := s.sentPacketHandler.TimeOfFirstRTO(); !rtoTime.IsZero() {
+ nextDeadline = utils.MinTime(nextDeadline, rtoTime)
+ }
+ if !s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() {
+ handshakeDeadline := s.sessionCreationTime.Add(protocol.MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake)
+ nextDeadline = utils.MinTime(nextDeadline, handshakeDeadline)
+ }
+
+ if nextDeadline.Equal(s.currentDeadline) {
+ // No need to reset the timer
+ return
+ }
+
+ // We need to drain the timer if the value from its channel was not read yet.
+ // See https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/golang-dev/c9UUfASVPoU
+ if !s.timer.Stop() && !s.timerRead {
+ <-s.timer.C
+ }
+ s.timer.Reset(nextDeadline.Sub(time.Now()))
+
+ s.timerRead = false
+ s.currentDeadline = nextDeadline
+}
+
+func (s *Session) idleTimeout() time.Duration {
+ if s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() {
+ return s.connectionParametersManager.GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime()
+ }
+ return protocol.InitialIdleTimeout
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handlePacketImpl(p *receivedPacket) error {
+ if p.rcvTime.IsZero() {
+ // To simplify testing
+ p.rcvTime = time.Now()
+ }
+
+ s.lastNetworkActivityTime = p.rcvTime
+ hdr := p.publicHeader
+ data := p.data
+
+ // Calculate packet number
+ hdr.PacketNumber = protocol.InferPacketNumber(
+ hdr.PacketNumberLen,
+ s.largestRcvdPacketNumber,
+ hdr.PacketNumber,
+ )
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Debugf("<- Reading packet 0x%x (%d bytes) for connection %x", hdr.PacketNumber, len(data)+len(hdr.Raw), hdr.ConnectionID)
+ }
+
+ // TODO: Only do this after authenticating
+ s.conn.setCurrentRemoteAddr(p.remoteAddr)
+
+ packet, err := s.unpacker.Unpack(hdr.Raw, hdr, data)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.lastRcvdPacketNumber = hdr.PacketNumber
+ // Only do this after decrypting, so we are sure the packet is not attacker-controlled
+ s.largestRcvdPacketNumber = utils.MaxPacketNumber(s.largestRcvdPacketNumber, hdr.PacketNumber)
+
+ err = s.receivedPacketHandler.ReceivedPacket(hdr.PacketNumber)
+ // ignore duplicate packets
+ if err == ackhandler.ErrDuplicatePacket {
+ utils.Infof("Ignoring packet 0x%x due to ErrDuplicatePacket", hdr.PacketNumber)
+ return nil
+ }
+ // ignore packets with packet numbers smaller than the LeastUnacked of a StopWaiting
+ if err == ackhandler.ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting {
+ utils.Infof("Ignoring packet 0x%x due to ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting", hdr.PacketNumber)
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ return s.handleFrames(packet.frames)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleFrames(fs []frames.Frame) error {
+ for _, ff := range fs {
+ var err error
+ frames.LogFrame(ff, false)
+ switch frame := ff.(type) {
+ case *frames.StreamFrame:
+ err = s.handleStreamFrame(frame)
+ // TODO: send RstStreamFrame
+ case *frames.AckFrame:
+ err = s.handleAckFrame(frame)
+ case *frames.ConnectionCloseFrame:
+ s.closeImpl(qerr.Error(frame.ErrorCode, frame.ReasonPhrase), true)
+ case *frames.GoawayFrame:
+ err = errors.New("unimplemented: handling GOAWAY frames")
+ case *frames.StopWaitingFrame:
+ err = s.receivedPacketHandler.ReceivedStopWaiting(frame)
+ case *frames.RstStreamFrame:
+ err = s.handleRstStreamFrame(frame)
+ case *frames.WindowUpdateFrame:
+ err = s.handleWindowUpdateFrame(frame)
+ case *frames.BlockedFrame:
+ case *frames.PingFrame:
+ default:
+ return errors.New("Session BUG: unexpected frame type")
+ }
+
+ if err != nil {
+ switch err {
+ case ackhandler.ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck:
+ // Can happen e.g. when packets thought missing arrive late
+ case errRstStreamOnInvalidStream:
+ // Can happen when RST_STREAMs arrive early or late (?)
+ utils.Errorf("Ignoring error in session: %s", err.Error())
+ case errWindowUpdateOnClosedStream:
+ // Can happen when we already sent the last StreamFrame with the FinBit, but the client already sent a WindowUpdate for this Stream
+ default:
+ return err
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// handlePacket is called by the server with a new packet
+func (s *Session) handlePacket(p *receivedPacket) {
+ // Discard packets once the amount of queued packets is larger than
+ // the channel size, protocol.MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets
+ select {
+ case s.receivedPackets <- p:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleStreamFrame(frame *frames.StreamFrame) error {
+ str, err := s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(frame.StreamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ // Stream is closed, ignore
+ return nil
+ }
+ err = str.AddStreamFrame(frame)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleWindowUpdateFrame(frame *frames.WindowUpdateFrame) error {
+ if frame.StreamID != 0 {
+ str, err := s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(frame.StreamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ return errWindowUpdateOnClosedStream
+ }
+ }
+ _, err := s.flowControlManager.UpdateWindow(frame.StreamID, frame.ByteOffset)
+ return err
+}
+
+// TODO: Handle frame.byteOffset
+func (s *Session) handleRstStreamFrame(frame *frames.RstStreamFrame) error {
+ str, err := s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(frame.StreamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ return errRstStreamOnInvalidStream
+ }
+ s.closeStreamWithError(str, fmt.Errorf("RST_STREAM received with code %d", frame.ErrorCode))
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleAckFrame(frame *frames.AckFrame) error {
+ if err := s.sentPacketHandler.ReceivedAck(frame, s.lastRcvdPacketNumber, s.lastNetworkActivityTime); err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Close the connection. If err is nil it will be set to qerr.PeerGoingAway.
+func (s *Session) Close(e error) error {
+ return s.closeImpl(e, false)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) closeImpl(e error, remoteClose bool) error {
+ // Only close once
+ if !atomic.CompareAndSwapUint32(&s.closed, 0, 1) {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if e == nil {
+ e = qerr.PeerGoingAway
+ }
+
+ quicErr := qerr.ToQuicError(e)
+
+ // Don't log 'normal' reasons
+ if quicErr.ErrorCode == qerr.PeerGoingAway || quicErr.ErrorCode == qerr.NetworkIdleTimeout {
+ utils.Infof("Closing connection %x", s.connectionID)
+ } else {
+ utils.Errorf("Closing session with error: %s", e.Error())
+ }
+
+ s.closeStreamsWithError(quicErr)
+ s.closeCallback(s.connectionID)
+
+ if remoteClose {
+ // If this is a remote close we don't need to send a CONNECTION_CLOSE
+ s.closeChan <- nil
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if quicErr.ErrorCode == qerr.DecryptionFailure {
+ // If we send a public reset, don't send a CONNECTION_CLOSE
+ s.closeChan <- nil
+ return s.sendPublicReset(s.lastRcvdPacketNumber)
+ }
+ s.closeChan <- quicErr
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Session) closeStreamsWithError(err error) {
+ s.streamsMap.Iterate(func(str *stream) (bool, error) {
+ s.closeStreamWithError(str, err)
+ return true, nil
+ })
+}
+
+func (s *Session) closeStreamWithError(str *stream, err error) {
+ str.RegisterError(err)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) sendPacket() error {
+ // Repeatedly try sending until we don't have any more data, or run out of the congestion window
+ for {
+ err := s.sentPacketHandler.CheckForError()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ // Do this before checking the congestion, since we might de-congestionize here :)
+ s.sentPacketHandler.MaybeQueueRTOs()
+
+ if !s.sentPacketHandler.SendingAllowed() {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ var controlFrames []frames.Frame
+
+ // check for retransmissions first
+ for {
+ retransmitPacket := s.sentPacketHandler.DequeuePacketForRetransmission()
+ if retransmitPacket == nil {
+ break
+ }
+ utils.Debugf("\tDequeueing retransmission for packet 0x%x", retransmitPacket.PacketNumber)
+
+ // resend the frames that were in the packet
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, retransmitPacket.GetControlFramesForRetransmission()...)
+ for _, streamFrame := range retransmitPacket.GetStreamFramesForRetransmission() {
+ s.streamFramer.AddFrameForRetransmission(streamFrame)
+ }
+ }
+
+ windowUpdateFrames, err := s.getWindowUpdateFrames()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ for _, wuf := range windowUpdateFrames {
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, wuf)
+ }
+
+ ack, err := s.receivedPacketHandler.GetAckFrame(false)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if ack != nil {
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, ack)
+ }
+
+ // Check whether we are allowed to send a packet containing only an ACK
+ maySendOnlyAck := time.Now().Sub(s.delayedAckOriginTime) > protocol.AckSendDelay
+ if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
+ maySendOnlyAck = true
+ }
+
+ hasRetransmission := s.streamFramer.HasFramesForRetransmission()
+
+ var stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame
+ if ack != nil || hasRetransmission {
+ stopWaitingFrame = s.sentPacketHandler.GetStopWaitingFrame(hasRetransmission)
+ }
+ packet, err := s.packer.PackPacket(stopWaitingFrame, controlFrames, s.sentPacketHandler.GetLeastUnacked(), maySendOnlyAck)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if packet == nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // Pop the ACK frame now that we are sure we're gonna send it
+ _, err = s.receivedPacketHandler.GetAckFrame(true)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ for _, f := range windowUpdateFrames {
+ s.packer.QueueControlFrameForNextPacket(f)
+ }
+
+ err = s.sentPacketHandler.SentPacket(&ackhandler.Packet{
+ PacketNumber: packet.number,
+ Frames: packet.frames,
+ Length: protocol.ByteCount(len(packet.raw)),
+ })
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.logPacket(packet)
+ s.delayedAckOriginTime = time.Time{}
+
+ err = s.conn.write(packet.raw)
+ putPacketBuffer(packet.raw)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) sendConnectionClose(quicErr *qerr.QuicError) error {
+ packet, err := s.packer.PackConnectionClose(&frames.ConnectionCloseFrame{ErrorCode: quicErr.ErrorCode, ReasonPhrase: quicErr.ErrorMessage}, s.sentPacketHandler.GetLeastUnacked())
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if packet == nil {
+ return errors.New("Session BUG: expected packet not to be nil")
+ }
+ s.logPacket(packet)
+ return s.conn.write(packet.raw)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) logPacket(packet *packedPacket) {
+ if !utils.Debug() {
+ // We don't need to allocate the slices for calling the format functions
+ return
+ }
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Debugf("-> Sending packet 0x%x (%d bytes)", packet.number, len(packet.raw))
+ for _, frame := range packet.frames {
+ frames.LogFrame(frame, true)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// GetOrOpenStream either returns an existing stream, a newly opened stream, or nil if a stream with the provided ID is already closed.
+// Newly opened streams should only originate from the client. To open a stream from the server, OpenStream should be used.
+func (s *Session) GetOrOpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (utils.Stream, error) {
+ return s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(id)
+}
+
+// OpenStream opens a stream from the server's side
+func (s *Session) OpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (utils.Stream, error) {
+ return s.streamsMap.OpenStream(id)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) newStreamImpl(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ return s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(id)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) newStream(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ stream, err := newStream(id, s.scheduleSending, s.flowControlManager)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ // TODO: find a better solution for determining which streams contribute to connection level flow control
+ if id == 1 || id == 3 {
+ s.flowControlManager.NewStream(id, false)
+ } else {
+ s.flowControlManager.NewStream(id, true)
+ }
+
+ s.streamCallback(s, stream)
+
+ return stream, nil
+}
+
+// garbageCollectStreams goes through all streams and removes EOF'ed streams
+// from the streams map.
+func (s *Session) garbageCollectStreams() {
+ s.streamsMap.Iterate(func(str *stream) (bool, error) {
+ id := str.StreamID()
+ if str.finished() {
+ err := s.streamsMap.RemoveStream(id)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ s.flowControlManager.RemoveStream(id)
+ }
+ return true, nil
+ })
+}
+
+func (s *Session) sendPublicReset(rejectedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber) error {
+ utils.Infof("Sending public reset for connection %x, packet number %d", s.connectionID, rejectedPacketNumber)
+ return s.conn.write(writePublicReset(s.connectionID, rejectedPacketNumber, 0))
+}
+
+// scheduleSending signals that we have data for sending
+func (s *Session) scheduleSending() {
+ select {
+ case s.sendingScheduled <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) tryQueueingUndecryptablePacket(p *receivedPacket) {
+ if s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() {
+ return
+ }
+ utils.Infof("Queueing packet 0x%x for later decryption", p.publicHeader.PacketNumber)
+ if len(s.undecryptablePackets)+1 >= protocol.MaxUndecryptablePackets {
+ s.Close(qerr.Error(qerr.DecryptionFailure, "too many undecryptable packets received"))
+ }
+ s.undecryptablePackets = append(s.undecryptablePackets, p)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) tryDecryptingQueuedPackets() {
+ for _, p := range s.undecryptablePackets {
+ s.handlePacket(p)
+ }
+ s.undecryptablePackets = s.undecryptablePackets[:0]
+}
+
+func (s *Session) getWindowUpdateFrames() ([]*frames.WindowUpdateFrame, error) {
+ updates := s.flowControlManager.GetWindowUpdates()
+ res := make([]*frames.WindowUpdateFrame, len(updates))
+ for i, u := range updates {
+ res[i] = &frames.WindowUpdateFrame{StreamID: u.StreamID, ByteOffset: u.Offset}
+ }
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+// RemoteAddr returns the net.UDPAddr of the client
+func (s *Session) RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr {
+ return s.conn.RemoteAddr()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fc73b1e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream.go
@@ -0,0 +1,267 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A Stream assembles the data from StreamFrames and provides a super-convenient Read-Interface
+//
+// Read() and Write() may be called concurrently, but multiple calls to Read() or Write() individually must be synchronized manually.
+type stream struct {
+ streamID protocol.StreamID
+ onData func()
+
+ readPosInFrame int
+ writeOffset protocol.ByteCount
+ readOffset protocol.ByteCount
+
+ // Once set, err must not be changed!
+ err error
+ mutex sync.Mutex
+
+ // eof is set if we are finished reading
+ eof int32 // really a bool
+ // closed is set when we are finished writing
+ closed int32 // really a bool
+
+ frameQueue *streamFrameSorter
+ newFrameOrErrCond sync.Cond
+
+ dataForWriting []byte
+ finSent bool
+ doneWritingOrErrCond sync.Cond
+
+ flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager
+}
+
+// newStream creates a new Stream
+func newStream(StreamID protocol.StreamID, onData func(), flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager) (*stream, error) {
+ s := &stream{
+ onData: onData,
+ streamID: StreamID,
+ flowControlManager: flowControlManager,
+ frameQueue: newStreamFrameSorter(),
+ }
+
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.L = &s.mutex
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.L = &s.mutex
+
+ return s, nil
+}
+
+// Read implements io.Reader. It is not thread safe!
+func (s *stream) Read(p []byte) (int, error) {
+ if atomic.LoadInt32(&s.eof) != 0 {
+ return 0, io.EOF
+ }
+
+ bytesRead := 0
+ for bytesRead < len(p) {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ frame := s.frameQueue.Head()
+
+ if frame == nil && bytesRead > 0 {
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return bytesRead, s.err
+ }
+
+ var err error
+ for {
+ // Stop waiting on errors
+ if s.err != nil {
+ err = s.err
+ break
+ }
+ if frame != nil {
+ s.readPosInFrame = int(s.readOffset - frame.Offset)
+ break
+ }
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.Wait()
+ frame = s.frameQueue.Head()
+ }
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ // Here, either frame != nil xor err != nil
+
+ if frame == nil {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.eof, 1)
+ // We have an err and no data, return the error
+ return bytesRead, err
+ }
+
+ m := utils.Min(len(p)-bytesRead, int(frame.DataLen())-s.readPosInFrame)
+
+ if bytesRead > len(p) {
+ return bytesRead, fmt.Errorf("BUG: bytesRead (%d) > len(p) (%d) in stream.Read", bytesRead, len(p))
+ }
+ if s.readPosInFrame > int(frame.DataLen()) {
+ return bytesRead, fmt.Errorf("BUG: readPosInFrame (%d) > frame.DataLen (%d) in stream.Read", s.readPosInFrame, frame.DataLen())
+ }
+ copy(p[bytesRead:], frame.Data[s.readPosInFrame:])
+
+ s.readPosInFrame += m
+ bytesRead += m
+ s.readOffset += protocol.ByteCount(m)
+
+ s.flowControlManager.AddBytesRead(s.streamID, protocol.ByteCount(m))
+ s.onData() // so that a possible WINDOW_UPDATE is sent
+
+ if s.readPosInFrame >= int(frame.DataLen()) {
+ fin := frame.FinBit
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ s.frameQueue.Pop()
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ if fin {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.eof, 1)
+ return bytesRead, io.EOF
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return bytesRead, nil
+}
+
+func (s *stream) Write(p []byte) (int, error) {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ if s.err != nil {
+ return 0, s.err
+ }
+
+ if len(p) == 0 {
+ return 0, nil
+ }
+
+ s.dataForWriting = make([]byte, len(p))
+ copy(s.dataForWriting, p)
+
+ s.onData()
+
+ for s.dataForWriting != nil && s.err == nil {
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.Wait()
+ }
+
+ if s.err != nil {
+ return 0, s.err
+ }
+
+ return len(p), nil
+}
+
+func (s *stream) lenOfDataForWriting() protocol.ByteCount {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ l := protocol.ByteCount(len(s.dataForWriting))
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return l
+}
+
+func (s *stream) getDataForWriting(maxBytes protocol.ByteCount) []byte {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ if s.dataForWriting == nil {
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return nil
+ }
+ var ret []byte
+ if protocol.ByteCount(len(s.dataForWriting)) > maxBytes {
+ ret = s.dataForWriting[:maxBytes]
+ s.dataForWriting = s.dataForWriting[maxBytes:]
+ } else {
+ ret = s.dataForWriting
+ s.dataForWriting = nil
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.Signal()
+ }
+ s.writeOffset += protocol.ByteCount(len(ret))
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return ret
+}
+
+// Close implements io.Closer
+func (s *stream) Close() error {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.closed, 1)
+ s.onData()
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *stream) shouldSendFin() bool {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ res := atomic.LoadInt32(&s.closed) != 0 && !s.finSent && s.err == nil && s.dataForWriting == nil
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return res
+}
+
+func (s *stream) sentFin() {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ s.finSent = true
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+}
+
+// AddStreamFrame adds a new stream frame
+func (s *stream) AddStreamFrame(frame *frames.StreamFrame) error {
+ maxOffset := frame.Offset + frame.DataLen()
+ err := s.flowControlManager.UpdateHighestReceived(s.streamID, maxOffset)
+
+ if err == flowcontrol.ErrStreamFlowControlViolation {
+ return qerr.FlowControlReceivedTooMuchData
+ }
+ if err == flowcontrol.ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation {
+ return qerr.FlowControlReceivedTooMuchData
+ }
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+ err = s.frameQueue.Push(frame)
+ if err != nil && err != errDuplicateStreamData {
+ return err
+ }
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.Signal()
+ return nil
+}
+
+// CloseRemote makes the stream receive a "virtual" FIN stream frame at a given offset
+func (s *stream) CloseRemote(offset protocol.ByteCount) {
+ s.AddStreamFrame(&frames.StreamFrame{FinBit: true, Offset: offset})
+}
+
+// RegisterError is called by session to indicate that an error occurred and the
+// stream should be closed.
+func (s *stream) RegisterError(err error) {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.closed, 1)
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+ if s.err != nil { // s.err must not be changed!
+ return
+ }
+ s.err = err
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.Signal()
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.Signal()
+}
+
+func (s *stream) finishedReading() bool {
+ return atomic.LoadInt32(&s.eof) != 0
+}
+
+func (s *stream) finishedWriting() bool {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return s.err != nil || (atomic.LoadInt32(&s.closed) != 0 && s.finSent)
+}
+
+func (s *stream) finished() bool {
+ return s.finishedReading() && s.finishedWriting()
+}
+
+func (s *stream) StreamID() protocol.StreamID {
+ return s.streamID
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_frame_sorter.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_frame_sorter.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7a95f1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_frame_sorter.go
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type streamFrameSorter struct {
+ queuedFrames map[protocol.ByteCount]*frames.StreamFrame
+ readPosition protocol.ByteCount
+ gaps *utils.ByteIntervalList
+}
+
+var (
+ errTooManyGapsInReceivedStreamData = errors.New("Too many gaps in received StreamFrame data")
+ errDuplicateStreamData = errors.New("Overlapping Stream Data")
+ errEmptyStreamData = errors.New("Stream Data empty")
+)
+
+func newStreamFrameSorter() *streamFrameSorter {
+ s := streamFrameSorter{
+ gaps: utils.NewByteIntervalList(),
+ queuedFrames: make(map[protocol.ByteCount]*frames.StreamFrame),
+ }
+ s.gaps.PushFront(utils.ByteInterval{Start: 0, End: protocol.MaxByteCount})
+ return &s
+}
+
+func (s *streamFrameSorter) Push(frame *frames.StreamFrame) error {
+ _, ok := s.queuedFrames[frame.Offset]
+ if ok {
+ return errDuplicateStreamData
+ }
+
+ start := frame.Offset
+ end := frame.Offset + frame.DataLen()
+
+ if start == end {
+ if frame.FinBit {
+ s.queuedFrames[frame.Offset] = frame
+ return nil
+ }
+ return errEmptyStreamData
+ }
+
+ var foundInGap bool
+
+ for gap := s.gaps.Front(); gap != nil; gap = gap.Next() {
+ // the complete frame lies before or after the gap
+ if end <= gap.Value.Start || start > gap.Value.End {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ if start < gap.Value.Start {
+ return qerr.Error(qerr.OverlappingStreamData, "start of gap in stream chunk")
+ }
+
+ if start < gap.Value.End && end > gap.Value.End {
+ return qerr.Error(qerr.OverlappingStreamData, "end of gap in stream chunk")
+ }
+
+ foundInGap = true
+
+ if start == gap.Value.Start {
+ if end == gap.Value.End {
+ s.gaps.Remove(gap)
+ break
+ }
+ if end < gap.Value.End {
+ gap.Value.Start = end
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if end == gap.Value.End {
+ gap.Value.End = start
+ break
+ }
+
+ if end < gap.Value.End {
+ intv := utils.ByteInterval{Start: end, End: gap.Value.End}
+ s.gaps.InsertAfter(intv, gap)
+ gap.Value.End = start
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if !foundInGap {
+ return errDuplicateStreamData
+ }
+
+ if s.gaps.Len() > protocol.MaxStreamFrameSorterGaps {
+ return errTooManyGapsInReceivedStreamData
+ }
+
+ s.queuedFrames[frame.Offset] = frame
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *streamFrameSorter) Pop() *frames.StreamFrame {
+ frame := s.Head()
+ if frame != nil {
+ s.readPosition += frame.DataLen()
+ delete(s.queuedFrames, frame.Offset)
+ }
+ return frame
+}
+
+func (s *streamFrameSorter) Head() *frames.StreamFrame {
+ frame, ok := s.queuedFrames[s.readPosition]
+ if ok {
+ return frame
+ }
+ return nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_framer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_framer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b702c28
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_framer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type streamFramer struct {
+ streamsMap *streamsMap
+
+ flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager
+
+ retransmissionQueue []*frames.StreamFrame
+ blockedFrameQueue []*frames.BlockedFrame
+}
+
+func newStreamFramer(streamsMap *streamsMap, flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager) *streamFramer {
+ return &streamFramer{
+ streamsMap: streamsMap,
+ flowControlManager: flowControlManager,
+ }
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) AddFrameForRetransmission(frame *frames.StreamFrame) {
+ f.retransmissionQueue = append(f.retransmissionQueue, frame)
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) PopStreamFrames(maxLen protocol.ByteCount) []*frames.StreamFrame {
+ fs, currentLen := f.maybePopFramesForRetransmission(maxLen)
+ return append(fs, f.maybePopNormalFrames(maxLen-currentLen)...)
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) PopBlockedFrame() *frames.BlockedFrame {
+ if len(f.blockedFrameQueue) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ frame := f.blockedFrameQueue[0]
+ f.blockedFrameQueue = f.blockedFrameQueue[1:]
+ return frame
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) HasFramesForRetransmission() bool {
+ return len(f.retransmissionQueue) > 0
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) maybePopFramesForRetransmission(maxLen protocol.ByteCount) (res []*frames.StreamFrame, currentLen protocol.ByteCount) {
+ for len(f.retransmissionQueue) > 0 {
+ frame := f.retransmissionQueue[0]
+ frame.DataLenPresent = true
+
+ frameHeaderLen, _ := frame.MinLength(protocol.VersionWhatever) // can never error
+ if currentLen+frameHeaderLen >= maxLen {
+ break
+ }
+
+ currentLen += frameHeaderLen
+
+ splitFrame := maybeSplitOffFrame(frame, maxLen-currentLen)
+ if splitFrame != nil { // StreamFrame was split
+ res = append(res, splitFrame)
+ currentLen += splitFrame.DataLen()
+ break
+ }
+
+ f.retransmissionQueue = f.retransmissionQueue[1:]
+ res = append(res, frame)
+ currentLen += frame.DataLen()
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) maybePopNormalFrames(maxBytes protocol.ByteCount) (res []*frames.StreamFrame) {
+ frame := &frames.StreamFrame{DataLenPresent: true}
+ var currentLen protocol.ByteCount
+
+ fn := func(s *stream) (bool, error) {
+ if s == nil {
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ frame.StreamID = s.streamID
+ // not perfect, but thread-safe since writeOffset is only written when getting data
+ frame.Offset = s.writeOffset
+ frameHeaderBytes, _ := frame.MinLength(protocol.VersionWhatever) // can never error
+ if currentLen+frameHeaderBytes > maxBytes {
+ return false, nil // theoretically, we could find another stream that fits, but this is quite unlikely, so we stop here
+ }
+ maxLen := maxBytes - currentLen - frameHeaderBytes
+
+ var sendWindowSize protocol.ByteCount
+ if s.lenOfDataForWriting() != 0 {
+ sendWindowSize, _ = f.flowControlManager.SendWindowSize(s.streamID)
+ maxLen = utils.MinByteCount(maxLen, sendWindowSize)
+ }
+
+ if maxLen == 0 {
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ data := s.getDataForWriting(maxLen)
+
+ // This is unlikely, but check it nonetheless, the scheduler might have jumped in. Seems to happen in ~20% of cases in the tests.
+ shouldSendFin := s.shouldSendFin()
+ if data == nil && !shouldSendFin {
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ if shouldSendFin {
+ frame.FinBit = true
+ s.sentFin()
+ }
+
+ frame.Data = data
+ f.flowControlManager.AddBytesSent(s.streamID, protocol.ByteCount(len(data)))
+
+ // Finally, check if we are now FC blocked and should queue a BLOCKED frame
+ if f.flowControlManager.RemainingConnectionWindowSize() == 0 {
+ // We are now connection-level FC blocked
+ f.blockedFrameQueue = append(f.blockedFrameQueue, &frames.BlockedFrame{StreamID: 0})
+ } else if sendWindowSize-frame.DataLen() == 0 {
+ // We are now stream-level FC blocked
+ f.blockedFrameQueue = append(f.blockedFrameQueue, &frames.BlockedFrame{StreamID: s.StreamID()})
+ }
+
+ res = append(res, frame)
+ currentLen += frameHeaderBytes + frame.DataLen()
+
+ if currentLen == maxBytes {
+ return false, nil
+ }
+
+ frame = &frames.StreamFrame{DataLenPresent: true}
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ f.streamsMap.RoundRobinIterate(fn)
+
+ return
+}
+
+// maybeSplitOffFrame removes the first n bytes and returns them as a separate frame. If n >= len(frame), nil is returned and nothing is modified.
+func maybeSplitOffFrame(frame *frames.StreamFrame, n protocol.ByteCount) *frames.StreamFrame {
+ if n >= frame.DataLen() {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ defer func() {
+ frame.Data = frame.Data[n:]
+ frame.Offset += n
+ }()
+
+ return &frames.StreamFrame{
+ FinBit: false,
+ StreamID: frame.StreamID,
+ Offset: frame.Offset,
+ Data: frame.Data[:n],
+ DataLenPresent: frame.DataLenPresent,
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/streams_map.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/streams_map.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8b41b86
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/streams_map.go
@@ -0,0 +1,219 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type streamsMap struct {
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+
+ streams map[protocol.StreamID]*stream
+ openStreams []protocol.StreamID
+
+ highestStreamOpenedByClient protocol.StreamID
+ streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect int
+
+ newStream newStreamLambda
+ maxNumStreams int
+
+ roundRobinIndex int
+}
+
+type streamLambda func(*stream) (bool, error)
+type newStreamLambda func(protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error)
+
+var (
+ errMapAccess = errors.New("streamsMap: Error accessing the streams map")
+)
+
+func newStreamsMap(newStream newStreamLambda) *streamsMap {
+ maxNumStreams := utils.Max(int(float32(protocol.MaxIncomingDynamicStreams)*protocol.MaxStreamsMultiplier), int(protocol.MaxIncomingDynamicStreams))
+
+ return &streamsMap{
+ streams: map[protocol.StreamID]*stream{},
+ openStreams: make([]protocol.StreamID, 0, maxNumStreams),
+ newStream: newStream,
+ maxNumStreams: maxNumStreams,
+ }
+}
+
+// GetOrOpenStream either returns an existing stream, a newly opened stream, or nil if a stream with the provided ID is already closed.
+// Newly opened streams should only originate from the client. To open a stream from the server, OpenStream should be used.
+func (m *streamsMap) GetOrOpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ m.mutex.RLock()
+ s, ok := m.streams[id]
+ m.mutex.RUnlock()
+ if ok {
+ return s, nil // s may be nil
+ }
+
+ // ... we don't have an existing stream, try opening a new one
+ m.mutex.Lock()
+ defer m.mutex.Unlock()
+ // We need to check whether another invocation has already created a stream (between RUnlock() and Lock()).
+ s, ok = m.streams[id]
+ if ok {
+ return s, nil
+ }
+ if len(m.openStreams) == m.maxNumStreams {
+ return nil, qerr.TooManyOpenStreams
+ }
+ if id%2 == 0 {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamID, fmt.Sprintf("attempted to open stream %d from client-side", id))
+ }
+ if id+protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta < m.highestStreamOpenedByClient {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamID, fmt.Sprintf("attempted to open stream %d, which is a lot smaller than the highest opened stream, %d", id, m.highestStreamOpenedByClient))
+ }
+
+ s, err := m.newStream(id)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if id > m.highestStreamOpenedByClient {
+ m.highestStreamOpenedByClient = id
+ }
+
+ m.streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect++
+ if m.streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect%protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta == 0 {
+ m.garbageCollectClosedStreams()
+ }
+
+ m.putStream(s)
+ return s, nil
+}
+
+// OpenStream opens a stream from the server's side
+func (m *streamsMap) OpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ panic("OpenStream: not implemented")
+}
+
+func (m *streamsMap) Iterate(fn streamLambda) error {
+ m.mutex.Lock()
+ defer m.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ for _, streamID := range m.openStreams {
+ cont, err := m.iterateFunc(streamID, fn)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if !cont {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// RoundRobinIterate executes the streamLambda for every open stream, until the streamLambda returns false
+// It uses a round-robin-like scheduling to ensure that every stream is considered fairly
+// It prioritizes the crypto- and the header-stream (StreamIDs 1 and 3)
+func (m *streamsMap) RoundRobinIterate(fn streamLambda) error {
+ m.mutex.Lock()
+ defer m.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ numStreams := len(m.openStreams)
+ startIndex := m.roundRobinIndex
+
+ for _, i := range []protocol.StreamID{1, 3} {
+ cont, err := m.iterateFunc(i, fn)
+ if err != nil && err != errMapAccess {
+ return err
+ }
+ if !cont {
+ return nil
+ }
+ }
+
+ for i := 0; i < numStreams; i++ {
+ streamID := m.openStreams[(i+startIndex)%numStreams]
+
+ if streamID == 1 || streamID == 3 {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ cont, err := m.iterateFunc(streamID, fn)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ m.roundRobinIndex = (m.roundRobinIndex + 1) % numStreams
+ if !cont {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (m *streamsMap) iterateFunc(streamID protocol.StreamID, fn streamLambda) (bool, error) {
+ str, ok := m.streams[streamID]
+ if !ok {
+ return true, errMapAccess
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ return false, fmt.Errorf("BUG: Stream %d is closed, but still in openStreams map", streamID)
+ }
+ return fn(str)
+}
+
+func (m *streamsMap) putStream(s *stream) error {
+ id := s.StreamID()
+ if _, ok := m.streams[id]; ok {
+ return fmt.Errorf("a stream with ID %d already exists", id)
+ }
+
+ m.streams[id] = s
+ m.openStreams = append(m.openStreams, id)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Attention: this function must only be called if a mutex has been acquired previously
+func (m *streamsMap) RemoveStream(id protocol.StreamID) error {
+ s, ok := m.streams[id]
+ if !ok || s == nil {
+ return fmt.Errorf("attempted to remove non-existing stream: %d", id)
+ }
+
+ m.streams[id] = nil
+
+ for i, s := range m.openStreams {
+ if s == id {
+ // delete the streamID from the openStreams slice
+ m.openStreams = m.openStreams[:i+copy(m.openStreams[i:], m.openStreams[i+1:])]
+ // adjust round-robin index, if necessary
+ if i < m.roundRobinIndex {
+ m.roundRobinIndex--
+ }
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// NumberOfStreams gets the number of open streams
+func (m *streamsMap) NumberOfStreams() int {
+ m.mutex.RLock()
+ n := len(m.openStreams)
+ m.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return n
+}
+
+// garbageCollectClosedStreams deletes nil values in the streams if they are smaller than protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta than the highest stream opened by the client
+// note that this garbage collection is relatively expensive, since it iterates over the whole streams map. It should not be called every time a stream is openend or closed
+func (m *streamsMap) garbageCollectClosedStreams() {
+ for id, str := range m.streams {
+ if str != nil {
+ continue
+ }
+ if id+protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta <= m.highestStreamOpenedByClient {
+ delete(m.streams, id)
+ }
+ }
+ m.streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect = 0
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/udp_conn.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/udp_conn.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2c1bafe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/udp_conn.go
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+package quic
+
+import "net"
+
+type connection interface {
+ write([]byte) error
+ setCurrentRemoteAddr(interface{})
+ RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr
+}
+
+type udpConn struct {
+ conn *net.UDPConn
+ currentAddr *net.UDPAddr
+}
+
+var _ connection = &udpConn{}
+
+func (c *udpConn) write(p []byte) error {
+ _, err := c.conn.WriteToUDP(p, c.currentAddr)
+ return err
+}
+
+func (c *udpConn) setCurrentRemoteAddr(addr interface{}) {
+ c.currentAddr = addr.(*net.UDPAddr)
+}
+
+func (c *udpConn) RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr {
+ return c.currentAddr
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/_gen.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/_gen.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..154515b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/_gen.go
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+package main
+
+import (
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/linkedlist"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/slice"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/stringer"
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..545fc20
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+// Generated by: main
+// TypeWriter: linkedlist
+// Directive: +gen on ByteInterval
+
+package utils
+
+// List is a modification of http://golang.org/pkg/container/list/
+// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+// ByteIntervalElement is an element of a linked list.
+type ByteIntervalElement struct {
+ // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
+ // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
+ // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
+ // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
+ // element (l.Front()).
+ next, prev *ByteIntervalElement
+
+ // The list to which this element belongs.
+ list *ByteIntervalList
+
+ // The value stored with this element.
+ Value ByteInterval
+}
+
+// Next returns the next list element or nil.
+func (e *ByteIntervalElement) Next() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
+func (e *ByteIntervalElement) Prev() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// ByteIntervalList represents a doubly linked list.
+// The zero value for ByteIntervalList is an empty list ready to use.
+type ByteIntervalList struct {
+ root ByteIntervalElement // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
+ len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
+}
+
+// Init initializes or clears list l.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Init() *ByteIntervalList {
+ l.root.next = &l.root
+ l.root.prev = &l.root
+ l.len = 0
+ return l
+}
+
+// NewByteIntervalList returns an initialized list.
+func NewByteIntervalList() *ByteIntervalList { return new(ByteIntervalList).Init() }
+
+// Len returns the number of elements of list l.
+// The complexity is O(1).
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Len() int { return l.len }
+
+// Front returns the first element of list l or nil.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Front() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.next
+}
+
+// Back returns the last element of list l or nil.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Back() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.prev
+}
+
+// lazyInit lazily initializes a zero ByteIntervalList value.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) lazyInit() {
+ if l.root.next == nil {
+ l.Init()
+ }
+}
+
+// insert inserts e after at, increments l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) insert(e, at *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ n := at.next
+ at.next = e
+ e.prev = at
+ e.next = n
+ n.prev = e
+ e.list = l
+ l.len++
+ return e
+}
+
+// insertValue is a convenience wrapper for insert(&ByteIntervalElement{Value: v}, at).
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) insertValue(v ByteInterval, at *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ return l.insert(&ByteIntervalElement{Value: v}, at)
+}
+
+// remove removes e from its list, decrements l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) remove(e *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ e.prev.next = e.next
+ e.next.prev = e.prev
+ e.next = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.prev = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.list = nil
+ l.len--
+ return e
+}
+
+// Remove removes e from l if e is an element of list l.
+// It returns the element value e.Value.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Remove(e *ByteIntervalElement) ByteInterval {
+ if e.list == l {
+ // if e.list == l, l must have been initialized when e was inserted
+ // in l or l == nil (e is a zero ByteIntervalElement) and l.remove will crash
+ l.remove(e)
+ }
+ return e.Value
+}
+
+// PushFront inserts a new element e with value v at the front of list l and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushFront(v ByteInterval) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, &l.root)
+}
+
+// PushBack inserts a new element e with value v at the back of list l and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushBack(v ByteInterval) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertBefore inserts a new element e with value v immediately before mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) InsertBefore(v ByteInterval, mark *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertAfter inserts a new element e with value v immediately after mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) InsertAfter(v ByteInterval, mark *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark)
+}
+
+// MoveToFront moves element e to the front of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveToFront(e *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.next == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), &l.root)
+}
+
+// MoveToBack moves element e to the back of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveToBack(e *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.prev == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveBefore moves element e to its new position before mark.
+// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveBefore(e, mark *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveAfter moves element e to its new position after mark.
+// If e is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveAfter(e, mark *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark)
+}
+
+// PushBackList inserts a copy of an other list at the back of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushBackList(other *ByteIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Front(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Next() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, l.root.prev)
+ }
+}
+
+// PushFrontList inserts a copy of an other list at the front of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushFrontList(other *ByteIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Back(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Prev() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, &l.root)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/float16.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/float16.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8abdb51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/float16.go
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "io"
+ "math"
+)
+
+// We define an unsigned 16-bit floating point value, inspired by IEEE floats
+// (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half_precision_floating-point_format),
+// with 5-bit exponent (bias 1), 11-bit mantissa (effective 12 with hidden
+// bit) and denormals, but without signs, transfinites or fractions. Wire format
+// 16 bits (little-endian byte order) are split into exponent (high 5) and
+// mantissa (low 11) and decoded as:
+// uint64_t value;
+// if (exponent == 0) value = mantissa;
+// else value = (mantissa | 1 << 11) << (exponent - 1)
+const uFloat16ExponentBits = 5
+const uFloat16MaxExponent = (1 << uFloat16ExponentBits) - 2 // 30
+const uFloat16MantissaBits = 16 - uFloat16ExponentBits // 11
+const uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits = uFloat16MantissaBits + 1 // 12
+const uFloat16MaxValue = ((uint64(1) << uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits) - 1) << uFloat16MaxExponent // 0x3FFC0000000
+
+// ReadUfloat16 reads a float in the QUIC-float16 format and returns its uint64 representation
+func ReadUfloat16(b io.ByteReader) (uint64, error) {
+ val, err := ReadUint16(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+
+ res := uint64(val)
+
+ if res < (1 << uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits) {
+ // Fast path: either the value is denormalized (no hidden bit), or
+ // normalized (hidden bit set, exponent offset by one) with exponent zero.
+ // Zero exponent offset by one sets the bit exactly where the hidden bit is.
+ // So in both cases the value encodes itself.
+ return res, nil
+ }
+
+ exponent := val >> uFloat16MantissaBits // No sign extend on uint!
+ // After the fast pass, the exponent is at least one (offset by one).
+ // Un-offset the exponent.
+ exponent--
+ // Here we need to clear the exponent and set the hidden bit. We have already
+ // decremented the exponent, so when we subtract it, it leaves behind the
+ // hidden bit.
+ res -= uint64(exponent) << uFloat16MantissaBits
+ res <<= exponent
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+// WriteUfloat16 writes a float in the QUIC-float16 format from its uint64 representation
+func WriteUfloat16(b *bytes.Buffer, value uint64) {
+ var result uint16
+ if value < (uint64(1) << uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits) {
+ // Fast path: either the value is denormalized, or has exponent zero.
+ // Both cases are represented by the value itself.
+ result = uint16(value)
+ } else if value >= uFloat16MaxValue {
+ // Value is out of range; clamp it to the maximum representable.
+ result = math.MaxUint16
+ } else {
+ // The highest bit is between position 13 and 42 (zero-based), which
+ // corresponds to exponent 1-30. In the output, mantissa is from 0 to 10,
+ // hidden bit is 11 and exponent is 11 to 15. Shift the highest bit to 11
+ // and count the shifts.
+ exponent := uint16(0)
+ for offset := uint16(16); offset > 0; offset /= 2 {
+ // Right-shift the value until the highest bit is in position 11.
+ // For offset of 16, 8, 4, 2 and 1 (binary search over 1-30),
+ // shift if the bit is at or above 11 + offset.
+ if value >= (uint64(1) << (uFloat16MantissaBits + offset)) {
+ exponent += offset
+ value >>= offset
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Hidden bit (position 11) is set. We should remove it and increment the
+ // exponent. Equivalently, we just add it to the exponent.
+ // This hides the bit.
+ result = (uint16(value) + (exponent << uFloat16MantissaBits))
+ }
+
+ WriteUint16(b, result)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/log.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/log.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..bb0f255
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/log.go
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "os"
+ "sync"
+)
+
+var out io.Writer = os.Stdout
+
+// LogLevel of quic-go
+type LogLevel uint8
+
+const (
+ // LogLevelDebug enables debug logs (e.g. packet contents)
+ LogLevelDebug LogLevel = iota
+ // LogLevelInfo enables info logs (e.g. packets)
+ LogLevelInfo
+ // LogLevelError enables err logs
+ LogLevelError
+ // LogLevelNothing disables
+ LogLevelNothing
+)
+
+var logLevel = LogLevelNothing
+
+var mutex sync.Mutex
+
+// SetLogWriter sets the log writer.
+func SetLogWriter(w io.Writer) {
+ out = w
+}
+
+// SetLogLevel sets the log level
+func SetLogLevel(level LogLevel) {
+ logLevel = level
+}
+
+// Debugf logs something
+func Debugf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
+ if logLevel == LogLevelDebug {
+ mutex.Lock()
+ fmt.Fprintf(out, format+"\n", args...)
+ mutex.Unlock()
+ }
+}
+
+// Infof logs something
+func Infof(format string, args ...interface{}) {
+ if logLevel <= LogLevelInfo {
+ mutex.Lock()
+ fmt.Fprintf(out, format+"\n", args...)
+ mutex.Unlock()
+ }
+}
+
+// Errorf logs something
+func Errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
+ if logLevel <= LogLevelError {
+ mutex.Lock()
+ fmt.Fprintf(out, format+"\n", args...)
+ mutex.Unlock()
+ }
+}
+
+// Debug returns true if the log level is LogLevelDebug
+func Debug() bool {
+ return logLevel == LogLevelDebug
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/minmax.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/minmax.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ec22139
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/minmax.go
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "math"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// InfDuration is a duration of infinite length
+const InfDuration = time.Duration(math.MaxInt64)
+
+// Max returns the maximum of two Ints
+func Max(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// MaxUint32 returns the maximum of two uint32
+func MaxUint32(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a < b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// MaxUint64 returns the maximum of two uint64
+func MaxUint64(a, b uint64) uint64 {
+ if a < b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// Min returns the minimum of two Ints
+func Min(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinUint32 returns the maximum of two uint32
+func MinUint32(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinInt64 returns the minimum of two int64
+func MinInt64(a, b int64) int64 {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MaxInt64 returns the minimum of two int64
+func MaxInt64(a, b int64) int64 {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinByteCount returns the minimum of two ByteCounts
+func MinByteCount(a, b protocol.ByteCount) protocol.ByteCount {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MaxDuration returns the max duration
+func MaxDuration(a, b time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinDuration returns the minimum duration
+func MinDuration(a, b time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ if a > b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// AbsDuration returns the absolute value of a time duration
+func AbsDuration(d time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ if d >= 0 {
+ return d
+ }
+ return -d
+}
+
+// MinTime returns the earlier time
+func MinTime(a, b time.Time) time.Time {
+ if a.After(b) {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// MaxPacketNumber returns the max packet number
+func MaxPacketNumber(a, b protocol.PacketNumber) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinPacketNumber returns the min packet number
+func MinPacketNumber(a, b protocol.PacketNumber) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packet_interval.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packet_interval.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..09800b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packet_interval.go
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+package utils
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// PacketInterval is an interval from one PacketNumber to the other
+// +gen linkedlist
+type PacketInterval struct {
+ Start protocol.PacketNumber
+ End protocol.PacketNumber
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e3431d6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+// Generated by: main
+// TypeWriter: linkedlist
+// Directive: +gen on PacketInterval
+
+package utils
+
+// List is a modification of http://golang.org/pkg/container/list/
+// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+// PacketIntervalElement is an element of a linked list.
+type PacketIntervalElement struct {
+ // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
+ // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
+ // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
+ // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
+ // element (l.Front()).
+ next, prev *PacketIntervalElement
+
+ // The list to which this element belongs.
+ list *PacketIntervalList
+
+ // The value stored with this element.
+ Value PacketInterval
+}
+
+// Next returns the next list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketIntervalElement) Next() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketIntervalElement) Prev() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// PacketIntervalList represents a doubly linked list.
+// The zero value for PacketIntervalList is an empty list ready to use.
+type PacketIntervalList struct {
+ root PacketIntervalElement // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
+ len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
+}
+
+// Init initializes or clears list l.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Init() *PacketIntervalList {
+ l.root.next = &l.root
+ l.root.prev = &l.root
+ l.len = 0
+ return l
+}
+
+// NewPacketIntervalList returns an initialized list.
+func NewPacketIntervalList() *PacketIntervalList { return new(PacketIntervalList).Init() }
+
+// Len returns the number of elements of list l.
+// The complexity is O(1).
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Len() int { return l.len }
+
+// Front returns the first element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Front() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.next
+}
+
+// Back returns the last element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Back() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.prev
+}
+
+// lazyInit lazily initializes a zero PacketIntervalList value.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) lazyInit() {
+ if l.root.next == nil {
+ l.Init()
+ }
+}
+
+// insert inserts e after at, increments l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) insert(e, at *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ n := at.next
+ at.next = e
+ e.prev = at
+ e.next = n
+ n.prev = e
+ e.list = l
+ l.len++
+ return e
+}
+
+// insertValue is a convenience wrapper for insert(&PacketIntervalElement{Value: v}, at).
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) insertValue(v PacketInterval, at *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ return l.insert(&PacketIntervalElement{Value: v}, at)
+}
+
+// remove removes e from its list, decrements l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) remove(e *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ e.prev.next = e.next
+ e.next.prev = e.prev
+ e.next = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.prev = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.list = nil
+ l.len--
+ return e
+}
+
+// Remove removes e from l if e is an element of list l.
+// It returns the element value e.Value.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Remove(e *PacketIntervalElement) PacketInterval {
+ if e.list == l {
+ // if e.list == l, l must have been initialized when e was inserted
+ // in l or l == nil (e is a zero PacketIntervalElement) and l.remove will crash
+ l.remove(e)
+ }
+ return e.Value
+}
+
+// PushFront inserts a new element e with value v at the front of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushFront(v PacketInterval) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, &l.root)
+}
+
+// PushBack inserts a new element e with value v at the back of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushBack(v PacketInterval) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertBefore inserts a new element e with value v immediately before mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) InsertBefore(v PacketInterval, mark *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertAfter inserts a new element e with value v immediately after mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) InsertAfter(v PacketInterval, mark *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark)
+}
+
+// MoveToFront moves element e to the front of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveToFront(e *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.next == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), &l.root)
+}
+
+// MoveToBack moves element e to the back of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveToBack(e *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.prev == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveBefore moves element e to its new position before mark.
+// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveBefore(e, mark *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveAfter moves element e to its new position after mark.
+// If e is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveAfter(e, mark *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark)
+}
+
+// PushBackList inserts a copy of an other list at the back of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushBackList(other *PacketIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Front(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Next() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, l.root.prev)
+ }
+}
+
+// PushFrontList inserts a copy of an other list at the front of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushFrontList(other *PacketIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Back(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Prev() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, &l.root)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/streamframe_interval.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/streamframe_interval.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c918b62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/streamframe_interval.go
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+package utils
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// ByteInterval is an interval from one ByteCount to the other
+// +gen linkedlist
+type ByteInterval struct {
+ Start protocol.ByteCount
+ End protocol.ByteCount
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/utils.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/utils.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cf25679
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/utils.go
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// Stream is the interface for QUIC streams
+type Stream interface {
+ io.Reader
+ io.Writer
+ io.Closer
+ StreamID() protocol.StreamID
+ CloseRemote(offset protocol.ByteCount)
+}
+
+// ReadUintN reads N bytes
+func ReadUintN(b io.ByteReader, length uint8) (uint64, error) {
+ var res uint64
+ for i := uint8(0); i < length; i++ {
+ bt, err := b.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ res ^= uint64(bt) << (i * 8)
+ }
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+// ReadUint64 reads a uint64
+func ReadUint64(b io.ByteReader) (uint64, error) {
+ var b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7, b8 uint8
+ var err error
+ if b1, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b2, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b3, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b4, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b5, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b6, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b7, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b8, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return uint64(b1) + uint64(b2)<<8 + uint64(b3)<<16 + uint64(b4)<<24 + uint64(b5)<<32 + uint64(b6)<<40 + uint64(b7)<<48 + uint64(b8)<<56, nil
+}
+
+// ReadUint32 reads a uint32
+func ReadUint32(b io.ByteReader) (uint32, error) {
+ var b1, b2, b3, b4 uint8
+ var err error
+ if b1, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b2, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b3, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b4, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return uint32(b1) + uint32(b2)<<8 + uint32(b3)<<16 + uint32(b4)<<24, nil
+}
+
+// ReadUint16 reads a uint16
+func ReadUint16(b io.ByteReader) (uint16, error) {
+ var b1, b2 uint8
+ var err error
+ if b1, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b2, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return uint16(b1) + uint16(b2)<<8, nil
+}
+
+// WriteUint64 writes a uint64
+func WriteUint64(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24),
+ uint8(i >> 32), uint8(i >> 40), uint8(i >> 48), uint8(i >> 56),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint56 writes 56 bit of a uint64
+func WriteUint56(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24),
+ uint8(i >> 32), uint8(i >> 40), uint8(i >> 48),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint48 writes 48 bit of a uint64
+func WriteUint48(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24),
+ uint8(i >> 32), uint8(i >> 40),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint40 writes 40 bit of a uint64
+func WriteUint40(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16),
+ uint8(i >> 24), uint8(i >> 32),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint32 writes a uint32
+func WriteUint32(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint32) {
+ b.Write([]byte{uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24)})
+}
+
+// WriteUint24 writes 24 bit of a uint32
+func WriteUint24(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint32) {
+ b.Write([]byte{uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16)})
+}
+
+// WriteUint16 writes a uint16
+func WriteUint16(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint16) {
+ b.Write([]byte{uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8)})
+}
+
+// Uint32Slice attaches the methods of sort.Interface to []uint32, sorting in increasing order.
+type Uint32Slice []uint32
+
+func (s Uint32Slice) Len() int { return len(s) }
+func (s Uint32Slice) Less(i, j int) bool { return s[i] < s[j] }
+func (s Uint32Slice) Swap(i, j int) { s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] }
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..835ba3e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+Copyright (c) 2015, Dave Cheney
+
+[](https://godoc.org/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go)
+[](https://travis-ci.org/lucas-clemente/quic-go)
+[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/lucas-clemente/quic-go/branch/master)
+[](https://codecov.io/gh/lucas-clemente/quic-go/)
+
+quic-go is an implementation of the [QUIC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QUIC) protocol in Go. While we're not far from being feature complete, there's still work to do regarding performance and security. At the moment, we do not recommend use in production systems. We appreciate any feedback :)
+
+## Roadmap
+
+Done:
+
+- Basic protocol with support for QUIC version 34-36
+- HTTP/2 support
+- Crypto (RSA / ECDSA certificates, Curve25519 for key exchange, AES-GCM or Chacha20-Poly1305 as stream cipher)
+- Loss detection and retransmission (currently fast retransmission & RTO)
+- Flow Control
+- Congestion control using cubic
+
+Major TODOs:
+
+- Security, especially DOS protections
+- Performance
+- Better packet loss detection
+- Connection migration
+- QUIC client
+
+## Guides
+
+Installing deps:
+
+ go get -t
+
+Running tests:
+
+ go test ./...
+
+Running the example server:
+
+ go run example/main.go -www /var/www/
+
+Using the `quic_client` from chromium:
+
+ quic_client --quic-version=32 --host=127.0.0.1 --port=6121 --v=1 https://quic.clemente.io
+
+Using Chrome:
+
+ /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome --user-data-dir=/tmp/chrome --no-proxy-server --enable-quic --origin-to-force-quic-on=quic.clemente.io:443 --host-resolver-rules='MAP quic.clemente.io:443 127.0.0.1:6121' https://quic.clemente.io
+
+## Usage
+
+See the [example server](example/main.go) or try out [Caddy](https://github.com/mholt/caddy) (from version 0.9, [instructions here](https://github.com/mholt/caddy/wiki/QUIC)). Starting a QUIC server is very similar to the standard lib http in go:
+
+```go
+http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.Dir(wwwDir)))
+h2quic.ListenAndServeQUIC("localhost:4242", "/path/to/cert/chain.pem", "/path/to/privkey.pem", nil)
+```
+
+## Building on Windows
+
+Due to the low Windows timer resolution (see [StackOverflow question](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/37706834/high-resolution-timers-millisecond-precision-in-go-on-windows)) available with Go 1.6.x, some optimizations might not work when compiled with this version of the compiler. Please use Go 1.7 on Windows.
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/_gen.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/_gen.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..154515b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/_gen.go
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+package main
+
+import (
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/linkedlist"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/slice"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/stringer"
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/interfaces.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/interfaces.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ee7ac59
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/interfaces.go
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// SentPacketHandler handles ACKs received for outgoing packets
+type SentPacketHandler interface {
+ SentPacket(packet *Packet) error
+ ReceivedAck(ackFrame *frames.AckFrame, withPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, recvTime time.Time) error
+
+ GetStopWaitingFrame(force bool) *frames.StopWaitingFrame
+
+ MaybeQueueRTOs()
+ DequeuePacketForRetransmission() (packet *Packet)
+
+ BytesInFlight() protocol.ByteCount
+ GetLeastUnacked() protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ SendingAllowed() bool
+ CheckForError() error
+
+ TimeOfFirstRTO() time.Time
+}
+
+// ReceivedPacketHandler handles ACKs needed to send for incoming packets
+type ReceivedPacketHandler interface {
+ ReceivedPacket(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) error
+ ReceivedStopWaiting(*frames.StopWaitingFrame) error
+
+ GetAckFrame(dequeue bool) (*frames.AckFrame, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6fe567c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet.go
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A Packet is a packet
+// +gen linkedlist
+type Packet struct {
+ PacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ Frames []frames.Frame
+ Length protocol.ByteCount
+
+ MissingReports uint8
+
+ SendTime time.Time
+}
+
+// GetStreamFramesForRetransmission gets all the streamframes for retransmission
+func (p *Packet) GetStreamFramesForRetransmission() []*frames.StreamFrame {
+ var streamFrames []*frames.StreamFrame
+ for _, frame := range p.Frames {
+ if streamFrame, isStreamFrame := frame.(*frames.StreamFrame); isStreamFrame {
+ streamFrames = append(streamFrames, streamFrame)
+ }
+ }
+ return streamFrames
+}
+
+// GetControlFramesForRetransmission gets all the control frames for retransmission
+func (p *Packet) GetControlFramesForRetransmission() []frames.Frame {
+ var controlFrames []frames.Frame
+ for _, frame := range p.Frames {
+ // omit ACKs
+ if _, isStreamFrame := frame.(*frames.StreamFrame); isStreamFrame {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ _, isAck := frame.(*frames.AckFrame)
+ _, isStopWaiting := frame.(*frames.StopWaitingFrame)
+ if !isAck && !isStopWaiting {
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, frame)
+ }
+ }
+ return controlFrames
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a827b21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+// Generated by: main
+// TypeWriter: linkedlist
+// Directive: +gen on Packet
+
+package ackhandler
+
+// List is a modification of http://golang.org/pkg/container/list/
+// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+// PacketElement is an element of a linked list.
+type PacketElement struct {
+ // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
+ // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
+ // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
+ // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
+ // element (l.Front()).
+ next, prev *PacketElement
+
+ // The list to which this element belongs.
+ list *PacketList
+
+ // The value stored with this element.
+ Value Packet
+}
+
+// Next returns the next list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketElement) Next() *PacketElement {
+ if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketElement) Prev() *PacketElement {
+ if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// PacketList represents a doubly linked list.
+// The zero value for PacketList is an empty list ready to use.
+type PacketList struct {
+ root PacketElement // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
+ len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
+}
+
+// Init initializes or clears list l.
+func (l *PacketList) Init() *PacketList {
+ l.root.next = &l.root
+ l.root.prev = &l.root
+ l.len = 0
+ return l
+}
+
+// NewPacketList returns an initialized list.
+func NewPacketList() *PacketList { return new(PacketList).Init() }
+
+// Len returns the number of elements of list l.
+// The complexity is O(1).
+func (l *PacketList) Len() int { return l.len }
+
+// Front returns the first element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketList) Front() *PacketElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.next
+}
+
+// Back returns the last element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketList) Back() *PacketElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.prev
+}
+
+// lazyInit lazily initializes a zero PacketList value.
+func (l *PacketList) lazyInit() {
+ if l.root.next == nil {
+ l.Init()
+ }
+}
+
+// insert inserts e after at, increments l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) insert(e, at *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ n := at.next
+ at.next = e
+ e.prev = at
+ e.next = n
+ n.prev = e
+ e.list = l
+ l.len++
+ return e
+}
+
+// insertValue is a convenience wrapper for insert(&PacketElement{Value: v}, at).
+func (l *PacketList) insertValue(v Packet, at *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ return l.insert(&PacketElement{Value: v}, at)
+}
+
+// remove removes e from its list, decrements l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) remove(e *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ e.prev.next = e.next
+ e.next.prev = e.prev
+ e.next = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.prev = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.list = nil
+ l.len--
+ return e
+}
+
+// Remove removes e from l if e is an element of list l.
+// It returns the element value e.Value.
+func (l *PacketList) Remove(e *PacketElement) Packet {
+ if e.list == l {
+ // if e.list == l, l must have been initialized when e was inserted
+ // in l or l == nil (e is a zero PacketElement) and l.remove will crash
+ l.remove(e)
+ }
+ return e.Value
+}
+
+// PushFront inserts a new element e with value v at the front of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) PushFront(v Packet) *PacketElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, &l.root)
+}
+
+// PushBack inserts a new element e with value v at the back of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketList) PushBack(v Packet) *PacketElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertBefore inserts a new element e with value v immediately before mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) InsertBefore(v Packet, mark *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertAfter inserts a new element e with value v immediately after mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) InsertAfter(v Packet, mark *PacketElement) *PacketElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark)
+}
+
+// MoveToFront moves element e to the front of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveToFront(e *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.next == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), &l.root)
+}
+
+// MoveToBack moves element e to the back of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveToBack(e *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.prev == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveBefore moves element e to its new position before mark.
+// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveBefore(e, mark *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveAfter moves element e to its new position after mark.
+// If e is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketList) MoveAfter(e, mark *PacketElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark)
+}
+
+// PushBackList inserts a copy of an other list at the back of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketList) PushBackList(other *PacketList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Front(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Next() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, l.root.prev)
+ }
+}
+
+// PushFrontList inserts a copy of an other list at the front of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketList) PushFrontList(other *PacketList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Back(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Prev() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, &l.root)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_handler.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_handler.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dcc1b30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_handler.go
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+)
+
+var (
+ // ErrDuplicatePacket occurres when a duplicate packet is received
+ ErrDuplicatePacket = errors.New("ReceivedPacketHandler: Duplicate Packet")
+ // ErrMapAccess occurs when a NACK contains invalid NACK ranges
+ ErrMapAccess = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, "Packet does not exist in PacketHistory")
+ // ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting occurs when a packet arrives with a packet number smaller than the largest LeastUnacked of a StopWaitingFrame. If this error occurs, the packet should be ignored
+ ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting = errors.New("ReceivedPacketHandler: Packet number smaller than highest StopWaiting")
+)
+
+var (
+ errInvalidPacketNumber = errors.New("ReceivedPacketHandler: Invalid packet number")
+ errTooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets = qerr.Error(qerr.TooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets, "")
+)
+
+type receivedPacketHandler struct {
+ largestInOrderObserved protocol.PacketNumber
+ largestObserved protocol.PacketNumber
+ ignorePacketsBelow protocol.PacketNumber
+ currentAckFrame *frames.AckFrame
+ stateChanged bool // has an ACK for this state already been sent? Will be set to false every time a new packet arrives, and to false every time an ACK is sent
+
+ packetHistory *receivedPacketHistory
+
+ receivedTimes map[protocol.PacketNumber]time.Time
+ lowestInReceivedTimes protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+// NewReceivedPacketHandler creates a new receivedPacketHandler
+func NewReceivedPacketHandler() ReceivedPacketHandler {
+ return &receivedPacketHandler{
+ receivedTimes: make(map[protocol.PacketNumber]time.Time),
+ packetHistory: newReceivedPacketHistory(),
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) ReceivedPacket(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) error {
+ if packetNumber == 0 {
+ return errInvalidPacketNumber
+ }
+
+ // if the packet number is smaller than the largest LeastUnacked value of a StopWaiting we received, we cannot detect if this packet has a duplicate number
+ // the packet has to be ignored anyway
+ if packetNumber <= h.ignorePacketsBelow {
+ return ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting
+ }
+
+ _, ok := h.receivedTimes[packetNumber]
+ if packetNumber <= h.largestInOrderObserved || ok {
+ return ErrDuplicatePacket
+ }
+
+ h.packetHistory.ReceivedPacket(packetNumber)
+
+ h.stateChanged = true
+ h.currentAckFrame = nil
+
+ if packetNumber > h.largestObserved {
+ h.largestObserved = packetNumber
+ }
+
+ if packetNumber == h.largestInOrderObserved+1 {
+ h.largestInOrderObserved = packetNumber
+ }
+
+ h.receivedTimes[packetNumber] = time.Now()
+
+ if protocol.PacketNumber(len(h.receivedTimes)) > protocol.MaxTrackedReceivedPackets {
+ return errTooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) ReceivedStopWaiting(f *frames.StopWaitingFrame) error {
+ // ignore if StopWaiting is unneeded, because we already received a StopWaiting with a higher LeastUnacked
+ if h.ignorePacketsBelow >= f.LeastUnacked {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ h.ignorePacketsBelow = f.LeastUnacked - 1
+ h.garbageCollectReceivedTimes()
+
+ // the LeastUnacked is the smallest packet number of any packet for which the sender is still awaiting an ack. So the largestInOrderObserved is one less than that
+ if f.LeastUnacked > h.largestInOrderObserved {
+ h.largestInOrderObserved = f.LeastUnacked - 1
+ }
+
+ h.packetHistory.DeleteBelow(f.LeastUnacked)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) GetAckFrame(dequeue bool) (*frames.AckFrame, error) {
+ if !h.stateChanged {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+
+ if dequeue {
+ h.stateChanged = false
+ }
+
+ if h.currentAckFrame != nil {
+ return h.currentAckFrame, nil
+ }
+
+ packetReceivedTime, ok := h.receivedTimes[h.largestObserved]
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, ErrMapAccess
+ }
+
+ ackRanges := h.packetHistory.GetAckRanges()
+ h.currentAckFrame = &frames.AckFrame{
+ LargestAcked: h.largestObserved,
+ LowestAcked: ackRanges[len(ackRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber,
+ PacketReceivedTime: packetReceivedTime,
+ }
+
+ if len(ackRanges) > 1 {
+ h.currentAckFrame.AckRanges = ackRanges
+ }
+
+ return h.currentAckFrame, nil
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHandler) garbageCollectReceivedTimes() {
+ for i := h.lowestInReceivedTimes; i <= h.ignorePacketsBelow; i++ {
+ delete(h.receivedTimes, i)
+ }
+ if h.ignorePacketsBelow > h.lowestInReceivedTimes {
+ h.lowestInReceivedTimes = h.ignorePacketsBelow + 1
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_history.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_history.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..14bb08f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/received_packet_history.go
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type receivedPacketHistory struct {
+ ranges *utils.PacketIntervalList
+
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+}
+
+// newReceivedPacketHistory creates a new received packet history
+func newReceivedPacketHistory() *receivedPacketHistory {
+ return &receivedPacketHistory{
+ ranges: utils.NewPacketIntervalList(),
+ }
+}
+
+// ReceivedPacket registers a packet with PacketNumber p and updates the ranges
+func (h *receivedPacketHistory) ReceivedPacket(p protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ if h.ranges.Len() == 0 {
+ h.ranges.PushBack(utils.PacketInterval{Start: p, End: p})
+ return
+ }
+
+ for el := h.ranges.Back(); el != nil; el = el.Prev() {
+ // p already included in an existing range. Nothing to do here
+ if p >= el.Value.Start && p <= el.Value.End {
+ return
+ }
+
+ var rangeExtended bool
+ if el.Value.End == p-1 { // extend a range at the end
+ rangeExtended = true
+ el.Value.End = p
+ } else if el.Value.Start == p+1 { // extend a range at the beginning
+ rangeExtended = true
+ el.Value.Start = p
+ }
+
+ // if a range was extended (either at the beginning or at the end, maybe it is possible to merge two ranges into one)
+ if rangeExtended {
+ prev := el.Prev()
+ if prev != nil && prev.Value.End+1 == el.Value.Start { // merge two ranges
+ prev.Value.End = el.Value.End
+ h.ranges.Remove(el)
+ return
+ }
+ return // if the two ranges were not merge, we're done here
+ }
+
+ // create a new range at the end
+ if p > el.Value.End {
+ h.ranges.InsertAfter(utils.PacketInterval{Start: p, End: p}, el)
+ return
+ }
+ }
+
+ // create a new range at the beginning
+ h.ranges.InsertBefore(utils.PacketInterval{Start: p, End: p}, h.ranges.Front())
+}
+
+func (h *receivedPacketHistory) DeleteBelow(leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ nextEl := h.ranges.Front()
+ for el := h.ranges.Front(); nextEl != nil; el = nextEl {
+ nextEl = el.Next()
+
+ if leastUnacked > el.Value.Start && leastUnacked <= el.Value.End {
+ el.Value.Start = leastUnacked
+ }
+ if el.Value.End < leastUnacked { // delete a whole range
+ h.ranges.Remove(el)
+ } else {
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// GetAckRanges gets a slice of all AckRanges that can be used in an AckFrame
+func (h *receivedPacketHistory) GetAckRanges() []frames.AckRange {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if h.ranges.Len() == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ var ackRanges []frames.AckRange
+
+ for el := h.ranges.Back(); el != nil; el = el.Prev() {
+ ackRanges = append(ackRanges, frames.AckRange{FirstPacketNumber: el.Value.Start, LastPacketNumber: el.Value.End})
+ }
+
+ return ackRanges
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/sent_packet_handler.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/sent_packet_handler.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..531a99a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/sent_packet_handler.go
@@ -0,0 +1,350 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ // ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck occurs when a duplicate or an out-of-order ACK is received
+ ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck = errors.New("SentPacketHandler: Duplicate or out-of-order ACK")
+ // ErrTooManyTrackedSentPackets occurs when the sentPacketHandler has to keep track of too many packets
+ ErrTooManyTrackedSentPackets = errors.New("Too many outstanding non-acked and non-retransmitted packets")
+ // ErrAckForSkippedPacket occurs when the client sent an ACK for a packet number that we intentionally skipped
+ ErrAckForSkippedPacket = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, "Received an ACK for a skipped packet number")
+ errAckForUnsentPacket = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, "Received ACK for an unsent package")
+)
+
+var errPacketNumberNotIncreasing = errors.New("Already sent a packet with a higher packet number.")
+
+type sentPacketHandler struct {
+ lastSentPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ lastSentPacketTime time.Time
+ skippedPackets []protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ LargestAcked protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ largestReceivedPacketWithAck protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ packetHistory *PacketList
+ stopWaitingManager stopWaitingManager
+
+ retransmissionQueue []*Packet
+
+ bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount
+
+ rttStats *congestion.RTTStats
+ congestion congestion.SendAlgorithm
+
+ consecutiveRTOCount uint32
+}
+
+// NewSentPacketHandler creates a new sentPacketHandler
+func NewSentPacketHandler() SentPacketHandler {
+ rttStats := &congestion.RTTStats{}
+
+ congestion := congestion.NewCubicSender(
+ congestion.DefaultClock{},
+ rttStats,
+ false, /* don't use reno since chromium doesn't (why?) */
+ protocol.InitialCongestionWindow,
+ protocol.DefaultMaxCongestionWindow,
+ )
+
+ return &sentPacketHandler{
+ packetHistory: NewPacketList(),
+ stopWaitingManager: stopWaitingManager{},
+ rttStats: rttStats,
+ congestion: congestion,
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) ackPacket(packetElement *PacketElement) {
+ packet := &packetElement.Value
+ h.bytesInFlight -= packet.Length
+ h.packetHistory.Remove(packetElement)
+}
+
+// nackPacket NACKs a packet
+// it returns true if a FastRetransmissions was triggered
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) nackPacket(packetElement *PacketElement) bool {
+ packet := &packetElement.Value
+
+ packet.MissingReports++
+
+ if packet.MissingReports > protocol.RetransmissionThreshold {
+ utils.Debugf("\tQueueing packet 0x%x for retransmission (fast)", packet.PacketNumber)
+ h.queuePacketForRetransmission(packetElement)
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+// does NOT set packet.Retransmitted. This variable is not needed anymore
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) queuePacketForRetransmission(packetElement *PacketElement) {
+ packet := &packetElement.Value
+ h.bytesInFlight -= packet.Length
+ h.retransmissionQueue = append(h.retransmissionQueue, packet)
+
+ h.packetHistory.Remove(packetElement)
+
+ // strictly speaking, this is only necessary for RTO retransmissions
+ // this is because FastRetransmissions are triggered by missing ranges in ACKs, and then the LargestAcked will already be higher than the packet number of the retransmitted packet
+ h.stopWaitingManager.QueuedRetransmissionForPacketNumber(packet.PacketNumber)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) largestInOrderAcked() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if f := h.packetHistory.Front(); f != nil {
+ return f.Value.PacketNumber - 1
+ }
+ return h.LargestAcked
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) SentPacket(packet *Packet) error {
+ if packet.PacketNumber <= h.lastSentPacketNumber {
+ return errPacketNumberNotIncreasing
+ }
+
+ for p := h.lastSentPacketNumber + 1; p < packet.PacketNumber; p++ {
+ h.skippedPackets = append(h.skippedPackets, p)
+
+ if len(h.skippedPackets) > protocol.MaxTrackedSkippedPackets {
+ h.skippedPackets = h.skippedPackets[1:]
+ }
+ }
+
+ now := time.Now()
+ h.lastSentPacketTime = now
+ packet.SendTime = now
+ if packet.Length == 0 {
+ return errors.New("SentPacketHandler: packet cannot be empty")
+ }
+ h.bytesInFlight += packet.Length
+
+ h.lastSentPacketNumber = packet.PacketNumber
+ h.packetHistory.PushBack(*packet)
+
+ h.congestion.OnPacketSent(
+ now,
+ h.BytesInFlight(),
+ packet.PacketNumber,
+ packet.Length,
+ true, /* TODO: is retransmittable */
+ )
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) ReceivedAck(ackFrame *frames.AckFrame, withPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, rcvTime time.Time) error {
+ if ackFrame.LargestAcked > h.lastSentPacketNumber {
+ return errAckForUnsentPacket
+ }
+
+ // duplicate or out-of-order ACK
+ if withPacketNumber <= h.largestReceivedPacketWithAck {
+ return ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck
+ }
+
+ h.largestReceivedPacketWithAck = withPacketNumber
+
+ // ignore repeated ACK (ACKs that don't have a higher LargestAcked than the last ACK)
+ if ackFrame.LargestAcked <= h.largestInOrderAcked() {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // check if it acks any packets that were skipped
+ for _, p := range h.skippedPackets {
+ if ackFrame.AcksPacket(p) {
+ return ErrAckForSkippedPacket
+ }
+ }
+
+ h.LargestAcked = ackFrame.LargestAcked
+
+ var ackedPackets congestion.PacketVector
+ var lostPackets congestion.PacketVector
+ ackRangeIndex := 0
+ rttUpdated := false
+
+ var el, elNext *PacketElement
+ for el = h.packetHistory.Front(); el != nil; el = elNext {
+ // determine the next list element right at the beginning, because el.Next() is not avaible anymore, when the list element is deleted (i.e. when the packet is ACKed)
+ elNext = el.Next()
+ packet := el.Value
+ packetNumber := packet.PacketNumber
+
+ // NACK packets below the LowestAcked
+ if packetNumber < ackFrame.LowestAcked {
+ retransmitted := h.nackPacket(el)
+ if retransmitted {
+ lostPackets = append(lostPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ }
+ continue
+ }
+
+ // Update the RTT
+ if packetNumber == h.LargestAcked {
+ rttUpdated = true
+ timeDelta := rcvTime.Sub(packet.SendTime)
+ h.rttStats.UpdateRTT(timeDelta, ackFrame.DelayTime, rcvTime)
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Debugf("\tEstimated RTT: %dms", h.rttStats.SmoothedRTT()/time.Millisecond)
+ }
+ }
+
+ if packetNumber > ackFrame.LargestAcked {
+ break
+ }
+
+ if ackFrame.HasMissingRanges() {
+ ackRange := ackFrame.AckRanges[len(ackFrame.AckRanges)-1-ackRangeIndex]
+
+ for packetNumber > ackRange.LastPacketNumber && ackRangeIndex < len(ackFrame.AckRanges)-1 {
+ ackRangeIndex++
+ ackRange = ackFrame.AckRanges[len(ackFrame.AckRanges)-1-ackRangeIndex]
+ }
+
+ if packetNumber >= ackRange.FirstPacketNumber { // packet i contained in ACK range
+ if packetNumber > ackRange.LastPacketNumber {
+ return fmt.Errorf("BUG: ackhandler would have acked wrong packet 0x%x, while evaluating range 0x%x -> 0x%x", packetNumber, ackRange.FirstPacketNumber, ackRange.LastPacketNumber)
+ }
+ h.ackPacket(el)
+ ackedPackets = append(ackedPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ } else {
+ retransmitted := h.nackPacket(el)
+ if retransmitted {
+ lostPackets = append(lostPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ h.ackPacket(el)
+ ackedPackets = append(ackedPackets, congestion.PacketInfo{Number: packetNumber, Length: packet.Length})
+ }
+ }
+
+ if rttUpdated {
+ // Reset counter if a new packet was acked
+ h.consecutiveRTOCount = 0
+ }
+
+ h.garbageCollectSkippedPackets()
+
+ h.stopWaitingManager.ReceivedAck(ackFrame)
+
+ h.congestion.OnCongestionEvent(
+ rttUpdated,
+ h.BytesInFlight(),
+ ackedPackets,
+ lostPackets,
+ )
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) DequeuePacketForRetransmission() *Packet {
+ if len(h.retransmissionQueue) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if len(h.retransmissionQueue) > 0 {
+ queueLen := len(h.retransmissionQueue)
+ // packets are usually NACKed in descending order. So use the slice as a stack
+ packet := h.retransmissionQueue[queueLen-1]
+ h.retransmissionQueue = h.retransmissionQueue[:queueLen-1]
+ return packet
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) BytesInFlight() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return h.bytesInFlight
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) GetLeastUnacked() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ return h.largestInOrderAcked() + 1
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) GetStopWaitingFrame(force bool) *frames.StopWaitingFrame {
+ return h.stopWaitingManager.GetStopWaitingFrame(force)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) SendingAllowed() bool {
+ congestionLimited := h.BytesInFlight() > h.congestion.GetCongestionWindow()
+ maxTrackedLimited := protocol.PacketNumber(len(h.retransmissionQueue)+h.packetHistory.Len()) >= protocol.MaxTrackedSentPackets
+ return !(congestionLimited || maxTrackedLimited)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) CheckForError() error {
+ length := len(h.retransmissionQueue) + h.packetHistory.Len()
+ if protocol.PacketNumber(length) > protocol.MaxTrackedSentPackets {
+ return ErrTooManyTrackedSentPackets
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) MaybeQueueRTOs() {
+ if time.Now().Before(h.TimeOfFirstRTO()) {
+ return
+ }
+
+ // Always queue the two oldest packets
+ if h.packetHistory.Front() != nil {
+ h.queueRTO(h.packetHistory.Front())
+ }
+ if h.packetHistory.Front() != nil {
+ h.queueRTO(h.packetHistory.Front())
+ }
+
+ // Reset the RTO timer here, since it's not clear that this packet contained any retransmittable frames
+ h.lastSentPacketTime = time.Now()
+ h.consecutiveRTOCount++
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) queueRTO(el *PacketElement) {
+ packet := &el.Value
+ packetsLost := congestion.PacketVector{congestion.PacketInfo{
+ Number: packet.PacketNumber,
+ Length: packet.Length,
+ }}
+ h.congestion.OnCongestionEvent(false, h.BytesInFlight(), nil, packetsLost)
+ h.congestion.OnRetransmissionTimeout(true)
+ utils.Debugf("\tQueueing packet 0x%x for retransmission (RTO)", packet.PacketNumber)
+ h.queuePacketForRetransmission(el)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) getRTO() time.Duration {
+ rto := h.congestion.RetransmissionDelay()
+ if rto == 0 {
+ rto = protocol.DefaultRetransmissionTime
+ }
+ rto = utils.MaxDuration(rto, protocol.MinRetransmissionTime)
+ // Exponential backoff
+ rto *= 1 << h.consecutiveRTOCount
+ return utils.MinDuration(rto, protocol.MaxRetransmissionTime)
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) TimeOfFirstRTO() time.Time {
+ if h.lastSentPacketTime.IsZero() {
+ return time.Time{}
+ }
+ return h.lastSentPacketTime.Add(h.getRTO())
+}
+
+func (h *sentPacketHandler) garbageCollectSkippedPackets() {
+ lioa := h.largestInOrderAcked()
+ deleteIndex := 0
+ for i, p := range h.skippedPackets {
+ if p <= lioa {
+ deleteIndex = i + 1
+ }
+ }
+ h.skippedPackets = h.skippedPackets[deleteIndex:]
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/stop_waiting_manager.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/stop_waiting_manager.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dfd79ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler/stop_waiting_manager.go
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+package ackhandler
+
+import (
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// This stopWaitingManager is not supposed to satisfy the StopWaitingManager interface, which is a remnant of the legacy AckHandler, and should be remove once we drop support for QUIC 33
+type stopWaitingManager struct {
+ largestLeastUnackedSent protocol.PacketNumber
+ nextLeastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ lastStopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame
+}
+
+func (s *stopWaitingManager) GetStopWaitingFrame(force bool) *frames.StopWaitingFrame {
+ if s.nextLeastUnacked <= s.largestLeastUnackedSent {
+ if force {
+ return s.lastStopWaitingFrame
+ }
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ s.largestLeastUnackedSent = s.nextLeastUnacked
+ swf := &frames.StopWaitingFrame{
+ LeastUnacked: s.nextLeastUnacked,
+ }
+ s.lastStopWaitingFrame = swf
+ return swf
+}
+
+func (s *stopWaitingManager) ReceivedAck(ack *frames.AckFrame) {
+ if ack.LargestAcked >= s.nextLeastUnacked {
+ s.nextLeastUnacked = ack.LargestAcked + 1
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *stopWaitingManager) QueuedRetransmissionForPacketNumber(p protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ if p >= s.nextLeastUnacked {
+ s.nextLeastUnacked = p + 1
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/appveyor.yml b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/appveyor.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..837facc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/appveyor.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+version: "{build}"
+
+os: Windows Server 2012 R2
+
+environment:
+ GOPATH: c:\gopath
+ CGO_ENABLED: 0
+ matrix:
+ - GOARCH: 386
+ - GOARCH: amd64
+
+clone_folder: c:\gopath\src\github.com\lucas-clemente\quic-go
+
+install:
+ - rmdir c:\go /s /q
+ - appveyor DownloadFile https://storage.googleapis.com/golang/go1.7.1.windows-amd64.zip
+ - 7z x go1.7.1.windows-amd64.zip -y -oC:\ > NUL
+ - set PATH=%PATH%;%GOPATH%\bin\windows_%GOARCH%;%GOPATH%\bin
+ - echo %PATH%
+ - echo %GOPATH%
+ - git submodule update --init --recursive
+ - go get github.com/onsi/ginkgo/ginkgo
+ - go get github.com/onsi/gomega
+ - go version
+ - go env
+ - go get -v -t ./...
+
+build_script:
+ - rm -r integrationtests
+ - ginkgo -r --randomizeAllSpecs --randomizeSuites --trace --progress
+
+test: off
+
+deploy: off
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/buffer_pool.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/buffer_pool.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..bb4feb3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/buffer_pool.go
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+var bufferPool sync.Pool
+
+func getPacketBuffer() []byte {
+ return bufferPool.Get().([]byte)
+}
+
+func putPacketBuffer(buf []byte) {
+ if cap(buf) != int(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ panic("putPacketBuffer called with packet of wrong size!")
+ }
+ bufferPool.Put(buf[:0])
+}
+
+func init() {
+ bufferPool.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, 0, protocol.MaxPacketSize)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/codecov.yml b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/codecov.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4e4e039
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/codecov.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+coverage:
+ round: nearest
+ ignore:
+ - ackhandler/packet_linkedlist.go
+ - utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go
+ - utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go
+ status:
+ project:
+ default:
+ threshold: 0.5
+ patch: false
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/bandwidth.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/bandwidth.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2c7ff23
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/bandwidth.go
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// Bandwidth of a connection
+type Bandwidth uint64
+
+const (
+ // BitsPerSecond is 1 bit per second
+ BitsPerSecond Bandwidth = 1
+ // KBitsPerSecond is 1000 bits per second
+ KBitsPerSecond = 1000 * BitsPerSecond
+ // BytesPerSecond is 1 byte per second
+ BytesPerSecond = 8 * BitsPerSecond
+ // KBytesPerSecond is 1000 bytes per second
+ KBytesPerSecond = 1000 * BytesPerSecond
+)
+
+// BandwidthFromDelta calculates the bandwidth from a number of bytes and a time delta
+func BandwidthFromDelta(bytes protocol.ByteCount, delta time.Duration) Bandwidth {
+ return Bandwidth(bytes) * Bandwidth(time.Second) / Bandwidth(delta) * BytesPerSecond
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/clock.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/clock.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..405fae7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/clock.go
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package congestion
+
+import "time"
+
+// A Clock returns the current time
+type Clock interface {
+ Now() time.Time
+}
+
+// DefaultClock implements the Clock interface using the Go stdlib clock.
+type DefaultClock struct{}
+
+var _ Clock = DefaultClock{}
+
+// Now gets the current time
+func (DefaultClock) Now() time.Time {
+ return time.Now()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/congestion_vector.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/congestion_vector.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9c6ebb4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/congestion_vector.go
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+package congestion
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// PacketInfo combines packet number and length of a packet for congestion calculation
+type PacketInfo struct {
+ Number protocol.PacketNumber
+ Length protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// PacketVector is passed to the congestion algorithm
+type PacketVector []PacketInfo
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e6e8bf6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic.go
@@ -0,0 +1,218 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "math"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// This cubic implementation is based on the one found in Chromiums's QUIC
+// implementation, in the files net/quic/congestion_control/cubic.{hh,cc}.
+
+// Constants based on TCP defaults.
+// The following constants are in 2^10 fractions of a second instead of ms to
+// allow a 10 shift right to divide.
+
+// 1024*1024^3 (first 1024 is from 0.100^3)
+// where 0.100 is 100 ms which is the scaling
+// round trip time.
+const cubeScale = 40
+const cubeCongestionWindowScale = 410
+const cubeFactor protocol.PacketNumber = 1 << cubeScale / cubeCongestionWindowScale
+
+const defaultNumConnections = 2
+
+// Default Cubic backoff factor
+const beta float32 = 0.7
+
+// Additional backoff factor when loss occurs in the concave part of the Cubic
+// curve. This additional backoff factor is expected to give up bandwidth to
+// new concurrent flows and speed up convergence.
+const betaLastMax float32 = 0.85
+
+// If true, Cubic's epoch is shifted when the sender is application-limited.
+const shiftQuicCubicEpochWhenAppLimited = true
+
+const maxCubicTimeInterval = 30 * time.Millisecond
+
+// Cubic implements the cubic algorithm from TCP
+type Cubic struct {
+ clock Clock
+ // Number of connections to simulate.
+ numConnections int
+ // Time when this cycle started, after last loss event.
+ epoch time.Time
+ // Time when sender went into application-limited period. Zero if not in
+ // application-limited period.
+ appLimitedStartTime time.Time
+ // Time when we updated last_congestion_window.
+ lastUpdateTime time.Time
+ // Last congestion window (in packets) used.
+ lastCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Max congestion window (in packets) used just before last loss event.
+ // Note: to improve fairness to other streams an additional back off is
+ // applied to this value if the new value is below our latest value.
+ lastMaxCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Number of acked packets since the cycle started (epoch).
+ ackedPacketsCount protocol.PacketNumber
+ // TCP Reno equivalent congestion window in packets.
+ estimatedTCPcongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Origin point of cubic function.
+ originPointCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Time to origin point of cubic function in 2^10 fractions of a second.
+ timeToOriginPoint uint32
+ // Last congestion window in packets computed by cubic function.
+ lastTargetCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+// NewCubic returns a new Cubic instance
+func NewCubic(clock Clock) *Cubic {
+ c := &Cubic{
+ clock: clock,
+ numConnections: defaultNumConnections,
+ }
+ c.Reset()
+ return c
+}
+
+// Reset is called after a timeout to reset the cubic state
+func (c *Cubic) Reset() {
+ c.epoch = time.Time{}
+ c.appLimitedStartTime = time.Time{}
+ c.lastUpdateTime = time.Time{}
+ c.lastCongestionWindow = 0
+ c.lastMaxCongestionWindow = 0
+ c.ackedPacketsCount = 0
+ c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow = 0
+ c.originPointCongestionWindow = 0
+ c.timeToOriginPoint = 0
+ c.lastTargetCongestionWindow = 0
+}
+
+func (c *Cubic) alpha() float32 {
+ // TCPFriendly alpha is described in Section 3.3 of the CUBIC paper. Note that
+ // beta here is a cwnd multiplier, and is equal to 1-beta from the paper.
+ // We derive the equivalent alpha for an N-connection emulation as:
+ b := c.beta()
+ return 3 * float32(c.numConnections) * float32(c.numConnections) * (1 - b) / (1 + b)
+}
+
+func (c *Cubic) beta() float32 {
+ // kNConnectionBeta is the backoff factor after loss for our N-connection
+ // emulation, which emulates the effective backoff of an ensemble of N
+ // TCP-Reno connections on a single loss event. The effective multiplier is
+ // computed as:
+ return (float32(c.numConnections) - 1 + beta) / float32(c.numConnections)
+}
+
+// OnApplicationLimited is called on ack arrival when sender is unable to use
+// the available congestion window. Resets Cubic state during quiescence.
+func (c *Cubic) OnApplicationLimited() {
+ if shiftQuicCubicEpochWhenAppLimited {
+ // When sender is not using the available congestion window, Cubic's epoch
+ // should not continue growing. Record the time when sender goes into an
+ // app-limited period here, to compensate later when cwnd growth happens.
+ if c.appLimitedStartTime.IsZero() {
+ c.appLimitedStartTime = c.clock.Now()
+ }
+ } else {
+ // When sender is not using the available congestion window, Cubic's epoch
+ // should not continue growing. Reset the epoch when in such a period.
+ c.epoch = time.Time{}
+ }
+}
+
+// CongestionWindowAfterPacketLoss computes a new congestion window to use after
+// a loss event. Returns the new congestion window in packets. The new
+// congestion window is a multiplicative decrease of our current window.
+func (c *Cubic) CongestionWindowAfterPacketLoss(currentCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if currentCongestionWindow < c.lastMaxCongestionWindow {
+ // We never reached the old max, so assume we are competing with another
+ // flow. Use our extra back off factor to allow the other flow to go up.
+ c.lastMaxCongestionWindow = protocol.PacketNumber(betaLastMax * float32(currentCongestionWindow))
+ } else {
+ c.lastMaxCongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ }
+ c.epoch = time.Time{} // Reset time.
+ return protocol.PacketNumber(float32(currentCongestionWindow) * c.beta())
+}
+
+// CongestionWindowAfterAck computes a new congestion window to use after a received ACK.
+// Returns the new congestion window in packets. The new congestion window
+// follows a cubic function that depends on the time passed since last
+// packet loss.
+func (c *Cubic) CongestionWindowAfterAck(currentCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber, delayMin time.Duration) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ c.ackedPacketsCount++ // Packets acked.
+ currentTime := c.clock.Now()
+
+ // Cubic is "independent" of RTT, the update is limited by the time elapsed.
+ if c.lastCongestionWindow == currentCongestionWindow && (currentTime.Sub(c.lastUpdateTime) <= maxCubicTimeInterval) {
+ return utils.MaxPacketNumber(c.lastTargetCongestionWindow, c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow)
+ }
+ c.lastCongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ c.lastUpdateTime = currentTime
+
+ if c.epoch.IsZero() {
+ // First ACK after a loss event.
+ c.epoch = currentTime // Start of epoch.
+ c.ackedPacketsCount = 1 // Reset count.
+ // Reset estimated_tcp_congestion_window_ to be in sync with cubic.
+ c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ if c.lastMaxCongestionWindow <= currentCongestionWindow {
+ c.timeToOriginPoint = 0
+ c.originPointCongestionWindow = currentCongestionWindow
+ } else {
+ c.timeToOriginPoint = uint32(math.Cbrt(float64(cubeFactor * (c.lastMaxCongestionWindow - currentCongestionWindow))))
+ c.originPointCongestionWindow = c.lastMaxCongestionWindow
+ }
+ } else {
+ // If sender was app-limited, then freeze congestion window growth during
+ // app-limited period. Continue growth now by shifting the epoch-start
+ // through the app-limited period.
+ if shiftQuicCubicEpochWhenAppLimited && !c.appLimitedStartTime.IsZero() {
+ shift := currentTime.Sub(c.appLimitedStartTime)
+ c.epoch = c.epoch.Add(shift)
+ c.appLimitedStartTime = time.Time{}
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Change the time unit from microseconds to 2^10 fractions per second. Take
+ // the round trip time in account. This is done to allow us to use shift as a
+ // divide operator.
+ elapsedTime := int64((currentTime.Add(delayMin).Sub(c.epoch)/time.Microsecond)<<10) / 1000000
+
+ offset := int64(c.timeToOriginPoint) - elapsedTime
+ deltaCongestionWindow := protocol.PacketNumber((cubeCongestionWindowScale * offset * offset * offset) >> cubeScale)
+ targetCongestionWindow := c.originPointCongestionWindow - deltaCongestionWindow
+
+ // With dynamic beta/alpha based on number of active streams, it is possible
+ // for the required_ack_count to become much lower than acked_packets_count_
+ // suddenly, leading to more than one iteration through the following loop.
+ for {
+ // Update estimated TCP congestion_window.
+ requiredAckCount := protocol.PacketNumber(float32(c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow) / c.alpha())
+ if c.ackedPacketsCount < requiredAckCount {
+ break
+ }
+ c.ackedPacketsCount -= requiredAckCount
+ c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow++
+ }
+
+ // We have a new cubic congestion window.
+ c.lastTargetCongestionWindow = targetCongestionWindow
+
+ // Compute target congestion_window based on cubic target and estimated TCP
+ // congestion_window, use highest (fastest).
+ if targetCongestionWindow < c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow {
+ targetCongestionWindow = c.estimatedTCPcongestionWindow
+ }
+
+ return targetCongestionWindow
+}
+
+// SetNumConnections sets the number of emulated connections
+func (c *Cubic) SetNumConnections(n int) {
+ c.numConnections = n
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic_sender.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic_sender.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a34a69d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/cubic_sender.go
@@ -0,0 +1,309 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+const (
+ maxBurstBytes = 3 * protocol.DefaultTCPMSS
+ defaultMinimumCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber = 2
+ renoBeta float32 = 0.7 // Reno backoff factor.
+)
+
+type cubicSender struct {
+ hybridSlowStart HybridSlowStart
+ prr PrrSender
+ rttStats *RTTStats
+ stats connectionStats
+ cubic *Cubic
+
+ reno bool
+
+ // Track the largest packet that has been sent.
+ largestSentPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Track the largest packet that has been acked.
+ largestAckedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Track the largest packet number outstanding when a CWND cutback occurs.
+ largestSentAtLastCutback protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Congestion window in packets.
+ congestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Slow start congestion window in packets, aka ssthresh.
+ slowstartThreshold protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Whether the last loss event caused us to exit slowstart.
+ // Used for stats collection of slowstartPacketsLost
+ lastCutbackExitedSlowstart bool
+
+ // When true, exit slow start with large cutback of congestion window.
+ slowStartLargeReduction bool
+
+ // Minimum congestion window in packets.
+ minCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Maximum number of outstanding packets for tcp.
+ maxTCPCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ // Number of connections to simulate.
+ numConnections int
+
+ // ACK counter for the Reno implementation.
+ congestionWindowCount protocol.ByteCount
+
+ initialCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+ initialMaxCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+// NewCubicSender makes a new cubic sender
+func NewCubicSender(clock Clock, rttStats *RTTStats, reno bool, initialCongestionWindow, initialMaxCongestionWindow protocol.PacketNumber) SendAlgorithmWithDebugInfo {
+ return &cubicSender{
+ rttStats: rttStats,
+ initialCongestionWindow: initialCongestionWindow,
+ initialMaxCongestionWindow: initialMaxCongestionWindow,
+ congestionWindow: initialCongestionWindow,
+ minCongestionWindow: defaultMinimumCongestionWindow,
+ slowstartThreshold: initialMaxCongestionWindow,
+ maxTCPCongestionWindow: initialMaxCongestionWindow,
+ numConnections: defaultNumConnections,
+ cubic: NewCubic(clock),
+ reno: reno,
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) TimeUntilSend(now time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) time.Duration {
+ if c.InRecovery() {
+ // PRR is used when in recovery.
+ return c.prr.TimeUntilSend(c.GetCongestionWindow(), bytesInFlight, c.GetSlowStartThreshold())
+ }
+ if c.GetCongestionWindow() > bytesInFlight {
+ return 0
+ }
+ return utils.InfDuration
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) OnPacketSent(sentTime time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, bytes protocol.ByteCount, isRetransmittable bool) bool {
+ // Only update bytesInFlight for data packets.
+ if !isRetransmittable {
+ return false
+ }
+ if c.InRecovery() {
+ // PRR is used when in recovery.
+ c.prr.OnPacketSent(bytes)
+ }
+ c.largestSentPacketNumber = packetNumber
+ c.hybridSlowStart.OnPacketSent(packetNumber)
+ return true
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) InRecovery() bool {
+ return c.largestAckedPacketNumber <= c.largestSentAtLastCutback && c.largestAckedPacketNumber != 0
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) InSlowStart() bool {
+ return c.GetCongestionWindow() < c.GetSlowStartThreshold()
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) GetCongestionWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(c.congestionWindow) * protocol.DefaultTCPMSS
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) GetSlowStartThreshold() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(c.slowstartThreshold) * protocol.DefaultTCPMSS
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) ExitSlowstart() {
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) SlowstartThreshold() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ return c.slowstartThreshold
+}
+
+// OnCongestionEvent indicates an update to the congestion state, caused either by an incoming
+// ack or loss event timeout. |rttUpdated| indicates whether a new
+// latest_rtt sample has been taken, |byte_in_flight| the bytes in flight
+// prior to the congestion event. |ackedPackets| and |lostPackets| are
+// any packets considered acked or lost as a result of the congestion event.
+func (c *cubicSender) OnCongestionEvent(rttUpdated bool, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, ackedPackets PacketVector, lostPackets PacketVector) {
+ if rttUpdated && c.InSlowStart() && c.hybridSlowStart.ShouldExitSlowStart(c.rttStats.LatestRTT(), c.rttStats.MinRTT(), c.GetCongestionWindow()/protocol.DefaultTCPMSS) {
+ c.ExitSlowstart()
+ }
+ for _, i := range lostPackets {
+ c.onPacketLost(i.Number, i.Length, bytesInFlight)
+ }
+ for _, i := range ackedPackets {
+ c.onPacketAcked(i.Number, i.Length, bytesInFlight)
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) onPacketAcked(ackedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, ackedBytes protocol.ByteCount, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.largestAckedPacketNumber = utils.MaxPacketNumber(ackedPacketNumber, c.largestAckedPacketNumber)
+ if c.InRecovery() {
+ // PRR is used when in recovery.
+ c.prr.OnPacketAcked(ackedBytes)
+ return
+ }
+ c.maybeIncreaseCwnd(ackedPacketNumber, ackedBytes, bytesInFlight)
+ if c.InSlowStart() {
+ c.hybridSlowStart.OnPacketAcked(ackedPacketNumber)
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) onPacketLost(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, lostBytes protocol.ByteCount, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ // TCP NewReno (RFC6582) says that once a loss occurs, any losses in packets
+ // already sent should be treated as a single loss event, since it's expected.
+ if packetNumber <= c.largestSentAtLastCutback {
+ if c.lastCutbackExitedSlowstart {
+ c.stats.slowstartPacketsLost++
+ c.stats.slowstartBytesLost += lostBytes
+ if c.slowStartLargeReduction {
+ if c.stats.slowstartPacketsLost == 1 || (c.stats.slowstartBytesLost/protocol.DefaultTCPMSS) > (c.stats.slowstartBytesLost-lostBytes)/protocol.DefaultTCPMSS {
+ // Reduce congestion window by 1 for every mss of bytes lost.
+ c.congestionWindow = utils.MaxPacketNumber(c.congestionWindow-1, c.minCongestionWindow)
+ }
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow
+ }
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ c.lastCutbackExitedSlowstart = c.InSlowStart()
+ if c.InSlowStart() {
+ c.stats.slowstartPacketsLost++
+ }
+
+ c.prr.OnPacketLost(bytesInFlight)
+
+ // TODO(chromium): Separate out all of slow start into a separate class.
+ if c.slowStartLargeReduction && c.InSlowStart() {
+ c.congestionWindow = c.congestionWindow - 1
+ } else if c.reno {
+ c.congestionWindow = protocol.PacketNumber(float32(c.congestionWindow) * c.RenoBeta())
+ } else {
+ c.congestionWindow = c.cubic.CongestionWindowAfterPacketLoss(c.congestionWindow)
+ }
+ // Enforce a minimum congestion window.
+ if c.congestionWindow < c.minCongestionWindow {
+ c.congestionWindow = c.minCongestionWindow
+ }
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow
+ c.largestSentAtLastCutback = c.largestSentPacketNumber
+ // reset packet count from congestion avoidance mode. We start
+ // counting again when we're out of recovery.
+ c.congestionWindowCount = 0
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) RenoBeta() float32 {
+ // kNConnectionBeta is the backoff factor after loss for our N-connection
+ // emulation, which emulates the effective backoff of an ensemble of N
+ // TCP-Reno connections on a single loss event. The effective multiplier is
+ // computed as:
+ return (float32(c.numConnections) - 1. + renoBeta) / float32(c.numConnections)
+}
+
+// Called when we receive an ack. Normal TCP tracks how many packets one ack
+// represents, but quic has a separate ack for each packet.
+func (c *cubicSender) maybeIncreaseCwnd(ackedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, ackedBytes protocol.ByteCount, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ // Do not increase the congestion window unless the sender is close to using
+ // the current window.
+ if !c.isCwndLimited(bytesInFlight) {
+ c.cubic.OnApplicationLimited()
+ return
+ }
+ if c.congestionWindow >= c.maxTCPCongestionWindow {
+ return
+ }
+ if c.InSlowStart() {
+ // TCP slow start, exponential growth, increase by one for each ACK.
+ c.congestionWindow++
+ return
+ }
+ if c.reno {
+ // Classic Reno congestion avoidance.
+ c.congestionWindowCount++
+ // Divide by num_connections to smoothly increase the CWND at a faster
+ // rate than conventional Reno.
+ if protocol.PacketNumber(c.congestionWindowCount*protocol.ByteCount(c.numConnections)) >= c.congestionWindow {
+ c.congestionWindow++
+ c.congestionWindowCount = 0
+ }
+ } else {
+ c.congestionWindow = utils.MinPacketNumber(c.maxTCPCongestionWindow, c.cubic.CongestionWindowAfterAck(c.congestionWindow, c.rttStats.MinRTT()))
+ }
+}
+
+func (c *cubicSender) isCwndLimited(bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) bool {
+ congestionWindow := c.GetCongestionWindow()
+ if bytesInFlight >= congestionWindow {
+ return true
+ }
+ availableBytes := congestionWindow - bytesInFlight
+ slowStartLimited := c.InSlowStart() && bytesInFlight > congestionWindow/2
+ return slowStartLimited || availableBytes <= maxBurstBytes
+}
+
+// BandwidthEstimate returns the current bandwidth estimate
+func (c *cubicSender) BandwidthEstimate() Bandwidth {
+ srtt := c.rttStats.SmoothedRTT()
+ if srtt == 0 {
+ // If we haven't measured an rtt, the bandwidth estimate is unknown.
+ return 0
+ }
+ return BandwidthFromDelta(c.GetCongestionWindow(), srtt)
+}
+
+// HybridSlowStart returns the hybrid slow start instance for testing
+func (c *cubicSender) HybridSlowStart() *HybridSlowStart {
+ return &c.hybridSlowStart
+}
+
+// SetNumEmulatedConnections sets the number of emulated connections
+func (c *cubicSender) SetNumEmulatedConnections(n int) {
+ c.numConnections = utils.Max(n, 1)
+ c.cubic.SetNumConnections(c.numConnections)
+}
+
+// OnRetransmissionTimeout is called on an retransmission timeout
+func (c *cubicSender) OnRetransmissionTimeout(packetsRetransmitted bool) {
+ c.largestSentAtLastCutback = 0
+ if !packetsRetransmitted {
+ return
+ }
+ c.hybridSlowStart.Restart()
+ c.cubic.Reset()
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.congestionWindow / 2
+ c.congestionWindow = c.minCongestionWindow
+}
+
+// OnConnectionMigration is called when the connection is migrated (?)
+func (c *cubicSender) OnConnectionMigration() {
+ c.hybridSlowStart.Restart()
+ c.prr = PrrSender{}
+ c.largestSentPacketNumber = 0
+ c.largestAckedPacketNumber = 0
+ c.largestSentAtLastCutback = 0
+ c.lastCutbackExitedSlowstart = false
+ c.cubic.Reset()
+ c.congestionWindowCount = 0
+ c.congestionWindow = c.initialCongestionWindow
+ c.slowstartThreshold = c.initialMaxCongestionWindow
+ c.maxTCPCongestionWindow = c.initialMaxCongestionWindow
+}
+
+// SetSlowStartLargeReduction allows enabling the SSLR experiment
+func (c *cubicSender) SetSlowStartLargeReduction(enabled bool) {
+ c.slowStartLargeReduction = enabled
+}
+
+// RetransmissionDelay gives the time to retransmission
+func (c *cubicSender) RetransmissionDelay() time.Duration {
+ if c.rttStats.SmoothedRTT() == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ return c.rttStats.SmoothedRTT() + c.rttStats.MeanDeviation()*4
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/hybrid_slow_start.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/hybrid_slow_start.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..29204ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/hybrid_slow_start.go
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// Note(pwestin): the magic clamping numbers come from the original code in
+// tcp_cubic.c.
+const hybridStartLowWindow = protocol.ByteCount(16)
+
+// Number of delay samples for detecting the increase of delay.
+const hybridStartMinSamples = uint32(8)
+
+// Exit slow start if the min rtt has increased by more than 1/8th.
+const hybridStartDelayFactorExp = 3 // 2^3 = 8
+// The original paper specifies 2 and 8ms, but those have changed over time.
+const hybridStartDelayMinThresholdUs = int64(4000)
+const hybridStartDelayMaxThresholdUs = int64(16000)
+
+// HybridSlowStart implements the TCP hybrid slow start algorithm
+type HybridSlowStart struct {
+ endPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ lastSentPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ started bool
+ currentMinRTT time.Duration
+ rttSampleCount uint32
+ hystartFound bool
+}
+
+// StartReceiveRound is called for the start of each receive round (burst) in the slow start phase.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) StartReceiveRound(lastSent protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ s.endPacketNumber = lastSent
+ s.currentMinRTT = 0
+ s.rttSampleCount = 0
+ s.started = true
+}
+
+// IsEndOfRound returns true if this ack is the last packet number of our current slow start round.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) IsEndOfRound(ack protocol.PacketNumber) bool {
+ return s.endPacketNumber < ack
+}
+
+// ShouldExitSlowStart should be called on every new ack frame, since a new
+// RTT measurement can be made then.
+// rtt: the RTT for this ack packet.
+// minRTT: is the lowest delay (RTT) we have seen during the session.
+// congestionWindow: the congestion window in packets.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) ShouldExitSlowStart(latestRTT time.Duration, minRTT time.Duration, congestionWindow protocol.ByteCount) bool {
+ if !s.started {
+ // Time to start the hybrid slow start.
+ s.StartReceiveRound(s.lastSentPacketNumber)
+ }
+ if s.hystartFound {
+ return true
+ }
+ // Second detection parameter - delay increase detection.
+ // Compare the minimum delay (s.currentMinRTT) of the current
+ // burst of packets relative to the minimum delay during the session.
+ // Note: we only look at the first few(8) packets in each burst, since we
+ // only want to compare the lowest RTT of the burst relative to previous
+ // bursts.
+ s.rttSampleCount++
+ if s.rttSampleCount <= hybridStartMinSamples {
+ if s.currentMinRTT == 0 || s.currentMinRTT > latestRTT {
+ s.currentMinRTT = latestRTT
+ }
+ }
+ // We only need to check this once per round.
+ if s.rttSampleCount == hybridStartMinSamples {
+ // Divide minRTT by 8 to get a rtt increase threshold for exiting.
+ minRTTincreaseThresholdUs := int64(minRTT / time.Microsecond >> hybridStartDelayFactorExp)
+ // Ensure the rtt threshold is never less than 2ms or more than 16ms.
+ minRTTincreaseThresholdUs = utils.MinInt64(minRTTincreaseThresholdUs, hybridStartDelayMaxThresholdUs)
+ minRTTincreaseThreshold := time.Duration(utils.MaxInt64(minRTTincreaseThresholdUs, hybridStartDelayMinThresholdUs)) * time.Microsecond
+
+ if s.currentMinRTT > (minRTT + minRTTincreaseThreshold) {
+ s.hystartFound = true
+ }
+ }
+ // Exit from slow start if the cwnd is greater than 16 and
+ // increasing delay is found.
+ return congestionWindow >= hybridStartLowWindow && s.hystartFound
+}
+
+// OnPacketSent is called when a packet was sent
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) OnPacketSent(packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ s.lastSentPacketNumber = packetNumber
+}
+
+// OnPacketAcked gets invoked after ShouldExitSlowStart, so it's best to end
+// the round when the final packet of the burst is received and start it on
+// the next incoming ack.
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) OnPacketAcked(ackedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber) {
+ if s.IsEndOfRound(ackedPacketNumber) {
+ s.started = false
+ }
+}
+
+// Started returns true if started
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) Started() bool {
+ return s.started
+}
+
+// Restart the slow start phase
+func (s *HybridSlowStart) Restart() {
+ s.started = false
+ s.hystartFound = false
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/interface.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/interface.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..593c09e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/interface.go
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A SendAlgorithm performs congestion control and calculates the congestion window
+type SendAlgorithm interface {
+ TimeUntilSend(now time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) time.Duration
+ OnPacketSent(sentTime time.Time, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, bytes protocol.ByteCount, isRetransmittable bool) bool
+ GetCongestionWindow() protocol.ByteCount
+ OnCongestionEvent(rttUpdated bool, bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount, ackedPackets PacketVector, lostPackets PacketVector)
+ SetNumEmulatedConnections(n int)
+ OnRetransmissionTimeout(packetsRetransmitted bool)
+ OnConnectionMigration()
+ RetransmissionDelay() time.Duration
+
+ // Experiments
+ SetSlowStartLargeReduction(enabled bool)
+}
+
+// SendAlgorithmWithDebugInfo adds some debug functions to SendAlgorithm
+type SendAlgorithmWithDebugInfo interface {
+ SendAlgorithm
+ BandwidthEstimate() Bandwidth
+
+ // Stuff only used in testing
+
+ HybridSlowStart() *HybridSlowStart
+ SlowstartThreshold() protocol.PacketNumber
+ RenoBeta() float32
+ InRecovery() bool
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/prr_sender.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/prr_sender.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f8e6d59
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/prr_sender.go
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// PrrSender implements the Proportional Rate Reduction (PRR) per RFC 6937
+type PrrSender struct {
+ bytesSentSinceLoss protocol.ByteCount
+ bytesDeliveredSinceLoss protocol.ByteCount
+ ackCountSinceLoss protocol.ByteCount
+ bytesInFlightBeforeLoss protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// OnPacketSent should be called after a packet was sent
+func (p *PrrSender) OnPacketSent(sentBytes protocol.ByteCount) {
+ p.bytesSentSinceLoss += sentBytes
+}
+
+// OnPacketLost should be called on the first loss that triggers a recovery
+// period and all other methods in this class should only be called when in
+// recovery.
+func (p *PrrSender) OnPacketLost(bytesInFlight protocol.ByteCount) {
+ p.bytesSentSinceLoss = 0
+ p.bytesInFlightBeforeLoss = bytesInFlight
+ p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss = 0
+ p.ackCountSinceLoss = 0
+}
+
+// OnPacketAcked should be called after a packet was acked
+func (p *PrrSender) OnPacketAcked(ackedBytes protocol.ByteCount) {
+ p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss += ackedBytes
+ p.ackCountSinceLoss++
+}
+
+// TimeUntilSend calculates the time until a packet can be sent
+func (p *PrrSender) TimeUntilSend(congestionWindow, bytesInFlight, slowstartThreshold protocol.ByteCount) time.Duration {
+ // Return QuicTime::Zero In order to ensure limited transmit always works.
+ if p.bytesSentSinceLoss == 0 || bytesInFlight < protocol.DefaultTCPMSS {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if congestionWindow > bytesInFlight {
+ // During PRR-SSRB, limit outgoing packets to 1 extra MSS per ack, instead
+ // of sending the entire available window. This prevents burst retransmits
+ // when more packets are lost than the CWND reduction.
+ // limit = MAX(prr_delivered - prr_out, DeliveredData) + MSS
+ if p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss+p.ackCountSinceLoss*protocol.DefaultTCPMSS <= p.bytesSentSinceLoss {
+ return utils.InfDuration
+ }
+ return 0
+ }
+ // Implement Proportional Rate Reduction (RFC6937).
+ // Checks a simplified version of the PRR formula that doesn't use division:
+ // AvailableSendWindow =
+ // CEIL(prr_delivered * ssthresh / BytesInFlightAtLoss) - prr_sent
+ if p.bytesDeliveredSinceLoss*slowstartThreshold > p.bytesSentSinceLoss*p.bytesInFlightBeforeLoss {
+ return 0
+ }
+ return utils.InfDuration
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/rtt_stats.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/rtt_stats.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0bf7b05
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/rtt_stats.go
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+package congestion
+
+import (
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+const (
+ initialRTTus = 100 * 1000
+ rttAlpha float32 = 0.125
+ oneMinusAlpha float32 = (1 - rttAlpha)
+ rttBeta float32 = 0.25
+ oneMinusBeta float32 = (1 - rttBeta)
+ halfWindow float32 = 0.5
+ quarterWindow float32 = 0.25
+)
+
+type rttSample struct {
+ rtt time.Duration
+ time time.Time
+}
+
+// RTTStats provides round-trip statistics
+type RTTStats struct {
+ initialRTTus int64
+
+ recentMinRTTwindow time.Duration
+ minRTT time.Duration
+ latestRTT time.Duration
+ smoothedRTT time.Duration
+ meanDeviation time.Duration
+
+ numMinRTTsamplesRemaining uint32
+
+ newMinRTT rttSample
+ recentMinRTT rttSample
+ halfWindowRTT rttSample
+ quarterWindowRTT rttSample
+}
+
+// NewRTTStats makes a properly initialized RTTStats object
+func NewRTTStats() *RTTStats {
+ return &RTTStats{
+ initialRTTus: initialRTTus,
+ recentMinRTTwindow: utils.InfDuration,
+ }
+}
+
+// InitialRTTus is the initial RTT in us
+func (r *RTTStats) InitialRTTus() int64 { return r.initialRTTus }
+
+// MinRTT Returns the minRTT for the entire connection.
+// May return Zero if no valid updates have occurred.
+func (r *RTTStats) MinRTT() time.Duration { return r.minRTT }
+
+// LatestRTT returns the most recent rtt measurement.
+// May return Zero if no valid updates have occurred.
+func (r *RTTStats) LatestRTT() time.Duration { return r.latestRTT }
+
+// RecentMinRTT the minRTT since SampleNewRecentMinRtt has been called, or the
+// minRTT for the entire connection if SampleNewMinRtt was never called.
+func (r *RTTStats) RecentMinRTT() time.Duration { return r.recentMinRTT.rtt }
+
+// SmoothedRTT returns the EWMA smoothed RTT for the connection.
+// May return Zero if no valid updates have occurred.
+func (r *RTTStats) SmoothedRTT() time.Duration { return r.smoothedRTT }
+
+// GetQuarterWindowRTT gets the quarter window RTT
+func (r *RTTStats) GetQuarterWindowRTT() time.Duration { return r.quarterWindowRTT.rtt }
+
+// GetHalfWindowRTT gets the half window RTT
+func (r *RTTStats) GetHalfWindowRTT() time.Duration { return r.halfWindowRTT.rtt }
+
+// MeanDeviation gets the mean deviation
+func (r *RTTStats) MeanDeviation() time.Duration { return r.meanDeviation }
+
+// SetRecentMinRTTwindow sets how old a recent min rtt sample can be.
+func (r *RTTStats) SetRecentMinRTTwindow(recentMinRTTwindow time.Duration) {
+ r.recentMinRTTwindow = recentMinRTTwindow
+}
+
+// UpdateRTT updates the RTT based on a new sample.
+func (r *RTTStats) UpdateRTT(sendDelta, ackDelay time.Duration, now time.Time) {
+ if sendDelta == utils.InfDuration || sendDelta <= 0 {
+ utils.Debugf("Ignoring measured sendDelta, because it's is either infinite, zero, or negative: %d", sendDelta/time.Microsecond)
+ return
+ }
+
+ // Update r.minRTT first. r.minRTT does not use an rttSample corrected for
+ // ackDelay but the raw observed sendDelta, since poor clock granularity at
+ // the client may cause a high ackDelay to result in underestimation of the
+ // r.minRTT.
+ if r.minRTT == 0 || r.minRTT > sendDelta {
+ r.minRTT = sendDelta
+ }
+ r.updateRecentMinRTT(sendDelta, now)
+
+ // Correct for ackDelay if information received from the peer results in a
+ // positive RTT sample. Otherwise, we use the sendDelta as a reasonable
+ // measure for smoothedRTT.
+ sample := sendDelta
+ if sample > ackDelay {
+ sample -= ackDelay
+ }
+ r.latestRTT = sample
+ // First time call.
+ if r.smoothedRTT == 0 {
+ r.smoothedRTT = sample
+ r.meanDeviation = sample / 2
+ } else {
+ r.meanDeviation = time.Duration(oneMinusBeta*float32(r.meanDeviation/time.Microsecond)+rttBeta*float32(utils.AbsDuration(r.smoothedRTT-sample)/time.Microsecond)) * time.Microsecond
+ r.smoothedRTT = time.Duration((float32(r.smoothedRTT/time.Microsecond)*oneMinusAlpha)+(float32(sample/time.Microsecond)*rttAlpha)) * time.Microsecond
+ }
+}
+
+func (r *RTTStats) updateRecentMinRTT(sample time.Duration, now time.Time) { // Recent minRTT update.
+ if r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining > 0 {
+ r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining--
+ if r.newMinRTT.rtt == 0 || sample <= r.newMinRTT.rtt {
+ r.newMinRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ }
+ if r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining == 0 {
+ r.recentMinRTT = r.newMinRTT
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.newMinRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = r.newMinRTT
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Update the three recent rtt samples.
+ if r.recentMinRTT.rtt == 0 || sample <= r.recentMinRTT.rtt {
+ r.recentMinRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.recentMinRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = r.recentMinRTT
+ } else if sample <= r.halfWindowRTT.rtt {
+ r.halfWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = r.halfWindowRTT
+ } else if sample <= r.quarterWindowRTT.rtt {
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ }
+
+ // Expire old min rtt samples.
+ if r.recentMinRTT.time.Before(now.Add(-r.recentMinRTTwindow)) {
+ r.recentMinRTT = r.halfWindowRTT
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.quarterWindowRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ } else if r.halfWindowRTT.time.Before(now.Add(-time.Duration(float32(r.recentMinRTTwindow/time.Microsecond)*halfWindow) * time.Microsecond)) {
+ r.halfWindowRTT = r.quarterWindowRTT
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ } else if r.quarterWindowRTT.time.Before(now.Add(-time.Duration(float32(r.recentMinRTTwindow/time.Microsecond)*quarterWindow) * time.Microsecond)) {
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{rtt: sample, time: now}
+ }
+}
+
+// SampleNewRecentMinRTT forces RttStats to sample a new recent min rtt within the next
+// |numSamples| UpdateRTT calls.
+func (r *RTTStats) SampleNewRecentMinRTT(numSamples uint32) {
+ r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining = numSamples
+ r.newMinRTT = rttSample{}
+}
+
+// OnConnectionMigration is called when connection migrates and rtt measurement needs to be reset.
+func (r *RTTStats) OnConnectionMigration() {
+ r.latestRTT = 0
+ r.minRTT = 0
+ r.smoothedRTT = 0
+ r.meanDeviation = 0
+ r.initialRTTus = initialRTTus
+ r.numMinRTTsamplesRemaining = 0
+ r.recentMinRTTwindow = utils.InfDuration
+ r.recentMinRTT = rttSample{}
+ r.halfWindowRTT = rttSample{}
+ r.quarterWindowRTT = rttSample{}
+}
+
+// ExpireSmoothedMetrics causes the smoothed_rtt to be increased to the latest_rtt if the latest_rtt
+// is larger. The mean deviation is increased to the most recent deviation if
+// it's larger.
+func (r *RTTStats) ExpireSmoothedMetrics() {
+ r.meanDeviation = utils.MaxDuration(r.meanDeviation, utils.AbsDuration(r.smoothedRTT-r.latestRTT))
+ r.smoothedRTT = utils.MaxDuration(r.smoothedRTT, r.latestRTT)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/stats.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/stats.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8f272b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion/stats.go
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+package congestion
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+type connectionStats struct {
+ slowstartPacketsLost protocol.PacketNumber
+ slowstartBytesLost protocol.ByteCount
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/AEAD.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/AEAD.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a59ce6e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/AEAD.go
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+package crypto
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// An AEAD implements QUIC's authenticated encryption and associated data
+type AEAD interface {
+ Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error)
+ Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/aesgcm_aead.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/aesgcm_aead.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a738cc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/aesgcm_aead.go
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/aes12"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type aeadAESGCM struct {
+ otherIV []byte
+ myIV []byte
+ encrypter cipher.AEAD
+ decrypter cipher.AEAD
+}
+
+// NewAEADAESGCM creates a AEAD using AES-GCM with 12 bytes tag size
+//
+// AES-GCM support is a bit hacky, since the go stdlib does not support 12 byte
+// tag size, and couples the cipher and aes packages closely.
+// See https://github.com/lucas-clemente/aes12.
+func NewAEADAESGCM(otherKey []byte, myKey []byte, otherIV []byte, myIV []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+ if len(myKey) != 16 || len(otherKey) != 16 || len(myIV) != 4 || len(otherIV) != 4 {
+ return nil, errors.New("AES-GCM: expected 16-byte keys and 4-byte IVs")
+ }
+ encrypterCipher, err := aes12.NewCipher(myKey)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ encrypter, err := aes12.NewGCM(encrypterCipher)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ decrypterCipher, err := aes12.NewCipher(otherKey)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ decrypter, err := aes12.NewGCM(decrypterCipher)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return &aeadAESGCM{
+ otherIV: otherIV,
+ myIV: myIV,
+ encrypter: encrypter,
+ decrypter: decrypter,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadAESGCM) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return aead.decrypter.Open(dst, makeNonce(aead.otherIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadAESGCM) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ return aead.encrypter.Seal(dst, makeNonce(aead.myIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_cache.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_cache.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3ebdc1a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_cache.go
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "hash/fnv"
+
+ "github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+var (
+ compressedCertsCache *lru.Cache
+)
+
+func getCompressedCert(chain [][]byte, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ // Hash all inputs
+ hasher := fnv.New64a()
+ for _, v := range chain {
+ hasher.Write(v)
+ }
+ hasher.Write(pCommonSetHashes)
+ hasher.Write(pCachedHashes)
+ hash := hasher.Sum64()
+
+ var result []byte
+
+ resultI, isCached := compressedCertsCache.Get(hash)
+ if isCached {
+ result = resultI.([]byte)
+ } else {
+ var err error
+ result, err = compressChain(chain, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ compressedCertsCache.Add(hash, result)
+ }
+
+ return result, nil
+}
+
+func init() {
+ var err error
+ compressedCertsCache, err = lru.New(protocol.NumCachedCertificates)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(fmt.Sprintf("fatal error in quic-go: could not create lru cache: %s", err.Error()))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_compression.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_compression.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8fdb257
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_compression.go
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "compress/flate"
+ "compress/zlib"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "hash/fnv"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type entryType uint8
+
+const (
+ entryCompressed entryType = 1
+ entryCached entryType = 2
+ entryCommon entryType = 3
+)
+
+type entry struct {
+ t entryType
+ h uint64
+ i uint32
+}
+
+func compressChain(chain [][]byte, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ res := &bytes.Buffer{}
+
+ cachedHashes, err := splitHashes(pCachedHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ setHashes, err := splitHashes(pCommonSetHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ chainHashes := make([]uint64, len(chain))
+ for i := range chain {
+ chainHashes[i] = hashCert(chain[i])
+ }
+
+ entries := buildEntries(chain, chainHashes, cachedHashes, setHashes)
+
+ totalUncompressedLen := 0
+ for i, e := range entries {
+ res.WriteByte(uint8(e.t))
+ switch e.t {
+ case entryCached:
+ utils.WriteUint64(res, e.h)
+ case entryCommon:
+ utils.WriteUint64(res, e.h)
+ utils.WriteUint32(res, e.i)
+ case entryCompressed:
+ totalUncompressedLen += 4 + len(chain[i])
+ }
+ }
+ res.WriteByte(0) // end of list
+
+ if totalUncompressedLen > 0 {
+ gz, err := zlib.NewWriterLevelDict(res, flate.BestCompression, buildZlibDictForEntries(entries, chain))
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, fmt.Errorf("cert compression failed: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+
+ utils.WriteUint32(res, uint32(totalUncompressedLen))
+
+ for i, e := range entries {
+ if e.t != entryCompressed {
+ continue
+ }
+ lenCert := len(chain[i])
+ gz.Write([]byte{
+ byte(lenCert & 0xff),
+ byte((lenCert >> 8) & 0xff),
+ byte((lenCert >> 16) & 0xff),
+ byte((lenCert >> 24) & 0xff),
+ })
+ gz.Write(chain[i])
+ }
+
+ gz.Close()
+ }
+
+ return res.Bytes(), nil
+}
+
+func buildEntries(chain [][]byte, chainHashes, cachedHashes, setHashes []uint64) []entry {
+ res := make([]entry, len(chain))
+chainLoop:
+ for i := range chain {
+ // Check if hash is in cachedHashes
+ for j := range cachedHashes {
+ if chainHashes[i] == cachedHashes[j] {
+ res[i] = entry{t: entryCached, h: chainHashes[i]}
+ continue chainLoop
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Go through common sets and check if it's in there
+ for _, setHash := range setHashes {
+ set, ok := certSets[setHash]
+ if !ok {
+ // We don't have this set
+ continue
+ }
+ // We have this set, check if chain[i] is in the set
+ pos := set.findCertInSet(chain[i])
+ if pos >= 0 {
+ // Found
+ res[i] = entry{t: entryCommon, h: setHash, i: uint32(pos)}
+ continue chainLoop
+ }
+ }
+
+ res[i] = entry{t: entryCompressed}
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func buildZlibDictForEntries(entries []entry, chain [][]byte) []byte {
+ var dict bytes.Buffer
+
+ // First the cached and common in reverse order
+ for i := len(entries) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
+ if entries[i].t == entryCompressed {
+ continue
+ }
+ dict.Write(chain[i])
+ }
+
+ dict.Write(certDictZlib)
+ return dict.Bytes()
+}
+
+func splitHashes(hashes []byte) ([]uint64, error) {
+ if len(hashes)%8 != 0 {
+ return nil, errors.New("expected a multiple of 8 bytes for CCS / CCRT hashes")
+ }
+ n := len(hashes) / 8
+ res := make([]uint64, n)
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ res[i] = binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(hashes[i*8 : (i+1)*8])
+ }
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+func hashCert(cert []byte) uint64 {
+ h := fnv.New64()
+ h.Write(cert)
+ return h.Sum64()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_dict.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_dict.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..300ec71
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_dict.go
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+package crypto
+
+var certDictZlib = []byte{
+ 0x04, 0x02, 0x30, 0x00, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x25, 0x04,
+ 0x16, 0x30, 0x14, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x03,
+ 0x01, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x03, 0x02, 0x30,
+ 0x5f, 0x06, 0x09, 0x60, 0x86, 0x48, 0x01, 0x86, 0xf8, 0x42, 0x04, 0x01,
+ 0x06, 0x06, 0x0b, 0x60, 0x86, 0x48, 0x01, 0x86, 0xfd, 0x6d, 0x01, 0x07,
+ 0x17, 0x01, 0x30, 0x33, 0x20, 0x45, 0x78, 0x74, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x64, 0x65,
+ 0x64, 0x20, 0x56, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x69, 0x64, 0x61, 0x74, 0x69, 0x6f, 0x6e,
+ 0x20, 0x53, 0x20, 0x4c, 0x69, 0x6d, 0x69, 0x74, 0x65, 0x64, 0x31, 0x34,
+ 0x20, 0x53, 0x53, 0x4c, 0x20, 0x43, 0x41, 0x30, 0x1e, 0x17, 0x0d, 0x31,
+ 0x32, 0x20, 0x53, 0x65, 0x63, 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x20, 0x53, 0x65, 0x72,
+ 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x20, 0x43, 0x41, 0x30, 0x2d, 0x61, 0x69, 0x61, 0x2e,
+ 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d,
+ 0x2f, 0x45, 0x2d, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x2e, 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73,
+ 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x45, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x65,
+ 0x72, 0x30, 0x0d, 0x06, 0x09, 0x2a, 0x86, 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01,
+ 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x00, 0x03, 0x82, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0x4a, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x73, 0x6f, 0x75, 0x72, 0x63, 0x65, 0x73,
+ 0x2f, 0x63, 0x70, 0x73, 0x20, 0x28, 0x63, 0x29, 0x30, 0x30, 0x09, 0x06,
+ 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x13, 0x04, 0x02, 0x30, 0x00, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x30, 0x0d,
+ 0x06, 0x09, 0x2a, 0x86, 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05,
+ 0x00, 0x03, 0x82, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0x7b, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55,
+ 0x1d, 0x0e, 0x30, 0x82, 0x01, 0x22, 0x30, 0x0d, 0x06, 0x09, 0x2a, 0x86,
+ 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01, 0x01, 0x01, 0x05, 0x00, 0x03, 0x82, 0x01,
+ 0x0f, 0x00, 0x30, 0x82, 0x01, 0x0a, 0x02, 0x82, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0xd2,
+ 0x6f, 0x64, 0x6f, 0x63, 0x61, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x43, 0x2e,
+ 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x0e, 0x04, 0x16,
+ 0x04, 0x14, 0xb4, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x62, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x73, 0x69,
+ 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x30, 0x0b, 0x06, 0x03,
+ 0x55, 0x1d, 0x0f, 0x04, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x01, 0x30, 0x0d, 0x06, 0x09,
+ 0x2a, 0x86, 0x48, 0x86, 0xf7, 0x0d, 0x01, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x00, 0x30,
+ 0x81, 0xca, 0x31, 0x0b, 0x30, 0x09, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x06, 0x13,
+ 0x02, 0x55, 0x53, 0x31, 0x10, 0x30, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x08,
+ 0x13, 0x07, 0x41, 0x72, 0x69, 0x7a, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x61, 0x31, 0x13, 0x30,
+ 0x11, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x07, 0x13, 0x0a, 0x53, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x74,
+ 0x74, 0x73, 0x64, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x65, 0x31, 0x1a, 0x30, 0x18, 0x06, 0x03,
+ 0x55, 0x04, 0x0a, 0x13, 0x11, 0x47, 0x6f, 0x44, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79,
+ 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2c, 0x20, 0x49, 0x6e, 0x63, 0x2e, 0x31, 0x33,
+ 0x30, 0x31, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x2a, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74,
+ 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x65, 0x72, 0x74, 0x69, 0x66, 0x69, 0x63,
+ 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x73, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79,
+ 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6f, 0x73, 0x69, 0x74,
+ 0x6f, 0x72, 0x79, 0x31, 0x30, 0x30, 0x2e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x03,
+ 0x13, 0x27, 0x47, 0x6f, 0x20, 0x44, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x20, 0x53,
+ 0x65, 0x63, 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x20, 0x43, 0x65, 0x72, 0x74, 0x69, 0x66,
+ 0x69, 0x63, 0x61, 0x74, 0x69, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x41, 0x75, 0x74, 0x68,
+ 0x6f, 0x72, 0x69, 0x74, 0x79, 0x31, 0x11, 0x30, 0x0f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55,
+ 0x04, 0x05, 0x13, 0x08, 0x30, 0x37, 0x39, 0x36, 0x39, 0x32, 0x38, 0x37,
+ 0x30, 0x1e, 0x17, 0x0d, 0x31, 0x31, 0x30, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d,
+ 0x0f, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff, 0x04, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x05, 0xa0, 0x30, 0x0c,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x13, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff, 0x04, 0x02, 0x30, 0x00,
+ 0x30, 0x1d, 0x30, 0x0f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x13, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff,
+ 0x04, 0x05, 0x30, 0x03, 0x01, 0x01, 0x00, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55,
+ 0x1d, 0x25, 0x04, 0x16, 0x30, 0x14, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05,
+ 0x05, 0x07, 0x03, 0x01, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07,
+ 0x03, 0x02, 0x30, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x0f, 0x01, 0x01, 0xff,
+ 0x04, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x05, 0xa0, 0x30, 0x33, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d,
+ 0x1f, 0x04, 0x2c, 0x30, 0x2a, 0x30, 0x28, 0xa0, 0x26, 0xa0, 0x24, 0x86,
+ 0x22, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x2e,
+ 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f,
+ 0x67, 0x64, 0x73, 0x31, 0x2d, 0x32, 0x30, 0x2a, 0x30, 0x28, 0x06, 0x08,
+ 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x02, 0x01, 0x16, 0x1c, 0x68, 0x74,
+ 0x74, 0x70, 0x73, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x76, 0x65,
+ 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x63,
+ 0x70, 0x73, 0x30, 0x34, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x30, 0x5a, 0x17,
+ 0x0d, 0x31, 0x33, 0x30, 0x35, 0x30, 0x39, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01,
+ 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x30, 0x02, 0x86, 0x2d, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a,
+ 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x73, 0x30, 0x39, 0x30, 0x37, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01,
+ 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x02, 0x30, 0x44, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x20, 0x04,
+ 0x3d, 0x30, 0x3b, 0x30, 0x39, 0x06, 0x0b, 0x60, 0x86, 0x48, 0x01, 0x86,
+ 0xf8, 0x45, 0x01, 0x07, 0x17, 0x06, 0x31, 0x0b, 0x30, 0x09, 0x06, 0x03,
+ 0x55, 0x04, 0x06, 0x13, 0x02, 0x47, 0x42, 0x31, 0x1b, 0x53, 0x31, 0x17,
+ 0x30, 0x15, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0a, 0x13, 0x0e, 0x56, 0x65, 0x72,
+ 0x69, 0x53, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2c, 0x20, 0x49, 0x6e, 0x63, 0x2e, 0x31,
+ 0x1f, 0x30, 0x1d, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x16, 0x56, 0x65,
+ 0x72, 0x69, 0x53, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x54, 0x72, 0x75, 0x73, 0x74,
+ 0x20, 0x4e, 0x65, 0x74, 0x77, 0x6f, 0x72, 0x6b, 0x31, 0x3b, 0x30, 0x39,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x32, 0x54, 0x65, 0x72, 0x6d, 0x73,
+ 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x20, 0x75, 0x73, 0x65, 0x20, 0x61, 0x74, 0x20, 0x68,
+ 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x73, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x76,
+ 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f,
+ 0x72, 0x70, 0x61, 0x20, 0x28, 0x63, 0x29, 0x30, 0x31, 0x10, 0x30, 0x0e,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x07, 0x13, 0x07, 0x53, 0x31, 0x13, 0x30, 0x11,
+ 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x0a, 0x47, 0x31, 0x13, 0x30, 0x11,
+ 0x06, 0x0b, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x04, 0x01, 0x82, 0x37, 0x3c, 0x02, 0x01,
+ 0x03, 0x13, 0x02, 0x55, 0x31, 0x16, 0x30, 0x14, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04,
+ 0x03, 0x14, 0x31, 0x19, 0x30, 0x17, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x03, 0x13,
+ 0x31, 0x1d, 0x30, 0x1b, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0f, 0x13, 0x14, 0x50,
+ 0x72, 0x69, 0x76, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x20, 0x4f, 0x72, 0x67, 0x61, 0x6e,
+ 0x69, 0x7a, 0x61, 0x74, 0x69, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x31, 0x12, 0x31, 0x21, 0x30,
+ 0x1f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x18, 0x44, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x61,
+ 0x69, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x43, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x74, 0x72, 0x6f, 0x6c, 0x20, 0x56,
+ 0x61, 0x6c, 0x69, 0x64, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x64, 0x31, 0x14, 0x31, 0x31,
+ 0x30, 0x2f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0b, 0x13, 0x28, 0x53, 0x65, 0x65,
+ 0x20, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x72, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x73, 0x65, 0x63,
+ 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x47, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x62, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x53,
+ 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x31, 0x53, 0x65, 0x72, 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x43, 0x41,
+ 0x2e, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x56, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x53, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e,
+ 0x20, 0x43, 0x6c, 0x61, 0x73, 0x73, 0x20, 0x33, 0x20, 0x45, 0x63, 0x72,
+ 0x6c, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x65, 0x6f, 0x74, 0x72, 0x75, 0x73, 0x74, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x72, 0x6c, 0x73, 0x2f, 0x73, 0x64, 0x31, 0x1a,
+ 0x30, 0x18, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x04, 0x0a, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a,
+ 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x45, 0x56, 0x49, 0x6e, 0x74, 0x6c, 0x2d, 0x63, 0x63, 0x72,
+ 0x74, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x77, 0x77, 0x77, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x69, 0x63, 0x65, 0x72,
+ 0x74, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x31, 0x6f, 0x63, 0x73, 0x70, 0x2e,
+ 0x76, 0x65, 0x72, 0x69, 0x73, 0x69, 0x67, 0x6e, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d,
+ 0x30, 0x39, 0x72, 0x61, 0x70, 0x69, 0x64, 0x73, 0x73, 0x6c, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x73, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63,
+ 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6f, 0x73, 0x69, 0x74, 0x6f, 0x72,
+ 0x79, 0x2f, 0x30, 0x81, 0x80, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05,
+ 0x07, 0x01, 0x01, 0x04, 0x74, 0x30, 0x72, 0x30, 0x24, 0x06, 0x08, 0x2b,
+ 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x30, 0x01, 0x86, 0x18, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74,
+ 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x6f, 0x63, 0x73, 0x70, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64,
+ 0x61, 0x64, 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x30, 0x4a, 0x06,
+ 0x08, 0x2b, 0x06, 0x01, 0x05, 0x05, 0x07, 0x30, 0x02, 0x86, 0x3e, 0x68,
+ 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x65, 0x72, 0x74, 0x69, 0x66,
+ 0x69, 0x63, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x73, 0x2e, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x61, 0x64,
+ 0x64, 0x79, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x6f, 0x6d, 0x2f, 0x72, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6f, 0x73,
+ 0x69, 0x74, 0x6f, 0x72, 0x79, 0x2f, 0x67, 0x64, 0x5f, 0x69, 0x6e, 0x74,
+ 0x65, 0x72, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x64, 0x69, 0x61, 0x74, 0x65, 0x2e, 0x63, 0x72,
+ 0x74, 0x30, 0x1f, 0x06, 0x03, 0x55, 0x1d, 0x23, 0x04, 0x18, 0x30, 0x16,
+ 0x80, 0x14, 0xfd, 0xac, 0x61, 0x32, 0x93, 0x6c, 0x45, 0xd6, 0xe2, 0xee,
+ 0x85, 0x5f, 0x9a, 0xba, 0xe7, 0x76, 0x99, 0x68, 0xcc, 0xe7, 0x30, 0x27,
+ 0x86, 0x29, 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x63, 0x86, 0x30,
+ 0x68, 0x74, 0x74, 0x70, 0x3a, 0x2f, 0x2f, 0x73,
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_sets.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_sets.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1552668
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/cert_sets.go
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go-certificates"
+)
+
+type certSet [][]byte
+
+var certSets = map[uint64]certSet{
+ certsets.CertSet2Hash: certsets.CertSet2,
+ certsets.CertSet3Hash: certsets.CertSet3,
+}
+
+// findCertInSet searches for the cert in the set. Negative return value means not found.
+func (s *certSet) findCertInSet(cert []byte) int {
+ for i, c := range *s {
+ if bytes.Equal(c, cert) {
+ return i
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5c58c4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead.go
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+// +build ignore
+
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/aead/chacha20"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type aeadChacha20Poly1305 struct {
+ otherIV []byte
+ myIV []byte
+ encrypter cipher.AEAD
+ decrypter cipher.AEAD
+}
+
+// NewAEADChacha20Poly1305 creates a AEAD using chacha20poly1305
+func NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(otherKey []byte, myKey []byte, otherIV []byte, myIV []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+ if len(myKey) != 32 || len(otherKey) != 32 || len(myIV) != 4 || len(otherIV) != 4 {
+ return nil, errors.New("chacha20poly1305: expected 32-byte keys and 4-byte IVs")
+ }
+ // copy because ChaCha20Poly1305 expects array pointers
+ var MyKey, OtherKey [32]byte
+ copy(MyKey[:], myKey)
+ copy(OtherKey[:], otherKey)
+
+ encrypter, err := chacha20.NewChaCha20Poly1305WithTagSize(&MyKey, 12)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ decrypter, err := chacha20.NewChaCha20Poly1305WithTagSize(&OtherKey, 12)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return &aeadChacha20Poly1305{
+ otherIV: otherIV,
+ myIV: myIV,
+ encrypter: encrypter,
+ decrypter: decrypter,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadChacha20Poly1305) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return aead.decrypter.Open(dst, makeNonce(aead.otherIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
+
+func (aead *aeadChacha20Poly1305) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ return aead.encrypter.Seal(dst, makeNonce(aead.myIV, packetNumber), src, associatedData)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead_test.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead_test.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9d5197b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/chacha20poly1305_aead_test.go
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+// +build ignore
+
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+
+ . "github.com/onsi/ginkgo"
+ . "github.com/onsi/gomega"
+)
+
+var _ = Describe("Chacha20poly1305", func() {
+ var (
+ alice, bob AEAD
+ keyAlice, keyBob, ivAlice, ivBob []byte
+ )
+
+ BeforeEach(func() {
+ keyAlice = make([]byte, 32)
+ keyBob = make([]byte, 32)
+ ivAlice = make([]byte, 4)
+ ivBob = make([]byte, 4)
+ rand.Reader.Read(keyAlice)
+ rand.Reader.Read(keyBob)
+ rand.Reader.Read(ivAlice)
+ rand.Reader.Read(ivBob)
+ var err error
+ alice, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice, ivBob, ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ bob, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyAlice, keyBob, ivAlice, ivBob)
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ })
+
+ It("seals and opens", func() {
+ b := alice.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ text, err := bob.Open(nil, b, 42, []byte("aad"))
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ Expect(text).To(Equal([]byte("foobar")))
+ })
+
+ It("seals and opens reverse", func() {
+ b := bob.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ text, err := alice.Open(nil, b, 42, []byte("aad"))
+ Expect(err).ToNot(HaveOccurred())
+ Expect(text).To(Equal([]byte("foobar")))
+ })
+
+ It("has the proper length", func() {
+ b := bob.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ Expect(b).To(HaveLen(6 + 12))
+ })
+
+ It("fails with wrong aad", func() {
+ b := alice.Seal(nil, []byte("foobar"), 42, []byte("aad"))
+ _, err := bob.Open(nil, b, 42, []byte("aad2"))
+ Expect(err).To(HaveOccurred())
+ })
+
+ It("rejects wrong key and iv sizes", func() {
+ var err error
+ e := "chacha20poly1305: expected 32-byte keys and 4-byte IVs"
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob[1:], keyAlice, ivBob, ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice[1:], ivBob, ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice, ivBob[1:], ivAlice)
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ _, err = NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(keyBob, keyAlice, ivBob, ivAlice[1:])
+ Expect(err).To(MatchError(e))
+ })
+})
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/curve_25519.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/curve_25519.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a570d6b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/curve_25519.go
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "errors"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/curve25519"
+)
+
+// KeyExchange manages the exchange of keys
+type curve25519KEX struct {
+ secret [32]byte
+ public [32]byte
+}
+
+var _ KeyExchange = &curve25519KEX{}
+
+// NewCurve25519KEX creates a new KeyExchange using Curve25519, see https://cr.yp.to/ecdh.html
+func NewCurve25519KEX() (KeyExchange, error) {
+ c := &curve25519KEX{}
+ if _, err := rand.Read(c.secret[:]); err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.New("Curve25519: could not create private key")
+ }
+ // See https://cr.yp.to/ecdh.html
+ c.secret[0] &= 248
+ c.secret[31] &= 127
+ c.secret[31] |= 64
+ curve25519.ScalarBaseMult(&c.public, &c.secret)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+func (c *curve25519KEX) PublicKey() []byte {
+ return c.public[:]
+}
+
+func (c *curve25519KEX) CalculateSharedKey(otherPublic []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ if len(otherPublic) != 32 {
+ return nil, errors.New("Curve25519: expected public key of 32 byte")
+ }
+ var res [32]byte
+ var otherPublicArray [32]byte
+ copy(otherPublicArray[:], otherPublic)
+ curve25519.ScalarMult(&res, &c.secret, &otherPublicArray)
+ return res[:], nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_derivation.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_derivation.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..60648d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_derivation.go
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/sha256"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/hkdf"
+)
+
+// DeriveKeysChacha20 derives the client and server keys and creates a matching chacha20poly1305 AEAD instance
+// func DeriveKeysChacha20(version protocol.VersionNumber, forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo []byte, scfg []byte, cert []byte, divNonce []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+// otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV, err := deriveKeys(version, forwardSecure, sharedSecret, nonces, connID, chlo, scfg, cert, divNonce, 32)
+// if err != nil {
+// return nil, err
+// }
+// return NewAEADChacha20Poly1305(otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV)
+// }
+
+// DeriveKeysAESGCM derives the client and server keys and creates a matching AES-GCM AEAD instance
+func DeriveKeysAESGCM(forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo []byte, scfg []byte, cert []byte, divNonce []byte) (AEAD, error) {
+ otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV, err := deriveKeys(forwardSecure, sharedSecret, nonces, connID, chlo, scfg, cert, divNonce, 16)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return NewAEADAESGCM(otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV)
+}
+
+func deriveKeys(forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo, scfg, cert, divNonce []byte, keyLen int) ([]byte, []byte, []byte, []byte, error) {
+ var info bytes.Buffer
+ if forwardSecure {
+ info.Write([]byte("QUIC forward secure key expansion\x00"))
+ } else {
+ info.Write([]byte("QUIC key expansion\x00"))
+ }
+ utils.WriteUint64(&info, uint64(connID))
+ info.Write(chlo)
+ info.Write(scfg)
+ info.Write(cert)
+
+ r := hkdf.New(sha256.New, sharedSecret, nonces, info.Bytes())
+
+ s := make([]byte, 2*keyLen+2*4)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, s); err != nil {
+ return nil, nil, nil, nil, err
+ }
+ otherKey := s[:keyLen]
+ myKey := s[keyLen : 2*keyLen]
+ otherIV := s[2*keyLen : 2*keyLen+4]
+ myIV := s[2*keyLen+4:]
+
+ if !forwardSecure {
+ if err := diversify(myKey, myIV, divNonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, nil, nil, nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ return otherKey, myKey, otherIV, myIV, nil
+}
+
+func diversify(key, iv, divNonce []byte) error {
+ secret := make([]byte, len(key)+len(iv))
+ copy(secret, key)
+ copy(secret[len(key):], iv)
+
+ r := hkdf.New(sha256.New, secret, divNonce, []byte("QUIC key diversification"))
+
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, key); err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, iv); err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_exchange.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_exchange.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d240b9c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/key_exchange.go
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+package crypto
+
+// KeyExchange manages the exchange of keys
+type KeyExchange interface {
+ PublicKey() []byte
+ CalculateSharedKey(otherPublic []byte) ([]byte, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/nonce.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/nonce.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9b6d416
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/nonce.go
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+func makeNonce(iv []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber) []byte {
+ res := make([]byte, 12)
+ copy(res[0:4], iv)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(res[4:12], uint64(packetNumber))
+ return res
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/null_aead.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/null_aead.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5aa198c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/null_aead.go
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/fnv128a"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// NullAEAD handles not-yet encrypted packets
+type NullAEAD struct{}
+
+var _ AEAD = &NullAEAD{}
+
+// Open and verify the ciphertext
+func (NullAEAD) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ if len(src) < 12 {
+ return nil, errors.New("NullAEAD: ciphertext cannot be less than 12 bytes long")
+ }
+
+ hash := fnv128a.New()
+ hash.Write(associatedData)
+ hash.Write(src[12:])
+ testHigh, testLow := hash.Sum128()
+
+ low := binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(src)
+ high := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(src[8:])
+
+ if uint32(testHigh&0xffffffff) != high || testLow != low {
+ return nil, errors.New("NullAEAD: failed to authenticate received data")
+ }
+ return src[12:], nil
+}
+
+// Seal writes hash and ciphertext to the buffer
+func (NullAEAD) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ if cap(dst) < 12+len(src) {
+ dst = make([]byte, 12+len(src))
+ } else {
+ dst = dst[:12+len(src)]
+ }
+
+ hash := fnv128a.New()
+ hash.Write(associatedData)
+ hash.Write(src)
+ high, low := hash.Sum128()
+
+ copy(dst[12:], src)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(dst, low)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(dst[8:], uint32(high))
+ return dst
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/proof_source.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/proof_source.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6af8072
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/proof_source.go
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto"
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "crypto/rsa"
+ "crypto/sha256"
+ "crypto/tls"
+ "errors"
+ "strings"
+)
+
+// proofSource stores a key and a certificate for the server proof
+type proofSource struct {
+ config *tls.Config
+}
+
+// NewProofSource loads the key and cert from files
+func NewProofSource(tlsConfig *tls.Config) (Signer, error) {
+ return &proofSource{config: tlsConfig}, nil
+}
+
+// SignServerProof signs CHLO and server config for use in the server proof
+func (ps *proofSource) SignServerProof(sni string, chlo []byte, serverConfigData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ cert, err := ps.getCertForSNI(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ hash := sha256.New()
+ hash.Write([]byte("QUIC CHLO and server config signature\x00"))
+ chloHash := sha256.Sum256(chlo)
+ hash.Write([]byte{32, 0, 0, 0})
+ hash.Write(chloHash[:])
+ hash.Write(serverConfigData)
+
+ key, ok := cert.PrivateKey.(crypto.Signer)
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, errors.New("expected PrivateKey to implement crypto.Signer")
+ }
+
+ opts := crypto.SignerOpts(crypto.SHA256)
+
+ if _, ok = key.(*rsa.PrivateKey); ok {
+ opts = &rsa.PSSOptions{SaltLength: 32, Hash: crypto.SHA256}
+ }
+
+ return key.Sign(rand.Reader, hash.Sum(nil), opts)
+}
+
+// GetCertsCompressed gets the certificate in the format described by the QUIC crypto doc
+func (ps *proofSource) GetCertsCompressed(sni string, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ cert, err := ps.getCertForSNI(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return getCompressedCert(cert.Certificate, pCommonSetHashes, pCachedHashes)
+}
+
+// GetLeafCert gets the leaf certificate
+func (ps *proofSource) GetLeafCert(sni string) ([]byte, error) {
+ cert, err := ps.getCertForSNI(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return cert.Certificate[0], nil
+}
+
+func (ps *proofSource) getCertForSNI(sni string) (*tls.Certificate, error) {
+ if ps.config.GetCertificate != nil {
+ cert, err := ps.config.GetCertificate(&tls.ClientHelloInfo{ServerName: sni})
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ if cert != nil {
+ return cert, nil
+ }
+ }
+ if len(ps.config.NameToCertificate) != 0 {
+ if cert, ok := ps.config.NameToCertificate[sni]; ok {
+ return cert, nil
+ }
+ wildcardSNI := "*" + strings.TrimLeftFunc(sni, func(r rune) bool { return r != '.' })
+ if cert, ok := ps.config.NameToCertificate[wildcardSNI]; ok {
+ return cert, nil
+ }
+ }
+ if len(ps.config.Certificates) != 0 {
+ return &ps.config.Certificates[0], nil
+ }
+ return nil, errors.New("no matching certificate found")
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/signer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/signer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0d9ba4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/signer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+package crypto
+
+// A Signer holds a certificate and a private key
+type Signer interface {
+ SignServerProof(sni string, chlo []byte, serverConfigData []byte) ([]byte, error)
+ GetCertsCompressed(sni string, commonSetHashes, cachedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error)
+ GetLeafCert(sni string) ([]byte, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/source_address_token.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/source_address_token.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6afdacd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto/source_address_token.go
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+package crypto
+
+import (
+ "crypto/aes"
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "crypto/sha256"
+ "crypto/subtle"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "net"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/hkdf"
+)
+
+// StkSource is used to create and verify source address tokens
+type StkSource interface {
+ // NewToken creates a new token for a given IP address
+ NewToken(ip net.IP) ([]byte, error)
+ // VerifyToken verifies if a token matches a given IP address and is not outdated
+ VerifyToken(ip net.IP, data []byte) error
+}
+
+type sourceAddressToken struct {
+ ip net.IP
+ // unix timestamp in seconds
+ timestamp uint64
+}
+
+func (t *sourceAddressToken) serialize() []byte {
+ res := make([]byte, 8+len(t.ip))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(res, t.timestamp)
+ copy(res[8:], t.ip)
+ return res
+}
+
+func parseToken(data []byte) (*sourceAddressToken, error) {
+ if len(data) != 8+4 && len(data) != 8+16 {
+ return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid STK length: %d", len(data))
+ }
+ return &sourceAddressToken{
+ ip: data[8:],
+ timestamp: binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(data),
+ }, nil
+}
+
+type stkSource struct {
+ aead cipher.AEAD
+}
+
+const stkKeySize = 16
+
+// Chrome currently sets this to 12, but discusses changing it to 16. We start
+// at 16 :)
+const stkNonceSize = 16
+
+// NewStkSource creates a source for source address tokens
+func NewStkSource(secret []byte) (StkSource, error) {
+ key, err := deriveKey(secret)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ aead, err := cipher.NewGCMWithNonceSize(c, stkNonceSize)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return &stkSource{aead: aead}, nil
+}
+
+func (s *stkSource) NewToken(ip net.IP) ([]byte, error) {
+ return encryptToken(s.aead, &sourceAddressToken{
+ ip: ip,
+ timestamp: uint64(time.Now().Unix()),
+ })
+}
+
+func (s *stkSource) VerifyToken(ip net.IP, data []byte) error {
+ if len(data) < stkNonceSize {
+ return errors.New("STK too short")
+ }
+ nonce := data[:stkNonceSize]
+
+ res, err := s.aead.Open(nil, nonce, data[stkNonceSize:], nil)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ token, err := parseToken(res)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ if subtle.ConstantTimeCompare(token.ip, ip) != 1 {
+ return errors.New("invalid ip in STK")
+ }
+
+ if time.Now().Unix() > int64(token.timestamp)+protocol.STKExpiryTimeSec {
+ return errors.New("STK expired")
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func deriveKey(secret []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ r := hkdf.New(sha256.New, secret, nil, []byte("QUIC source address token key"))
+ key := make([]byte, stkKeySize)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, key); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return key, nil
+}
+
+func encryptToken(aead cipher.AEAD, token *sourceAddressToken) ([]byte, error) {
+ nonce := make([]byte, stkNonceSize)
+ if _, err := rand.Read(nonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return aead.Seal(nonce, nonce, token.serialize(), nil), nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_control_manager.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_control_manager.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0ab6363
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_control_manager.go
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
+package flowcontrol
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type flowControlManager struct {
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+ streamFlowController map[protocol.StreamID]*flowController
+ contributesToConnectionFlowControl map[protocol.StreamID]bool
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+}
+
+var (
+ // ErrStreamFlowControlViolation is a stream flow control violation
+ ErrStreamFlowControlViolation = errors.New("Stream level flow control violation")
+ // ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation is a connection level flow control violation
+ ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation = errors.New("Connection level flow control violation")
+)
+
+var errMapAccess = errors.New("Error accessing the flowController map.")
+
+// NewFlowControlManager creates a new flow control manager
+func NewFlowControlManager(connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager) FlowControlManager {
+ fcm := flowControlManager{
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ streamFlowController: make(map[protocol.StreamID]*flowController),
+ contributesToConnectionFlowControl: make(map[protocol.StreamID]bool),
+ }
+ // initialize connection level flow controller
+ fcm.streamFlowController[0] = newFlowController(0, connectionParametersManager)
+ fcm.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[0] = false
+ return &fcm
+}
+
+// NewStream creates new flow controllers for a stream
+func (f *flowControlManager) NewStream(streamID protocol.StreamID, contributesToConnectionFlow bool) {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ if _, ok := f.streamFlowController[streamID]; ok {
+ return
+ }
+
+ f.streamFlowController[streamID] = newFlowController(streamID, f.connectionParametersManager)
+ f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] = contributesToConnectionFlow
+}
+
+// RemoveStream removes a closed stream from flow control
+func (f *flowControlManager) RemoveStream(streamID protocol.StreamID) {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ delete(f.streamFlowController, streamID)
+ delete(f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl, streamID)
+ f.mutex.Unlock()
+}
+
+// UpdateHighestReceived updates the highest received byte offset for a stream
+// it adds the number of additional bytes to connection level flow control
+// streamID must not be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) UpdateHighestReceived(streamID protocol.StreamID, byteOffset protocol.ByteCount) error {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ increment := streamFlowController.UpdateHighestReceived(byteOffset)
+
+ if streamFlowController.CheckFlowControlViolation() {
+ return ErrStreamFlowControlViolation
+ }
+
+ if f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] {
+ connectionFlowController := f.streamFlowController[0]
+ connectionFlowController.IncrementHighestReceived(increment)
+ if connectionFlowController.CheckFlowControlViolation() {
+ return ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation
+ }
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// streamID must not be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) AddBytesRead(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ streamFlowController.AddBytesRead(n)
+
+ if f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] {
+ f.streamFlowController[0].AddBytesRead(n)
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (f *flowControlManager) GetWindowUpdates() (res []WindowUpdate) {
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ defer f.mutex.Unlock()
+ for id, fc := range f.streamFlowController {
+ if necessary, offset := fc.MaybeTriggerWindowUpdate(); necessary {
+ res = append(res, WindowUpdate{StreamID: id, Offset: offset})
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+// streamID must not be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) AddBytesSent(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ f.mutex.Unlock()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ streamFlowController.AddBytesSent(n)
+
+ if f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID] {
+ f.streamFlowController[0].AddBytesSent(n)
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// must not be called with StreamID 0
+func (f *flowControlManager) SendWindowSize(streamID protocol.StreamID) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.RLock()
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ f.mutex.RUnlock()
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ res := streamFlowController.SendWindowSize()
+
+ contributes, ok := f.contributesToConnectionFlowControl[streamID]
+ if !ok {
+ return 0, errMapAccess
+ }
+ if contributes {
+ res = utils.MinByteCount(res, f.streamFlowController[0].SendWindowSize())
+ }
+
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+func (f *flowControlManager) RemainingConnectionWindowSize() protocol.ByteCount {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.RLock()
+ res := f.streamFlowController[0].SendWindowSize()
+ f.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return res
+}
+
+// streamID may be 0 here
+func (f *flowControlManager) UpdateWindow(streamID protocol.StreamID, offset protocol.ByteCount) (bool, error) {
+ // Only lock the part reading from the map, since send-windows are only accessed from the session goroutine.
+ f.mutex.Lock()
+ streamFlowController, err := f.getFlowController(streamID)
+ f.mutex.Unlock()
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+
+ return streamFlowController.UpdateSendWindow(offset), nil
+}
+
+func (f *flowControlManager) getFlowController(streamID protocol.StreamID) (*flowController, error) {
+ streamFlowController, ok := f.streamFlowController[streamID]
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, errMapAccess
+ }
+ return streamFlowController, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_controller.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_controller.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..21020ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/flow_controller.go
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+package flowcontrol
+
+import (
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type flowController struct {
+ streamID protocol.StreamID
+
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ bytesSent protocol.ByteCount
+ sendFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+
+ bytesRead protocol.ByteCount
+ highestReceived protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// newFlowController gets a new flow controller
+func newFlowController(streamID protocol.StreamID, connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager) *flowController {
+ fc := flowController{
+ streamID: streamID,
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ }
+
+ if streamID == 0 {
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindow = connectionParametersManager.GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow()
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement = fc.receiveFlowControlWindow
+ } else {
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindow = connectionParametersManager.GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow()
+ fc.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement = fc.receiveFlowControlWindow
+ }
+
+ return &fc
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) getSendFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ if c.sendFlowControlWindow == 0 {
+ if c.streamID == 0 {
+ return c.connectionParametersManager.GetSendConnectionFlowControlWindow()
+ }
+ return c.connectionParametersManager.GetSendStreamFlowControlWindow()
+ }
+ return c.sendFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) AddBytesSent(n protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.bytesSent += n
+}
+
+// UpdateSendWindow should be called after receiving a WindowUpdateFrame
+// it returns true if the window was actually updated
+func (c *flowController) UpdateSendWindow(newOffset protocol.ByteCount) bool {
+ if newOffset > c.sendFlowControlWindow {
+ c.sendFlowControlWindow = newOffset
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) SendWindowSize() protocol.ByteCount {
+ sendFlowControlWindow := c.getSendFlowControlWindow()
+
+ if c.bytesSent > sendFlowControlWindow { // should never happen, but make sure we don't do an underflow here
+ return 0
+ }
+ return sendFlowControlWindow - c.bytesSent
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) SendWindowOffset() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return c.getSendFlowControlWindow()
+}
+
+// UpdateHighestReceived updates the highestReceived value, if the byteOffset is higher
+// Should **only** be used for the stream-level FlowController
+func (c *flowController) UpdateHighestReceived(byteOffset protocol.ByteCount) protocol.ByteCount {
+ if byteOffset > c.highestReceived {
+ increment := byteOffset - c.highestReceived
+ c.highestReceived = byteOffset
+ return increment
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// IncrementHighestReceived adds an increment to the highestReceived value
+// Should **only** be used for the connection-level FlowController
+func (c *flowController) IncrementHighestReceived(increment protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.highestReceived += increment
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) AddBytesRead(n protocol.ByteCount) {
+ c.bytesRead += n
+}
+
+// MaybeTriggerWindowUpdate determines if it is necessary to send a WindowUpdate
+// if so, it returns true and the offset of the window
+func (c *flowController) MaybeTriggerWindowUpdate() (bool, protocol.ByteCount) {
+ diff := c.receiveFlowControlWindow - c.bytesRead
+ // Chromium implements the same threshold
+ if diff < (c.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement / 2) {
+ c.receiveFlowControlWindow = c.bytesRead + c.receiveFlowControlWindowIncrement
+ return true, c.receiveFlowControlWindow
+ }
+ return false, 0
+}
+
+func (c *flowController) CheckFlowControlViolation() bool {
+ if c.highestReceived > c.receiveFlowControlWindow {
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/interface.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/interface.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3f4b089
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol/interface.go
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package flowcontrol
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// WindowUpdate provides the data for WindowUpdateFrames.
+type WindowUpdate struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ Offset protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+// A FlowControlManager manages the flow control
+type FlowControlManager interface {
+ NewStream(streamID protocol.StreamID, contributesToConnectionFlow bool)
+ RemoveStream(streamID protocol.StreamID)
+ // methods needed for receiving data
+ UpdateHighestReceived(streamID protocol.StreamID, byteOffset protocol.ByteCount) error
+ AddBytesRead(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error
+ GetWindowUpdates() []WindowUpdate
+ // methods needed for sending data
+ AddBytesSent(streamID protocol.StreamID, n protocol.ByteCount) error
+ SendWindowSize(streamID protocol.StreamID) (protocol.ByteCount, error)
+ RemainingConnectionWindowSize() protocol.ByteCount
+ UpdateWindow(streamID protocol.StreamID, offset protocol.ByteCount) (bool, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b68b448
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,466 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ // ErrInvalidAckRanges occurs when a client sends inconsistent ACK ranges
+ ErrInvalidAckRanges = errors.New("AckFrame: ACK frame contains invalid ACK ranges")
+ // ErrInvalidFirstAckRange occurs when the first ACK range contains no packets
+ ErrInvalidFirstAckRange = errors.New("AckFrame: ACK frame has invalid first ACK range")
+)
+
+var (
+ errInconsistentAckLargestAcked = errors.New("internal inconsistency: LargestAcked does not match ACK ranges")
+ errInconsistentAckLowestAcked = errors.New("internal inconsistency: LowestAcked does not match ACK ranges")
+)
+
+// An AckFrame is an ACK frame in QUIC
+type AckFrame struct {
+ LargestAcked protocol.PacketNumber
+ LowestAcked protocol.PacketNumber
+ AckRanges []AckRange // has to be ordered. The ACK range with the highest FirstPacketNumber goes first, the ACK range with the lowest FirstPacketNumber goes last
+
+ DelayTime time.Duration
+ PacketReceivedTime time.Time // only for received packets. Will not be modified for received ACKs frames
+}
+
+// ParseAckFrame reads an ACK frame
+func ParseAckFrame(r *bytes.Reader, version protocol.VersionNumber) (*AckFrame, error) {
+ frame := &AckFrame{}
+
+ typeByte, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ hasMissingRanges := false
+ if typeByte&0x20 == 0x20 {
+ hasMissingRanges = true
+ }
+
+ largestAckedLen := 2 * ((typeByte & 0x0C) >> 2)
+ if largestAckedLen == 0 {
+ largestAckedLen = 1
+ }
+
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen := 2 * (typeByte & 0x03)
+ if missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen == 0 {
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen = 1
+ }
+
+ largestAcked, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, largestAckedLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.LargestAcked = protocol.PacketNumber(largestAcked)
+
+ delay, err := utils.ReadUfloat16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.DelayTime = time.Duration(delay) * time.Microsecond
+
+ var numAckBlocks uint8
+ if hasMissingRanges {
+ numAckBlocks, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if hasMissingRanges && numAckBlocks == 0 {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidAckRanges
+ }
+
+ ackBlockLength, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ if ackBlockLength < 1 {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidFirstAckRange
+ }
+
+ if ackBlockLength > largestAcked {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidAckRanges
+ }
+
+ if hasMissingRanges {
+ ackRange := AckRange{
+ FirstPacketNumber: protocol.PacketNumber(largestAcked-ackBlockLength) + 1,
+ LastPacketNumber: frame.LargestAcked,
+ }
+ frame.AckRanges = append(frame.AckRanges, ackRange)
+
+ var inLongBlock bool
+ var lastRangeComplete bool
+ for i := uint8(0); i < numAckBlocks; i++ {
+ var gap uint8
+ gap, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ ackBlockLength, err = utils.ReadUintN(r, missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ length := protocol.PacketNumber(ackBlockLength)
+
+ if inLongBlock {
+ frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber -= protocol.PacketNumber(gap) + length
+ frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].LastPacketNumber -= protocol.PacketNumber(gap)
+ } else {
+ lastRangeComplete = false
+ ackRange := AckRange{
+ LastPacketNumber: frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber - protocol.PacketNumber(gap) - 1,
+ }
+ ackRange.FirstPacketNumber = ackRange.LastPacketNumber - length + 1
+ frame.AckRanges = append(frame.AckRanges, ackRange)
+ }
+
+ if length > 0 {
+ lastRangeComplete = true
+ }
+
+ inLongBlock = (ackBlockLength == 0)
+ }
+
+ // if the last range was not complete, FirstPacketNumber and LastPacketNumber make no sense
+ // remove the range from frame.AckRanges
+ if !lastRangeComplete {
+ frame.AckRanges = frame.AckRanges[:len(frame.AckRanges)-1]
+ }
+
+ frame.LowestAcked = frame.AckRanges[len(frame.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber
+ } else {
+ frame.LowestAcked = protocol.PacketNumber(largestAcked + 1 - ackBlockLength)
+ }
+
+ if !frame.validateAckRanges() {
+ return nil, ErrInvalidAckRanges
+ }
+
+ var numTimestamp byte
+ numTimestamp, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if numTimestamp > 0 {
+ // Delta Largest acked
+ _, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ // First Timestamp
+ _, err = utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ for i := 0; i < int(numTimestamp)-1; i++ {
+ // Delta Largest acked
+ _, err = r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ // Time Since Previous Timestamp
+ _, err = utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+// Write writes an ACK frame.
+func (f *AckFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ largestAckedLen := protocol.GetPacketNumberLength(f.LargestAcked)
+
+ typeByte := uint8(0x40)
+
+ if largestAckedLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen1 {
+ typeByte ^= (uint8(largestAckedLen / 2)) << 2
+ }
+
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen := f.getMissingSequenceNumberDeltaLen()
+ if missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen1 {
+ typeByte ^= (uint8(missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen / 2))
+ }
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ typeByte |= 0x20
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ switch largestAckedLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(f.LargestAcked))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(f.LargestAcked))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.LargestAcked))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(f.LargestAcked))
+ }
+
+ f.DelayTime = time.Now().Sub(f.PacketReceivedTime)
+ utils.WriteUfloat16(b, uint64(f.DelayTime/time.Microsecond))
+
+ var numRanges uint64
+ var numRangesWritten uint64
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ numRanges = f.numWritableNackRanges()
+ if numRanges > 0xFF {
+ panic("AckFrame: Too many ACK ranges")
+ }
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(numRanges - 1))
+ }
+
+ var firstAckBlockLength protocol.PacketNumber
+ if !f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ firstAckBlockLength = f.LargestAcked - f.LowestAcked + 1
+ } else {
+ if f.LargestAcked != f.AckRanges[0].LastPacketNumber {
+ return errInconsistentAckLargestAcked
+ }
+ if f.LowestAcked != f.AckRanges[len(f.AckRanges)-1].FirstPacketNumber {
+ return errInconsistentAckLowestAcked
+ }
+ firstAckBlockLength = f.LargestAcked - f.AckRanges[0].FirstPacketNumber + 1
+ numRangesWritten++
+ }
+
+ switch missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(firstAckBlockLength))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(firstAckBlockLength))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(firstAckBlockLength))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(firstAckBlockLength))
+ }
+
+ for i, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if i == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ length := ackRange.LastPacketNumber - ackRange.FirstPacketNumber + 1
+ gap := f.AckRanges[i-1].FirstPacketNumber - ackRange.LastPacketNumber - 1
+
+ num := gap/0xFF + 1
+ if gap%0xFF == 0 {
+ num--
+ }
+
+ if num == 1 {
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(gap))
+ switch missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(length))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(length))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(length))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(length))
+ }
+ numRangesWritten++
+ } else {
+ for i := 0; i < int(num); i++ {
+ var lengthWritten uint64
+ var gapWritten uint8
+
+ if i == int(num)-1 { // last block
+ lengthWritten = uint64(length)
+ gapWritten = uint8(1 + ((gap - 1) % 255))
+ } else {
+ lengthWritten = 0
+ gapWritten = 0xFF
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(gapWritten)
+ switch missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(lengthWritten))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(lengthWritten))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(lengthWritten))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, lengthWritten)
+ }
+
+ numRangesWritten++
+ }
+ }
+
+ // this is needed if not all AckRanges can be written to the ACK frame (if there are more than 0xFF)
+ if numRangesWritten >= numRanges {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if numRanges != numRangesWritten {
+ return errors.New("BUG: Inconsistent number of ACK ranges written")
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(0) // no timestamps
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *AckFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ var length protocol.ByteCount
+ length = 1 + 2 + 1 // 1 TypeByte, 2 ACK delay time, 1 Num Timestamp
+ length += protocol.ByteCount(protocol.GetPacketNumberLength(f.LargestAcked))
+
+ missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen := protocol.ByteCount(f.getMissingSequenceNumberDeltaLen())
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ length += (1 + missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen) * protocol.ByteCount(f.numWritableNackRanges())
+ } else {
+ length += missingSequenceNumberDeltaLen
+ }
+
+ length += (1 + 2) * 0 /* TODO: num_timestamps */
+
+ return length, nil
+}
+
+// HasMissingRanges returns if this frame reports any missing packets
+func (f *AckFrame) HasMissingRanges() bool {
+ if len(f.AckRanges) > 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func (f *AckFrame) validateAckRanges() bool {
+ if len(f.AckRanges) == 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+
+ // if there are missing packets, there will always be at least 2 ACK ranges
+ if len(f.AckRanges) == 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+
+ if f.AckRanges[0].LastPacketNumber != f.LargestAcked {
+ return false
+ }
+
+ // check the validity of every single ACK range
+ for _, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if ackRange.FirstPacketNumber > ackRange.LastPacketNumber {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+
+ // check the consistency for ACK with multiple NACK ranges
+ for i, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if i == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+ lastAckRange := f.AckRanges[i-1]
+ if lastAckRange.FirstPacketNumber <= ackRange.FirstPacketNumber {
+ return false
+ }
+ if lastAckRange.FirstPacketNumber <= ackRange.LastPacketNumber+1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+
+ return true
+}
+
+// numWritableNackRanges calculates the number of ACK blocks that are about to be written
+// this number is different from len(f.AckRanges) for the case of long gaps (> 255 packets)
+func (f *AckFrame) numWritableNackRanges() uint64 {
+ if len(f.AckRanges) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+
+ var numRanges uint64
+ for i, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if i == 0 {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ lastAckRange := f.AckRanges[i-1]
+ gap := lastAckRange.FirstPacketNumber - ackRange.LastPacketNumber - 1
+ rangeLength := 1 + uint64(gap)/0xFF
+ if uint64(gap)%0xFF == 0 {
+ rangeLength--
+ }
+
+ if numRanges+rangeLength < 0xFF {
+ numRanges += rangeLength
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ return numRanges + 1
+}
+
+func (f *AckFrame) getMissingSequenceNumberDeltaLen() protocol.PacketNumberLen {
+ var maxRangeLength protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ for _, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ rangeLength := ackRange.LastPacketNumber - ackRange.FirstPacketNumber + 1
+ if rangeLength > maxRangeLength {
+ maxRangeLength = rangeLength
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ maxRangeLength = f.LargestAcked - f.LowestAcked + 1
+ }
+
+ if maxRangeLength <= 0xFF {
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen1
+ }
+ if maxRangeLength <= 0xFFFF {
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen2
+ }
+ if maxRangeLength <= 0xFFFFFFFF {
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen4
+ }
+
+ return protocol.PacketNumberLen6
+}
+
+// AcksPacket determines if this ACK frame acks a certain packet number
+func (f *AckFrame) AcksPacket(p protocol.PacketNumber) bool {
+ if p < f.LowestAcked || p > f.LargestAcked { // this is just a performance optimization
+ return false
+ }
+
+ if f.HasMissingRanges() {
+ // TODO: this could be implemented as a binary search
+ for _, ackRange := range f.AckRanges {
+ if p >= ackRange.FirstPacketNumber && p <= ackRange.LastPacketNumber {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+ // if packet doesn't have missing ranges
+ return (p >= f.LowestAcked && p <= f.LargestAcked)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_range.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_range.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ac65d33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ack_range.go
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+package frames
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// AckRange is an ACK range
+type AckRange struct {
+ FirstPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ LastPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/blocked_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/blocked_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b7e640c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/blocked_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A BlockedFrame in QUIC
+type BlockedFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+}
+
+//Write writes a BlockedFrame frame
+func (f *BlockedFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ b.WriteByte(0x05)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *BlockedFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4, nil
+}
+
+// ParseBlockedFrame parses a BLOCKED frame
+func ParseBlockedFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*BlockedFrame, error) {
+ frame := &BlockedFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/connection_close_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/connection_close_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5681414
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/connection_close_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "io"
+ "math"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A ConnectionCloseFrame in QUIC
+type ConnectionCloseFrame struct {
+ ErrorCode qerr.ErrorCode
+ ReasonPhrase string
+}
+
+// ParseConnectionCloseFrame reads a CONNECTION_CLOSE frame
+func ParseConnectionCloseFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*ConnectionCloseFrame, error) {
+ frame := &ConnectionCloseFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ errorCode, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ErrorCode = qerr.ErrorCode(errorCode)
+
+ reasonPhraseLen, err := utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if reasonPhraseLen > uint16(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidConnectionCloseData, "reason phrase too long")
+ }
+
+ reasonPhrase := make([]byte, reasonPhraseLen)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, reasonPhrase); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ReasonPhrase = string(reasonPhrase)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *ConnectionCloseFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4 + 2 + protocol.ByteCount(len(f.ReasonPhrase)), nil
+}
+
+// Write writes an CONNECTION_CLOSE frame.
+func (f *ConnectionCloseFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ b.WriteByte(0x02)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.ErrorCode))
+
+ if len(f.ReasonPhrase) > math.MaxUint16 {
+ return errors.New("ConnectionFrame: ReasonPhrase too long")
+ }
+
+ reasonPhraseLen := uint16(len(f.ReasonPhrase))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, reasonPhraseLen)
+ b.WriteString(f.ReasonPhrase)
+
+ return nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..464e669
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A Frame in QUIC
+type Frame interface {
+ Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error
+ MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/goaway_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/goaway_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7d452d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/goaway_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A GoawayFrame is a GOAWAY frame
+type GoawayFrame struct {
+ ErrorCode qerr.ErrorCode
+ LastGoodStream protocol.StreamID
+ ReasonPhrase string
+}
+
+// ParseGoawayFrame parses a GOAWAY frame
+func ParseGoawayFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*GoawayFrame, error) {
+ frame := &GoawayFrame{}
+
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ errorCode, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ErrorCode = qerr.ErrorCode(errorCode)
+
+ lastGoodStream, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.LastGoodStream = protocol.StreamID(lastGoodStream)
+
+ reasonPhraseLen, err := utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if reasonPhraseLen > uint16(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidGoawayData, "reason phrase too long")
+ }
+
+ reasonPhrase := make([]byte, reasonPhraseLen)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, reasonPhrase); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ReasonPhrase = string(reasonPhrase)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+func (f *GoawayFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ typeByte := uint8(0x03)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.ErrorCode))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.LastGoodStream))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(len(f.ReasonPhrase)))
+ b.WriteString(f.ReasonPhrase)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *GoawayFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(1 + 4 + 4 + 2 + len(f.ReasonPhrase)), nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/log.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/log.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ac548c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/log.go
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package frames
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+
+// LogFrame logs a frame, either sent or received
+func LogFrame(frame Frame, sent bool) {
+ if !utils.Debug() {
+ return
+ }
+ dir := "<-"
+ if sent {
+ dir = "->"
+ }
+ if sf, ok := frame.(*StreamFrame); ok {
+ utils.Debugf("\t%s &frames.StreamFrame{StreamID: %d, FinBit: %t, Offset: 0x%x, Data length: 0x%x, Offset + Data length: 0x%x}", dir, sf.StreamID, sf.FinBit, sf.Offset, sf.DataLen(), sf.Offset+sf.DataLen())
+ return
+ }
+ utils.Debugf("\t%s %#v", dir, frame)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ping_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ping_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8486af5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/ping_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// A PingFrame is a ping frame
+type PingFrame struct{}
+
+// ParsePingFrame parses a Ping frame
+func ParsePingFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*PingFrame, error) {
+ frame := &PingFrame{}
+
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+func (f *PingFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ typeByte := uint8(0x07)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *PingFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/rst_stream_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/rst_stream_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8777875
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/rst_stream_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A RstStreamFrame in QUIC
+type RstStreamFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ ErrorCode uint32
+ ByteOffset protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+//Write writes a RST_STREAM frame
+func (f *RstStreamFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ b.WriteByte(0x01)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(f.ByteOffset))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, f.ErrorCode)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *RstStreamFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4 + 8 + 4, nil
+}
+
+// ParseRstStreamFrame parses a RST_STREAM frame
+func ParseRstStreamFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*RstStreamFrame, error) {
+ frame := &RstStreamFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ byteOffset, err := utils.ReadUint64(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ByteOffset = protocol.ByteCount(byteOffset)
+
+ frame.ErrorCode, err = utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stop_waiting_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stop_waiting_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8267825
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stop_waiting_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A StopWaitingFrame in QUIC
+type StopWaitingFrame struct {
+ LeastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber
+ PacketNumberLen protocol.PacketNumberLen
+ PacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+var (
+ errLeastUnackedHigherThanPacketNumber = errors.New("StopWaitingFrame: LeastUnacked can't be greater than the packet number")
+ errPacketNumberNotSet = errors.New("StopWaitingFrame: PacketNumber not set")
+ errPacketNumberLenNotSet = errors.New("StopWaitingFrame: PacketNumberLen not set")
+)
+
+func (f *StopWaitingFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ // packetNumber is the packet number of the packet that this StopWaitingFrame will be sent with
+ typeByte := uint8(0x06)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ // make sure the PacketNumber was set
+ if f.PacketNumber == protocol.PacketNumber(0) {
+ return errPacketNumberNotSet
+ }
+
+ if f.LeastUnacked > f.PacketNumber {
+ return errLeastUnackedHigherThanPacketNumber
+ }
+
+ leastUnackedDelta := uint64(f.PacketNumber - f.LeastUnacked)
+
+ switch f.PacketNumberLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(leastUnackedDelta))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(leastUnackedDelta))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(leastUnackedDelta))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, leastUnackedDelta)
+ default:
+ return errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *StopWaitingFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ var minLength protocol.ByteCount
+ minLength = 1 // typeByte
+
+ if f.PacketNumberLen == protocol.PacketNumberLenInvalid {
+ return 0, errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+ minLength += protocol.ByteCount(f.PacketNumberLen)
+
+ return minLength, nil
+}
+
+// ParseStopWaitingFrame parses a StopWaiting frame
+func ParseStopWaitingFrame(r *bytes.Reader, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, packetNumberLen protocol.PacketNumberLen, version protocol.VersionNumber) (*StopWaitingFrame, error) {
+ frame := &StopWaitingFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ leastUnackedDelta, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, uint8(packetNumberLen))
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if leastUnackedDelta > uint64(packetNumber) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStopWaitingData, "invalid LeastUnackedDelta")
+ }
+
+ frame.LeastUnacked = protocol.PacketNumber(uint64(packetNumber) - leastUnackedDelta)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stream_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stream_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fa833f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/stream_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A StreamFrame of QUIC
+type StreamFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ FinBit bool
+ DataLenPresent bool
+ Offset protocol.ByteCount
+ Data []byte
+}
+
+var (
+ errInvalidStreamIDLen = errors.New("StreamFrame: Invalid StreamID length")
+ errInvalidOffsetLen = errors.New("StreamFrame: Invalid offset length")
+)
+
+// ParseStreamFrame reads a stream frame. The type byte must not have been read yet.
+func ParseStreamFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*StreamFrame, error) {
+ frame := &StreamFrame{}
+
+ typeByte, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ frame.FinBit = typeByte&0x40 > 0
+ frame.DataLenPresent = typeByte&0x20 > 0
+ offsetLen := typeByte & 0x1C >> 2
+ if offsetLen != 0 {
+ offsetLen++
+ }
+ streamIDLen := typeByte&0x03 + 1
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, streamIDLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ offset, err := utils.ReadUintN(r, offsetLen)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.Offset = protocol.ByteCount(offset)
+
+ var dataLen uint16
+ if frame.DataLenPresent {
+ dataLen, err = utils.ReadUint16(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if dataLen > uint16(protocol.MaxPacketSize) {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamData, "data len too large")
+ }
+
+ if dataLen == 0 {
+ // The rest of the packet is data
+ dataLen = uint16(r.Len())
+ }
+ if dataLen != 0 {
+ frame.Data = make([]byte, dataLen)
+ n, err := r.Read(frame.Data)
+ if n != int(dataLen) {
+ return nil, errors.New("BUG: StreamFrame could not read dataLen bytes")
+ }
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if !frame.FinBit && len(frame.Data) == 0 {
+ return nil, qerr.EmptyStreamFrameNoFin
+ }
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
+
+// WriteStreamFrame writes a stream frame.
+func (f *StreamFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ if len(f.Data) == 0 && !f.FinBit {
+ return errors.New("StreamFrame: attempting to write empty frame without FIN")
+ }
+
+ typeByte := uint8(0x80) // sets the leftmost bit to 1
+
+ if f.FinBit {
+ typeByte ^= 0x40
+ }
+
+ if f.DataLenPresent {
+ typeByte ^= 0x20
+ }
+
+ offsetLength := f.getOffsetLength()
+
+ if offsetLength > 0 {
+ typeByte ^= (uint8(offsetLength) - 1) << 2
+ }
+
+ streamIDLen := f.calculateStreamIDLength()
+ typeByte ^= streamIDLen - 1
+
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ switch streamIDLen {
+ case 1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(f.StreamID))
+ case 2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(f.StreamID))
+ case 3:
+ utils.WriteUint24(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ case 4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ default:
+ return errInvalidStreamIDLen
+ }
+
+ switch offsetLength {
+ case 0:
+ case 2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(f.Offset))
+ case 3:
+ utils.WriteUint24(b, uint32(f.Offset))
+ case 4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.Offset))
+ case 5:
+ utils.WriteUint40(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ case 6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ case 7:
+ utils.WriteUint56(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ case 8:
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(f.Offset))
+ default:
+ return errInvalidOffsetLen
+ }
+
+ if f.DataLenPresent {
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(len(f.Data)))
+ }
+
+ b.Write(f.Data)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (f *StreamFrame) calculateStreamIDLength() uint8 {
+ if f.StreamID < (1 << 8) {
+ return 1
+ } else if f.StreamID < (1 << 16) {
+ return 2
+ } else if f.StreamID < (1 << 24) {
+ return 3
+ }
+ return 4
+}
+
+func (f *StreamFrame) getOffsetLength() protocol.ByteCount {
+ if f.Offset == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 16) {
+ return 2
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 24) {
+ return 3
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 32) {
+ return 4
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 40) {
+ return 5
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 48) {
+ return 6
+ }
+ if f.Offset < (1 << 56) {
+ return 7
+ }
+ return 8
+}
+
+// MinLength returns the length of the header of a StreamFrame
+// the total length of the StreamFrame is frame.MinLength() + frame.DataLen()
+func (f *StreamFrame) MinLength(protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ length := protocol.ByteCount(1) + protocol.ByteCount(f.calculateStreamIDLength()) + f.getOffsetLength()
+ if f.DataLenPresent {
+ length += 2
+ }
+
+ return length, nil
+}
+
+// DataLen gives the length of data in bytes
+func (f *StreamFrame) DataLen() protocol.ByteCount {
+ return protocol.ByteCount(len(f.Data))
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/window_update_frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/window_update_frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..93e7f8c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames/window_update_frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+package frames
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A WindowUpdateFrame in QUIC
+type WindowUpdateFrame struct {
+ StreamID protocol.StreamID
+ ByteOffset protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+//Write writes a RST_STREAM frame
+func (f *WindowUpdateFrame) Write(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ typeByte := uint8(0x04)
+ b.WriteByte(typeByte)
+
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(f.StreamID))
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(f.ByteOffset))
+ return nil
+}
+
+// MinLength of a written frame
+func (f *WindowUpdateFrame) MinLength(version protocol.VersionNumber) (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ return 1 + 4 + 8, nil
+}
+
+// ParseWindowUpdateFrame parses a RST_STREAM frame
+func ParseWindowUpdateFrame(r *bytes.Reader) (*WindowUpdateFrame, error) {
+ frame := &WindowUpdateFrame{}
+
+ // read the TypeByte
+ _, err := r.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ sid, err := utils.ReadUint32(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.StreamID = protocol.StreamID(sid)
+
+ byteOffset, err := utils.ReadUint64(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ frame.ByteOffset = protocol.ByteCount(byteOffset)
+
+ return frame, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/request.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/request.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f2e0fa5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/request.go
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+package h2quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "net/http"
+ "net/url"
+
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack"
+)
+
+func requestFromHeaders(headers []hpack.HeaderField) (*http.Request, error) {
+ var path, authority, method string
+ httpHeaders := http.Header{}
+
+ for _, h := range headers {
+ switch h.Name {
+ case ":path":
+ path = h.Value
+ case ":method":
+ method = h.Value
+ case ":authority":
+ authority = h.Value
+ default:
+ if !h.IsPseudo() {
+ httpHeaders.Add(h.Name, h.Value)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ if len(path) == 0 || len(authority) == 0 || len(method) == 0 {
+ return nil, errors.New(":path, :authority and :method must not be empty")
+ }
+
+ u, err := url.Parse(path)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return &http.Request{
+ Method: method,
+ URL: u,
+ Proto: "HTTP/2.0",
+ ProtoMajor: 2,
+ ProtoMinor: 0,
+ Header: httpHeaders,
+ Body: nil,
+ // ContentLength: -1,
+ Host: authority,
+ RequestURI: path,
+ }, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/response_writer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/response_writer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0b5e930
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/response_writer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+package h2quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "net/http"
+ "strconv"
+ "strings"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack"
+)
+
+type responseWriter struct {
+ dataStreamID protocol.StreamID
+ dataStream utils.Stream
+
+ headerStream utils.Stream
+ headerStreamMutex *sync.Mutex
+
+ header http.Header
+ headerWritten bool
+}
+
+func newResponseWriter(headerStream utils.Stream, headerStreamMutex *sync.Mutex, dataStream utils.Stream, dataStreamID protocol.StreamID) *responseWriter {
+ return &responseWriter{
+ header: http.Header{},
+ headerStream: headerStream,
+ headerStreamMutex: headerStreamMutex,
+ dataStream: dataStream,
+ dataStreamID: dataStreamID,
+ }
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) Header() http.Header {
+ return w.header
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) WriteHeader(status int) {
+ if w.headerWritten {
+ return
+ }
+ w.headerWritten = true
+
+ var headers bytes.Buffer
+ enc := hpack.NewEncoder(&headers)
+ enc.WriteField(hpack.HeaderField{Name: ":status", Value: strconv.Itoa(status)})
+
+ for k, v := range w.header {
+ for index := range v {
+ enc.WriteField(hpack.HeaderField{Name: strings.ToLower(k), Value: v[index]})
+ }
+ }
+
+ utils.Infof("Responding with %d", status)
+ w.headerStreamMutex.Lock()
+ defer w.headerStreamMutex.Unlock()
+ h2framer := http2.NewFramer(w.headerStream, nil)
+ err := h2framer.WriteHeaders(http2.HeadersFrameParam{
+ StreamID: uint32(w.dataStreamID),
+ EndHeaders: true,
+ BlockFragment: headers.Bytes(),
+ })
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("could not write h2 header: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) Write(p []byte) (int, error) {
+ if !w.headerWritten {
+ w.WriteHeader(200)
+ }
+ return w.dataStream.Write(p)
+}
+
+func (w *responseWriter) Flush() {}
+
+// test that we implement http.Flusher
+var _ http.Flusher = &responseWriter{}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/server.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/server.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4e301b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic/server.go
@@ -0,0 +1,335 @@
+package h2quic
+
+import (
+ "crypto/tls"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "io/ioutil"
+ "net"
+ "net/http"
+ "runtime"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2"
+ "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack"
+)
+
+type streamCreator interface {
+ GetOrOpenStream(protocol.StreamID) (utils.Stream, error)
+ Close(error) error
+ RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr
+}
+
+// Server is a HTTP2 server listening for QUIC connections.
+type Server struct {
+ *http.Server
+
+ // Private flag for demo, do not use
+ CloseAfterFirstRequest bool
+
+ port uint32 // used atomically
+
+ server *quic.Server
+ serverMutex sync.Mutex
+}
+
+// ListenAndServe listens on the UDP address s.Addr and calls s.Handler to handle HTTP/2 requests on incoming connections.
+func (s *Server) ListenAndServe() error {
+ if s.Server == nil {
+ return errors.New("use of h2quic.Server without http.Server")
+ }
+ return s.serveImpl(s.TLSConfig, nil)
+}
+
+// ListenAndServeTLS listens on the UDP address s.Addr and calls s.Handler to handle HTTP/2 requests on incoming connections.
+func (s *Server) ListenAndServeTLS(certFile, keyFile string) error {
+ var err error
+ certs := make([]tls.Certificate, 1)
+ certs[0], err = tls.LoadX509KeyPair(certFile, keyFile)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ // We currently only use the cert-related stuff from tls.Config,
+ // so we don't need to make a full copy.
+ config := &tls.Config{
+ Certificates: certs,
+ }
+ return s.serveImpl(config, nil)
+}
+
+// Serve an existing UDP connection.
+func (s *Server) Serve(conn *net.UDPConn) error {
+ return s.serveImpl(s.TLSConfig, conn)
+}
+
+func (s *Server) serveImpl(tlsConfig *tls.Config, conn *net.UDPConn) error {
+ if s.Server == nil {
+ return errors.New("use of h2quic.Server without http.Server")
+ }
+ s.serverMutex.Lock()
+ if s.server != nil {
+ s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ return errors.New("ListenAndServe may only be called once")
+ }
+ var err error
+ server, err := quic.NewServer(s.Addr, tlsConfig, s.handleStreamCb)
+ if err != nil {
+ s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ return err
+ }
+ s.server = server
+ s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ if conn == nil {
+ return server.ListenAndServe()
+ }
+ return server.Serve(conn)
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handleStreamCb(session *quic.Session, stream utils.Stream) {
+ s.handleStream(session, stream)
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handleStream(session streamCreator, stream utils.Stream) {
+ if stream.StreamID() != 3 {
+ return
+ }
+
+ hpackDecoder := hpack.NewDecoder(4096, nil)
+ h2framer := http2.NewFramer(nil, stream)
+
+ go func() {
+ var headerStreamMutex sync.Mutex // Protects concurrent calls to Write()
+ for {
+ if err := s.handleRequest(session, stream, &headerStreamMutex, hpackDecoder, h2framer); err != nil {
+ // QuicErrors must originate from stream.Read() returning an error.
+ // In this case, the session has already logged the error, so we don't
+ // need to log it again.
+ if _, ok := err.(*qerr.QuicError); !ok {
+ utils.Errorf("error handling h2 request: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ }
+ }()
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handleRequest(session streamCreator, headerStream utils.Stream, headerStreamMutex *sync.Mutex, hpackDecoder *hpack.Decoder, h2framer *http2.Framer) error {
+ h2frame, err := h2framer.ReadFrame()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ h2headersFrame := h2frame.(*http2.HeadersFrame)
+ if !h2headersFrame.HeadersEnded() {
+ return errors.New("http2 header continuation not implemented")
+ }
+ headers, err := hpackDecoder.DecodeFull(h2headersFrame.HeaderBlockFragment())
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("invalid http2 headers encoding: %s", err.Error())
+ return err
+ }
+
+ req, err := requestFromHeaders(headers)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ req.RemoteAddr = session.RemoteAddr().String()
+
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Infof("%s %s%s, on data stream %d", req.Method, req.Host, req.RequestURI, h2headersFrame.StreamID)
+ } else {
+ utils.Infof("%s %s%s", req.Method, req.Host, req.RequestURI)
+ }
+
+ dataStream, err := session.GetOrOpenStream(protocol.StreamID(h2headersFrame.StreamID))
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ if h2headersFrame.StreamEnded() {
+ dataStream.CloseRemote(0)
+ _, _ = dataStream.Read([]byte{0}) // read the eof
+ }
+
+ // stream's Close() closes the write side, not the read side
+ req.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(dataStream)
+
+ responseWriter := newResponseWriter(headerStream, headerStreamMutex, dataStream, protocol.StreamID(h2headersFrame.StreamID))
+
+ go func() {
+ handler := s.Handler
+ if handler == nil {
+ handler = http.DefaultServeMux
+ }
+ panicked := false
+ func() {
+ defer func() {
+ if p := recover(); p != nil {
+ // Copied from net/http/server.go
+ const size = 64 << 10
+ buf := make([]byte, size)
+ buf = buf[:runtime.Stack(buf, false)]
+ utils.Errorf("http: panic serving: %v\n%s", p, buf)
+ panicked = true
+ }
+ }()
+ handler.ServeHTTP(responseWriter, req)
+ }()
+ if panicked {
+ responseWriter.WriteHeader(500)
+ } else {
+ responseWriter.WriteHeader(200)
+ }
+ if responseWriter.dataStream != nil {
+ responseWriter.dataStream.Close()
+ }
+ if s.CloseAfterFirstRequest {
+ time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
+ session.Close(nil)
+ }
+ }()
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Close the server immediately, aborting requests and sending CONNECTION_CLOSE frames to connected clients.
+// Close in combination with ListenAndServe() (instead of Serve()) may race if it is called before a UDP socket is established.
+func (s *Server) Close() error {
+ s.serverMutex.Lock()
+ defer s.serverMutex.Unlock()
+ if s.server != nil {
+ err := s.server.Close()
+ s.server = nil
+ return err
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// CloseGracefully shuts down the server gracefully. The server sends a GOAWAY frame first, then waits for either timeout to trigger, or for all running requests to complete.
+// CloseGracefully in combination with ListenAndServe() (instead of Serve()) may race if it is called before a UDP socket is established.
+func (s *Server) CloseGracefully(timeout time.Duration) error {
+ // TODO: implement
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetQuicHeaders can be used to set the proper headers that announce that this server supports QUIC.
+// The values that are set depend on the port information from s.Server.Addr, and currently look like this (if Addr has port 443):
+// Alternate-Protocol: 443:quic
+// Alt-Svc: quic=":443"; ma=2592000; v="33,32,31,30"
+func (s *Server) SetQuicHeaders(hdr http.Header) error {
+ port := atomic.LoadUint32(&s.port)
+
+ if port == 0 {
+ // Extract port from s.Server.Addr
+ _, portStr, err := net.SplitHostPort(s.Server.Addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ portInt, err := net.LookupPort("tcp", portStr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ port = uint32(portInt)
+ atomic.StoreUint32(&s.port, port)
+ }
+
+ hdr.Add("Alternate-Protocol", fmt.Sprintf("%d:quic", port))
+ hdr.Add("Alt-Svc", fmt.Sprintf(`quic=":%d"; ma=2592000; v="%s"`, port, protocol.SupportedVersionsAsString))
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// ListenAndServeQUIC listens on the UDP network address addr and calls the
+// handler for HTTP/2 requests on incoming connections. http.DefaultServeMux is
+// used when handler is nil.
+func ListenAndServeQUIC(addr, certFile, keyFile string, handler http.Handler) error {
+ server := &Server{
+ Server: &http.Server{
+ Addr: addr,
+ Handler: handler,
+ },
+ }
+ return server.ListenAndServeTLS(certFile, keyFile)
+}
+
+// ListenAndServe listens on the given network address for both, TLS and QUIC
+// connetions in parallel. It returns if one of the two returns an error.
+// http.DefaultServeMux is used when handler is nil.
+// The correct Alt-Svc headers for QUIC are set.
+func ListenAndServe(addr, certFile, keyFile string, handler http.Handler) error {
+ // Load certs
+ var err error
+ certs := make([]tls.Certificate, 1)
+ certs[0], err = tls.LoadX509KeyPair(certFile, keyFile)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ // We currently only use the cert-related stuff from tls.Config,
+ // so we don't need to make a full copy.
+ config := &tls.Config{
+ Certificates: certs,
+ }
+
+ // Open the listeners
+ udpAddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ udpConn, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", udpAddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ defer udpConn.Close()
+
+ tcpAddr, err := net.ResolveTCPAddr("tcp", addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ tcpConn, err := net.ListenTCP("tcp", tcpAddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ defer tcpConn.Close()
+
+ // Start the servers
+ httpServer := &http.Server{
+ Addr: addr,
+ TLSConfig: config,
+ }
+
+ quicServer := &Server{
+ Server: httpServer,
+ }
+
+ if handler == nil {
+ handler = http.DefaultServeMux
+ }
+ httpServer.Handler = http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
+ quicServer.SetQuicHeaders(w.Header())
+ handler.ServeHTTP(w, r)
+ })
+
+ hErr := make(chan error)
+ qErr := make(chan error)
+ go func() {
+ hErr <- httpServer.Serve(tcpConn)
+ }()
+ go func() {
+ qErr <- quicServer.Serve(udpConn)
+ }()
+
+ select {
+ case err := <-hErr:
+ quicServer.Close()
+ return err
+ case err := <-qErr:
+ // Cannot close the HTTP server or wait for requests to complete properly :/
+ return err
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/connection_parameters_manager.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/connection_parameters_manager.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..df26119
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/connection_parameters_manager.go
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "errors"
+ "sync"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// ConnectionParametersManager stores the connection parameters
+// Warning: Writes may only be done from the crypto stream, see the comment
+// in GetSHLOMap().
+type ConnectionParametersManager struct {
+ params map[Tag][]byte
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+
+ flowControlNegotiated bool // have the flow control parameters for sending already been negotiated
+
+ maxStreamsPerConnection uint32
+ idleConnectionStateLifetime time.Duration
+ sendStreamFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ sendConnectionFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveStreamFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+ receiveConnectionFlowControlWindow protocol.ByteCount
+}
+
+var errTagNotInConnectionParameterMap = errors.New("ConnectionParametersManager: Tag not found in ConnectionsParameter map")
+
+// ErrMalformedTag is returned when the tag value cannot be read
+var (
+ ErrMalformedTag = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidCryptoMessageParameter, "malformed Tag value")
+ ErrFlowControlRenegotiationNotSupported = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidCryptoMessageParameter, "renegotiation of flow control parameters not supported")
+)
+
+// NewConnectionParamatersManager creates a new connection parameters manager
+func NewConnectionParamatersManager() *ConnectionParametersManager {
+ return &ConnectionParametersManager{
+ params: make(map[Tag][]byte),
+ idleConnectionStateLifetime: protocol.DefaultIdleTimeout,
+ sendStreamFlowControlWindow: protocol.InitialStreamFlowControlWindow, // can only be changed by the client
+ sendConnectionFlowControlWindow: protocol.InitialConnectionFlowControlWindow, // can only be changed by the client
+ receiveStreamFlowControlWindow: protocol.ReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow,
+ receiveConnectionFlowControlWindow: protocol.ReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow,
+ maxStreamsPerConnection: protocol.MaxStreamsPerConnection,
+ }
+}
+
+// SetFromMap reads all params
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) SetFromMap(params map[Tag][]byte) error {
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ for key, value := range params {
+ switch key {
+ case TagTCID:
+ h.params[key] = value
+ case TagMSPC:
+ clientValue, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.maxStreamsPerConnection = h.negotiateMaxStreamsPerConnection(clientValue)
+ case TagICSL:
+ clientValue, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.idleConnectionStateLifetime = h.negotiateIdleConnectionStateLifetime(time.Duration(clientValue) * time.Second)
+ case TagSFCW:
+ if h.flowControlNegotiated {
+ return ErrFlowControlRenegotiationNotSupported
+ }
+ sendStreamFlowControlWindow, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.sendStreamFlowControlWindow = protocol.ByteCount(sendStreamFlowControlWindow)
+ case TagCFCW:
+ if h.flowControlNegotiated {
+ return ErrFlowControlRenegotiationNotSupported
+ }
+ sendConnectionFlowControlWindow, err := utils.ReadUint32(bytes.NewBuffer(value))
+ if err != nil {
+ return ErrMalformedTag
+ }
+ h.sendConnectionFlowControlWindow = protocol.ByteCount(sendConnectionFlowControlWindow)
+ }
+ }
+
+ _, containsSFCW := params[TagSFCW]
+ _, containsCFCW := params[TagCFCW]
+ if containsCFCW || containsSFCW {
+ h.flowControlNegotiated = true
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) negotiateMaxStreamsPerConnection(clientValue uint32) uint32 {
+ return utils.MinUint32(clientValue, protocol.MaxStreamsPerConnection)
+}
+
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) negotiateIdleConnectionStateLifetime(clientValue time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ return utils.MinDuration(clientValue, protocol.MaxIdleTimeout)
+}
+
+// getRawValue gets the byte-slice for a tag
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) getRawValue(tag Tag) ([]byte, error) {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ rawValue, ok := h.params[tag]
+ h.mutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if !ok {
+ return nil, errTagNotInConnectionParameterMap
+ }
+ return rawValue, nil
+}
+
+// GetSHLOMap gets all values (except crypto values) needed for the SHLO
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetSHLOMap() map[Tag][]byte {
+ sfcw := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(sfcw, uint32(h.GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow()))
+ cfcw := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(cfcw, uint32(h.GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow()))
+ mspc := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(mspc, h.GetMaxStreamsPerConnection())
+ mids := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(mids, protocol.MaxIncomingDynamicStreams)
+ icsl := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
+ utils.WriteUint32(icsl, uint32(h.GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime()/time.Second))
+
+ return map[Tag][]byte{
+ TagICSL: icsl.Bytes(),
+ TagMSPC: mspc.Bytes(),
+ TagMIDS: mids.Bytes(),
+ TagCFCW: cfcw.Bytes(),
+ TagSFCW: sfcw.Bytes(),
+ }
+}
+
+// GetSendStreamFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for sending data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetSendStreamFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.sendStreamFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetSendConnectionFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for sending data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetSendConnectionFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.sendConnectionFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.receiveStreamFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow gets the size of the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow() protocol.ByteCount {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.receiveConnectionFlowControlWindow
+}
+
+// GetMaxStreamsPerConnection gets the maximum number of streams per connection
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetMaxStreamsPerConnection() uint32 {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.maxStreamsPerConnection
+}
+
+// GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime gets the idle timeout
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime() time.Duration {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return h.idleConnectionStateLifetime
+}
+
+// TruncateConnectionID determines if the client requests truncated ConnectionIDs
+func (h *ConnectionParametersManager) TruncateConnectionID() bool {
+ rawValue, err := h.getRawValue(TagTCID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false
+ }
+ if len(rawValue) != 4 {
+ return false
+ }
+ value := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(rawValue)
+ if value == 0 {
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/crypto_setup.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/crypto_setup.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..56e9764
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/crypto_setup.go
@@ -0,0 +1,327 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "io"
+ "net"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// KeyDerivationFunction is used for key derivation
+type KeyDerivationFunction func(forwardSecure bool, sharedSecret, nonces []byte, connID protocol.ConnectionID, chlo []byte, scfg []byte, cert []byte, divNonce []byte) (crypto.AEAD, error)
+
+// KeyExchangeFunction is used to make a new KEX
+type KeyExchangeFunction func() crypto.KeyExchange
+
+// The CryptoSetup handles all things crypto for the Session
+type CryptoSetup struct {
+ connID protocol.ConnectionID
+ ip net.IP
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+ scfg *ServerConfig
+ diversificationNonce []byte
+
+ secureAEAD crypto.AEAD
+ forwardSecureAEAD crypto.AEAD
+ receivedForwardSecurePacket bool
+ receivedSecurePacket bool
+ aeadChanged chan struct{}
+
+ keyDerivation KeyDerivationFunction
+ keyExchange KeyExchangeFunction
+
+ cryptoStream utils.Stream
+
+ connectionParametersManager *ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+}
+
+var _ crypto.AEAD = &CryptoSetup{}
+
+// NewCryptoSetup creates a new CryptoSetup instance
+func NewCryptoSetup(
+ connID protocol.ConnectionID,
+ ip net.IP,
+ version protocol.VersionNumber,
+ scfg *ServerConfig,
+ cryptoStream utils.Stream,
+ connectionParametersManager *ConnectionParametersManager,
+ aeadChanged chan struct{},
+) (*CryptoSetup, error) {
+ return &CryptoSetup{
+ connID: connID,
+ ip: ip,
+ version: version,
+ scfg: scfg,
+ keyDerivation: crypto.DeriveKeysAESGCM,
+ keyExchange: getEphermalKEX,
+ cryptoStream: cryptoStream,
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ aeadChanged: aeadChanged,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+// HandleCryptoStream reads and writes messages on the crypto stream
+func (h *CryptoSetup) HandleCryptoStream() error {
+ for {
+ var chloData bytes.Buffer
+ messageTag, cryptoData, err := ParseHandshakeMessage(io.TeeReader(h.cryptoStream, &chloData))
+ if err != nil {
+ return qerr.HandshakeFailed
+ }
+ if messageTag != TagCHLO {
+ return qerr.InvalidCryptoMessageType
+ }
+
+ utils.Debugf("Got CHLO:\n%s", printHandshakeMessage(cryptoData))
+
+ done, err := h.handleMessage(chloData.Bytes(), cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if done {
+ return nil
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) handleMessage(chloData []byte, cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) (bool, error) {
+ sniSlice, ok := cryptoData[TagSNI]
+ if !ok {
+ return false, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoMessageParameterNotFound, "SNI required")
+ }
+ sni := string(sniSlice)
+ if sni == "" {
+ return false, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoMessageParameterNotFound, "SNI required")
+ }
+
+ var reply []byte
+ var err error
+ if !h.isInchoateCHLO(cryptoData) {
+ // We have a CHLO with a proper server config ID, do a 0-RTT handshake
+ reply, err = h.handleCHLO(sni, chloData, cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ _, err = h.cryptoStream.Write(reply)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ // We have an inchoate or non-matching CHLO, we now send a rejection
+ reply, err = h.handleInchoateCHLO(sni, chloData, cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ _, err = h.cryptoStream.Write(reply)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ return false, nil
+}
+
+// Open a message
+func (h *CryptoSetup) Open(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+ defer h.mutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if h.forwardSecureAEAD != nil {
+ res, err := h.forwardSecureAEAD.Open(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ if err == nil {
+ h.receivedForwardSecurePacket = true
+ return res, nil
+ }
+ if h.receivedForwardSecurePacket {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+ if h.secureAEAD != nil {
+ res, err := h.secureAEAD.Open(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ if err == nil {
+ h.receivedSecurePacket = true
+ return res, nil
+ }
+ if h.receivedSecurePacket {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+ return (&crypto.NullAEAD{}).Open(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+}
+
+// Seal a message, call LockForSealing() before!
+func (h *CryptoSetup) Seal(dst, src []byte, packetNumber protocol.PacketNumber, associatedData []byte) []byte {
+ if h.receivedForwardSecurePacket {
+ return h.forwardSecureAEAD.Seal(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ } else if h.secureAEAD != nil {
+ return h.secureAEAD.Seal(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ } else {
+ return (&crypto.NullAEAD{}).Seal(dst, src, packetNumber, associatedData)
+ }
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) isInchoateCHLO(cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) bool {
+ scid, ok := cryptoData[TagSCID]
+ if !ok || !bytes.Equal(h.scfg.ID, scid) {
+ return true
+ }
+ if _, ok := cryptoData[TagPUBS]; !ok {
+ return true
+ }
+ if err := h.scfg.stkSource.VerifyToken(h.ip, cryptoData[TagSTK]); err != nil {
+ utils.Infof("STK invalid: %s", err.Error())
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) handleInchoateCHLO(sni string, chlo []byte, cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ if len(chlo) < protocol.ClientHelloMinimumSize {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoInvalidValueLength, "CHLO too small")
+ }
+
+ token, err := h.scfg.stkSource.NewToken(h.ip)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ replyMap := map[Tag][]byte{
+ TagSCFG: h.scfg.Get(),
+ TagSTK: token,
+ TagSVID: []byte("quic-go"),
+ }
+
+ if h.scfg.stkSource.VerifyToken(h.ip, cryptoData[TagSTK]) == nil {
+ proof, err := h.scfg.Sign(sni, chlo)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ commonSetHashes := cryptoData[TagCCS]
+ cachedCertsHashes := cryptoData[TagCCRT]
+
+ certCompressed, err := h.scfg.GetCertsCompressed(sni, commonSetHashes, cachedCertsHashes)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ // Token was valid, send more details
+ replyMap[TagPROF] = proof
+ replyMap[TagCERT] = certCompressed
+ }
+
+ var serverReply bytes.Buffer
+ WriteHandshakeMessage(&serverReply, TagREJ, replyMap)
+ return serverReply.Bytes(), nil
+}
+
+func (h *CryptoSetup) handleCHLO(sni string, data []byte, cryptoData map[Tag][]byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ // We have a CHLO matching our server config, we can continue with the 0-RTT handshake
+ sharedSecret, err := h.scfg.kex.CalculateSharedKey(cryptoData[TagPUBS])
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ h.mutex.Lock()
+ defer h.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ certUncompressed, err := h.scfg.signer.GetLeafCert(sni)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ nonce := make([]byte, 32)
+ if _, err = rand.Read(nonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ h.diversificationNonce = make([]byte, 32)
+ if _, err = rand.Read(h.diversificationNonce); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ h.secureAEAD, err = h.keyDerivation(
+ false,
+ sharedSecret,
+ cryptoData[TagNONC],
+ h.connID,
+ data,
+ h.scfg.Get(),
+ certUncompressed,
+ h.diversificationNonce,
+ )
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ // Generate a new curve instance to derive the forward secure key
+ var fsNonce bytes.Buffer
+ fsNonce.Write(cryptoData[TagNONC])
+ fsNonce.Write(nonce)
+ ephermalKex := h.keyExchange()
+ ephermalSharedSecret, err := ephermalKex.CalculateSharedKey(cryptoData[TagPUBS])
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ h.forwardSecureAEAD, err = h.keyDerivation(
+ true,
+ ephermalSharedSecret,
+ fsNonce.Bytes(),
+ h.connID,
+ data,
+ h.scfg.Get(),
+ certUncompressed,
+ nil,
+ )
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ err = h.connectionParametersManager.SetFromMap(cryptoData)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ replyMap := h.connectionParametersManager.GetSHLOMap()
+ // add crypto parameters
+ replyMap[TagPUBS] = ephermalKex.PublicKey()
+ replyMap[TagSNO] = nonce
+ replyMap[TagVER] = protocol.SupportedVersionsAsTags
+
+ var reply bytes.Buffer
+ WriteHandshakeMessage(&reply, TagSHLO, replyMap)
+
+ h.aeadChanged <- struct{}{}
+
+ return reply.Bytes(), nil
+}
+
+// DiversificationNonce returns a diversification nonce if required in the next packet to be Seal'ed. See LockForSealing()!
+func (h *CryptoSetup) DiversificationNonce() []byte {
+ if h.receivedForwardSecurePacket || h.secureAEAD == nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return h.diversificationNonce
+}
+
+// LockForSealing should be called before Seal(). It is needed so that diversification nonces can be obtained before packets are sealed, and the AEADs are not changed in the meantime.
+func (h *CryptoSetup) LockForSealing() {
+ h.mutex.RLock()
+}
+
+// UnlockForSealing should be called after Seal() is complete, see LockForSealing().
+func (h *CryptoSetup) UnlockForSealing() {
+ h.mutex.RUnlock()
+}
+
+// HandshakeComplete returns true after the first forward secure packet was received form the client.
+func (h *CryptoSetup) HandshakeComplete() bool {
+ return h.receivedForwardSecurePacket
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/ephermal_cache.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/ephermal_cache.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..794bcbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/ephermal_cache.go
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "sync"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ kexLifetime = protocol.EphermalKeyLifetime
+ kexCurrent crypto.KeyExchange
+ kexCurrentTime time.Time
+ kexMutex sync.RWMutex
+)
+
+// getEphermalKEX returns the currently active KEX, which changes every protocol.EphermalKeyLifetime
+// See the explanation from the QUIC crypto doc:
+//
+// A single connection is the usual scope for forward security, but the security
+// difference between an ephemeral key used for a single connection, and one
+// used for all connections for 60 seconds is negligible. Thus we can amortise
+// the Diffie-Hellman key generation at the server over all the connections in a
+// small time span.
+func getEphermalKEX() (res crypto.KeyExchange) {
+ kexMutex.RLock()
+ res = kexCurrent
+ t := kexCurrentTime
+ kexMutex.RUnlock()
+ if res != nil && time.Now().Sub(t) < kexLifetime {
+ return res
+ }
+
+ kexMutex.Lock()
+ defer kexMutex.Unlock()
+ // Check if still unfulfilled
+ if kexCurrent == nil || time.Now().Sub(kexCurrentTime) > kexLifetime {
+ kex, err := crypto.NewCurve25519KEX()
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("could not set KEX: %s", err.Error())
+ return kexCurrent
+ }
+ kexCurrent = kex
+ kexCurrentTime = time.Now()
+ return kexCurrent
+ }
+ return kexCurrent
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/handshake_message.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/handshake_message.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..013c44b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/handshake_message.go
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "sort"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// ParseHandshakeMessage reads a crypto message
+func ParseHandshakeMessage(r io.Reader) (Tag, map[Tag][]byte, error) {
+ slice4 := make([]byte, 4)
+
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, slice4); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+ messageTag := Tag(binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(slice4))
+
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, slice4); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+ nPairs := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(slice4)
+
+ if nPairs > protocol.CryptoMaxParams {
+ return 0, nil, qerr.CryptoTooManyEntries
+ }
+
+ index := make([]byte, nPairs*8)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, index); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+
+ resultMap := map[Tag][]byte{}
+
+ var dataStart uint32
+ for indexPos := 0; indexPos < int(nPairs)*8; indexPos += 8 {
+ tag := Tag(binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(index[indexPos : indexPos+4]))
+ dataEnd := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(index[indexPos+4 : indexPos+8])
+
+ dataLen := dataEnd - dataStart
+ if dataLen > protocol.CryptoParameterMaxLength {
+ return 0, nil, qerr.Error(qerr.CryptoInvalidValueLength, "value too long")
+ }
+
+ data := make([]byte, dataLen)
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, data); err != nil {
+ return 0, nil, err
+ }
+
+ resultMap[tag] = data
+ dataStart = dataEnd
+ }
+
+ return messageTag, resultMap, nil
+}
+
+// WriteHandshakeMessage writes a crypto message
+func WriteHandshakeMessage(b *bytes.Buffer, messageTag Tag, data map[Tag][]byte) {
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(messageTag))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(len(data)))
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, 0)
+
+ // Save current position in the buffer, so that we can update the index in-place later
+ indexStart := b.Len()
+
+ indexData := make([]byte, 8*len(data))
+ b.Write(indexData) // Will be updated later
+
+ // Sort the tags
+ tags := make([]uint32, len(data))
+ i := 0
+ for t := range data {
+ tags[i] = uint32(t)
+ i++
+ }
+ sort.Sort(utils.Uint32Slice(tags))
+
+ offset := uint32(0)
+ for i, t := range tags {
+ v := data[Tag(t)]
+ b.Write(v)
+ offset += uint32(len(v))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(indexData[i*8:], t)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(indexData[i*8+4:], offset)
+ }
+
+ // Now we write the index data for real
+ copy(b.Bytes()[indexStart:], indexData)
+}
+
+func printHandshakeMessage(data map[Tag][]byte) string {
+ var res string
+ for k, v := range data {
+ if k == TagPAD {
+ continue
+ }
+ res += fmt.Sprintf("\t%s: %#v\n", tagToString(k), string(v))
+ }
+ return res
+}
+
+func tagToString(tag Tag) string {
+ b := make([]byte, 4)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(b, uint32(tag))
+ for i := range b {
+ if b[i] == 0 {
+ b[i] = ' '
+ }
+ }
+ return string(b)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/server_config.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/server_config.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dc33e97
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/server_config.go
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+package handshake
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/rand"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+)
+
+// ServerConfig is a server config
+type ServerConfig struct {
+ kex crypto.KeyExchange
+ signer crypto.Signer
+ ID []byte
+ stkSource crypto.StkSource
+}
+
+// NewServerConfig creates a new server config
+func NewServerConfig(kex crypto.KeyExchange, signer crypto.Signer) (*ServerConfig, error) {
+ id := make([]byte, 16)
+ _, err := rand.Read(id)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ stkSecret := make([]byte, 32)
+ if _, err = rand.Read(stkSecret); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ stkSource, err := crypto.NewStkSource(stkSecret)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return &ServerConfig{
+ kex: kex,
+ signer: signer,
+ ID: id,
+ stkSource: stkSource,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+// Get the server config binary representation
+func (s *ServerConfig) Get() []byte {
+ var serverConfig bytes.Buffer
+ WriteHandshakeMessage(&serverConfig, TagSCFG, map[Tag][]byte{
+ TagSCID: s.ID,
+ TagKEXS: []byte("C255"),
+ TagAEAD: []byte("AESG"),
+ TagPUBS: append([]byte{0x20, 0x00, 0x00}, s.kex.PublicKey()...),
+ TagOBIT: {0x0, 0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4, 0x5, 0x6, 0x7},
+ TagEXPY: {0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff},
+ })
+ return serverConfig.Bytes()
+}
+
+// Sign the server config and CHLO with the server's keyData
+func (s *ServerConfig) Sign(sni string, chlo []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return s.signer.SignServerProof(sni, chlo, s.Get())
+}
+
+// GetCertsCompressed returns the certificate data
+func (s *ServerConfig) GetCertsCompressed(sni string, commonSetHashes, compressedHashes []byte) ([]byte, error) {
+ return s.signer.GetCertsCompressed(sni, commonSetHashes, compressedHashes)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/tags.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/tags.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..92d4d84
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake/tags.go
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+package handshake
+
+// A Tag in the QUIC crypto
+type Tag uint32
+
+const (
+ // TagCHLO is a client hello
+ TagCHLO Tag = 'C' + 'H'<<8 + 'L'<<16 + 'O'<<24
+ // TagREJ is a server hello rejection
+ TagREJ Tag = 'R' + 'E'<<8 + 'J'<<16
+ // TagSCFG is a server config
+ TagSCFG Tag = 'S' + 'C'<<8 + 'F'<<16 + 'G'<<24
+
+ // TagPAD is padding
+ TagPAD Tag = 'P' + 'A'<<8 + 'D'<<16
+ // TagSNI is the server name indication
+ TagSNI Tag = 'S' + 'N'<<8 + 'I'<<16
+ // TagVER is the QUIC version
+ TagVER Tag = 'V' + 'E'<<8 + 'R'<<16
+ // TagCCS are the hashes of the common certificate sets
+ TagCCS Tag = 'C' + 'C'<<8 + 'S'<<16
+ // TagCCRT are the hashes of the cached certificates
+ TagCCRT Tag = 'C' + 'C'<<8 + 'R'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagMSPC is max streams per connection
+ TagMSPC Tag = 'M' + 'S'<<8 + 'P'<<16 + 'C'<<24
+ // TagMIDS is max incoming dyanamic streams
+ TagMIDS Tag = 'M' + 'I'<<8 + 'D'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagUAID is the user agent ID
+ TagUAID Tag = 'U' + 'A'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagSVID is the server ID (unofficial tag by us :)
+ TagSVID Tag = 'S' + 'V'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagTCID is truncation of the connection ID
+ TagTCID Tag = 'T' + 'C'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagPDMD is the proof demand
+ TagPDMD Tag = 'P' + 'D'<<8 + 'M'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagSRBF is the socket receive buffer
+ TagSRBF Tag = 'S' + 'R'<<8 + 'B'<<16 + 'F'<<24
+ // TagICSL is the idle connection state lifetime
+ TagICSL Tag = 'I' + 'C'<<8 + 'S'<<16 + 'L'<<24
+ // TagNONP is the client proof nonce
+ TagNONP Tag = 'N' + 'O'<<8 + 'N'<<16 + 'P'<<24
+ // TagSCLS is the silently close timeout
+ TagSCLS Tag = 'S' + 'C'<<8 + 'L'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagCSCT is the signed cert timestamp (RFC6962) of leaf cert
+ TagCSCT Tag = 'C' + 'S'<<8 + 'C'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagCOPT are the connection options
+ TagCOPT Tag = 'C' + 'O'<<8 + 'P'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagCFCW is the initial session/connection flow control receive window
+ TagCFCW Tag = 'C' + 'F'<<8 + 'C'<<16 + 'W'<<24
+ // TagSFCW is the initial stream flow control receive window.
+ TagSFCW Tag = 'S' + 'F'<<8 + 'C'<<16 + 'W'<<24
+
+ // TagSTK is the source-address token
+ TagSTK Tag = 'S' + 'T'<<8 + 'K'<<16
+ // TagSNO is the server nonce
+ TagSNO Tag = 'S' + 'N'<<8 + 'O'<<16
+ // TagPROF is the server proof
+ TagPROF Tag = 'P' + 'R'<<8 + 'O'<<16 + 'F'<<24
+
+ // TagNONC is the client nonce
+ TagNONC Tag = 'N' + 'O'<<8 + 'N'<<16 + 'C'<<24
+
+ // TagSCID is the server config ID
+ TagSCID Tag = 'S' + 'C'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagKEXS is the list of key exchange algos
+ TagKEXS Tag = 'K' + 'E'<<8 + 'X'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagAEAD is the list of AEAD algos
+ TagAEAD Tag = 'A' + 'E'<<8 + 'A'<<16 + 'D'<<24
+ // TagPUBS is the public value for the KEX
+ TagPUBS Tag = 'P' + 'U'<<8 + 'B'<<16 + 'S'<<24
+ // TagOBIT is the client orbit
+ TagOBIT Tag = 'O' + 'B'<<8 + 'I'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagEXPY is the server config expiry
+ TagEXPY Tag = 'E' + 'X'<<8 + 'P'<<16 + 'Y'<<24
+ // TagCERT is the CERT data
+ TagCERT Tag = 0xff545243
+
+ // TagSHLO is the server hello
+ TagSHLO Tag = 'S' + 'H'<<8 + 'L'<<16 + 'O'<<24
+
+ // TagPRST is the public reset tag
+ TagPRST Tag = 'P' + 'R'<<8 + 'S'<<16 + 'T'<<24
+ // TagRSEQ is the public reset rejected packet number
+ TagRSEQ Tag = 'R' + 'S'<<8 + 'E'<<16 + 'Q'<<24
+ // TagRNON is the public reset nonce
+ TagRNON Tag = 'R' + 'N'<<8 + 'O'<<16 + 'N'<<24
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_number_generator.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_number_generator.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..71ca9a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_number_generator.go
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "math"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// The packetNumberGenerator generates the packet number for the next packet
+// it randomly skips a packet number every averagePeriod packets (on average)
+// it is guarantued to never skip two consecutive packet numbers
+type packetNumberGenerator struct {
+ averagePeriod protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ next protocol.PacketNumber
+ nextToSkip protocol.PacketNumber
+}
+
+func newPacketNumberGenerator(averagePeriod protocol.PacketNumber) *packetNumberGenerator {
+ return &packetNumberGenerator{
+ next: 1,
+ averagePeriod: averagePeriod,
+ }
+}
+
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) Peek() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ return p.next
+}
+
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) Pop() protocol.PacketNumber {
+ next := p.next
+
+ // generate a new packet number for the next packet
+ p.next++
+
+ if p.next == p.nextToSkip {
+ p.next++
+ p.generateNewSkip()
+ }
+
+ return next
+}
+
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) generateNewSkip() error {
+ num, err := p.getRandomNumber()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ skip := protocol.PacketNumber(num) * (p.averagePeriod - 1) / (math.MaxUint16 / 2)
+ // make sure that there are never two consecutive packet numbers that are skipped
+ p.nextToSkip = p.next + 2 + skip
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// getRandomNumber() generates a cryptographically secure random number between 0 and MaxUint16 (= 65535)
+// The expectation value is 65535/2
+func (p *packetNumberGenerator) getRandomNumber() (uint16, error) {
+ b := make([]byte, 2)
+ _, err := rand.Read(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+
+ num := uint16(b[0])<<8 + uint16(b[1])
+ return num, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_packer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_packer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..359fa73
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_packer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,203 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+type packedPacket struct {
+ number protocol.PacketNumber
+ raw []byte
+ frames []frames.Frame
+}
+
+type packetPacker struct {
+ connectionID protocol.ConnectionID
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+ cryptoSetup *handshake.CryptoSetup
+
+ packetNumberGenerator *packetNumberGenerator
+
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ streamFramer *streamFramer
+ controlFrames []frames.Frame
+}
+
+func newPacketPacker(connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, cryptoSetup *handshake.CryptoSetup, connectionParametersHandler *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager, streamFramer *streamFramer, version protocol.VersionNumber) *packetPacker {
+ return &packetPacker{
+ cryptoSetup: cryptoSetup,
+ connectionID: connectionID,
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersHandler,
+ version: version,
+ streamFramer: streamFramer,
+ packetNumberGenerator: newPacketNumberGenerator(protocol.SkipPacketAveragePeriodLength),
+ }
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) PackConnectionClose(frame *frames.ConnectionCloseFrame, leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber) (*packedPacket, error) {
+ return p.packPacket(nil, []frames.Frame{frame}, leastUnacked, true, false)
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) PackPacket(stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame, controlFrames []frames.Frame, leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber, maySendOnlyAck bool) (*packedPacket, error) {
+ return p.packPacket(stopWaitingFrame, controlFrames, leastUnacked, false, maySendOnlyAck)
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) packPacket(stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame, controlFrames []frames.Frame, leastUnacked protocol.PacketNumber, onlySendOneControlFrame, maySendOnlyAck bool) (*packedPacket, error) {
+ if len(controlFrames) > 0 {
+ p.controlFrames = append(p.controlFrames, controlFrames...)
+ }
+
+ currentPacketNumber := p.packetNumberGenerator.Peek()
+
+ // cryptoSetup needs to be locked here, so that the AEADs are not changed between
+ // calling DiversificationNonce() and Seal().
+ p.cryptoSetup.LockForSealing()
+ defer p.cryptoSetup.UnlockForSealing()
+
+ packetNumberLen := protocol.GetPacketNumberLengthForPublicHeader(currentPacketNumber, leastUnacked)
+ responsePublicHeader := &PublicHeader{
+ ConnectionID: p.connectionID,
+ PacketNumber: currentPacketNumber,
+ PacketNumberLen: packetNumberLen,
+ TruncateConnectionID: p.connectionParametersManager.TruncateConnectionID(),
+ DiversificationNonce: p.cryptoSetup.DiversificationNonce(),
+ }
+
+ publicHeaderLength, err := responsePublicHeader.GetLength()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ stopWaitingFrame.PacketNumber = currentPacketNumber
+ stopWaitingFrame.PacketNumberLen = packetNumberLen
+ }
+
+ var payloadFrames []frames.Frame
+ if onlySendOneControlFrame {
+ payloadFrames = []frames.Frame{controlFrames[0]}
+ } else {
+ payloadFrames, err = p.composeNextPacket(stopWaitingFrame, publicHeaderLength)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Check if we have enough frames to send
+ if len(payloadFrames) == 0 {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ // Don't send out packets that only contain a StopWaitingFrame
+ if !onlySendOneControlFrame && len(payloadFrames) == 1 && stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ // Don't send out packets that only contain an ACK (plus optional STOP_WAITING), if requested
+ if !maySendOnlyAck {
+ if len(payloadFrames) == 1 {
+ if _, ok := payloadFrames[0].(*frames.AckFrame); ok {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ } else if len(payloadFrames) == 2 && stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ if _, ok := payloadFrames[1].(*frames.AckFrame); ok {
+ return nil, nil
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ raw := getPacketBuffer()
+ buffer := bytes.NewBuffer(raw)
+
+ if err = responsePublicHeader.WritePublicHeader(buffer, p.version); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ payloadStartIndex := buffer.Len()
+
+ for _, frame := range payloadFrames {
+ err := frame.Write(buffer, p.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ }
+
+ if protocol.ByteCount(buffer.Len()+12) > protocol.MaxPacketSize {
+ return nil, errors.New("PacketPacker BUG: packet too large")
+ }
+
+ raw = raw[0:buffer.Len()]
+ p.cryptoSetup.Seal(raw[payloadStartIndex:payloadStartIndex], raw[payloadStartIndex:], currentPacketNumber, raw[:payloadStartIndex])
+ raw = raw[0 : buffer.Len()+12]
+
+ num := p.packetNumberGenerator.Pop()
+ if num != currentPacketNumber {
+ return nil, errors.New("PacketPacker BUG: Peeked and Popped packet numbers do not match.")
+ }
+
+ return &packedPacket{
+ number: currentPacketNumber,
+ raw: raw,
+ frames: payloadFrames,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) composeNextPacket(stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame, publicHeaderLength protocol.ByteCount) ([]frames.Frame, error) {
+ var payloadLength protocol.ByteCount
+ var payloadFrames []frames.Frame
+
+ maxFrameSize := protocol.MaxFrameAndPublicHeaderSize - publicHeaderLength
+
+ if stopWaitingFrame != nil {
+ payloadFrames = append(payloadFrames, stopWaitingFrame)
+ minLength, err := stopWaitingFrame.MinLength(p.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ payloadLength += minLength
+ }
+
+ for len(p.controlFrames) > 0 {
+ frame := p.controlFrames[len(p.controlFrames)-1]
+ minLength, _ := frame.MinLength(p.version) // controlFrames does not contain any StopWaitingFrames. So it will *never* return an error
+ if payloadLength+minLength > maxFrameSize {
+ break
+ }
+ payloadFrames = append(payloadFrames, frame)
+ payloadLength += minLength
+ p.controlFrames = p.controlFrames[:len(p.controlFrames)-1]
+ }
+
+ if payloadLength > maxFrameSize {
+ return nil, fmt.Errorf("Packet Packer BUG: packet payload (%d) too large (%d)", payloadLength, maxFrameSize)
+ }
+
+ // temporarily increase the maxFrameSize by 2 bytes
+ // this leads to a properly sized packet in all cases, since we do all the packet length calculations with StreamFrames that have the DataLen set
+ // however, for the last StreamFrame in the packet, we can omit the DataLen, thus saving 2 bytes and yielding a packet of exactly the correct size
+ maxFrameSize += 2
+
+ fs := p.streamFramer.PopStreamFrames(maxFrameSize - payloadLength)
+ if len(fs) != 0 {
+ fs[len(fs)-1].DataLenPresent = false
+ }
+
+ // TODO: Simplify
+ for _, f := range fs {
+ payloadFrames = append(payloadFrames, f)
+ }
+
+ for b := p.streamFramer.PopBlockedFrame(); b != nil; b = p.streamFramer.PopBlockedFrame() {
+ p.controlFrames = append(p.controlFrames, b)
+ }
+
+ return payloadFrames, nil
+}
+
+func (p *packetPacker) QueueControlFrameForNextPacket(f frames.Frame) {
+ p.controlFrames = append(p.controlFrames, f)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_unpacker.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_unpacker.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3434751
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/packet_unpacker.go
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+)
+
+type unpackedPacket struct {
+ frames []frames.Frame
+}
+
+type packetUnpacker struct {
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+ aead crypto.AEAD
+}
+
+func (u *packetUnpacker) Unpack(publicHeaderBinary []byte, hdr *PublicHeader, data []byte) (*unpackedPacket, error) {
+ buf := getPacketBuffer()
+ defer putPacketBuffer(buf)
+ decrypted, err := u.aead.Open(buf, data, hdr.PacketNumber, publicHeaderBinary)
+ if err != nil {
+ // Wrap err in quicError so that public reset is sent by session
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.DecryptionFailure, err.Error())
+ }
+ r := bytes.NewReader(decrypted)
+
+ if r.Len() == 0 {
+ return nil, qerr.MissingPayload
+ }
+
+ fs := make([]frames.Frame, 0, 2)
+
+ // Read all frames in the packet
+ReadLoop:
+ for r.Len() > 0 {
+ typeByte, _ := r.ReadByte()
+ r.UnreadByte()
+
+ var frame frames.Frame
+ if typeByte&0x80 == 0x80 {
+ frame, err = frames.ParseStreamFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamData, err.Error())
+ }
+ } else if typeByte&0xc0 == 0x40 {
+ frame, err = frames.ParseAckFrame(r, u.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidAckData, err.Error())
+ }
+ } else if typeByte&0xe0 == 0x20 {
+ err = errors.New("unimplemented: CONGESTION_FEEDBACK")
+ } else {
+ switch typeByte {
+ case 0x0: // PAD, end of frames
+ break ReadLoop
+ case 0x01:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseRstStreamFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidRstStreamData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x02:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseConnectionCloseFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidConnectionCloseData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x03:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseGoawayFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidGoawayData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x04:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseWindowUpdateFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidWindowUpdateData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x05:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseBlockedFrame(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidBlockedData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x06:
+ frame, err = frames.ParseStopWaitingFrame(r, hdr.PacketNumber, hdr.PacketNumberLen, u.version)
+ if err != nil {
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStopWaitingData, err.Error())
+ }
+ case 0x07:
+ frame, err = frames.ParsePingFrame(r)
+ default:
+ err = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidFrameData, fmt.Sprintf("unknown type byte 0x%x", typeByte))
+ }
+ }
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ if frame != nil {
+ fs = append(fs, frame)
+ }
+ }
+
+ return &unpackedPacket{
+ frames: fs,
+ }, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/packet_number.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/packet_number.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c4f468a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/packet_number.go
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+package protocol
+
+// InferPacketNumber calculates the packet number based on the received packet number, its length and the last seen packet number
+func InferPacketNumber(packetNumberLength PacketNumberLen, lastPacketNumber PacketNumber, wirePacketNumber PacketNumber) PacketNumber {
+ epochDelta := PacketNumber(1) << (uint8(packetNumberLength) * 8)
+ epoch := lastPacketNumber & ^(epochDelta - 1)
+ prevEpochBegin := epoch - epochDelta
+ nextEpochBegin := epoch + epochDelta
+ return closestTo(
+ lastPacketNumber+1,
+ epoch+wirePacketNumber,
+ closestTo(lastPacketNumber+1, prevEpochBegin+wirePacketNumber, nextEpochBegin+wirePacketNumber),
+ )
+}
+
+func closestTo(target, a, b PacketNumber) PacketNumber {
+ if delta(target, a) < delta(target, b) {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+func delta(a, b PacketNumber) PacketNumber {
+ if a < b {
+ return b - a
+ }
+ return a - b
+}
+
+// GetPacketNumberLengthForPublicHeader gets the length of the packet number for the public header
+// it never chooses a PacketNumberLen of 1 byte, since this is too short under certain circumstances
+func GetPacketNumberLengthForPublicHeader(packetNumber PacketNumber, leastUnacked PacketNumber) PacketNumberLen {
+ diff := uint64(packetNumber - leastUnacked)
+ if diff < (2 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen2)*8 - 2)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen2
+ }
+ if diff < (2 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen4)*8 - 2)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen4
+ }
+ // we do not check if there are less than 2^46 packets in flight, since flow control and congestion control will limit this number *a lot* sooner
+ return PacketNumberLen6
+}
+
+// GetPacketNumberLength gets the minimum length needed to fully represent the packet number
+func GetPacketNumberLength(packetNumber PacketNumber) PacketNumberLen {
+ if packetNumber < (1 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen1) * 8)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen1
+ }
+ if packetNumber < (1 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen2) * 8)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen2
+ }
+ if packetNumber < (1 << (uint8(PacketNumberLen4) * 8)) {
+ return PacketNumberLen4
+ }
+ return PacketNumberLen6
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/protocol.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/protocol.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aae2e0a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/protocol.go
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+package protocol
+
+import (
+ "math"
+ "time"
+)
+
+// A PacketNumber in QUIC
+type PacketNumber uint64
+
+// PacketNumberLen is the length of the packet number in bytes
+type PacketNumberLen uint8
+
+const (
+ // PacketNumberLenInvalid is the default value and not a valid length for a packet number
+ PacketNumberLenInvalid PacketNumberLen = 0
+ // PacketNumberLen1 is a packet number length of 1 byte
+ PacketNumberLen1 PacketNumberLen = 1
+ // PacketNumberLen2 is a packet number length of 2 bytes
+ PacketNumberLen2 PacketNumberLen = 2
+ // PacketNumberLen4 is a packet number length of 4 bytes
+ PacketNumberLen4 PacketNumberLen = 4
+ // PacketNumberLen6 is a packet number length of 6 bytes
+ PacketNumberLen6 PacketNumberLen = 6
+)
+
+// A ConnectionID in QUIC
+type ConnectionID uint64
+
+// A StreamID in QUIC
+type StreamID uint32
+
+// A ByteCount in QUIC
+type ByteCount uint64
+
+// MaxByteCount is the maximum value of a ByteCount
+const MaxByteCount = math.MaxUint64
+
+// MaxPacketSize is the maximum packet size, including the public header
+// This is the value used by Chromium for a QUIC packet sent using IPv6 (for IPv4 it would be 1370)
+const MaxPacketSize ByteCount = 1350
+
+// MaxFrameAndPublicHeaderSize is the maximum size of a QUIC frame plus PublicHeader
+const MaxFrameAndPublicHeaderSize = MaxPacketSize - 12 /*crypto signature*/
+
+// DefaultTCPMSS is the default maximum packet size used in the Linux TCP implementation.
+// Used in QUIC for congestion window computations in bytes.
+const DefaultTCPMSS ByteCount = 1460
+
+// InitialStreamFlowControlWindow is the initial stream-level flow control window for sending
+const InitialStreamFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 14) // 16 kB
+
+// InitialConnectionFlowControlWindow is the initial connection-level flow control window for sending
+const InitialConnectionFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 14) // 16 kB
+
+// DefaultRetransmissionTime is the RTO time on new connections
+const DefaultRetransmissionTime = 500 * time.Millisecond
+
+// MinRetransmissionTime is the minimum RTO time
+const MinRetransmissionTime = 200 * time.Millisecond
+
+// MaxRetransmissionTime is the maximum RTO time
+const MaxRetransmissionTime = 60 * time.Second
+
+// ClientHelloMinimumSize is the minimum size the server expects an inchoate CHLO to have.
+const ClientHelloMinimumSize = 1024
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/server_parameters.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/server_parameters.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..99894a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/server_parameters.go
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+package protocol
+
+import "time"
+
+// DefaultMaxCongestionWindow is the default for the max congestion window
+const DefaultMaxCongestionWindow PacketNumber = 1000
+
+// InitialCongestionWindow is the initial congestion window in QUIC packets
+const InitialCongestionWindow PacketNumber = 32
+
+// MaxUndecryptablePackets limits the number of undecryptable packets that a
+// session queues for later until it sends a public reset.
+const MaxUndecryptablePackets = 10
+
+// AckSendDelay is the maximal time delay applied to packets containing only ACKs
+const AckSendDelay = 5 * time.Millisecond
+
+// ReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow is the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+// This is the value that Google servers are using
+const ReceiveStreamFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 20) // 1 MB
+
+// ReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow is the stream-level flow control window for receiving data
+// This is the value that Google servers are using
+const ReceiveConnectionFlowControlWindow ByteCount = (1 << 20) * 1.5 // 1.5 MB
+
+// MaxStreamsPerConnection is the maximum value accepted for the number of streams per connection
+const MaxStreamsPerConnection = 100
+
+// MaxIncomingDynamicStreams is the maximum value accepted for the incoming number of dynamic streams per connection
+const MaxIncomingDynamicStreams = 100
+
+// MaxStreamsMultiplier is the slack the client is allowed for the maximum number of streams per connection, needed e.g. when packets are out of order or dropped. The minimum of this procentual increase and the absolute increment specified by MaxStreamsMinimumIncrement is used.
+const MaxStreamsMultiplier = 1.1
+
+// MaxStreamsMinimumIncrement is the slack the client is allowed for the maximum number of streams per connection, needed e.g. when packets are out of order or dropped. The minimum of this absolute increment and the procentual increase specified by MaxStreamsMultiplier is used.
+const MaxStreamsMinimumIncrement = 10
+
+// MaxNewStreamIDDelta is the maximum difference between and a newly opened Stream and the highest StreamID that a client has ever opened
+// note that the number of streams is half this value, since the client can only open streams with open StreamID
+const MaxNewStreamIDDelta = 4 * MaxStreamsPerConnection
+
+// MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets is the max number of packets stored in each session that are not yet processed.
+const MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets = DefaultMaxCongestionWindow
+
+// RetransmissionThreshold + 1 is the number of times a packet has to be NACKed so that it gets retransmitted
+const RetransmissionThreshold = 3
+
+// SkipPacketAveragePeriodLength is the average period length in which one packet number is skipped to prevent an Optimistic ACK attack
+const SkipPacketAveragePeriodLength PacketNumber = 500
+
+// MaxTrackedSkippedPackets is the maximum number of skipped packet numbers the SentPacketHandler keep track of for Optimistic ACK attack mitigation
+const MaxTrackedSkippedPackets = 10
+
+// STKExpiryTimeSec is the valid time of a source address token in seconds
+const STKExpiryTimeSec = 24 * 60 * 60
+
+// MaxTrackedSentPackets is maximum number of sent packets saved for either later retransmission or entropy calculation
+const MaxTrackedSentPackets = 2 * DefaultMaxCongestionWindow
+
+// MaxTrackedReceivedPackets is the maximum number of received packets saved for doing the entropy calculations
+const MaxTrackedReceivedPackets = 2 * DefaultMaxCongestionWindow
+
+// MaxStreamFrameSorterGaps is the maximum number of gaps between received StreamFrames
+// prevents DOS attacks against the streamFrameSorter
+const MaxStreamFrameSorterGaps = 1000
+
+// CryptoMaxParams is the upper limit for the number of parameters in a crypto message.
+// Value taken from Chrome.
+const CryptoMaxParams = 128
+
+// CryptoParameterMaxLength is the upper limit for the length of a parameter in a crypto message.
+const CryptoParameterMaxLength = 2000
+
+// EphermalKeyLifetime is the lifetime of the ephermal key during the handshake, see handshake.getEphermalKEX.
+const EphermalKeyLifetime = time.Minute
+
+// InitialIdleTimeout is the timeout before the handshake succeeds.
+const InitialIdleTimeout = 5 * time.Second
+
+// DefaultIdleTimeout is the default idle timeout.
+const DefaultIdleTimeout = 30 * time.Second
+
+// MaxIdleTimeout is the maximum idle timeout that can be negotiated.
+const MaxIdleTimeout = 1 * time.Minute
+
+// MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake is the default timeout for a connection until the crypto handshake succeeds.
+const MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake = 10 * time.Second
+
+// NumCachedCertificates is the number of cached compressed certificate chains, each taking ~1K space
+const NumCachedCertificates = 128
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/version.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/version.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cd0cd47
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol/version.go
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+package protocol
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "strconv"
+)
+
+// VersionNumber is a version number as int
+type VersionNumber int
+
+// The version numbers, making grepping easier
+const (
+ Version34 VersionNumber = 34 + iota
+ Version35
+ Version36
+ VersionWhatever = 0 // for when the version doesn't matter
+)
+
+// SupportedVersions lists the versions that the server supports
+var SupportedVersions = []VersionNumber{
+ Version34, Version35, Version36,
+}
+
+// SupportedVersionsAsTags is needed for the SHLO crypto message
+var SupportedVersionsAsTags []byte
+
+// SupportedVersionsAsString is needed for the Alt-Scv HTTP header
+var SupportedVersionsAsString string
+
+// VersionNumberToTag maps version numbers ('32') to tags ('Q032')
+func VersionNumberToTag(vn VersionNumber) uint32 {
+ v := uint32(vn)
+ return 'Q' + ((v/100%10)+'0')<<8 + ((v/10%10)+'0')<<16 + ((v%10)+'0')<<24
+}
+
+// VersionTagToNumber is built from VersionNumberToTag in init()
+func VersionTagToNumber(v uint32) VersionNumber {
+ return VersionNumber(((v>>8)&0xff-'0')*100 + ((v>>16)&0xff-'0')*10 + ((v>>24)&0xff - '0'))
+}
+
+// IsSupportedVersion returns true if the server supports this version
+func IsSupportedVersion(v VersionNumber) bool {
+ for _, t := range SupportedVersions {
+ if t == v {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+}
+
+func init() {
+ var b bytes.Buffer
+ for _, v := range SupportedVersions {
+ s := make([]byte, 4)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(s, VersionNumberToTag(v))
+ b.Write(s)
+ }
+ SupportedVersionsAsTags = b.Bytes()
+
+ for i := len(SupportedVersions) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
+ SupportedVersionsAsString += strconv.Itoa(int(SupportedVersions[i]))
+ if i != 0 {
+ SupportedVersionsAsString += ","
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_header.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_header.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..475c1b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_header.go
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "errors"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+var (
+ errPacketNumberLenNotSet = errors.New("PublicHeader: PacketNumberLen not set")
+ errResetAndVersionFlagSet = errors.New("PublicHeader: Reset Flag and Version Flag should not be set at the same time")
+ errReceivedTruncatedConnectionID = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidPacketHeader, "receiving packets with truncated ConnectionID is not supported")
+ errInvalidConnectionID = qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidPacketHeader, "connection ID cannot be 0")
+ errGetLengthOnlyForRegularPackets = errors.New("PublicHeader: GetLength can only be called for regular packets")
+)
+
+// The PublicHeader of a QUIC packet
+type PublicHeader struct {
+ Raw []byte
+ ConnectionID protocol.ConnectionID
+ VersionFlag bool
+ ResetFlag bool
+ TruncateConnectionID bool
+ PacketNumberLen protocol.PacketNumberLen
+ PacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ VersionNumber protocol.VersionNumber
+ DiversificationNonce []byte
+}
+
+// WritePublicHeader writes a public header
+func (h *PublicHeader) WritePublicHeader(b *bytes.Buffer, version protocol.VersionNumber) error {
+ publicFlagByte := uint8(0x00)
+ if h.VersionFlag && h.ResetFlag {
+ return errResetAndVersionFlagSet
+ }
+ if h.VersionFlag {
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x01
+ }
+ if h.ResetFlag {
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x02
+ }
+ if !h.TruncateConnectionID {
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x08
+ }
+
+ if len(h.DiversificationNonce) > 0 {
+ if len(h.DiversificationNonce) != 32 {
+ return errors.New("invalid diversification nonce length")
+ }
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x04
+ }
+
+ if !h.ResetFlag && !h.VersionFlag {
+ switch h.PacketNumberLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x00
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x10
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x20
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ publicFlagByte |= 0x30
+ }
+ }
+
+ b.WriteByte(publicFlagByte)
+
+ if !h.TruncateConnectionID {
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(h.ConnectionID))
+ }
+
+ if len(h.DiversificationNonce) > 0 {
+ b.Write(h.DiversificationNonce)
+ }
+
+ if !h.ResetFlag && !h.VersionFlag {
+ switch h.PacketNumberLen {
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen1:
+ b.WriteByte(uint8(h.PacketNumber))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen2:
+ utils.WriteUint16(b, uint16(h.PacketNumber))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen4:
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(h.PacketNumber))
+ case protocol.PacketNumberLen6:
+ utils.WriteUint48(b, uint64(h.PacketNumber))
+ default:
+ return errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// ParsePublicHeader parses a QUIC packet's public header
+func ParsePublicHeader(b io.ByteReader) (*PublicHeader, error) {
+ header := &PublicHeader{}
+
+ // First byte
+ publicFlagByte, err := b.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.VersionFlag = publicFlagByte&0x01 > 0
+ header.ResetFlag = publicFlagByte&0x02 > 0
+
+ // TODO: activate this check once Chrome sends the correct value
+ // see https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/issues/232
+ // if publicFlagByte&0x04 > 0 {
+ // return nil, errors.New("diversification nonces should only be sent by servers")
+ // }
+
+ if publicFlagByte&0x08 == 0 {
+ return nil, errReceivedTruncatedConnectionID
+ }
+
+ switch publicFlagByte & 0x30 {
+ case 0x30:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen6
+ case 0x20:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen4
+ case 0x10:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen2
+ case 0x00:
+ header.PacketNumberLen = protocol.PacketNumberLen1
+ }
+
+ // Connection ID
+ connID, err := utils.ReadUint64(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.ConnectionID = protocol.ConnectionID(connID)
+ if header.ConnectionID == 0 {
+ return nil, errInvalidConnectionID
+ }
+
+ // Version (optional)
+ if header.VersionFlag {
+ var versionTag uint32
+ versionTag, err = utils.ReadUint32(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.VersionNumber = protocol.VersionTagToNumber(versionTag)
+ }
+
+ // Packet number
+ packetNumber, err := utils.ReadUintN(b, uint8(header.PacketNumberLen))
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ header.PacketNumber = protocol.PacketNumber(packetNumber)
+
+ return header, nil
+}
+
+// GetLength gets the length of the publicHeader in bytes
+// can only be called for regular packets
+func (h *PublicHeader) GetLength() (protocol.ByteCount, error) {
+ if h.VersionFlag || h.ResetFlag {
+ return 0, errGetLengthOnlyForRegularPackets
+ }
+
+ length := protocol.ByteCount(1) // 1 byte for public flags
+ if h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen1 && h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen2 && h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen4 && h.PacketNumberLen != protocol.PacketNumberLen6 {
+ return 0, errPacketNumberLenNotSet
+ }
+ if !h.TruncateConnectionID {
+ length += 8 // 8 bytes for the connection ID
+ }
+ length += protocol.ByteCount(len(h.DiversificationNonce))
+ length += protocol.ByteCount(h.PacketNumberLen)
+ return length, nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_reset.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_reset.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7cceb2e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/public_reset.go
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+func writePublicReset(connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, rejectedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber, nonceProof uint64) []byte {
+ b := &bytes.Buffer{}
+ b.WriteByte(0x0a)
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(connectionID))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(handshake.TagPRST))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, 2)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(handshake.TagRNON))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, 8)
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, uint32(handshake.TagRSEQ))
+ utils.WriteUint32(b, 16)
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, nonceProof)
+ utils.WriteUint64(b, uint64(rejectedPacketNumber))
+ return b.Bytes()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/error_codes.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/error_codes.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4797530
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/error_codes.go
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+package qerr
+
+// The error codes defined by QUIC
+// Remember to run `go generate ./...` whenever the error codes change.
+//go:generate stringer -type=ErrorCode
+const (
+ InternalError ErrorCode = 1
+ // There were data frames after the a fin or reset.
+ StreamDataAfterTermination ErrorCode = 2
+ // Control frame is malformed.
+ InvalidPacketHeader ErrorCode = 3
+ // Frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidFrameData ErrorCode = 4
+ // The packet contained no payload.
+ MissingPayload ErrorCode = 48
+ // FEC data is malformed.
+ InvalidFecData ErrorCode = 5
+ // STREAM frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidStreamData ErrorCode = 46
+ // STREAM frame data overlaps with buffered data.
+ OverlappingStreamData ErrorCode = 87
+ // Received STREAM frame data is not encrypted.
+ UnencryptedStreamData ErrorCode = 61
+ // Attempt to send unencrypted STREAM frame.
+ AttemptToSendUnencryptedStreamData ErrorCode = 88
+ // FEC frame data is not encrypted.
+ UnencryptedFecData ErrorCode = 77
+ // RST_STREAM frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidRstStreamData ErrorCode = 6
+ // CONNECTION_CLOSE frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidConnectionCloseData ErrorCode = 7
+ // GOAWAY frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidGoawayData ErrorCode = 8
+ // WINDOW_UPDATE frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidWindowUpdateData ErrorCode = 57
+ // BLOCKED frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidBlockedData ErrorCode = 58
+ // STOP_WAITING frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidStopWaitingData ErrorCode = 60
+ // PATH_CLOSE frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidPathCloseData ErrorCode = 78
+ // ACK frame data is malformed.
+ InvalidAckData ErrorCode = 9
+
+ // Version negotiation packet is malformed.
+ InvalidVersionNegotiationPacket ErrorCode = 10
+ // Public RST packet is malformed.
+ InvalidPublicRstPacket ErrorCode = 11
+ // There was an error decrypting.
+ DecryptionFailure ErrorCode = 12
+ // There was an error encrypting.
+ EncryptionFailure ErrorCode = 13
+ // The packet exceeded kMaxPacketSize.
+ PacketTooLarge ErrorCode = 14
+ // The peer is going away. May be a client or server.
+ PeerGoingAway ErrorCode = 16
+ // A stream ID was invalid.
+ InvalidStreamID ErrorCode = 17
+ // A priority was invalid.
+ InvalidPriority ErrorCode = 49
+ // Too many streams already open.
+ TooManyOpenStreams ErrorCode = 18
+ // The peer created too many available streams.
+ TooManyAvailableStreams ErrorCode = 76
+ // Received public reset for this connection.
+ PublicReset ErrorCode = 19
+ // Invalid protocol version.
+ InvalidVersion ErrorCode = 20
+
+ // The Header ID for a stream was too far from the previous.
+ InvalidHeaderID ErrorCode = 22
+ // Negotiable parameter received during handshake had invalid value.
+ InvalidNegotiatedValue ErrorCode = 23
+ // There was an error decompressing data.
+ DecompressionFailure ErrorCode = 24
+ // The connection timed out due to no network activity.
+ NetworkIdleTimeout ErrorCode = 25
+ // The connection timed out waiting for the handshake to complete.
+ HandshakeTimeout ErrorCode = 67
+ // There was an error encountered migrating addresses.
+ ErrorMigratingAddress ErrorCode = 26
+ // There was an error encountered migrating port only.
+ ErrorMigratingPort ErrorCode = 86
+ // There was an error while writing to the socket.
+ PacketWriteError ErrorCode = 27
+ // There was an error while reading from the socket.
+ PacketReadError ErrorCode = 51
+ // We received a STREAM_FRAME with no data and no fin flag set.
+ EmptyStreamFrameNoFin ErrorCode = 50
+ // We received invalid data on the headers stream.
+ InvalidHeadersStreamData ErrorCode = 56
+ // The peer received too much data, violating flow control.
+ FlowControlReceivedTooMuchData ErrorCode = 59
+ // The peer sent too much data, violating flow control.
+ FlowControlSentTooMuchData ErrorCode = 63
+ // The peer received an invalid flow control window.
+ FlowControlInvalidWindow ErrorCode = 64
+ // The connection has been IP pooled into an existing connection.
+ ConnectionIPPooled ErrorCode = 62
+ // The connection has too many outstanding sent packets.
+ TooManyOutstandingSentPackets ErrorCode = 68
+ // The connection has too many outstanding received packets.
+ TooManyOutstandingReceivedPackets ErrorCode = 69
+ // The quic connection has been cancelled.
+ ConnectionCancelled ErrorCode = 70
+ // Disabled QUIC because of high packet loss rate.
+ BadPacketLossRate ErrorCode = 71
+ // Disabled QUIC because of too many PUBLIC_RESETs post handshake.
+ PublicResetsPostHandshake ErrorCode = 73
+ // Disabled QUIC because of too many timeouts with streams open.
+ TimeoutsWithOpenStreams ErrorCode = 74
+ // Closed because we failed to serialize a packet.
+ FailedToSerializePacket ErrorCode = 75
+ // QUIC timed out after too many RTOs.
+ TooManyRtos ErrorCode = 85
+
+ // Crypto errors.
+
+ // Hanshake failed.
+ HandshakeFailed ErrorCode = 28
+ // Handshake message contained out of order tags.
+ CryptoTagsOutOfOrder ErrorCode = 29
+ // Handshake message contained too many entries.
+ CryptoTooManyEntries ErrorCode = 30
+ // Handshake message contained an invalid value length.
+ CryptoInvalidValueLength ErrorCode = 31
+ // A crypto message was received after the handshake was complete.
+ CryptoMessageAfterHandshakeComplete ErrorCode = 32
+ // A crypto message was received with an illegal message tag.
+ InvalidCryptoMessageType ErrorCode = 33
+ // A crypto message was received with an illegal parameter.
+ InvalidCryptoMessageParameter ErrorCode = 34
+ // An invalid channel id signature was supplied.
+ InvalidChannelIDSignature ErrorCode = 52
+ // A crypto message was received with a mandatory parameter missing.
+ CryptoMessageParameterNotFound ErrorCode = 35
+ // A crypto message was received with a parameter that has no overlap
+ // with the local parameter.
+ CryptoMessageParameterNoOverlap ErrorCode = 36
+ // A crypto message was received that contained a parameter with too few
+ // values.
+ CryptoMessageIndexNotFound ErrorCode = 37
+ // An internal error occurred in crypto processing.
+ CryptoInternalError ErrorCode = 38
+ // A crypto handshake message specified an unsupported version.
+ CryptoVersionNotSupported ErrorCode = 39
+ // A crypto handshake message resulted in a stateless reject.
+ CryptoHandshakeStatelessReject ErrorCode = 72
+ // There was no intersection between the crypto primitives supported by the
+ // peer and ourselves.
+ CryptoNoSupport ErrorCode = 40
+ // The server rejected our client hello messages too many times.
+ CryptoTooManyRejects ErrorCode = 41
+ // The client rejected the server's certificate chain or signature.
+ ProofInvalid ErrorCode = 42
+ // A crypto message was received with a duplicate tag.
+ CryptoDuplicateTag ErrorCode = 43
+ // A crypto message was received with the wrong encryption level (i.e. it
+ // should have been encrypted but was not.)
+ CryptoEncryptionLevelIncorrect ErrorCode = 44
+ // The server config for a server has expired.
+ CryptoServerConfigExpired ErrorCode = 45
+ // We failed to setup the symmetric keys for a connection.
+ CryptoSymmetricKeySetupFailed ErrorCode = 53
+ // A handshake message arrived, but we are still validating the
+ // previous handshake message.
+ CryptoMessageWhileValidatingClientHello ErrorCode = 54
+ // A server config update arrived before the handshake is complete.
+ CryptoUpdateBeforeHandshakeComplete ErrorCode = 65
+ // This connection involved a version negotiation which appears to have been
+ // tampered with.
+ VersionNegotiationMismatch ErrorCode = 55
+
+ // Multipath is not enabled, but a packet with multipath flag on is received.
+ BadMultipathFlag ErrorCode = 79
+
+ // IP address changed causing connection close.
+ IPAddressChanged ErrorCode = 80
+
+ // Connection migration errors.
+ // Network changed, but connection had no migratable streams.
+ ConnectionMigrationNoMigratableStreams ErrorCode = 81
+ // Connection changed networks too many times.
+ ConnectionMigrationTooManyChanges ErrorCode = 82
+ // Connection migration was attempted, but there was no new network to
+ // migrate to.
+ ConnectionMigrationNoNewNetwork ErrorCode = 83
+ // Network changed, but connection had one or more non-migratable streams.
+ ConnectionMigrationNonMigratableStream ErrorCode = 84
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/errorcode_string.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/errorcode_string.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aadd657
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/errorcode_string.go
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+// Code generated by "stringer -type=ErrorCode"; DO NOT EDIT
+
+package qerr
+
+import "fmt"
+
+const (
+ _ErrorCode_name_0 = "InternalErrorStreamDataAfterTerminationInvalidPacketHeaderInvalidFrameDataInvalidFecDataInvalidRstStreamDataInvalidConnectionCloseDataInvalidGoawayDataInvalidAckDataInvalidVersionNegotiationPacketInvalidPublicRstPacketDecryptionFailureEncryptionFailurePacketTooLarge"
+ _ErrorCode_name_1 = "PeerGoingAwayInvalidStreamIDTooManyOpenStreamsPublicResetInvalidVersion"
+ _ErrorCode_name_2 = "InvalidHeaderIDInvalidNegotiatedValueDecompressionFailureNetworkIdleTimeoutErrorMigratingAddressPacketWriteErrorHandshakeFailedCryptoTagsOutOfOrderCryptoTooManyEntriesCryptoInvalidValueLengthCryptoMessageAfterHandshakeCompleteInvalidCryptoMessageTypeInvalidCryptoMessageParameterCryptoMessageParameterNotFoundCryptoMessageParameterNoOverlapCryptoMessageIndexNotFoundCryptoInternalErrorCryptoVersionNotSupportedCryptoNoSupportCryptoTooManyRejectsProofInvalidCryptoDuplicateTagCryptoEncryptionLevelIncorrectCryptoServerConfigExpiredInvalidStreamData"
+ _ErrorCode_name_3 = "MissingPayloadInvalidPriorityEmptyStreamFrameNoFinPacketReadErrorInvalidChannelIDSignatureCryptoSymmetricKeySetupFailedCryptoMessageWhileValidatingClientHelloVersionNegotiationMismatchInvalidHeadersStreamDataInvalidWindowUpdateDataInvalidBlockedDataFlowControlReceivedTooMuchDataInvalidStopWaitingDataUnencryptedStreamDataConnectionIPPooledFlowControlSentTooMuchDataFlowControlInvalidWindowCryptoUpdateBeforeHandshakeComplete"
+ _ErrorCode_name_4 = "HandshakeTimeoutTooManyOutstandingSentPacketsTooManyOutstandingReceivedPacketsConnectionCancelledBadPacketLossRateCryptoHandshakeStatelessRejectPublicResetsPostHandshakeTimeoutsWithOpenStreamsFailedToSerializePacketTooManyAvailableStreamsUnencryptedFecDataInvalidPathCloseDataBadMultipathFlagIPAddressChangedConnectionMigrationNoMigratableStreamsConnectionMigrationTooManyChangesConnectionMigrationNoNewNetworkConnectionMigrationNonMigratableStreamTooManyRtosErrorMigratingPortOverlappingStreamDataAttemptToSendUnencryptedStreamData"
+)
+
+var (
+ _ErrorCode_index_0 = [...]uint16{0, 13, 39, 58, 74, 88, 108, 134, 151, 165, 196, 218, 235, 252, 266}
+ _ErrorCode_index_1 = [...]uint8{0, 13, 28, 46, 57, 71}
+ _ErrorCode_index_2 = [...]uint16{0, 15, 37, 57, 75, 96, 112, 127, 147, 167, 191, 226, 250, 279, 309, 340, 366, 385, 410, 425, 445, 457, 475, 505, 530, 547}
+ _ErrorCode_index_3 = [...]uint16{0, 14, 29, 50, 65, 90, 119, 158, 184, 208, 231, 249, 279, 301, 322, 340, 366, 390, 425}
+ _ErrorCode_index_4 = [...]uint16{0, 16, 45, 78, 97, 114, 144, 169, 192, 215, 238, 256, 276, 292, 308, 346, 379, 410, 448, 459, 477, 498, 532}
+)
+
+func (i ErrorCode) String() string {
+ switch {
+ case 1 <= i && i <= 14:
+ i--
+ return _ErrorCode_name_0[_ErrorCode_index_0[i]:_ErrorCode_index_0[i+1]]
+ case 16 <= i && i <= 20:
+ i -= 16
+ return _ErrorCode_name_1[_ErrorCode_index_1[i]:_ErrorCode_index_1[i+1]]
+ case 22 <= i && i <= 46:
+ i -= 22
+ return _ErrorCode_name_2[_ErrorCode_index_2[i]:_ErrorCode_index_2[i+1]]
+ case 48 <= i && i <= 65:
+ i -= 48
+ return _ErrorCode_name_3[_ErrorCode_index_3[i]:_ErrorCode_index_3[i+1]]
+ case 67 <= i && i <= 88:
+ i -= 67
+ return _ErrorCode_name_4[_ErrorCode_index_4[i]:_ErrorCode_index_4[i+1]]
+ default:
+ return fmt.Sprintf("ErrorCode(%d)", i)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/quic_error.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/quic_error.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6259476
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr/quic_error.go
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+package qerr
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// ErrorCode can be used as a normal error without reason.
+type ErrorCode uint32
+
+func (e ErrorCode) Error() string {
+ return e.String()
+}
+
+// A QuicError consists of an error code plus a error reason
+type QuicError struct {
+ ErrorCode ErrorCode
+ ErrorMessage string
+}
+
+// Error creates a new QuicError instance
+func Error(errorCode ErrorCode, errorMessage string) *QuicError {
+ return &QuicError{
+ ErrorCode: errorCode,
+ ErrorMessage: errorMessage,
+ }
+}
+
+func (e *QuicError) Error() string {
+ return fmt.Sprintf("%s: %s", e.ErrorCode.String(), e.ErrorMessage)
+}
+
+// ToQuicError converts an arbitrary error to a QuicError. It leaves QuicErrors
+// unchanged, and properly handles `ErrorCode`s.
+func ToQuicError(err error) *QuicError {
+ switch e := err.(type) {
+ case *QuicError:
+ return e
+ case ErrorCode:
+ return Error(e, "")
+ }
+ utils.Errorf("Internal error: %v", err)
+ return Error(InternalError, err.Error())
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/server.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/server.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..54ccc6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/server.go
@@ -0,0 +1,205 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "crypto/tls"
+ "net"
+ "strings"
+ "sync"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// packetHandler handles packets
+type packetHandler interface {
+ handlePacket(*receivedPacket)
+ run()
+ Close(error) error
+}
+
+// A Server of QUIC
+type Server struct {
+ addr *net.UDPAddr
+
+ conn *net.UDPConn
+ connMutex sync.Mutex
+
+ signer crypto.Signer
+ scfg *handshake.ServerConfig
+
+ sessions map[protocol.ConnectionID]packetHandler
+ sessionsMutex sync.RWMutex
+
+ streamCallback StreamCallback
+
+ newSession func(conn connection, v protocol.VersionNumber, connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, sCfg *handshake.ServerConfig, streamCallback StreamCallback, closeCallback closeCallback) (packetHandler, error)
+}
+
+// NewServer makes a new server
+func NewServer(addr string, tlsConfig *tls.Config, cb StreamCallback) (*Server, error) {
+ signer, err := crypto.NewProofSource(tlsConfig)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ kex, err := crypto.NewCurve25519KEX()
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ scfg, err := handshake.NewServerConfig(kex, signer)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ udpAddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ return &Server{
+ addr: udpAddr,
+ signer: signer,
+ scfg: scfg,
+ streamCallback: cb,
+ sessions: map[protocol.ConnectionID]packetHandler{},
+ newSession: newSession,
+ }, nil
+}
+
+// ListenAndServe listens and serves a connection
+func (s *Server) ListenAndServe() error {
+ conn, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", s.addr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ return s.Serve(conn)
+}
+
+// Serve on an existing UDP connection.
+func (s *Server) Serve(conn *net.UDPConn) error {
+ s.connMutex.Lock()
+ s.conn = conn
+ s.connMutex.Unlock()
+
+ for {
+ data := getPacketBuffer()
+ data = data[:protocol.MaxPacketSize]
+ n, remoteAddr, err := conn.ReadFromUDP(data)
+ if err != nil {
+ if strings.HasSuffix(err.Error(), "use of closed network connection") {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return err
+ }
+ data = data[:n]
+ if err := s.handlePacket(conn, remoteAddr, data); err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("error handling packet: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// Close the server
+func (s *Server) Close() error {
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ for _, session := range s.sessions {
+ if session != nil {
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+ _ = session.Close(nil)
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ }
+ }
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+
+ s.connMutex.Lock()
+ conn := s.conn
+ s.conn = nil
+ s.connMutex.Unlock()
+
+ if conn == nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return conn.Close()
+}
+
+func (s *Server) handlePacket(conn *net.UDPConn, remoteAddr *net.UDPAddr, packet []byte) error {
+ if protocol.ByteCount(len(packet)) > protocol.MaxPacketSize {
+ return qerr.PacketTooLarge
+ }
+
+ rcvTime := time.Now()
+
+ r := bytes.NewReader(packet)
+
+ hdr, err := ParsePublicHeader(r)
+ if err != nil {
+ return qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidPacketHeader, err.Error())
+ }
+ hdr.Raw = packet[:len(packet)-r.Len()]
+
+ // Send Version Negotiation Packet if the client is speaking a different protocol version
+ if hdr.VersionFlag && !protocol.IsSupportedVersion(hdr.VersionNumber) {
+ utils.Infof("Client offered version %d, sending VersionNegotiationPacket", hdr.VersionNumber)
+ _, err = conn.WriteToUDP(composeVersionNegotiation(hdr.ConnectionID), remoteAddr)
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.sessionsMutex.RLock()
+ session, ok := s.sessions[hdr.ConnectionID]
+ s.sessionsMutex.RUnlock()
+
+ if !ok {
+ utils.Infof("Serving new connection: %x, version %d from %v", hdr.ConnectionID, hdr.VersionNumber, remoteAddr)
+ session, err = s.newSession(
+ &udpConn{conn: conn, currentAddr: remoteAddr},
+ hdr.VersionNumber,
+ hdr.ConnectionID,
+ s.scfg,
+ s.streamCallback,
+ s.closeCallback,
+ )
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ go session.run()
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ s.sessions[hdr.ConnectionID] = session
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+ }
+ if session == nil {
+ // Late packet for closed session
+ return nil
+ }
+ session.handlePacket(&receivedPacket{
+ remoteAddr: remoteAddr,
+ publicHeader: hdr,
+ data: packet[len(packet)-r.Len():],
+ rcvTime: rcvTime,
+ })
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Server) closeCallback(id protocol.ConnectionID) {
+ s.sessionsMutex.Lock()
+ s.sessions[id] = nil
+ s.sessionsMutex.Unlock()
+}
+
+func composeVersionNegotiation(connectionID protocol.ConnectionID) []byte {
+ fullReply := &bytes.Buffer{}
+ responsePublicHeader := PublicHeader{
+ ConnectionID: connectionID,
+ PacketNumber: 1,
+ VersionFlag: true,
+ }
+ err := responsePublicHeader.WritePublicHeader(fullReply, protocol.Version35)
+ if err != nil {
+ utils.Errorf("error composing version negotiation packet: %s", err.Error())
+ }
+ fullReply.Write(protocol.SupportedVersionsAsTags)
+ return fullReply.Bytes()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/session.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/session.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2f75299
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/session.go
@@ -0,0 +1,673 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "net"
+ "runtime"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type unpacker interface {
+ Unpack(publicHeaderBinary []byte, hdr *PublicHeader, data []byte) (*unpackedPacket, error)
+}
+
+type receivedPacket struct {
+ remoteAddr interface{}
+ publicHeader *PublicHeader
+ data []byte
+ rcvTime time.Time
+}
+
+var (
+ errRstStreamOnInvalidStream = errors.New("RST_STREAM received for unknown stream")
+ errWindowUpdateOnClosedStream = errors.New("WINDOW_UPDATE received for an already closed stream")
+)
+
+// StreamCallback gets a stream frame and returns a reply frame
+type StreamCallback func(*Session, utils.Stream)
+
+// closeCallback is called when a session is closed
+type closeCallback func(id protocol.ConnectionID)
+
+// A Session is a QUIC session
+type Session struct {
+ connectionID protocol.ConnectionID
+ version protocol.VersionNumber
+
+ streamCallback StreamCallback
+ closeCallback closeCallback
+
+ conn connection
+
+ streamsMap *streamsMap
+
+ sentPacketHandler ackhandler.SentPacketHandler
+ receivedPacketHandler ackhandler.ReceivedPacketHandler
+ streamFramer *streamFramer
+
+ flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager
+
+ unpacker unpacker
+ packer *packetPacker
+
+ cryptoSetup *handshake.CryptoSetup
+
+ receivedPackets chan *receivedPacket
+ sendingScheduled chan struct{}
+ // closeChan is used to notify the run loop that it should terminate.
+ // If the value is not nil, the error is sent as a CONNECTION_CLOSE.
+ closeChan chan *qerr.QuicError
+ closed uint32 // atomic bool
+
+ undecryptablePackets []*receivedPacket
+ aeadChanged chan struct{}
+
+ delayedAckOriginTime time.Time
+
+ connectionParametersManager *handshake.ConnectionParametersManager
+
+ lastRcvdPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+ // Used to calculate the next packet number from the truncated wire
+ // representation, and sent back in public reset packets
+ largestRcvdPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber
+
+ sessionCreationTime time.Time
+ lastNetworkActivityTime time.Time
+
+ timer *time.Timer
+ currentDeadline time.Time
+ timerRead bool
+}
+
+// newSession makes a new session
+func newSession(conn connection, v protocol.VersionNumber, connectionID protocol.ConnectionID, sCfg *handshake.ServerConfig, streamCallback StreamCallback, closeCallback closeCallback) (packetHandler, error) {
+ connectionParametersManager := handshake.NewConnectionParamatersManager()
+ flowControlManager := flowcontrol.NewFlowControlManager(connectionParametersManager)
+
+ var sentPacketHandler ackhandler.SentPacketHandler
+ var receivedPacketHandler ackhandler.ReceivedPacketHandler
+
+ sentPacketHandler = ackhandler.NewSentPacketHandler()
+ receivedPacketHandler = ackhandler.NewReceivedPacketHandler()
+
+ now := time.Now()
+ session := &Session{
+ conn: conn,
+ connectionID: connectionID,
+ version: v,
+
+ streamCallback: streamCallback,
+ closeCallback: closeCallback,
+
+ connectionParametersManager: connectionParametersManager,
+ sentPacketHandler: sentPacketHandler,
+ receivedPacketHandler: receivedPacketHandler,
+ flowControlManager: flowControlManager,
+
+ receivedPackets: make(chan *receivedPacket, protocol.MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets),
+ closeChan: make(chan *qerr.QuicError, 1),
+ sendingScheduled: make(chan struct{}, 1),
+ undecryptablePackets: make([]*receivedPacket, 0, protocol.MaxUndecryptablePackets),
+ aeadChanged: make(chan struct{}, 1),
+
+ timer: time.NewTimer(0),
+ lastNetworkActivityTime: now,
+ sessionCreationTime: now,
+ }
+
+ session.streamsMap = newStreamsMap(session.newStream)
+
+ cryptoStream, _ := session.GetOrOpenStream(1)
+ var err error
+ session.cryptoSetup, err = handshake.NewCryptoSetup(connectionID, conn.RemoteAddr().IP, v, sCfg, cryptoStream, session.connectionParametersManager, session.aeadChanged)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ session.streamFramer = newStreamFramer(session.streamsMap, flowControlManager)
+ session.packer = newPacketPacker(connectionID, session.cryptoSetup, session.connectionParametersManager, session.streamFramer, v)
+ session.unpacker = &packetUnpacker{aead: session.cryptoSetup, version: v}
+
+ return session, err
+}
+
+// run the session main loop
+func (s *Session) run() {
+ // Start the crypto stream handler
+ go func() {
+ if err := s.cryptoSetup.HandleCryptoStream(); err != nil {
+ s.Close(err)
+ }
+ }()
+
+ for {
+ // Close immediately if requested
+ select {
+ case errForConnClose := <-s.closeChan:
+ if errForConnClose != nil {
+ s.sendConnectionClose(errForConnClose)
+ }
+ return
+ default:
+ }
+
+ s.maybeResetTimer()
+
+ var err error
+ select {
+ case errForConnClose := <-s.closeChan:
+ if errForConnClose != nil {
+ s.sendConnectionClose(errForConnClose)
+ }
+ return
+ case <-s.timer.C:
+ s.timerRead = true
+ // We do all the interesting stuff after the switch statement, so
+ // nothing to see here.
+ case <-s.sendingScheduled:
+ // We do all the interesting stuff after the switch statement, so
+ // nothing to see here.
+ case p := <-s.receivedPackets:
+ err = s.handlePacketImpl(p)
+ if qErr, ok := err.(*qerr.QuicError); ok && qErr.ErrorCode == qerr.DecryptionFailure {
+ s.tryQueueingUndecryptablePacket(p)
+ continue
+ }
+ // This is a bit unclean, but works properly, since the packet always
+ // begins with the public header and we never copy it.
+ putPacketBuffer(p.publicHeader.Raw)
+ if s.delayedAckOriginTime.IsZero() {
+ s.delayedAckOriginTime = p.rcvTime
+ }
+ case <-s.aeadChanged:
+ s.tryDecryptingQueuedPackets()
+ }
+
+ if err != nil {
+ s.Close(err)
+ }
+
+ if err := s.sendPacket(); err != nil {
+ s.Close(err)
+ }
+ if time.Now().Sub(s.lastNetworkActivityTime) >= s.idleTimeout() {
+ s.Close(qerr.Error(qerr.NetworkIdleTimeout, "No recent network activity."))
+ }
+ if !s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() && time.Now().Sub(s.sessionCreationTime) >= protocol.MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake {
+ s.Close(qerr.Error(qerr.NetworkIdleTimeout, "Crypto handshake did not complete in time."))
+ }
+ s.garbageCollectStreams()
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) maybeResetTimer() {
+ nextDeadline := s.lastNetworkActivityTime.Add(s.idleTimeout())
+
+ if !s.delayedAckOriginTime.IsZero() {
+ nextDeadline = utils.MinTime(nextDeadline, s.delayedAckOriginTime.Add(protocol.AckSendDelay))
+ }
+ if rtoTime := s.sentPacketHandler.TimeOfFirstRTO(); !rtoTime.IsZero() {
+ nextDeadline = utils.MinTime(nextDeadline, rtoTime)
+ }
+ if !s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() {
+ handshakeDeadline := s.sessionCreationTime.Add(protocol.MaxTimeForCryptoHandshake)
+ nextDeadline = utils.MinTime(nextDeadline, handshakeDeadline)
+ }
+
+ if nextDeadline.Equal(s.currentDeadline) {
+ // No need to reset the timer
+ return
+ }
+
+ // We need to drain the timer if the value from its channel was not read yet.
+ // See https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/golang-dev/c9UUfASVPoU
+ if !s.timer.Stop() && !s.timerRead {
+ <-s.timer.C
+ }
+ s.timer.Reset(nextDeadline.Sub(time.Now()))
+
+ s.timerRead = false
+ s.currentDeadline = nextDeadline
+}
+
+func (s *Session) idleTimeout() time.Duration {
+ if s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() {
+ return s.connectionParametersManager.GetIdleConnectionStateLifetime()
+ }
+ return protocol.InitialIdleTimeout
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handlePacketImpl(p *receivedPacket) error {
+ if p.rcvTime.IsZero() {
+ // To simplify testing
+ p.rcvTime = time.Now()
+ }
+
+ s.lastNetworkActivityTime = p.rcvTime
+ hdr := p.publicHeader
+ data := p.data
+
+ // Calculate packet number
+ hdr.PacketNumber = protocol.InferPacketNumber(
+ hdr.PacketNumberLen,
+ s.largestRcvdPacketNumber,
+ hdr.PacketNumber,
+ )
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Debugf("<- Reading packet 0x%x (%d bytes) for connection %x", hdr.PacketNumber, len(data)+len(hdr.Raw), hdr.ConnectionID)
+ }
+
+ // TODO: Only do this after authenticating
+ s.conn.setCurrentRemoteAddr(p.remoteAddr)
+
+ packet, err := s.unpacker.Unpack(hdr.Raw, hdr, data)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.lastRcvdPacketNumber = hdr.PacketNumber
+ // Only do this after decrypting, so we are sure the packet is not attacker-controlled
+ s.largestRcvdPacketNumber = utils.MaxPacketNumber(s.largestRcvdPacketNumber, hdr.PacketNumber)
+
+ err = s.receivedPacketHandler.ReceivedPacket(hdr.PacketNumber)
+ // ignore duplicate packets
+ if err == ackhandler.ErrDuplicatePacket {
+ utils.Infof("Ignoring packet 0x%x due to ErrDuplicatePacket", hdr.PacketNumber)
+ return nil
+ }
+ // ignore packets with packet numbers smaller than the LeastUnacked of a StopWaiting
+ if err == ackhandler.ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting {
+ utils.Infof("Ignoring packet 0x%x due to ErrPacketSmallerThanLastStopWaiting", hdr.PacketNumber)
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ return s.handleFrames(packet.frames)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleFrames(fs []frames.Frame) error {
+ for _, ff := range fs {
+ var err error
+ frames.LogFrame(ff, false)
+ switch frame := ff.(type) {
+ case *frames.StreamFrame:
+ err = s.handleStreamFrame(frame)
+ // TODO: send RstStreamFrame
+ case *frames.AckFrame:
+ err = s.handleAckFrame(frame)
+ case *frames.ConnectionCloseFrame:
+ s.closeImpl(qerr.Error(frame.ErrorCode, frame.ReasonPhrase), true)
+ case *frames.GoawayFrame:
+ err = errors.New("unimplemented: handling GOAWAY frames")
+ case *frames.StopWaitingFrame:
+ err = s.receivedPacketHandler.ReceivedStopWaiting(frame)
+ case *frames.RstStreamFrame:
+ err = s.handleRstStreamFrame(frame)
+ case *frames.WindowUpdateFrame:
+ err = s.handleWindowUpdateFrame(frame)
+ case *frames.BlockedFrame:
+ case *frames.PingFrame:
+ default:
+ return errors.New("Session BUG: unexpected frame type")
+ }
+
+ if err != nil {
+ switch err {
+ case ackhandler.ErrDuplicateOrOutOfOrderAck:
+ // Can happen e.g. when packets thought missing arrive late
+ case errRstStreamOnInvalidStream:
+ // Can happen when RST_STREAMs arrive early or late (?)
+ utils.Errorf("Ignoring error in session: %s", err.Error())
+ case errWindowUpdateOnClosedStream:
+ // Can happen when we already sent the last StreamFrame with the FinBit, but the client already sent a WindowUpdate for this Stream
+ default:
+ return err
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// handlePacket is called by the server with a new packet
+func (s *Session) handlePacket(p *receivedPacket) {
+ // Discard packets once the amount of queued packets is larger than
+ // the channel size, protocol.MaxSessionUnprocessedPackets
+ select {
+ case s.receivedPackets <- p:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleStreamFrame(frame *frames.StreamFrame) error {
+ str, err := s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(frame.StreamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ // Stream is closed, ignore
+ return nil
+ }
+ err = str.AddStreamFrame(frame)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleWindowUpdateFrame(frame *frames.WindowUpdateFrame) error {
+ if frame.StreamID != 0 {
+ str, err := s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(frame.StreamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ return errWindowUpdateOnClosedStream
+ }
+ }
+ _, err := s.flowControlManager.UpdateWindow(frame.StreamID, frame.ByteOffset)
+ return err
+}
+
+// TODO: Handle frame.byteOffset
+func (s *Session) handleRstStreamFrame(frame *frames.RstStreamFrame) error {
+ str, err := s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(frame.StreamID)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ return errRstStreamOnInvalidStream
+ }
+ s.closeStreamWithError(str, fmt.Errorf("RST_STREAM received with code %d", frame.ErrorCode))
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Session) handleAckFrame(frame *frames.AckFrame) error {
+ if err := s.sentPacketHandler.ReceivedAck(frame, s.lastRcvdPacketNumber, s.lastNetworkActivityTime); err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Close the connection. If err is nil it will be set to qerr.PeerGoingAway.
+func (s *Session) Close(e error) error {
+ return s.closeImpl(e, false)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) closeImpl(e error, remoteClose bool) error {
+ // Only close once
+ if !atomic.CompareAndSwapUint32(&s.closed, 0, 1) {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if e == nil {
+ e = qerr.PeerGoingAway
+ }
+
+ quicErr := qerr.ToQuicError(e)
+
+ // Don't log 'normal' reasons
+ if quicErr.ErrorCode == qerr.PeerGoingAway || quicErr.ErrorCode == qerr.NetworkIdleTimeout {
+ utils.Infof("Closing connection %x", s.connectionID)
+ } else {
+ utils.Errorf("Closing session with error: %s", e.Error())
+ }
+
+ s.closeStreamsWithError(quicErr)
+ s.closeCallback(s.connectionID)
+
+ if remoteClose {
+ // If this is a remote close we don't need to send a CONNECTION_CLOSE
+ s.closeChan <- nil
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ if quicErr.ErrorCode == qerr.DecryptionFailure {
+ // If we send a public reset, don't send a CONNECTION_CLOSE
+ s.closeChan <- nil
+ return s.sendPublicReset(s.lastRcvdPacketNumber)
+ }
+ s.closeChan <- quicErr
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *Session) closeStreamsWithError(err error) {
+ s.streamsMap.Iterate(func(str *stream) (bool, error) {
+ s.closeStreamWithError(str, err)
+ return true, nil
+ })
+}
+
+func (s *Session) closeStreamWithError(str *stream, err error) {
+ str.RegisterError(err)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) sendPacket() error {
+ // Repeatedly try sending until we don't have any more data, or run out of the congestion window
+ for {
+ err := s.sentPacketHandler.CheckForError()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ // Do this before checking the congestion, since we might de-congestionize here :)
+ s.sentPacketHandler.MaybeQueueRTOs()
+
+ if !s.sentPacketHandler.SendingAllowed() {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ var controlFrames []frames.Frame
+
+ // check for retransmissions first
+ for {
+ retransmitPacket := s.sentPacketHandler.DequeuePacketForRetransmission()
+ if retransmitPacket == nil {
+ break
+ }
+ utils.Debugf("\tDequeueing retransmission for packet 0x%x", retransmitPacket.PacketNumber)
+
+ // resend the frames that were in the packet
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, retransmitPacket.GetControlFramesForRetransmission()...)
+ for _, streamFrame := range retransmitPacket.GetStreamFramesForRetransmission() {
+ s.streamFramer.AddFrameForRetransmission(streamFrame)
+ }
+ }
+
+ windowUpdateFrames, err := s.getWindowUpdateFrames()
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ for _, wuf := range windowUpdateFrames {
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, wuf)
+ }
+
+ ack, err := s.receivedPacketHandler.GetAckFrame(false)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if ack != nil {
+ controlFrames = append(controlFrames, ack)
+ }
+
+ // Check whether we are allowed to send a packet containing only an ACK
+ maySendOnlyAck := time.Now().Sub(s.delayedAckOriginTime) > protocol.AckSendDelay
+ if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
+ maySendOnlyAck = true
+ }
+
+ hasRetransmission := s.streamFramer.HasFramesForRetransmission()
+
+ var stopWaitingFrame *frames.StopWaitingFrame
+ if ack != nil || hasRetransmission {
+ stopWaitingFrame = s.sentPacketHandler.GetStopWaitingFrame(hasRetransmission)
+ }
+ packet, err := s.packer.PackPacket(stopWaitingFrame, controlFrames, s.sentPacketHandler.GetLeastUnacked(), maySendOnlyAck)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if packet == nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ // Pop the ACK frame now that we are sure we're gonna send it
+ _, err = s.receivedPacketHandler.GetAckFrame(true)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ for _, f := range windowUpdateFrames {
+ s.packer.QueueControlFrameForNextPacket(f)
+ }
+
+ err = s.sentPacketHandler.SentPacket(&ackhandler.Packet{
+ PacketNumber: packet.number,
+ Frames: packet.frames,
+ Length: protocol.ByteCount(len(packet.raw)),
+ })
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.logPacket(packet)
+ s.delayedAckOriginTime = time.Time{}
+
+ err = s.conn.write(packet.raw)
+ putPacketBuffer(packet.raw)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) sendConnectionClose(quicErr *qerr.QuicError) error {
+ packet, err := s.packer.PackConnectionClose(&frames.ConnectionCloseFrame{ErrorCode: quicErr.ErrorCode, ReasonPhrase: quicErr.ErrorMessage}, s.sentPacketHandler.GetLeastUnacked())
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if packet == nil {
+ return errors.New("Session BUG: expected packet not to be nil")
+ }
+ s.logPacket(packet)
+ return s.conn.write(packet.raw)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) logPacket(packet *packedPacket) {
+ if !utils.Debug() {
+ // We don't need to allocate the slices for calling the format functions
+ return
+ }
+ if utils.Debug() {
+ utils.Debugf("-> Sending packet 0x%x (%d bytes)", packet.number, len(packet.raw))
+ for _, frame := range packet.frames {
+ frames.LogFrame(frame, true)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// GetOrOpenStream either returns an existing stream, a newly opened stream, or nil if a stream with the provided ID is already closed.
+// Newly opened streams should only originate from the client. To open a stream from the server, OpenStream should be used.
+func (s *Session) GetOrOpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (utils.Stream, error) {
+ return s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(id)
+}
+
+// OpenStream opens a stream from the server's side
+func (s *Session) OpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (utils.Stream, error) {
+ return s.streamsMap.OpenStream(id)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) newStreamImpl(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ return s.streamsMap.GetOrOpenStream(id)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) newStream(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ stream, err := newStream(id, s.scheduleSending, s.flowControlManager)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ // TODO: find a better solution for determining which streams contribute to connection level flow control
+ if id == 1 || id == 3 {
+ s.flowControlManager.NewStream(id, false)
+ } else {
+ s.flowControlManager.NewStream(id, true)
+ }
+
+ s.streamCallback(s, stream)
+
+ return stream, nil
+}
+
+// garbageCollectStreams goes through all streams and removes EOF'ed streams
+// from the streams map.
+func (s *Session) garbageCollectStreams() {
+ s.streamsMap.Iterate(func(str *stream) (bool, error) {
+ id := str.StreamID()
+ if str.finished() {
+ err := s.streamsMap.RemoveStream(id)
+ if err != nil {
+ return false, err
+ }
+ s.flowControlManager.RemoveStream(id)
+ }
+ return true, nil
+ })
+}
+
+func (s *Session) sendPublicReset(rejectedPacketNumber protocol.PacketNumber) error {
+ utils.Infof("Sending public reset for connection %x, packet number %d", s.connectionID, rejectedPacketNumber)
+ return s.conn.write(writePublicReset(s.connectionID, rejectedPacketNumber, 0))
+}
+
+// scheduleSending signals that we have data for sending
+func (s *Session) scheduleSending() {
+ select {
+ case s.sendingScheduled <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) tryQueueingUndecryptablePacket(p *receivedPacket) {
+ if s.cryptoSetup.HandshakeComplete() {
+ return
+ }
+ utils.Infof("Queueing packet 0x%x for later decryption", p.publicHeader.PacketNumber)
+ if len(s.undecryptablePackets)+1 >= protocol.MaxUndecryptablePackets {
+ s.Close(qerr.Error(qerr.DecryptionFailure, "too many undecryptable packets received"))
+ }
+ s.undecryptablePackets = append(s.undecryptablePackets, p)
+}
+
+func (s *Session) tryDecryptingQueuedPackets() {
+ for _, p := range s.undecryptablePackets {
+ s.handlePacket(p)
+ }
+ s.undecryptablePackets = s.undecryptablePackets[:0]
+}
+
+func (s *Session) getWindowUpdateFrames() ([]*frames.WindowUpdateFrame, error) {
+ updates := s.flowControlManager.GetWindowUpdates()
+ res := make([]*frames.WindowUpdateFrame, len(updates))
+ for i, u := range updates {
+ res[i] = &frames.WindowUpdateFrame{StreamID: u.StreamID, ByteOffset: u.Offset}
+ }
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+// RemoteAddr returns the net.UDPAddr of the client
+func (s *Session) RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr {
+ return s.conn.RemoteAddr()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fc73b1e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream.go
@@ -0,0 +1,267 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+// A Stream assembles the data from StreamFrames and provides a super-convenient Read-Interface
+//
+// Read() and Write() may be called concurrently, but multiple calls to Read() or Write() individually must be synchronized manually.
+type stream struct {
+ streamID protocol.StreamID
+ onData func()
+
+ readPosInFrame int
+ writeOffset protocol.ByteCount
+ readOffset protocol.ByteCount
+
+ // Once set, err must not be changed!
+ err error
+ mutex sync.Mutex
+
+ // eof is set if we are finished reading
+ eof int32 // really a bool
+ // closed is set when we are finished writing
+ closed int32 // really a bool
+
+ frameQueue *streamFrameSorter
+ newFrameOrErrCond sync.Cond
+
+ dataForWriting []byte
+ finSent bool
+ doneWritingOrErrCond sync.Cond
+
+ flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager
+}
+
+// newStream creates a new Stream
+func newStream(StreamID protocol.StreamID, onData func(), flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager) (*stream, error) {
+ s := &stream{
+ onData: onData,
+ streamID: StreamID,
+ flowControlManager: flowControlManager,
+ frameQueue: newStreamFrameSorter(),
+ }
+
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.L = &s.mutex
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.L = &s.mutex
+
+ return s, nil
+}
+
+// Read implements io.Reader. It is not thread safe!
+func (s *stream) Read(p []byte) (int, error) {
+ if atomic.LoadInt32(&s.eof) != 0 {
+ return 0, io.EOF
+ }
+
+ bytesRead := 0
+ for bytesRead < len(p) {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ frame := s.frameQueue.Head()
+
+ if frame == nil && bytesRead > 0 {
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return bytesRead, s.err
+ }
+
+ var err error
+ for {
+ // Stop waiting on errors
+ if s.err != nil {
+ err = s.err
+ break
+ }
+ if frame != nil {
+ s.readPosInFrame = int(s.readOffset - frame.Offset)
+ break
+ }
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.Wait()
+ frame = s.frameQueue.Head()
+ }
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ // Here, either frame != nil xor err != nil
+
+ if frame == nil {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.eof, 1)
+ // We have an err and no data, return the error
+ return bytesRead, err
+ }
+
+ m := utils.Min(len(p)-bytesRead, int(frame.DataLen())-s.readPosInFrame)
+
+ if bytesRead > len(p) {
+ return bytesRead, fmt.Errorf("BUG: bytesRead (%d) > len(p) (%d) in stream.Read", bytesRead, len(p))
+ }
+ if s.readPosInFrame > int(frame.DataLen()) {
+ return bytesRead, fmt.Errorf("BUG: readPosInFrame (%d) > frame.DataLen (%d) in stream.Read", s.readPosInFrame, frame.DataLen())
+ }
+ copy(p[bytesRead:], frame.Data[s.readPosInFrame:])
+
+ s.readPosInFrame += m
+ bytesRead += m
+ s.readOffset += protocol.ByteCount(m)
+
+ s.flowControlManager.AddBytesRead(s.streamID, protocol.ByteCount(m))
+ s.onData() // so that a possible WINDOW_UPDATE is sent
+
+ if s.readPosInFrame >= int(frame.DataLen()) {
+ fin := frame.FinBit
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ s.frameQueue.Pop()
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ if fin {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.eof, 1)
+ return bytesRead, io.EOF
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return bytesRead, nil
+}
+
+func (s *stream) Write(p []byte) (int, error) {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ if s.err != nil {
+ return 0, s.err
+ }
+
+ if len(p) == 0 {
+ return 0, nil
+ }
+
+ s.dataForWriting = make([]byte, len(p))
+ copy(s.dataForWriting, p)
+
+ s.onData()
+
+ for s.dataForWriting != nil && s.err == nil {
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.Wait()
+ }
+
+ if s.err != nil {
+ return 0, s.err
+ }
+
+ return len(p), nil
+}
+
+func (s *stream) lenOfDataForWriting() protocol.ByteCount {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ l := protocol.ByteCount(len(s.dataForWriting))
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return l
+}
+
+func (s *stream) getDataForWriting(maxBytes protocol.ByteCount) []byte {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ if s.dataForWriting == nil {
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return nil
+ }
+ var ret []byte
+ if protocol.ByteCount(len(s.dataForWriting)) > maxBytes {
+ ret = s.dataForWriting[:maxBytes]
+ s.dataForWriting = s.dataForWriting[maxBytes:]
+ } else {
+ ret = s.dataForWriting
+ s.dataForWriting = nil
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.Signal()
+ }
+ s.writeOffset += protocol.ByteCount(len(ret))
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return ret
+}
+
+// Close implements io.Closer
+func (s *stream) Close() error {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.closed, 1)
+ s.onData()
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *stream) shouldSendFin() bool {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ res := atomic.LoadInt32(&s.closed) != 0 && !s.finSent && s.err == nil && s.dataForWriting == nil
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return res
+}
+
+func (s *stream) sentFin() {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ s.finSent = true
+ s.mutex.Unlock()
+}
+
+// AddStreamFrame adds a new stream frame
+func (s *stream) AddStreamFrame(frame *frames.StreamFrame) error {
+ maxOffset := frame.Offset + frame.DataLen()
+ err := s.flowControlManager.UpdateHighestReceived(s.streamID, maxOffset)
+
+ if err == flowcontrol.ErrStreamFlowControlViolation {
+ return qerr.FlowControlReceivedTooMuchData
+ }
+ if err == flowcontrol.ErrConnectionFlowControlViolation {
+ return qerr.FlowControlReceivedTooMuchData
+ }
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+ err = s.frameQueue.Push(frame)
+ if err != nil && err != errDuplicateStreamData {
+ return err
+ }
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.Signal()
+ return nil
+}
+
+// CloseRemote makes the stream receive a "virtual" FIN stream frame at a given offset
+func (s *stream) CloseRemote(offset protocol.ByteCount) {
+ s.AddStreamFrame(&frames.StreamFrame{FinBit: true, Offset: offset})
+}
+
+// RegisterError is called by session to indicate that an error occurred and the
+// stream should be closed.
+func (s *stream) RegisterError(err error) {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.closed, 1)
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+ if s.err != nil { // s.err must not be changed!
+ return
+ }
+ s.err = err
+ s.doneWritingOrErrCond.Signal()
+ s.newFrameOrErrCond.Signal()
+}
+
+func (s *stream) finishedReading() bool {
+ return atomic.LoadInt32(&s.eof) != 0
+}
+
+func (s *stream) finishedWriting() bool {
+ s.mutex.Lock()
+ defer s.mutex.Unlock()
+ return s.err != nil || (atomic.LoadInt32(&s.closed) != 0 && s.finSent)
+}
+
+func (s *stream) finished() bool {
+ return s.finishedReading() && s.finishedWriting()
+}
+
+func (s *stream) StreamID() protocol.StreamID {
+ return s.streamID
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_frame_sorter.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_frame_sorter.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7a95f1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_frame_sorter.go
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type streamFrameSorter struct {
+ queuedFrames map[protocol.ByteCount]*frames.StreamFrame
+ readPosition protocol.ByteCount
+ gaps *utils.ByteIntervalList
+}
+
+var (
+ errTooManyGapsInReceivedStreamData = errors.New("Too many gaps in received StreamFrame data")
+ errDuplicateStreamData = errors.New("Overlapping Stream Data")
+ errEmptyStreamData = errors.New("Stream Data empty")
+)
+
+func newStreamFrameSorter() *streamFrameSorter {
+ s := streamFrameSorter{
+ gaps: utils.NewByteIntervalList(),
+ queuedFrames: make(map[protocol.ByteCount]*frames.StreamFrame),
+ }
+ s.gaps.PushFront(utils.ByteInterval{Start: 0, End: protocol.MaxByteCount})
+ return &s
+}
+
+func (s *streamFrameSorter) Push(frame *frames.StreamFrame) error {
+ _, ok := s.queuedFrames[frame.Offset]
+ if ok {
+ return errDuplicateStreamData
+ }
+
+ start := frame.Offset
+ end := frame.Offset + frame.DataLen()
+
+ if start == end {
+ if frame.FinBit {
+ s.queuedFrames[frame.Offset] = frame
+ return nil
+ }
+ return errEmptyStreamData
+ }
+
+ var foundInGap bool
+
+ for gap := s.gaps.Front(); gap != nil; gap = gap.Next() {
+ // the complete frame lies before or after the gap
+ if end <= gap.Value.Start || start > gap.Value.End {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ if start < gap.Value.Start {
+ return qerr.Error(qerr.OverlappingStreamData, "start of gap in stream chunk")
+ }
+
+ if start < gap.Value.End && end > gap.Value.End {
+ return qerr.Error(qerr.OverlappingStreamData, "end of gap in stream chunk")
+ }
+
+ foundInGap = true
+
+ if start == gap.Value.Start {
+ if end == gap.Value.End {
+ s.gaps.Remove(gap)
+ break
+ }
+ if end < gap.Value.End {
+ gap.Value.Start = end
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if end == gap.Value.End {
+ gap.Value.End = start
+ break
+ }
+
+ if end < gap.Value.End {
+ intv := utils.ByteInterval{Start: end, End: gap.Value.End}
+ s.gaps.InsertAfter(intv, gap)
+ gap.Value.End = start
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if !foundInGap {
+ return errDuplicateStreamData
+ }
+
+ if s.gaps.Len() > protocol.MaxStreamFrameSorterGaps {
+ return errTooManyGapsInReceivedStreamData
+ }
+
+ s.queuedFrames[frame.Offset] = frame
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (s *streamFrameSorter) Pop() *frames.StreamFrame {
+ frame := s.Head()
+ if frame != nil {
+ s.readPosition += frame.DataLen()
+ delete(s.queuedFrames, frame.Offset)
+ }
+ return frame
+}
+
+func (s *streamFrameSorter) Head() *frames.StreamFrame {
+ frame, ok := s.queuedFrames[s.readPosition]
+ if ok {
+ return frame
+ }
+ return nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_framer.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_framer.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b702c28
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/stream_framer.go
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type streamFramer struct {
+ streamsMap *streamsMap
+
+ flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager
+
+ retransmissionQueue []*frames.StreamFrame
+ blockedFrameQueue []*frames.BlockedFrame
+}
+
+func newStreamFramer(streamsMap *streamsMap, flowControlManager flowcontrol.FlowControlManager) *streamFramer {
+ return &streamFramer{
+ streamsMap: streamsMap,
+ flowControlManager: flowControlManager,
+ }
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) AddFrameForRetransmission(frame *frames.StreamFrame) {
+ f.retransmissionQueue = append(f.retransmissionQueue, frame)
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) PopStreamFrames(maxLen protocol.ByteCount) []*frames.StreamFrame {
+ fs, currentLen := f.maybePopFramesForRetransmission(maxLen)
+ return append(fs, f.maybePopNormalFrames(maxLen-currentLen)...)
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) PopBlockedFrame() *frames.BlockedFrame {
+ if len(f.blockedFrameQueue) == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ frame := f.blockedFrameQueue[0]
+ f.blockedFrameQueue = f.blockedFrameQueue[1:]
+ return frame
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) HasFramesForRetransmission() bool {
+ return len(f.retransmissionQueue) > 0
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) maybePopFramesForRetransmission(maxLen protocol.ByteCount) (res []*frames.StreamFrame, currentLen protocol.ByteCount) {
+ for len(f.retransmissionQueue) > 0 {
+ frame := f.retransmissionQueue[0]
+ frame.DataLenPresent = true
+
+ frameHeaderLen, _ := frame.MinLength(protocol.VersionWhatever) // can never error
+ if currentLen+frameHeaderLen >= maxLen {
+ break
+ }
+
+ currentLen += frameHeaderLen
+
+ splitFrame := maybeSplitOffFrame(frame, maxLen-currentLen)
+ if splitFrame != nil { // StreamFrame was split
+ res = append(res, splitFrame)
+ currentLen += splitFrame.DataLen()
+ break
+ }
+
+ f.retransmissionQueue = f.retransmissionQueue[1:]
+ res = append(res, frame)
+ currentLen += frame.DataLen()
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+func (f *streamFramer) maybePopNormalFrames(maxBytes protocol.ByteCount) (res []*frames.StreamFrame) {
+ frame := &frames.StreamFrame{DataLenPresent: true}
+ var currentLen protocol.ByteCount
+
+ fn := func(s *stream) (bool, error) {
+ if s == nil {
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ frame.StreamID = s.streamID
+ // not perfect, but thread-safe since writeOffset is only written when getting data
+ frame.Offset = s.writeOffset
+ frameHeaderBytes, _ := frame.MinLength(protocol.VersionWhatever) // can never error
+ if currentLen+frameHeaderBytes > maxBytes {
+ return false, nil // theoretically, we could find another stream that fits, but this is quite unlikely, so we stop here
+ }
+ maxLen := maxBytes - currentLen - frameHeaderBytes
+
+ var sendWindowSize protocol.ByteCount
+ if s.lenOfDataForWriting() != 0 {
+ sendWindowSize, _ = f.flowControlManager.SendWindowSize(s.streamID)
+ maxLen = utils.MinByteCount(maxLen, sendWindowSize)
+ }
+
+ if maxLen == 0 {
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ data := s.getDataForWriting(maxLen)
+
+ // This is unlikely, but check it nonetheless, the scheduler might have jumped in. Seems to happen in ~20% of cases in the tests.
+ shouldSendFin := s.shouldSendFin()
+ if data == nil && !shouldSendFin {
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ if shouldSendFin {
+ frame.FinBit = true
+ s.sentFin()
+ }
+
+ frame.Data = data
+ f.flowControlManager.AddBytesSent(s.streamID, protocol.ByteCount(len(data)))
+
+ // Finally, check if we are now FC blocked and should queue a BLOCKED frame
+ if f.flowControlManager.RemainingConnectionWindowSize() == 0 {
+ // We are now connection-level FC blocked
+ f.blockedFrameQueue = append(f.blockedFrameQueue, &frames.BlockedFrame{StreamID: 0})
+ } else if sendWindowSize-frame.DataLen() == 0 {
+ // We are now stream-level FC blocked
+ f.blockedFrameQueue = append(f.blockedFrameQueue, &frames.BlockedFrame{StreamID: s.StreamID()})
+ }
+
+ res = append(res, frame)
+ currentLen += frameHeaderBytes + frame.DataLen()
+
+ if currentLen == maxBytes {
+ return false, nil
+ }
+
+ frame = &frames.StreamFrame{DataLenPresent: true}
+ return true, nil
+ }
+
+ f.streamsMap.RoundRobinIterate(fn)
+
+ return
+}
+
+// maybeSplitOffFrame removes the first n bytes and returns them as a separate frame. If n >= len(frame), nil is returned and nothing is modified.
+func maybeSplitOffFrame(frame *frames.StreamFrame, n protocol.ByteCount) *frames.StreamFrame {
+ if n >= frame.DataLen() {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ defer func() {
+ frame.Data = frame.Data[n:]
+ frame.Offset += n
+ }()
+
+ return &frames.StreamFrame{
+ FinBit: false,
+ StreamID: frame.StreamID,
+ Offset: frame.Offset,
+ Data: frame.Data[:n],
+ DataLenPresent: frame.DataLenPresent,
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/streams_map.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/streams_map.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8b41b86
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/streams_map.go
@@ -0,0 +1,219 @@
+package quic
+
+import (
+ "errors"
+ "fmt"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr"
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils"
+)
+
+type streamsMap struct {
+ mutex sync.RWMutex
+
+ streams map[protocol.StreamID]*stream
+ openStreams []protocol.StreamID
+
+ highestStreamOpenedByClient protocol.StreamID
+ streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect int
+
+ newStream newStreamLambda
+ maxNumStreams int
+
+ roundRobinIndex int
+}
+
+type streamLambda func(*stream) (bool, error)
+type newStreamLambda func(protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error)
+
+var (
+ errMapAccess = errors.New("streamsMap: Error accessing the streams map")
+)
+
+func newStreamsMap(newStream newStreamLambda) *streamsMap {
+ maxNumStreams := utils.Max(int(float32(protocol.MaxIncomingDynamicStreams)*protocol.MaxStreamsMultiplier), int(protocol.MaxIncomingDynamicStreams))
+
+ return &streamsMap{
+ streams: map[protocol.StreamID]*stream{},
+ openStreams: make([]protocol.StreamID, 0, maxNumStreams),
+ newStream: newStream,
+ maxNumStreams: maxNumStreams,
+ }
+}
+
+// GetOrOpenStream either returns an existing stream, a newly opened stream, or nil if a stream with the provided ID is already closed.
+// Newly opened streams should only originate from the client. To open a stream from the server, OpenStream should be used.
+func (m *streamsMap) GetOrOpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ m.mutex.RLock()
+ s, ok := m.streams[id]
+ m.mutex.RUnlock()
+ if ok {
+ return s, nil // s may be nil
+ }
+
+ // ... we don't have an existing stream, try opening a new one
+ m.mutex.Lock()
+ defer m.mutex.Unlock()
+ // We need to check whether another invocation has already created a stream (between RUnlock() and Lock()).
+ s, ok = m.streams[id]
+ if ok {
+ return s, nil
+ }
+ if len(m.openStreams) == m.maxNumStreams {
+ return nil, qerr.TooManyOpenStreams
+ }
+ if id%2 == 0 {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamID, fmt.Sprintf("attempted to open stream %d from client-side", id))
+ }
+ if id+protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta < m.highestStreamOpenedByClient {
+ return nil, qerr.Error(qerr.InvalidStreamID, fmt.Sprintf("attempted to open stream %d, which is a lot smaller than the highest opened stream, %d", id, m.highestStreamOpenedByClient))
+ }
+
+ s, err := m.newStream(id)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+
+ if id > m.highestStreamOpenedByClient {
+ m.highestStreamOpenedByClient = id
+ }
+
+ m.streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect++
+ if m.streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect%protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta == 0 {
+ m.garbageCollectClosedStreams()
+ }
+
+ m.putStream(s)
+ return s, nil
+}
+
+// OpenStream opens a stream from the server's side
+func (m *streamsMap) OpenStream(id protocol.StreamID) (*stream, error) {
+ panic("OpenStream: not implemented")
+}
+
+func (m *streamsMap) Iterate(fn streamLambda) error {
+ m.mutex.Lock()
+ defer m.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ for _, streamID := range m.openStreams {
+ cont, err := m.iterateFunc(streamID, fn)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ if !cont {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// RoundRobinIterate executes the streamLambda for every open stream, until the streamLambda returns false
+// It uses a round-robin-like scheduling to ensure that every stream is considered fairly
+// It prioritizes the crypto- and the header-stream (StreamIDs 1 and 3)
+func (m *streamsMap) RoundRobinIterate(fn streamLambda) error {
+ m.mutex.Lock()
+ defer m.mutex.Unlock()
+
+ numStreams := len(m.openStreams)
+ startIndex := m.roundRobinIndex
+
+ for _, i := range []protocol.StreamID{1, 3} {
+ cont, err := m.iterateFunc(i, fn)
+ if err != nil && err != errMapAccess {
+ return err
+ }
+ if !cont {
+ return nil
+ }
+ }
+
+ for i := 0; i < numStreams; i++ {
+ streamID := m.openStreams[(i+startIndex)%numStreams]
+
+ if streamID == 1 || streamID == 3 {
+ continue
+ }
+
+ cont, err := m.iterateFunc(streamID, fn)
+ if err != nil {
+ return err
+ }
+ m.roundRobinIndex = (m.roundRobinIndex + 1) % numStreams
+ if !cont {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+func (m *streamsMap) iterateFunc(streamID protocol.StreamID, fn streamLambda) (bool, error) {
+ str, ok := m.streams[streamID]
+ if !ok {
+ return true, errMapAccess
+ }
+ if str == nil {
+ return false, fmt.Errorf("BUG: Stream %d is closed, but still in openStreams map", streamID)
+ }
+ return fn(str)
+}
+
+func (m *streamsMap) putStream(s *stream) error {
+ id := s.StreamID()
+ if _, ok := m.streams[id]; ok {
+ return fmt.Errorf("a stream with ID %d already exists", id)
+ }
+
+ m.streams[id] = s
+ m.openStreams = append(m.openStreams, id)
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Attention: this function must only be called if a mutex has been acquired previously
+func (m *streamsMap) RemoveStream(id protocol.StreamID) error {
+ s, ok := m.streams[id]
+ if !ok || s == nil {
+ return fmt.Errorf("attempted to remove non-existing stream: %d", id)
+ }
+
+ m.streams[id] = nil
+
+ for i, s := range m.openStreams {
+ if s == id {
+ // delete the streamID from the openStreams slice
+ m.openStreams = m.openStreams[:i+copy(m.openStreams[i:], m.openStreams[i+1:])]
+ // adjust round-robin index, if necessary
+ if i < m.roundRobinIndex {
+ m.roundRobinIndex--
+ }
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// NumberOfStreams gets the number of open streams
+func (m *streamsMap) NumberOfStreams() int {
+ m.mutex.RLock()
+ n := len(m.openStreams)
+ m.mutex.RUnlock()
+ return n
+}
+
+// garbageCollectClosedStreams deletes nil values in the streams if they are smaller than protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta than the highest stream opened by the client
+// note that this garbage collection is relatively expensive, since it iterates over the whole streams map. It should not be called every time a stream is openend or closed
+func (m *streamsMap) garbageCollectClosedStreams() {
+ for id, str := range m.streams {
+ if str != nil {
+ continue
+ }
+ if id+protocol.MaxNewStreamIDDelta <= m.highestStreamOpenedByClient {
+ delete(m.streams, id)
+ }
+ }
+ m.streamsOpenedAfterLastGarbageCollect = 0
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/udp_conn.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/udp_conn.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2c1bafe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/udp_conn.go
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+package quic
+
+import "net"
+
+type connection interface {
+ write([]byte) error
+ setCurrentRemoteAddr(interface{})
+ RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr
+}
+
+type udpConn struct {
+ conn *net.UDPConn
+ currentAddr *net.UDPAddr
+}
+
+var _ connection = &udpConn{}
+
+func (c *udpConn) write(p []byte) error {
+ _, err := c.conn.WriteToUDP(p, c.currentAddr)
+ return err
+}
+
+func (c *udpConn) setCurrentRemoteAddr(addr interface{}) {
+ c.currentAddr = addr.(*net.UDPAddr)
+}
+
+func (c *udpConn) RemoteAddr() *net.UDPAddr {
+ return c.currentAddr
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/_gen.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/_gen.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..154515b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/_gen.go
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+package main
+
+import (
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/linkedlist"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/slice"
+ _ "github.com/clipperhouse/stringer"
+)
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..545fc20
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/byteinterval_linkedlist.go
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+// Generated by: main
+// TypeWriter: linkedlist
+// Directive: +gen on ByteInterval
+
+package utils
+
+// List is a modification of http://golang.org/pkg/container/list/
+// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+// ByteIntervalElement is an element of a linked list.
+type ByteIntervalElement struct {
+ // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
+ // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
+ // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
+ // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
+ // element (l.Front()).
+ next, prev *ByteIntervalElement
+
+ // The list to which this element belongs.
+ list *ByteIntervalList
+
+ // The value stored with this element.
+ Value ByteInterval
+}
+
+// Next returns the next list element or nil.
+func (e *ByteIntervalElement) Next() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
+func (e *ByteIntervalElement) Prev() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// ByteIntervalList represents a doubly linked list.
+// The zero value for ByteIntervalList is an empty list ready to use.
+type ByteIntervalList struct {
+ root ByteIntervalElement // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
+ len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
+}
+
+// Init initializes or clears list l.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Init() *ByteIntervalList {
+ l.root.next = &l.root
+ l.root.prev = &l.root
+ l.len = 0
+ return l
+}
+
+// NewByteIntervalList returns an initialized list.
+func NewByteIntervalList() *ByteIntervalList { return new(ByteIntervalList).Init() }
+
+// Len returns the number of elements of list l.
+// The complexity is O(1).
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Len() int { return l.len }
+
+// Front returns the first element of list l or nil.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Front() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.next
+}
+
+// Back returns the last element of list l or nil.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Back() *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.prev
+}
+
+// lazyInit lazily initializes a zero ByteIntervalList value.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) lazyInit() {
+ if l.root.next == nil {
+ l.Init()
+ }
+}
+
+// insert inserts e after at, increments l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) insert(e, at *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ n := at.next
+ at.next = e
+ e.prev = at
+ e.next = n
+ n.prev = e
+ e.list = l
+ l.len++
+ return e
+}
+
+// insertValue is a convenience wrapper for insert(&ByteIntervalElement{Value: v}, at).
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) insertValue(v ByteInterval, at *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ return l.insert(&ByteIntervalElement{Value: v}, at)
+}
+
+// remove removes e from its list, decrements l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) remove(e *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ e.prev.next = e.next
+ e.next.prev = e.prev
+ e.next = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.prev = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.list = nil
+ l.len--
+ return e
+}
+
+// Remove removes e from l if e is an element of list l.
+// It returns the element value e.Value.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) Remove(e *ByteIntervalElement) ByteInterval {
+ if e.list == l {
+ // if e.list == l, l must have been initialized when e was inserted
+ // in l or l == nil (e is a zero ByteIntervalElement) and l.remove will crash
+ l.remove(e)
+ }
+ return e.Value
+}
+
+// PushFront inserts a new element e with value v at the front of list l and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushFront(v ByteInterval) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, &l.root)
+}
+
+// PushBack inserts a new element e with value v at the back of list l and returns e.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushBack(v ByteInterval) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertBefore inserts a new element e with value v immediately before mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) InsertBefore(v ByteInterval, mark *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertAfter inserts a new element e with value v immediately after mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) InsertAfter(v ByteInterval, mark *ByteIntervalElement) *ByteIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark)
+}
+
+// MoveToFront moves element e to the front of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveToFront(e *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.next == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), &l.root)
+}
+
+// MoveToBack moves element e to the back of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveToBack(e *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.prev == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in ByteIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveBefore moves element e to its new position before mark.
+// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveBefore(e, mark *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveAfter moves element e to its new position after mark.
+// If e is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) MoveAfter(e, mark *ByteIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark)
+}
+
+// PushBackList inserts a copy of an other list at the back of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushBackList(other *ByteIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Front(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Next() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, l.root.prev)
+ }
+}
+
+// PushFrontList inserts a copy of an other list at the front of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *ByteIntervalList) PushFrontList(other *ByteIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Back(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Prev() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, &l.root)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/float16.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/float16.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8abdb51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/float16.go
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "io"
+ "math"
+)
+
+// We define an unsigned 16-bit floating point value, inspired by IEEE floats
+// (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half_precision_floating-point_format),
+// with 5-bit exponent (bias 1), 11-bit mantissa (effective 12 with hidden
+// bit) and denormals, but without signs, transfinites or fractions. Wire format
+// 16 bits (little-endian byte order) are split into exponent (high 5) and
+// mantissa (low 11) and decoded as:
+// uint64_t value;
+// if (exponent == 0) value = mantissa;
+// else value = (mantissa | 1 << 11) << (exponent - 1)
+const uFloat16ExponentBits = 5
+const uFloat16MaxExponent = (1 << uFloat16ExponentBits) - 2 // 30
+const uFloat16MantissaBits = 16 - uFloat16ExponentBits // 11
+const uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits = uFloat16MantissaBits + 1 // 12
+const uFloat16MaxValue = ((uint64(1) << uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits) - 1) << uFloat16MaxExponent // 0x3FFC0000000
+
+// ReadUfloat16 reads a float in the QUIC-float16 format and returns its uint64 representation
+func ReadUfloat16(b io.ByteReader) (uint64, error) {
+ val, err := ReadUint16(b)
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+
+ res := uint64(val)
+
+ if res < (1 << uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits) {
+ // Fast path: either the value is denormalized (no hidden bit), or
+ // normalized (hidden bit set, exponent offset by one) with exponent zero.
+ // Zero exponent offset by one sets the bit exactly where the hidden bit is.
+ // So in both cases the value encodes itself.
+ return res, nil
+ }
+
+ exponent := val >> uFloat16MantissaBits // No sign extend on uint!
+ // After the fast pass, the exponent is at least one (offset by one).
+ // Un-offset the exponent.
+ exponent--
+ // Here we need to clear the exponent and set the hidden bit. We have already
+ // decremented the exponent, so when we subtract it, it leaves behind the
+ // hidden bit.
+ res -= uint64(exponent) << uFloat16MantissaBits
+ res <<= exponent
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+// WriteUfloat16 writes a float in the QUIC-float16 format from its uint64 representation
+func WriteUfloat16(b *bytes.Buffer, value uint64) {
+ var result uint16
+ if value < (uint64(1) << uFloat16MantissaEffectiveBits) {
+ // Fast path: either the value is denormalized, or has exponent zero.
+ // Both cases are represented by the value itself.
+ result = uint16(value)
+ } else if value >= uFloat16MaxValue {
+ // Value is out of range; clamp it to the maximum representable.
+ result = math.MaxUint16
+ } else {
+ // The highest bit is between position 13 and 42 (zero-based), which
+ // corresponds to exponent 1-30. In the output, mantissa is from 0 to 10,
+ // hidden bit is 11 and exponent is 11 to 15. Shift the highest bit to 11
+ // and count the shifts.
+ exponent := uint16(0)
+ for offset := uint16(16); offset > 0; offset /= 2 {
+ // Right-shift the value until the highest bit is in position 11.
+ // For offset of 16, 8, 4, 2 and 1 (binary search over 1-30),
+ // shift if the bit is at or above 11 + offset.
+ if value >= (uint64(1) << (uFloat16MantissaBits + offset)) {
+ exponent += offset
+ value >>= offset
+ }
+ }
+
+ // Hidden bit (position 11) is set. We should remove it and increment the
+ // exponent. Equivalently, we just add it to the exponent.
+ // This hides the bit.
+ result = (uint16(value) + (exponent << uFloat16MantissaBits))
+ }
+
+ WriteUint16(b, result)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/log.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/log.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..bb0f255
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/log.go
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "os"
+ "sync"
+)
+
+var out io.Writer = os.Stdout
+
+// LogLevel of quic-go
+type LogLevel uint8
+
+const (
+ // LogLevelDebug enables debug logs (e.g. packet contents)
+ LogLevelDebug LogLevel = iota
+ // LogLevelInfo enables info logs (e.g. packets)
+ LogLevelInfo
+ // LogLevelError enables err logs
+ LogLevelError
+ // LogLevelNothing disables
+ LogLevelNothing
+)
+
+var logLevel = LogLevelNothing
+
+var mutex sync.Mutex
+
+// SetLogWriter sets the log writer.
+func SetLogWriter(w io.Writer) {
+ out = w
+}
+
+// SetLogLevel sets the log level
+func SetLogLevel(level LogLevel) {
+ logLevel = level
+}
+
+// Debugf logs something
+func Debugf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
+ if logLevel == LogLevelDebug {
+ mutex.Lock()
+ fmt.Fprintf(out, format+"\n", args...)
+ mutex.Unlock()
+ }
+}
+
+// Infof logs something
+func Infof(format string, args ...interface{}) {
+ if logLevel <= LogLevelInfo {
+ mutex.Lock()
+ fmt.Fprintf(out, format+"\n", args...)
+ mutex.Unlock()
+ }
+}
+
+// Errorf logs something
+func Errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
+ if logLevel <= LogLevelError {
+ mutex.Lock()
+ fmt.Fprintf(out, format+"\n", args...)
+ mutex.Unlock()
+ }
+}
+
+// Debug returns true if the log level is LogLevelDebug
+func Debug() bool {
+ return logLevel == LogLevelDebug
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/minmax.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/minmax.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ec22139
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/minmax.go
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "math"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// InfDuration is a duration of infinite length
+const InfDuration = time.Duration(math.MaxInt64)
+
+// Max returns the maximum of two Ints
+func Max(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// MaxUint32 returns the maximum of two uint32
+func MaxUint32(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a < b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// MaxUint64 returns the maximum of two uint64
+func MaxUint64(a, b uint64) uint64 {
+ if a < b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// Min returns the minimum of two Ints
+func Min(a, b int) int {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinUint32 returns the maximum of two uint32
+func MinUint32(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinInt64 returns the minimum of two int64
+func MinInt64(a, b int64) int64 {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MaxInt64 returns the minimum of two int64
+func MaxInt64(a, b int64) int64 {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinByteCount returns the minimum of two ByteCounts
+func MinByteCount(a, b protocol.ByteCount) protocol.ByteCount {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MaxDuration returns the max duration
+func MaxDuration(a, b time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinDuration returns the minimum duration
+func MinDuration(a, b time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ if a > b {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// AbsDuration returns the absolute value of a time duration
+func AbsDuration(d time.Duration) time.Duration {
+ if d >= 0 {
+ return d
+ }
+ return -d
+}
+
+// MinTime returns the earlier time
+func MinTime(a, b time.Time) time.Time {
+ if a.After(b) {
+ return b
+ }
+ return a
+}
+
+// MaxPacketNumber returns the max packet number
+func MaxPacketNumber(a, b protocol.PacketNumber) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if a > b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
+
+// MinPacketNumber returns the min packet number
+func MinPacketNumber(a, b protocol.PacketNumber) protocol.PacketNumber {
+ if a < b {
+ return a
+ }
+ return b
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packet_interval.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packet_interval.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..09800b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packet_interval.go
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+package utils
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// PacketInterval is an interval from one PacketNumber to the other
+// +gen linkedlist
+type PacketInterval struct {
+ Start protocol.PacketNumber
+ End protocol.PacketNumber
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e3431d6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/packetinterval_linkedlist.go
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+// Generated by: main
+// TypeWriter: linkedlist
+// Directive: +gen on PacketInterval
+
+package utils
+
+// List is a modification of http://golang.org/pkg/container/list/
+// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+// PacketIntervalElement is an element of a linked list.
+type PacketIntervalElement struct {
+ // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
+ // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
+ // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
+ // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
+ // element (l.Front()).
+ next, prev *PacketIntervalElement
+
+ // The list to which this element belongs.
+ list *PacketIntervalList
+
+ // The value stored with this element.
+ Value PacketInterval
+}
+
+// Next returns the next list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketIntervalElement) Next() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
+func (e *PacketIntervalElement) Prev() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
+ return p
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// PacketIntervalList represents a doubly linked list.
+// The zero value for PacketIntervalList is an empty list ready to use.
+type PacketIntervalList struct {
+ root PacketIntervalElement // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
+ len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
+}
+
+// Init initializes or clears list l.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Init() *PacketIntervalList {
+ l.root.next = &l.root
+ l.root.prev = &l.root
+ l.len = 0
+ return l
+}
+
+// NewPacketIntervalList returns an initialized list.
+func NewPacketIntervalList() *PacketIntervalList { return new(PacketIntervalList).Init() }
+
+// Len returns the number of elements of list l.
+// The complexity is O(1).
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Len() int { return l.len }
+
+// Front returns the first element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Front() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.next
+}
+
+// Back returns the last element of list l or nil.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Back() *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if l.len == 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return l.root.prev
+}
+
+// lazyInit lazily initializes a zero PacketIntervalList value.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) lazyInit() {
+ if l.root.next == nil {
+ l.Init()
+ }
+}
+
+// insert inserts e after at, increments l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) insert(e, at *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ n := at.next
+ at.next = e
+ e.prev = at
+ e.next = n
+ n.prev = e
+ e.list = l
+ l.len++
+ return e
+}
+
+// insertValue is a convenience wrapper for insert(&PacketIntervalElement{Value: v}, at).
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) insertValue(v PacketInterval, at *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ return l.insert(&PacketIntervalElement{Value: v}, at)
+}
+
+// remove removes e from its list, decrements l.len, and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) remove(e *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ e.prev.next = e.next
+ e.next.prev = e.prev
+ e.next = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.prev = nil // avoid memory leaks
+ e.list = nil
+ l.len--
+ return e
+}
+
+// Remove removes e from l if e is an element of list l.
+// It returns the element value e.Value.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) Remove(e *PacketIntervalElement) PacketInterval {
+ if e.list == l {
+ // if e.list == l, l must have been initialized when e was inserted
+ // in l or l == nil (e is a zero PacketIntervalElement) and l.remove will crash
+ l.remove(e)
+ }
+ return e.Value
+}
+
+// PushFront inserts a new element e with value v at the front of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushFront(v PacketInterval) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, &l.root)
+}
+
+// PushBack inserts a new element e with value v at the back of list l and returns e.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushBack(v PacketInterval) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ return l.insertValue(v, l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertBefore inserts a new element e with value v immediately before mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) InsertBefore(v PacketInterval, mark *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark.prev)
+}
+
+// InsertAfter inserts a new element e with value v immediately after mark and returns e.
+// If mark is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) InsertAfter(v PacketInterval, mark *PacketIntervalElement) *PacketIntervalElement {
+ if mark.list != l {
+ return nil
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ return l.insertValue(v, mark)
+}
+
+// MoveToFront moves element e to the front of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveToFront(e *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.next == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), &l.root)
+}
+
+// MoveToBack moves element e to the back of list l.
+// If e is not an element of l, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveToBack(e *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || l.root.prev == e {
+ return
+ }
+ // see comment in PacketIntervalList.Remove about initialization of l
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), l.root.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveBefore moves element e to its new position before mark.
+// If e or mark is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveBefore(e, mark *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark.prev)
+}
+
+// MoveAfter moves element e to its new position after mark.
+// If e is not an element of l, or e == mark, the list is not modified.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) MoveAfter(e, mark *PacketIntervalElement) {
+ if e.list != l || e == mark || mark.list != l {
+ return
+ }
+ l.insert(l.remove(e), mark)
+}
+
+// PushBackList inserts a copy of an other list at the back of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushBackList(other *PacketIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Front(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Next() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, l.root.prev)
+ }
+}
+
+// PushFrontList inserts a copy of an other list at the front of list l.
+// The lists l and other may be the same.
+func (l *PacketIntervalList) PushFrontList(other *PacketIntervalList) {
+ l.lazyInit()
+ for i, e := other.Len(), other.Back(); i > 0; i, e = i-1, e.Prev() {
+ l.insertValue(e.Value, &l.root)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/streamframe_interval.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/streamframe_interval.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c918b62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/streamframe_interval.go
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
+package utils
+
+import "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+
+// ByteInterval is an interval from one ByteCount to the other
+// +gen linkedlist
+type ByteInterval struct {
+ Start protocol.ByteCount
+ End protocol.ByteCount
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/utils.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/utils.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cf25679
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils/utils.go
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
+package utils
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "io"
+
+ "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol"
+)
+
+// Stream is the interface for QUIC streams
+type Stream interface {
+ io.Reader
+ io.Writer
+ io.Closer
+ StreamID() protocol.StreamID
+ CloseRemote(offset protocol.ByteCount)
+}
+
+// ReadUintN reads N bytes
+func ReadUintN(b io.ByteReader, length uint8) (uint64, error) {
+ var res uint64
+ for i := uint8(0); i < length; i++ {
+ bt, err := b.ReadByte()
+ if err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ res ^= uint64(bt) << (i * 8)
+ }
+ return res, nil
+}
+
+// ReadUint64 reads a uint64
+func ReadUint64(b io.ByteReader) (uint64, error) {
+ var b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7, b8 uint8
+ var err error
+ if b1, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b2, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b3, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b4, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b5, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b6, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b7, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b8, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return uint64(b1) + uint64(b2)<<8 + uint64(b3)<<16 + uint64(b4)<<24 + uint64(b5)<<32 + uint64(b6)<<40 + uint64(b7)<<48 + uint64(b8)<<56, nil
+}
+
+// ReadUint32 reads a uint32
+func ReadUint32(b io.ByteReader) (uint32, error) {
+ var b1, b2, b3, b4 uint8
+ var err error
+ if b1, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b2, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b3, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b4, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return uint32(b1) + uint32(b2)<<8 + uint32(b3)<<16 + uint32(b4)<<24, nil
+}
+
+// ReadUint16 reads a uint16
+func ReadUint16(b io.ByteReader) (uint16, error) {
+ var b1, b2 uint8
+ var err error
+ if b1, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ if b2, err = b.ReadByte(); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return uint16(b1) + uint16(b2)<<8, nil
+}
+
+// WriteUint64 writes a uint64
+func WriteUint64(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24),
+ uint8(i >> 32), uint8(i >> 40), uint8(i >> 48), uint8(i >> 56),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint56 writes 56 bit of a uint64
+func WriteUint56(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24),
+ uint8(i >> 32), uint8(i >> 40), uint8(i >> 48),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint48 writes 48 bit of a uint64
+func WriteUint48(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24),
+ uint8(i >> 32), uint8(i >> 40),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint40 writes 40 bit of a uint64
+func WriteUint40(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint64) {
+ b.Write([]byte{
+ uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16),
+ uint8(i >> 24), uint8(i >> 32),
+ })
+}
+
+// WriteUint32 writes a uint32
+func WriteUint32(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint32) {
+ b.Write([]byte{uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16), uint8(i >> 24)})
+}
+
+// WriteUint24 writes 24 bit of a uint32
+func WriteUint24(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint32) {
+ b.Write([]byte{uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8), uint8(i >> 16)})
+}
+
+// WriteUint16 writes a uint16
+func WriteUint16(b *bytes.Buffer, i uint16) {
+ b.Write([]byte{uint8(i), uint8(i >> 8)})
+}
+
+// Uint32Slice attaches the methods of sort.Interface to []uint32, sorting in increasing order.
+type Uint32Slice []uint32
+
+func (s Uint32Slice) Len() int { return len(s) }
+func (s Uint32Slice) Less(i, j int) bool { return s[i] < s[j] }
+func (s Uint32Slice) Swap(i, j int) { s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] }
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..835ba3e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+Copyright (c) 2015, Dave Cheney HTTP Error 431
Request Header Field(s) Too Large
") +} + +// called from handler goroutines. +// h may be nil. +func (sc *serverConn) writeHeaders(st *stream, headerData *writeResHeaders) error { + sc.serveG.checkNotOn() // NOT on + var errc chan error + if headerData.h != nil { + // If there's a header map (which we don't own), so we have to block on + // waiting for this frame to be written, so an http.Flush mid-handler + // writes out the correct value of keys, before a handler later potentially + // mutates it. + errc = errChanPool.Get().(chan error) + } + if err := sc.writeFrameFromHandler(FrameWriteRequest{ + write: headerData, + stream: st, + done: errc, + }); err != nil { + return err + } + if errc != nil { + select { + case err := <-errc: + errChanPool.Put(errc) + return err + case <-sc.doneServing: + return errClientDisconnected + case <-st.cw: + return errStreamClosed + } + } + return nil +} + +// called from handler goroutines. +func (sc *serverConn) write100ContinueHeaders(st *stream) { + sc.writeFrameFromHandler(FrameWriteRequest{ + write: write100ContinueHeadersFrame{st.id}, + stream: st, + }) +} + +// A bodyReadMsg tells the server loop that the http.Handler read n +// bytes of the DATA from the client on the given stream. +type bodyReadMsg struct { + st *stream + n int +} + +// called from handler goroutines. +// Notes that the handler for the given stream ID read n bytes of its body +// and schedules flow control tokens to be sent. +func (sc *serverConn) noteBodyReadFromHandler(st *stream, n int, err error) { + sc.serveG.checkNotOn() // NOT on + if n > 0 { + select { + case sc.bodyReadCh <- bodyReadMsg{st, n}: + case <-sc.doneServing: + } + } + if err == io.EOF { + if buf := st.reqBuf; buf != nil { + st.reqBuf = nil // shouldn't matter; field unused by other + putRequestBodyBuf(buf) + } + } +} + +func (sc *serverConn) noteBodyRead(st *stream, n int) { + sc.serveG.check() + sc.sendWindowUpdate(nil, n) // conn-level + if st.state != stateHalfClosedRemote && st.state != stateClosed { + // Don't send this WINDOW_UPDATE if the stream is closed + // remotely. + sc.sendWindowUpdate(st, n) + } +} + +// st may be nil for conn-level +func (sc *serverConn) sendWindowUpdate(st *stream, n int) { + sc.serveG.check() + // "The legal range for the increment to the flow control + // window is 1 to 2^31-1 (2,147,483,647) octets." + // A Go Read call on 64-bit machines could in theory read + // a larger Read than this. Very unlikely, but we handle it here + // rather than elsewhere for now. + const maxUint31 = 1<<31 - 1 + for n >= maxUint31 { + sc.sendWindowUpdate32(st, maxUint31) + n -= maxUint31 + } + sc.sendWindowUpdate32(st, int32(n)) +} + +// st may be nil for conn-level +func (sc *serverConn) sendWindowUpdate32(st *stream, n int32) { + sc.serveG.check() + if n == 0 { + return + } + if n < 0 { + panic("negative update") + } + var streamID uint32 + if st != nil { + streamID = st.id + } + sc.writeFrame(FrameWriteRequest{ + write: writeWindowUpdate{streamID: streamID, n: uint32(n)}, + stream: st, + }) + var ok bool + if st == nil { + ok = sc.inflow.add(n) + } else { + ok = st.inflow.add(n) + } + if !ok { + panic("internal error; sent too many window updates without decrements?") + } +} + +// requestBody is the Handler's Request.Body type. +// Read and Close may be called concurrently. +type requestBody struct { + stream *stream + conn *serverConn + closed bool // for use by Close only + sawEOF bool // for use by Read only + pipe *pipe // non-nil if we have a HTTP entity message body + needsContinue bool // need to send a 100-continue +} + +func (b *requestBody) Close() error { + if b.pipe != nil && !b.closed { + b.pipe.BreakWithError(errClosedBody) + } + b.closed = true + return nil +} + +func (b *requestBody) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) { + if b.needsContinue { + b.needsContinue = false + b.conn.write100ContinueHeaders(b.stream) + } + if b.pipe == nil || b.sawEOF { + return 0, io.EOF + } + n, err = b.pipe.Read(p) + if err == io.EOF { + b.sawEOF = true + } + if b.conn == nil && inTests { + return + } + b.conn.noteBodyReadFromHandler(b.stream, n, err) + return +} + +// responseWriter is the http.ResponseWriter implementation. It's +// intentionally small (1 pointer wide) to minimize garbage. The +// responseWriterState pointer inside is zeroed at the end of a +// request (in handlerDone) and calls on the responseWriter thereafter +// simply crash (caller's mistake), but the much larger responseWriterState +// and buffers are reused between multiple requests. +type responseWriter struct { + rws *responseWriterState +} + +// Optional http.ResponseWriter interfaces implemented. +var ( + _ http.CloseNotifier = (*responseWriter)(nil) + _ http.Flusher = (*responseWriter)(nil) + _ stringWriter = (*responseWriter)(nil) +) + +type responseWriterState struct { + // immutable within a request: + stream *stream + req *http.Request + body *requestBody // to close at end of request, if DATA frames didn't + conn *serverConn + + // TODO: adjust buffer writing sizes based on server config, frame size updates from peer, etc + bw *bufio.Writer // writing to a chunkWriter{this *responseWriterState} + + // mutated by http.Handler goroutine: + handlerHeader http.Header // nil until called + snapHeader http.Header // snapshot of handlerHeader at WriteHeader time + trailers []string // set in writeChunk + status int // status code passed to WriteHeader + wroteHeader bool // WriteHeader called (explicitly or implicitly). Not necessarily sent to user yet. + sentHeader bool // have we sent the header frame? + handlerDone bool // handler has finished + + sentContentLen int64 // non-zero if handler set a Content-Length header + wroteBytes int64 + + closeNotifierMu sync.Mutex // guards closeNotifierCh + closeNotifierCh chan bool // nil until first used +} + +type chunkWriter struct{ rws *responseWriterState } + +func (cw chunkWriter) Write(p []byte) (n int, err error) { return cw.rws.writeChunk(p) } + +func (rws *responseWriterState) hasTrailers() bool { return len(rws.trailers) != 0 } + +// declareTrailer is called for each Trailer header when the +// response header is written. It notes that a header will need to be +// written in the trailers at the end of the response. +func (rws *responseWriterState) declareTrailer(k string) { + k = http.CanonicalHeaderKey(k) + if !ValidTrailerHeader(k) { + // Forbidden by RFC 2616 14.40. + rws.conn.logf("ignoring invalid trailer %q", k) + return + } + if !strSliceContains(rws.trailers, k) { + rws.trailers = append(rws.trailers, k) + } +} + +// writeChunk writes chunks from the bufio.Writer. But because +// bufio.Writer may bypass its chunking, sometimes p may be +// arbitrarily large. +// +// writeChunk is also responsible (on the first chunk) for sending the +// HEADER response. +func (rws *responseWriterState) writeChunk(p []byte) (n int, err error) { + if !rws.wroteHeader { + rws.writeHeader(200) + } + + isHeadResp := rws.req.Method == "HEAD" + if !rws.sentHeader { + rws.sentHeader = true + var ctype, clen string + if clen = rws.snapHeader.Get("Content-Length"); clen != "" { + rws.snapHeader.Del("Content-Length") + clen64, err := strconv.ParseInt(clen, 10, 64) + if err == nil && clen64 >= 0 { + rws.sentContentLen = clen64 + } else { + clen = "" + } + } + if clen == "" && rws.handlerDone && bodyAllowedForStatus(rws.status) && (len(p) > 0 || !isHeadResp) { + clen = strconv.Itoa(len(p)) + } + _, hasContentType := rws.snapHeader["Content-Type"] + if !hasContentType && bodyAllowedForStatus(rws.status) { + ctype = http.DetectContentType(p) + } + var date string + if _, ok := rws.snapHeader["Date"]; !ok { + // TODO(bradfitz): be faster here, like net/http? measure. + date = time.Now().UTC().Format(http.TimeFormat) + } + + for _, v := range rws.snapHeader["Trailer"] { + foreachHeaderElement(v, rws.declareTrailer) + } + + endStream := (rws.handlerDone && !rws.hasTrailers() && len(p) == 0) || isHeadResp + err = rws.conn.writeHeaders(rws.stream, &writeResHeaders{ + streamID: rws.stream.id, + httpResCode: rws.status, + h: rws.snapHeader, + endStream: endStream, + contentType: ctype, + contentLength: clen, + date: date, + }) + if err != nil { + return 0, err + } + if endStream { + return 0, nil + } + } + if isHeadResp { + return len(p), nil + } + if len(p) == 0 && !rws.handlerDone { + return 0, nil + } + + if rws.handlerDone { + rws.promoteUndeclaredTrailers() + } + + endStream := rws.handlerDone && !rws.hasTrailers() + if len(p) > 0 || endStream { + // only send a 0 byte DATA frame if we're ending the stream. + if err := rws.conn.writeDataFromHandler(rws.stream, p, endStream); err != nil { + return 0, err + } + } + + if rws.handlerDone && rws.hasTrailers() { + err = rws.conn.writeHeaders(rws.stream, &writeResHeaders{ + streamID: rws.stream.id, + h: rws.handlerHeader, + trailers: rws.trailers, + endStream: true, + }) + return len(p), err + } + return len(p), nil +} + +// TrailerPrefix is a magic prefix for ResponseWriter.Header map keys +// that, if present, signals that the map entry is actually for +// the response trailers, and not the response headers. The prefix +// is stripped after the ServeHTTP call finishes and the values are +// sent in the trailers. +// +// This mechanism is intended only for trailers that are not known +// prior to the headers being written. If the set of trailers is fixed +// or known before the header is written, the normal Go trailers mechanism +// is preferred: +// https://golang.org/pkg/net/http/#ResponseWriter +// https://golang.org/pkg/net/http/#example_ResponseWriter_trailers +const TrailerPrefix = "Trailer:" + +// promoteUndeclaredTrailers permits http.Handlers to set trailers +// after the header has already been flushed. Because the Go +// ResponseWriter interface has no way to set Trailers (only the +// Header), and because we didn't want to expand the ResponseWriter +// interface, and because nobody used trailers, and because RFC 2616 +// says you SHOULD (but not must) predeclare any trailers in the +// header, the official ResponseWriter rules said trailers in Go must +// be predeclared, and then we reuse the same ResponseWriter.Header() +// map to mean both Headers and Trailers. When it's time to write the +// Trailers, we pick out the fields of Headers that were declared as +// trailers. That worked for a while, until we found the first major +// user of Trailers in the wild: gRPC (using them only over http2), +// and gRPC libraries permit setting trailers mid-stream without +// predeclarnig them. So: change of plans. We still permit the old +// way, but we also permit this hack: if a Header() key begins with +// "Trailer:", the suffix of that key is a Trailer. Because ':' is an +// invalid token byte anyway, there is no ambiguity. (And it's already +// filtered out) It's mildly hacky, but not terrible. +// +// This method runs after the Handler is done and promotes any Header +// fields to be trailers. +func (rws *responseWriterState) promoteUndeclaredTrailers() { + for k, vv := range rws.handlerHeader { + if !strings.HasPrefix(k, TrailerPrefix) { + continue + } + trailerKey := strings.TrimPrefix(k, TrailerPrefix) + rws.declareTrailer(trailerKey) + rws.handlerHeader[http.CanonicalHeaderKey(trailerKey)] = vv + } + + if len(rws.trailers) > 1 { + sorter := sorterPool.Get().(*sorter) + sorter.SortStrings(rws.trailers) + sorterPool.Put(sorter) + } +} + +func (w *responseWriter) Flush() { + rws := w.rws + if rws == nil { + panic("Header called after Handler finished") + } + if rws.bw.Buffered() > 0 { + if err := rws.bw.Flush(); err != nil { + // Ignore the error. The frame writer already knows. + return + } + } else { + // The bufio.Writer won't call chunkWriter.Write + // (writeChunk with zero bytes, so we have to do it + // ourselves to force the HTTP response header and/or + // final DATA frame (with END_STREAM) to be sent. + rws.writeChunk(nil) + } +} + +func (w *responseWriter) CloseNotify() <-chan bool { + rws := w.rws + if rws == nil { + panic("CloseNotify called after Handler finished") + } + rws.closeNotifierMu.Lock() + ch := rws.closeNotifierCh + if ch == nil { + ch = make(chan bool, 1) + rws.closeNotifierCh = ch + go func() { + rws.stream.cw.Wait() // wait for close + ch <- true + }() + } + rws.closeNotifierMu.Unlock() + return ch +} + +func (w *responseWriter) Header() http.Header { + rws := w.rws + if rws == nil { + panic("Header called after Handler finished") + } + if rws.handlerHeader == nil { + rws.handlerHeader = make(http.Header) + } + return rws.handlerHeader +} + +func (w *responseWriter) WriteHeader(code int) { + rws := w.rws + if rws == nil { + panic("WriteHeader called after Handler finished") + } + rws.writeHeader(code) +} + +func (rws *responseWriterState) writeHeader(code int) { + if !rws.wroteHeader { + rws.wroteHeader = true + rws.status = code + if len(rws.handlerHeader) > 0 { + rws.snapHeader = cloneHeader(rws.handlerHeader) + } + } +} + +func cloneHeader(h http.Header) http.Header { + h2 := make(http.Header, len(h)) + for k, vv := range h { + vv2 := make([]string, len(vv)) + copy(vv2, vv) + h2[k] = vv2 + } + return h2 +} + +// The Life Of A Write is like this: +// +// * Handler calls w.Write or w.WriteString -> +// * -> rws.bw (*bufio.Writer) -> +// * (Handler migth call Flush) +// * -> chunkWriter{rws} +// * -> responseWriterState.writeChunk(p []byte) +// * -> responseWriterState.writeChunk (most of the magic; see comment there) +func (w *responseWriter) Write(p []byte) (n int, err error) { + return w.write(len(p), p, "") +} + +func (w *responseWriter) WriteString(s string) (n int, err error) { + return w.write(len(s), nil, s) +} + +// either dataB or dataS is non-zero. +func (w *responseWriter) write(lenData int, dataB []byte, dataS string) (n int, err error) { + rws := w.rws + if rws == nil { + panic("Write called after Handler finished") + } + if !rws.wroteHeader { + w.WriteHeader(200) + } + if !bodyAllowedForStatus(rws.status) { + return 0, http.ErrBodyNotAllowed + } + rws.wroteBytes += int64(len(dataB)) + int64(len(dataS)) // only one can be set + if rws.sentContentLen != 0 && rws.wroteBytes > rws.sentContentLen { + // TODO: send a RST_STREAM + return 0, errors.New("http2: handler wrote more than declared Content-Length") + } + + if dataB != nil { + return rws.bw.Write(dataB) + } else { + return rws.bw.WriteString(dataS) + } +} + +func (w *responseWriter) handlerDone() { + rws := w.rws + rws.handlerDone = true + w.Flush() + w.rws = nil + responseWriterStatePool.Put(rws) +} + +// foreachHeaderElement splits v according to the "#rule" construction +// in RFC 2616 section 2.1 and calls fn for each non-empty element. +func foreachHeaderElement(v string, fn func(string)) { + v = textproto.TrimString(v) + if v == "" { + return + } + if !strings.Contains(v, ",") { + fn(v) + return + } + for _, f := range strings.Split(v, ",") { + if f = textproto.TrimString(f); f != "" { + fn(f) + } + } +} + +// From http://httpwg.org/specs/rfc7540.html#rfc.section.8.1.2.2 +var connHeaders = []string{ + "Connection", + "Keep-Alive", + "Proxy-Connection", + "Transfer-Encoding", + "Upgrade", +} + +// checkValidHTTP2Request checks whether req is a valid HTTP/2 request, +// per RFC 7540 Section 8.1.2.2. +// The returned error is reported to users. +func checkValidHTTP2Request(req *http.Request) error { + for _, h := range connHeaders { + if _, ok := req.Header[h]; ok { + return fmt.Errorf("request header %q is not valid in HTTP/2", h) + } + } + te := req.Header["Te"] + if len(te) > 0 && (len(te) > 1 || (te[0] != "trailers" && te[0] != "")) { + return errors.New(`request header "TE" may only be "trailers" in HTTP/2`) + } + return nil +} + +func new400Handler(err error) http.HandlerFunc { + return func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { + http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest) + } +} + +// ValidTrailerHeader reports whether name is a valid header field name to appear +// in trailers. +// See: http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-4.1.2 +func ValidTrailerHeader(name string) bool { + name = http.CanonicalHeaderKey(name) + if strings.HasPrefix(name, "If-") || badTrailer[name] { + return false + } + return true +} + +var badTrailer = map[string]bool{ + "Authorization": true, + "Cache-Control": true, + "Connection": true, + "Content-Encoding": true, + "Content-Length": true, + "Content-Range": true, + "Content-Type": true, + "Expect": true, + "Host": true, + "Keep-Alive": true, + "Max-Forwards": true, + "Pragma": true, + "Proxy-Authenticate": true, + "Proxy-Authorization": true, + "Proxy-Connection": true, + "Range": true, + "Realm": true, + "Te": true, + "Trailer": true, + "Transfer-Encoding": true, + "Www-Authenticate": true, +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/transport.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/transport.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..129c8e0 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/transport.go @@ -0,0 +1,2063 @@ +// Copyright 2015 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +// Transport code. + +package http2 + +import ( + "bufio" + "bytes" + "compress/gzip" + "crypto/rand" + "crypto/tls" + "errors" + "fmt" + "io" + "io/ioutil" + "log" + "math" + "net" + "net/http" + "sort" + "strconv" + "strings" + "sync" + "time" + + "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack" + "golang.org/x/net/idna" + "golang.org/x/net/lex/httplex" +) + +const ( + // transportDefaultConnFlow is how many connection-level flow control + // tokens we give the server at start-up, past the default 64k. + transportDefaultConnFlow = 1 << 30 + + // transportDefaultStreamFlow is how many stream-level flow + // control tokens we announce to the peer, and how many bytes + // we buffer per stream. + transportDefaultStreamFlow = 4 << 20 + + // transportDefaultStreamMinRefresh is the minimum number of bytes we'll send + // a stream-level WINDOW_UPDATE for at a time. + transportDefaultStreamMinRefresh = 4 << 10 + + defaultUserAgent = "Go-http-client/2.0" +) + +// Transport is an HTTP/2 Transport. +// +// A Transport internally caches connections to servers. It is safe +// for concurrent use by multiple goroutines. +type Transport struct { + // DialTLS specifies an optional dial function for creating + // TLS connections for requests. + // + // If DialTLS is nil, tls.Dial is used. + // + // If the returned net.Conn has a ConnectionState method like tls.Conn, + // it will be used to set http.Response.TLS. + DialTLS func(network, addr string, cfg *tls.Config) (net.Conn, error) + + // TLSClientConfig specifies the TLS configuration to use with + // tls.Client. If nil, the default configuration is used. + TLSClientConfig *tls.Config + + // ConnPool optionally specifies an alternate connection pool to use. + // If nil, the default is used. + ConnPool ClientConnPool + + // DisableCompression, if true, prevents the Transport from + // requesting compression with an "Accept-Encoding: gzip" + // request header when the Request contains no existing + // Accept-Encoding value. If the Transport requests gzip on + // its own and gets a gzipped response, it's transparently + // decoded in the Response.Body. However, if the user + // explicitly requested gzip it is not automatically + // uncompressed. + DisableCompression bool + + // AllowHTTP, if true, permits HTTP/2 requests using the insecure, + // plain-text "http" scheme. Note that this does not enable h2c support. + AllowHTTP bool + + // MaxHeaderListSize is the http2 SETTINGS_MAX_HEADER_LIST_SIZE to + // send in the initial settings frame. It is how many bytes + // of response headers are allow. Unlike the http2 spec, zero here + // means to use a default limit (currently 10MB). If you actually + // want to advertise an ulimited value to the peer, Transport + // interprets the highest possible value here (0xffffffff or 1<<32-1) + // to mean no limit. + MaxHeaderListSize uint32 + + // t1, if non-nil, is the standard library Transport using + // this transport. Its settings are used (but not its + // RoundTrip method, etc). + t1 *http.Transport + + connPoolOnce sync.Once + connPoolOrDef ClientConnPool // non-nil version of ConnPool +} + +func (t *Transport) maxHeaderListSize() uint32 { + if t.MaxHeaderListSize == 0 { + return 10 << 20 + } + if t.MaxHeaderListSize == 0xffffffff { + return 0 + } + return t.MaxHeaderListSize +} + +func (t *Transport) disableCompression() bool { + return t.DisableCompression || (t.t1 != nil && t.t1.DisableCompression) +} + +var errTransportVersion = errors.New("http2: ConfigureTransport is only supported starting at Go 1.6") + +// ConfigureTransport configures a net/http HTTP/1 Transport to use HTTP/2. +// It requires Go 1.6 or later and returns an error if the net/http package is too old +// or if t1 has already been HTTP/2-enabled. +func ConfigureTransport(t1 *http.Transport) error { + _, err := configureTransport(t1) // in configure_transport.go (go1.6) or not_go16.go + return err +} + +func (t *Transport) connPool() ClientConnPool { + t.connPoolOnce.Do(t.initConnPool) + return t.connPoolOrDef +} + +func (t *Transport) initConnPool() { + if t.ConnPool != nil { + t.connPoolOrDef = t.ConnPool + } else { + t.connPoolOrDef = &clientConnPool{t: t} + } +} + +// ClientConn is the state of a single HTTP/2 client connection to an +// HTTP/2 server. +type ClientConn struct { + t *Transport + tconn net.Conn // usually *tls.Conn, except specialized impls + tlsState *tls.ConnectionState // nil only for specialized impls + singleUse bool // whether being used for a single http.Request + + // readLoop goroutine fields: + readerDone chan struct{} // closed on error + readerErr error // set before readerDone is closed + + idleTimeout time.Duration // or 0 for never + idleTimer *time.Timer + + mu sync.Mutex // guards following + cond *sync.Cond // hold mu; broadcast on flow/closed changes + flow flow // our conn-level flow control quota (cs.flow is per stream) + inflow flow // peer's conn-level flow control + closed bool + wantSettingsAck bool // we sent a SETTINGS frame and haven't heard back + goAway *GoAwayFrame // if non-nil, the GoAwayFrame we received + goAwayDebug string // goAway frame's debug data, retained as a string + streams map[uint32]*clientStream // client-initiated + nextStreamID uint32 + pings map[[8]byte]chan struct{} // in flight ping data to notification channel + bw *bufio.Writer + br *bufio.Reader + fr *Framer + lastActive time.Time + // Settings from peer: (also guarded by mu) + maxFrameSize uint32 + maxConcurrentStreams uint32 + initialWindowSize uint32 + + hbuf bytes.Buffer // HPACK encoder writes into this + henc *hpack.Encoder + freeBuf [][]byte + + wmu sync.Mutex // held while writing; acquire AFTER mu if holding both + werr error // first write error that has occurred +} + +// clientStream is the state for a single HTTP/2 stream. One of these +// is created for each Transport.RoundTrip call. +type clientStream struct { + cc *ClientConn + req *http.Request + trace *clientTrace // or nil + ID uint32 + resc chan resAndError + bufPipe pipe // buffered pipe with the flow-controlled response payload + requestedGzip bool + on100 func() // optional code to run if get a 100 continue response + + flow flow // guarded by cc.mu + inflow flow // guarded by cc.mu + bytesRemain int64 // -1 means unknown; owned by transportResponseBody.Read + readErr error // sticky read error; owned by transportResponseBody.Read + stopReqBody error // if non-nil, stop writing req body; guarded by cc.mu + + peerReset chan struct{} // closed on peer reset + resetErr error // populated before peerReset is closed + + done chan struct{} // closed when stream remove from cc.streams map; close calls guarded by cc.mu + + // owned by clientConnReadLoop: + firstByte bool // got the first response byte + pastHeaders bool // got first MetaHeadersFrame (actual headers) + pastTrailers bool // got optional second MetaHeadersFrame (trailers) + + trailer http.Header // accumulated trailers + resTrailer *http.Header // client's Response.Trailer +} + +// awaitRequestCancel runs in its own goroutine and waits for the user +// to cancel a RoundTrip request, its context to expire, or for the +// request to be done (any way it might be removed from the cc.streams +// map: peer reset, successful completion, TCP connection breakage, +// etc) +func (cs *clientStream) awaitRequestCancel(req *http.Request) { + ctx := reqContext(req) + if req.Cancel == nil && ctx.Done() == nil { + return + } + select { + case <-req.Cancel: + cs.bufPipe.CloseWithError(errRequestCanceled) + cs.cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, ErrCodeCancel, nil) + case <-ctx.Done(): + cs.bufPipe.CloseWithError(ctx.Err()) + cs.cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, ErrCodeCancel, nil) + case <-cs.done: + } +} + +// checkResetOrDone reports any error sent in a RST_STREAM frame by the +// server, or errStreamClosed if the stream is complete. +func (cs *clientStream) checkResetOrDone() error { + select { + case <-cs.peerReset: + return cs.resetErr + case <-cs.done: + return errStreamClosed + default: + return nil + } +} + +func (cs *clientStream) abortRequestBodyWrite(err error) { + if err == nil { + panic("nil error") + } + cc := cs.cc + cc.mu.Lock() + cs.stopReqBody = err + cc.cond.Broadcast() + cc.mu.Unlock() +} + +type stickyErrWriter struct { + w io.Writer + err *error +} + +func (sew stickyErrWriter) Write(p []byte) (n int, err error) { + if *sew.err != nil { + return 0, *sew.err + } + n, err = sew.w.Write(p) + *sew.err = err + return +} + +var ErrNoCachedConn = errors.New("http2: no cached connection was available") + +// RoundTripOpt are options for the Transport.RoundTripOpt method. +type RoundTripOpt struct { + // OnlyCachedConn controls whether RoundTripOpt may + // create a new TCP connection. If set true and + // no cached connection is available, RoundTripOpt + // will return ErrNoCachedConn. + OnlyCachedConn bool +} + +func (t *Transport) RoundTrip(req *http.Request) (*http.Response, error) { + return t.RoundTripOpt(req, RoundTripOpt{}) +} + +// authorityAddr returns a given authority (a host/IP, or host:port / ip:port) +// and returns a host:port. The port 443 is added if needed. +func authorityAddr(scheme string, authority string) (addr string) { + host, port, err := net.SplitHostPort(authority) + if err != nil { // authority didn't have a port + port = "443" + if scheme == "http" { + port = "80" + } + host = authority + } + if a, err := idna.ToASCII(host); err == nil { + host = a + } + return net.JoinHostPort(host, port) +} + +// RoundTripOpt is like RoundTrip, but takes options. +func (t *Transport) RoundTripOpt(req *http.Request, opt RoundTripOpt) (*http.Response, error) { + if !(req.URL.Scheme == "https" || (req.URL.Scheme == "http" && t.AllowHTTP)) { + return nil, errors.New("http2: unsupported scheme") + } + + addr := authorityAddr(req.URL.Scheme, req.URL.Host) + for { + cc, err := t.connPool().GetClientConn(req, addr) + if err != nil { + t.vlogf("http2: Transport failed to get client conn for %s: %v", addr, err) + return nil, err + } + traceGotConn(req, cc) + res, err := cc.RoundTrip(req) + if shouldRetryRequest(req, err) { + continue + } + if err != nil { + t.vlogf("RoundTrip failure: %v", err) + return nil, err + } + return res, nil + } +} + +// CloseIdleConnections closes any connections which were previously +// connected from previous requests but are now sitting idle. +// It does not interrupt any connections currently in use. +func (t *Transport) CloseIdleConnections() { + if cp, ok := t.connPool().(clientConnPoolIdleCloser); ok { + cp.closeIdleConnections() + } +} + +var ( + errClientConnClosed = errors.New("http2: client conn is closed") + errClientConnUnusable = errors.New("http2: client conn not usable") +) + +func shouldRetryRequest(req *http.Request, err error) bool { + // TODO: retry GET requests (no bodies) more aggressively, if shutdown + // before response. + return err == errClientConnUnusable +} + +func (t *Transport) dialClientConn(addr string, singleUse bool) (*ClientConn, error) { + host, _, err := net.SplitHostPort(addr) + if err != nil { + return nil, err + } + tconn, err := t.dialTLS()("tcp", addr, t.newTLSConfig(host)) + if err != nil { + return nil, err + } + return t.newClientConn(tconn, singleUse) +} + +func (t *Transport) newTLSConfig(host string) *tls.Config { + cfg := new(tls.Config) + if t.TLSClientConfig != nil { + *cfg = *cloneTLSConfig(t.TLSClientConfig) + } + if !strSliceContains(cfg.NextProtos, NextProtoTLS) { + cfg.NextProtos = append([]string{NextProtoTLS}, cfg.NextProtos...) + } + if cfg.ServerName == "" { + cfg.ServerName = host + } + return cfg +} + +func (t *Transport) dialTLS() func(string, string, *tls.Config) (net.Conn, error) { + if t.DialTLS != nil { + return t.DialTLS + } + return t.dialTLSDefault +} + +func (t *Transport) dialTLSDefault(network, addr string, cfg *tls.Config) (net.Conn, error) { + cn, err := tls.Dial(network, addr, cfg) + if err != nil { + return nil, err + } + if err := cn.Handshake(); err != nil { + return nil, err + } + if !cfg.InsecureSkipVerify { + if err := cn.VerifyHostname(cfg.ServerName); err != nil { + return nil, err + } + } + state := cn.ConnectionState() + if p := state.NegotiatedProtocol; p != NextProtoTLS { + return nil, fmt.Errorf("http2: unexpected ALPN protocol %q; want %q", p, NextProtoTLS) + } + if !state.NegotiatedProtocolIsMutual { + return nil, errors.New("http2: could not negotiate protocol mutually") + } + return cn, nil +} + +// disableKeepAlives reports whether connections should be closed as +// soon as possible after handling the first request. +func (t *Transport) disableKeepAlives() bool { + return t.t1 != nil && t.t1.DisableKeepAlives +} + +func (t *Transport) expectContinueTimeout() time.Duration { + if t.t1 == nil { + return 0 + } + return transportExpectContinueTimeout(t.t1) +} + +func (t *Transport) NewClientConn(c net.Conn) (*ClientConn, error) { + return t.newClientConn(c, false) +} + +func (t *Transport) newClientConn(c net.Conn, singleUse bool) (*ClientConn, error) { + cc := &ClientConn{ + t: t, + tconn: c, + readerDone: make(chan struct{}), + nextStreamID: 1, + maxFrameSize: 16 << 10, // spec default + initialWindowSize: 65535, // spec default + maxConcurrentStreams: 1000, // "infinite", per spec. 1000 seems good enough. + streams: make(map[uint32]*clientStream), + singleUse: singleUse, + wantSettingsAck: true, + pings: make(map[[8]byte]chan struct{}), + } + if d := t.idleConnTimeout(); d != 0 { + cc.idleTimeout = d + cc.idleTimer = time.AfterFunc(d, cc.onIdleTimeout) + } + if VerboseLogs { + t.vlogf("http2: Transport creating client conn %p to %v", cc, c.RemoteAddr()) + } + + cc.cond = sync.NewCond(&cc.mu) + cc.flow.add(int32(initialWindowSize)) + + // TODO: adjust this writer size to account for frame size + + // MTU + crypto/tls record padding. + cc.bw = bufio.NewWriter(stickyErrWriter{c, &cc.werr}) + cc.br = bufio.NewReader(c) + cc.fr = NewFramer(cc.bw, cc.br) + cc.fr.ReadMetaHeaders = hpack.NewDecoder(initialHeaderTableSize, nil) + cc.fr.MaxHeaderListSize = t.maxHeaderListSize() + + // TODO: SetMaxDynamicTableSize, SetMaxDynamicTableSizeLimit on + // henc in response to SETTINGS frames? + cc.henc = hpack.NewEncoder(&cc.hbuf) + + if cs, ok := c.(connectionStater); ok { + state := cs.ConnectionState() + cc.tlsState = &state + } + + initialSettings := []Setting{ + {ID: SettingEnablePush, Val: 0}, + {ID: SettingInitialWindowSize, Val: transportDefaultStreamFlow}, + } + if max := t.maxHeaderListSize(); max != 0 { + initialSettings = append(initialSettings, Setting{ID: SettingMaxHeaderListSize, Val: max}) + } + + cc.bw.Write(clientPreface) + cc.fr.WriteSettings(initialSettings...) + cc.fr.WriteWindowUpdate(0, transportDefaultConnFlow) + cc.inflow.add(transportDefaultConnFlow + initialWindowSize) + cc.bw.Flush() + if cc.werr != nil { + return nil, cc.werr + } + + go cc.readLoop() + return cc, nil +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) setGoAway(f *GoAwayFrame) { + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + + old := cc.goAway + cc.goAway = f + + // Merge the previous and current GoAway error frames. + if cc.goAwayDebug == "" { + cc.goAwayDebug = string(f.DebugData()) + } + if old != nil && old.ErrCode != ErrCodeNo { + cc.goAway.ErrCode = old.ErrCode + } +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) CanTakeNewRequest() bool { + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + return cc.canTakeNewRequestLocked() +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) canTakeNewRequestLocked() bool { + if cc.singleUse && cc.nextStreamID > 1 { + return false + } + return cc.goAway == nil && !cc.closed && + int64(len(cc.streams)+1) < int64(cc.maxConcurrentStreams) && + cc.nextStreamID < math.MaxInt32 +} + +// onIdleTimeout is called from a time.AfterFunc goroutine. It will +// only be called when we're idle, but because we're coming from a new +// goroutine, there could be a new request coming in at the same time, +// so this simply calls the synchronized closeIfIdle to shut down this +// connection. The timer could just call closeIfIdle, but this is more +// clear. +func (cc *ClientConn) onIdleTimeout() { + cc.closeIfIdle() +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) closeIfIdle() { + cc.mu.Lock() + if len(cc.streams) > 0 { + cc.mu.Unlock() + return + } + cc.closed = true + nextID := cc.nextStreamID + // TODO: do clients send GOAWAY too? maybe? Just Close: + cc.mu.Unlock() + + if VerboseLogs { + cc.vlogf("http2: Transport closing idle conn %p (forSingleUse=%v, maxStream=%v)", cc, cc.singleUse, nextID-2) + } + cc.tconn.Close() +} + +const maxAllocFrameSize = 512 << 10 + +// frameBuffer returns a scratch buffer suitable for writing DATA frames. +// They're capped at the min of the peer's max frame size or 512KB +// (kinda arbitrarily), but definitely capped so we don't allocate 4GB +// bufers. +func (cc *ClientConn) frameScratchBuffer() []byte { + cc.mu.Lock() + size := cc.maxFrameSize + if size > maxAllocFrameSize { + size = maxAllocFrameSize + } + for i, buf := range cc.freeBuf { + if len(buf) >= int(size) { + cc.freeBuf[i] = nil + cc.mu.Unlock() + return buf[:size] + } + } + cc.mu.Unlock() + return make([]byte, size) +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) putFrameScratchBuffer(buf []byte) { + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + const maxBufs = 4 // arbitrary; 4 concurrent requests per conn? investigate. + if len(cc.freeBuf) < maxBufs { + cc.freeBuf = append(cc.freeBuf, buf) + return + } + for i, old := range cc.freeBuf { + if old == nil { + cc.freeBuf[i] = buf + return + } + } + // forget about it. +} + +// errRequestCanceled is a copy of net/http's errRequestCanceled because it's not +// exported. At least they'll be DeepEqual for h1-vs-h2 comparisons tests. +var errRequestCanceled = errors.New("net/http: request canceled") + +func commaSeparatedTrailers(req *http.Request) (string, error) { + keys := make([]string, 0, len(req.Trailer)) + for k := range req.Trailer { + k = http.CanonicalHeaderKey(k) + switch k { + case "Transfer-Encoding", "Trailer", "Content-Length": + return "", &badStringError{"invalid Trailer key", k} + } + keys = append(keys, k) + } + if len(keys) > 0 { + sort.Strings(keys) + // TODO: could do better allocation-wise here, but trailers are rare, + // so being lazy for now. + return strings.Join(keys, ","), nil + } + return "", nil +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) responseHeaderTimeout() time.Duration { + if cc.t.t1 != nil { + return cc.t.t1.ResponseHeaderTimeout + } + // No way to do this (yet?) with just an http2.Transport. Probably + // no need. Request.Cancel this is the new way. We only need to support + // this for compatibility with the old http.Transport fields when + // we're doing transparent http2. + return 0 +} + +// checkConnHeaders checks whether req has any invalid connection-level headers. +// per RFC 7540 section 8.1.2.2: Connection-Specific Header Fields. +// Certain headers are special-cased as okay but not transmitted later. +func checkConnHeaders(req *http.Request) error { + if v := req.Header.Get("Upgrade"); v != "" { + return fmt.Errorf("http2: invalid Upgrade request header: %q", req.Header["Upgrade"]) + } + if vv := req.Header["Transfer-Encoding"]; len(vv) > 0 && (len(vv) > 1 || vv[0] != "" && vv[0] != "chunked") { + return fmt.Errorf("http2: invalid Transfer-Encoding request header: %q", vv) + } + if vv := req.Header["Connection"]; len(vv) > 0 && (len(vv) > 1 || vv[0] != "" && vv[0] != "close" && vv[0] != "keep-alive") { + return fmt.Errorf("http2: invalid Connection request header: %q", vv) + } + return nil +} + +// actualContentLength returns a sanitized version of +// req.ContentLength, where 0 actually means zero (not unknown) and -1 +// means unknown. +func actualContentLength(req *http.Request) int64 { + if req.Body == nil { + return 0 + } + if req.ContentLength != 0 { + return req.ContentLength + } + return -1 +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) RoundTrip(req *http.Request) (*http.Response, error) { + if err := checkConnHeaders(req); err != nil { + return nil, err + } + if cc.idleTimer != nil { + cc.idleTimer.Stop() + } + + trailers, err := commaSeparatedTrailers(req) + if err != nil { + return nil, err + } + hasTrailers := trailers != "" + + cc.mu.Lock() + cc.lastActive = time.Now() + if cc.closed || !cc.canTakeNewRequestLocked() { + cc.mu.Unlock() + return nil, errClientConnUnusable + } + + body := req.Body + hasBody := body != nil + contentLen := actualContentLength(req) + + // TODO(bradfitz): this is a copy of the logic in net/http. Unify somewhere? + var requestedGzip bool + if !cc.t.disableCompression() && + req.Header.Get("Accept-Encoding") == "" && + req.Header.Get("Range") == "" && + req.Method != "HEAD" { + // Request gzip only, not deflate. Deflate is ambiguous and + // not as universally supported anyway. + // See: http://www.gzip.org/zlib/zlib_faq.html#faq38 + // + // Note that we don't request this for HEAD requests, + // due to a bug in nginx: + // http://trac.nginx.org/nginx/ticket/358 + // https://golang.org/issue/5522 + // + // We don't request gzip if the request is for a range, since + // auto-decoding a portion of a gzipped document will just fail + // anyway. See https://golang.org/issue/8923 + requestedGzip = true + } + + // we send: HEADERS{1}, CONTINUATION{0,} + DATA{0,} (DATA is + // sent by writeRequestBody below, along with any Trailers, + // again in form HEADERS{1}, CONTINUATION{0,}) + hdrs, err := cc.encodeHeaders(req, requestedGzip, trailers, contentLen) + if err != nil { + cc.mu.Unlock() + return nil, err + } + + cs := cc.newStream() + cs.req = req + cs.trace = requestTrace(req) + cs.requestedGzip = requestedGzip + bodyWriter := cc.t.getBodyWriterState(cs, body) + cs.on100 = bodyWriter.on100 + + cc.wmu.Lock() + endStream := !hasBody && !hasTrailers + werr := cc.writeHeaders(cs.ID, endStream, hdrs) + cc.wmu.Unlock() + traceWroteHeaders(cs.trace) + cc.mu.Unlock() + + if werr != nil { + if hasBody { + req.Body.Close() // per RoundTripper contract + bodyWriter.cancel() + } + cc.forgetStreamID(cs.ID) + // Don't bother sending a RST_STREAM (our write already failed; + // no need to keep writing) + traceWroteRequest(cs.trace, werr) + return nil, werr + } + + var respHeaderTimer <-chan time.Time + if hasBody { + bodyWriter.scheduleBodyWrite() + } else { + traceWroteRequest(cs.trace, nil) + if d := cc.responseHeaderTimeout(); d != 0 { + timer := time.NewTimer(d) + defer timer.Stop() + respHeaderTimer = timer.C + } + } + + readLoopResCh := cs.resc + bodyWritten := false + ctx := reqContext(req) + + handleReadLoopResponse := func(re resAndError) (*http.Response, error) { + res := re.res + if re.err != nil || res.StatusCode > 299 { + // On error or status code 3xx, 4xx, 5xx, etc abort any + // ongoing write, assuming that the server doesn't care + // about our request body. If the server replied with 1xx or + // 2xx, however, then assume the server DOES potentially + // want our body (e.g. full-duplex streaming: + // golang.org/issue/13444). If it turns out the server + // doesn't, they'll RST_STREAM us soon enough. This is a + // heuristic to avoid adding knobs to Transport. Hopefully + // we can keep it. + bodyWriter.cancel() + cs.abortRequestBodyWrite(errStopReqBodyWrite) + } + if re.err != nil { + cc.forgetStreamID(cs.ID) + return nil, re.err + } + res.Request = req + res.TLS = cc.tlsState + return res, nil + } + + for { + select { + case re := <-readLoopResCh: + return handleReadLoopResponse(re) + case <-respHeaderTimer: + cc.forgetStreamID(cs.ID) + if !hasBody || bodyWritten { + cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, ErrCodeCancel, nil) + } else { + bodyWriter.cancel() + cs.abortRequestBodyWrite(errStopReqBodyWriteAndCancel) + } + return nil, errTimeout + case <-ctx.Done(): + cc.forgetStreamID(cs.ID) + if !hasBody || bodyWritten { + cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, ErrCodeCancel, nil) + } else { + bodyWriter.cancel() + cs.abortRequestBodyWrite(errStopReqBodyWriteAndCancel) + } + return nil, ctx.Err() + case <-req.Cancel: + cc.forgetStreamID(cs.ID) + if !hasBody || bodyWritten { + cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, ErrCodeCancel, nil) + } else { + bodyWriter.cancel() + cs.abortRequestBodyWrite(errStopReqBodyWriteAndCancel) + } + return nil, errRequestCanceled + case <-cs.peerReset: + // processResetStream already removed the + // stream from the streams map; no need for + // forgetStreamID. + return nil, cs.resetErr + case err := <-bodyWriter.resc: + // Prefer the read loop's response, if available. Issue 16102. + select { + case re := <-readLoopResCh: + return handleReadLoopResponse(re) + default: + } + if err != nil { + return nil, err + } + bodyWritten = true + if d := cc.responseHeaderTimeout(); d != 0 { + timer := time.NewTimer(d) + defer timer.Stop() + respHeaderTimer = timer.C + } + } + } +} + +// requires cc.wmu be held +func (cc *ClientConn) writeHeaders(streamID uint32, endStream bool, hdrs []byte) error { + first := true // first frame written (HEADERS is first, then CONTINUATION) + frameSize := int(cc.maxFrameSize) + for len(hdrs) > 0 && cc.werr == nil { + chunk := hdrs + if len(chunk) > frameSize { + chunk = chunk[:frameSize] + } + hdrs = hdrs[len(chunk):] + endHeaders := len(hdrs) == 0 + if first { + cc.fr.WriteHeaders(HeadersFrameParam{ + StreamID: streamID, + BlockFragment: chunk, + EndStream: endStream, + EndHeaders: endHeaders, + }) + first = false + } else { + cc.fr.WriteContinuation(streamID, endHeaders, chunk) + } + } + // TODO(bradfitz): this Flush could potentially block (as + // could the WriteHeaders call(s) above), which means they + // wouldn't respond to Request.Cancel being readable. That's + // rare, but this should probably be in a goroutine. + cc.bw.Flush() + return cc.werr +} + +// internal error values; they don't escape to callers +var ( + // abort request body write; don't send cancel + errStopReqBodyWrite = errors.New("http2: aborting request body write") + + // abort request body write, but send stream reset of cancel. + errStopReqBodyWriteAndCancel = errors.New("http2: canceling request") +) + +func (cs *clientStream) writeRequestBody(body io.Reader, bodyCloser io.Closer) (err error) { + cc := cs.cc + sentEnd := false // whether we sent the final DATA frame w/ END_STREAM + buf := cc.frameScratchBuffer() + defer cc.putFrameScratchBuffer(buf) + + defer func() { + traceWroteRequest(cs.trace, err) + // TODO: write h12Compare test showing whether + // Request.Body is closed by the Transport, + // and in multiple cases: server replies <=299 and >299 + // while still writing request body + cerr := bodyCloser.Close() + if err == nil { + err = cerr + } + }() + + req := cs.req + hasTrailers := req.Trailer != nil + + var sawEOF bool + for !sawEOF { + n, err := body.Read(buf) + if err == io.EOF { + sawEOF = true + err = nil + } else if err != nil { + return err + } + + remain := buf[:n] + for len(remain) > 0 && err == nil { + var allowed int32 + allowed, err = cs.awaitFlowControl(len(remain)) + switch { + case err == errStopReqBodyWrite: + return err + case err == errStopReqBodyWriteAndCancel: + cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, ErrCodeCancel, nil) + return err + case err != nil: + return err + } + cc.wmu.Lock() + data := remain[:allowed] + remain = remain[allowed:] + sentEnd = sawEOF && len(remain) == 0 && !hasTrailers + err = cc.fr.WriteData(cs.ID, sentEnd, data) + if err == nil { + // TODO(bradfitz): this flush is for latency, not bandwidth. + // Most requests won't need this. Make this opt-in or + // opt-out? Use some heuristic on the body type? Nagel-like + // timers? Based on 'n'? Only last chunk of this for loop, + // unless flow control tokens are low? For now, always. + // If we change this, see comment below. + err = cc.bw.Flush() + } + cc.wmu.Unlock() + } + if err != nil { + return err + } + } + + if sentEnd { + // Already sent END_STREAM (which implies we have no + // trailers) and flushed, because currently all + // WriteData frames above get a flush. So we're done. + return nil + } + + var trls []byte + if hasTrailers { + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + trls = cc.encodeTrailers(req) + } + + cc.wmu.Lock() + defer cc.wmu.Unlock() + + // Two ways to send END_STREAM: either with trailers, or + // with an empty DATA frame. + if len(trls) > 0 { + err = cc.writeHeaders(cs.ID, true, trls) + } else { + err = cc.fr.WriteData(cs.ID, true, nil) + } + if ferr := cc.bw.Flush(); ferr != nil && err == nil { + err = ferr + } + return err +} + +// awaitFlowControl waits for [1, min(maxBytes, cc.cs.maxFrameSize)] flow +// control tokens from the server. +// It returns either the non-zero number of tokens taken or an error +// if the stream is dead. +func (cs *clientStream) awaitFlowControl(maxBytes int) (taken int32, err error) { + cc := cs.cc + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + for { + if cc.closed { + return 0, errClientConnClosed + } + if cs.stopReqBody != nil { + return 0, cs.stopReqBody + } + if err := cs.checkResetOrDone(); err != nil { + return 0, err + } + if a := cs.flow.available(); a > 0 { + take := a + if int(take) > maxBytes { + + take = int32(maxBytes) // can't truncate int; take is int32 + } + if take > int32(cc.maxFrameSize) { + take = int32(cc.maxFrameSize) + } + cs.flow.take(take) + return take, nil + } + cc.cond.Wait() + } +} + +type badStringError struct { + what string + str string +} + +func (e *badStringError) Error() string { return fmt.Sprintf("%s %q", e.what, e.str) } + +// requires cc.mu be held. +func (cc *ClientConn) encodeHeaders(req *http.Request, addGzipHeader bool, trailers string, contentLength int64) ([]byte, error) { + cc.hbuf.Reset() + + host := req.Host + if host == "" { + host = req.URL.Host + } + host, err := httplex.PunycodeHostPort(host) + if err != nil { + return nil, err + } + + var path string + if req.Method != "CONNECT" { + path = req.URL.RequestURI() + if !validPseudoPath(path) { + orig := path + path = strings.TrimPrefix(path, req.URL.Scheme+"://"+host) + if !validPseudoPath(path) { + if req.URL.Opaque != "" { + return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid request :path %q from URL.Opaque = %q", orig, req.URL.Opaque) + } else { + return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid request :path %q", orig) + } + } + } + } + + // Check for any invalid headers and return an error before we + // potentially pollute our hpack state. (We want to be able to + // continue to reuse the hpack encoder for future requests) + for k, vv := range req.Header { + if !httplex.ValidHeaderFieldName(k) { + return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid HTTP header name %q", k) + } + for _, v := range vv { + if !httplex.ValidHeaderFieldValue(v) { + return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid HTTP header value %q for header %q", v, k) + } + } + } + + // 8.1.2.3 Request Pseudo-Header Fields + // The :path pseudo-header field includes the path and query parts of the + // target URI (the path-absolute production and optionally a '?' character + // followed by the query production (see Sections 3.3 and 3.4 of + // [RFC3986]). + cc.writeHeader(":authority", host) + cc.writeHeader(":method", req.Method) + if req.Method != "CONNECT" { + cc.writeHeader(":path", path) + cc.writeHeader(":scheme", req.URL.Scheme) + } + if trailers != "" { + cc.writeHeader("trailer", trailers) + } + + var didUA bool + for k, vv := range req.Header { + lowKey := strings.ToLower(k) + switch lowKey { + case "host", "content-length": + // Host is :authority, already sent. + // Content-Length is automatic, set below. + continue + case "connection", "proxy-connection", "transfer-encoding", "upgrade", "keep-alive": + // Per 8.1.2.2 Connection-Specific Header + // Fields, don't send connection-specific + // fields. We have already checked if any + // are error-worthy so just ignore the rest. + continue + case "user-agent": + // Match Go's http1 behavior: at most one + // User-Agent. If set to nil or empty string, + // then omit it. Otherwise if not mentioned, + // include the default (below). + didUA = true + if len(vv) < 1 { + continue + } + vv = vv[:1] + if vv[0] == "" { + continue + } + } + for _, v := range vv { + cc.writeHeader(lowKey, v) + } + } + if shouldSendReqContentLength(req.Method, contentLength) { + cc.writeHeader("content-length", strconv.FormatInt(contentLength, 10)) + } + if addGzipHeader { + cc.writeHeader("accept-encoding", "gzip") + } + if !didUA { + cc.writeHeader("user-agent", defaultUserAgent) + } + return cc.hbuf.Bytes(), nil +} + +// shouldSendReqContentLength reports whether the http2.Transport should send +// a "content-length" request header. This logic is basically a copy of the net/http +// transferWriter.shouldSendContentLength. +// The contentLength is the corrected contentLength (so 0 means actually 0, not unknown). +// -1 means unknown. +func shouldSendReqContentLength(method string, contentLength int64) bool { + if contentLength > 0 { + return true + } + if contentLength < 0 { + return false + } + // For zero bodies, whether we send a content-length depends on the method. + // It also kinda doesn't matter for http2 either way, with END_STREAM. + switch method { + case "POST", "PUT", "PATCH": + return true + default: + return false + } +} + +// requires cc.mu be held. +func (cc *ClientConn) encodeTrailers(req *http.Request) []byte { + cc.hbuf.Reset() + for k, vv := range req.Trailer { + // Transfer-Encoding, etc.. have already been filter at the + // start of RoundTrip + lowKey := strings.ToLower(k) + for _, v := range vv { + cc.writeHeader(lowKey, v) + } + } + return cc.hbuf.Bytes() +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) writeHeader(name, value string) { + if VerboseLogs { + log.Printf("http2: Transport encoding header %q = %q", name, value) + } + cc.henc.WriteField(hpack.HeaderField{Name: name, Value: value}) +} + +type resAndError struct { + res *http.Response + err error +} + +// requires cc.mu be held. +func (cc *ClientConn) newStream() *clientStream { + cs := &clientStream{ + cc: cc, + ID: cc.nextStreamID, + resc: make(chan resAndError, 1), + peerReset: make(chan struct{}), + done: make(chan struct{}), + } + cs.flow.add(int32(cc.initialWindowSize)) + cs.flow.setConnFlow(&cc.flow) + cs.inflow.add(transportDefaultStreamFlow) + cs.inflow.setConnFlow(&cc.inflow) + cc.nextStreamID += 2 + cc.streams[cs.ID] = cs + return cs +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) forgetStreamID(id uint32) { + cc.streamByID(id, true) +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) streamByID(id uint32, andRemove bool) *clientStream { + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + cs := cc.streams[id] + if andRemove && cs != nil && !cc.closed { + cc.lastActive = time.Now() + delete(cc.streams, id) + if len(cc.streams) == 0 && cc.idleTimer != nil { + cc.idleTimer.Reset(cc.idleTimeout) + } + close(cs.done) + cc.cond.Broadcast() // wake up checkResetOrDone via clientStream.awaitFlowControl + } + return cs +} + +// clientConnReadLoop is the state owned by the clientConn's frame-reading readLoop. +type clientConnReadLoop struct { + cc *ClientConn + activeRes map[uint32]*clientStream // keyed by streamID + closeWhenIdle bool +} + +// readLoop runs in its own goroutine and reads and dispatches frames. +func (cc *ClientConn) readLoop() { + rl := &clientConnReadLoop{ + cc: cc, + activeRes: make(map[uint32]*clientStream), + } + + defer rl.cleanup() + cc.readerErr = rl.run() + if ce, ok := cc.readerErr.(ConnectionError); ok { + cc.wmu.Lock() + cc.fr.WriteGoAway(0, ErrCode(ce), nil) + cc.wmu.Unlock() + } +} + +// GoAwayError is returned by the Transport when the server closes the +// TCP connection after sending a GOAWAY frame. +type GoAwayError struct { + LastStreamID uint32 + ErrCode ErrCode + DebugData string +} + +func (e GoAwayError) Error() string { + return fmt.Sprintf("http2: server sent GOAWAY and closed the connection; LastStreamID=%v, ErrCode=%v, debug=%q", + e.LastStreamID, e.ErrCode, e.DebugData) +} + +func isEOFOrNetReadError(err error) bool { + if err == io.EOF { + return true + } + ne, ok := err.(*net.OpError) + return ok && ne.Op == "read" +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) cleanup() { + cc := rl.cc + defer cc.tconn.Close() + defer cc.t.connPool().MarkDead(cc) + defer close(cc.readerDone) + + if cc.idleTimer != nil { + cc.idleTimer.Stop() + } + + // Close any response bodies if the server closes prematurely. + // TODO: also do this if we've written the headers but not + // gotten a response yet. + err := cc.readerErr + cc.mu.Lock() + if cc.goAway != nil && isEOFOrNetReadError(err) { + err = GoAwayError{ + LastStreamID: cc.goAway.LastStreamID, + ErrCode: cc.goAway.ErrCode, + DebugData: cc.goAwayDebug, + } + } else if err == io.EOF { + err = io.ErrUnexpectedEOF + } + for _, cs := range rl.activeRes { + cs.bufPipe.CloseWithError(err) + } + for _, cs := range cc.streams { + select { + case cs.resc <- resAndError{err: err}: + default: + } + close(cs.done) + } + cc.closed = true + cc.cond.Broadcast() + cc.mu.Unlock() +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) run() error { + cc := rl.cc + rl.closeWhenIdle = cc.t.disableKeepAlives() || cc.singleUse + gotReply := false // ever saw a HEADERS reply + gotSettings := false + for { + f, err := cc.fr.ReadFrame() + if err != nil { + cc.vlogf("http2: Transport readFrame error on conn %p: (%T) %v", cc, err, err) + } + if se, ok := err.(StreamError); ok { + if cs := cc.streamByID(se.StreamID, true /*ended; remove it*/); cs != nil { + cs.cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, se.Code, err) + if se.Cause == nil { + se.Cause = cc.fr.errDetail + } + rl.endStreamError(cs, se) + } + continue + } else if err != nil { + return err + } + if VerboseLogs { + cc.vlogf("http2: Transport received %s", summarizeFrame(f)) + } + if !gotSettings { + if _, ok := f.(*SettingsFrame); !ok { + cc.logf("protocol error: received %T before a SETTINGS frame", f) + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) + } + gotSettings = true + } + maybeIdle := false // whether frame might transition us to idle + + switch f := f.(type) { + case *MetaHeadersFrame: + err = rl.processHeaders(f) + maybeIdle = true + gotReply = true + case *DataFrame: + err = rl.processData(f) + maybeIdle = true + case *GoAwayFrame: + err = rl.processGoAway(f) + maybeIdle = true + case *RSTStreamFrame: + err = rl.processResetStream(f) + maybeIdle = true + case *SettingsFrame: + err = rl.processSettings(f) + case *PushPromiseFrame: + err = rl.processPushPromise(f) + case *WindowUpdateFrame: + err = rl.processWindowUpdate(f) + case *PingFrame: + err = rl.processPing(f) + default: + cc.logf("Transport: unhandled response frame type %T", f) + } + if err != nil { + if VerboseLogs { + cc.vlogf("http2: Transport conn %p received error from processing frame %v: %v", cc, summarizeFrame(f), err) + } + return err + } + if rl.closeWhenIdle && gotReply && maybeIdle && len(rl.activeRes) == 0 { + cc.closeIfIdle() + } + } +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processHeaders(f *MetaHeadersFrame) error { + cc := rl.cc + cs := cc.streamByID(f.StreamID, f.StreamEnded()) + if cs == nil { + // We'd get here if we canceled a request while the + // server had its response still in flight. So if this + // was just something we canceled, ignore it. + return nil + } + if !cs.firstByte { + if cs.trace != nil { + // TODO(bradfitz): move first response byte earlier, + // when we first read the 9 byte header, not waiting + // until all the HEADERS+CONTINUATION frames have been + // merged. This works for now. + traceFirstResponseByte(cs.trace) + } + cs.firstByte = true + } + if !cs.pastHeaders { + cs.pastHeaders = true + } else { + return rl.processTrailers(cs, f) + } + + res, err := rl.handleResponse(cs, f) + if err != nil { + if _, ok := err.(ConnectionError); ok { + return err + } + // Any other error type is a stream error. + cs.cc.writeStreamReset(f.StreamID, ErrCodeProtocol, err) + cs.resc <- resAndError{err: err} + return nil // return nil from process* funcs to keep conn alive + } + if res == nil { + // (nil, nil) special case. See handleResponse docs. + return nil + } + if res.Body != noBody { + rl.activeRes[cs.ID] = cs + } + cs.resTrailer = &res.Trailer + cs.resc <- resAndError{res: res} + return nil +} + +// may return error types nil, or ConnectionError. Any other error value +// is a StreamError of type ErrCodeProtocol. The returned error in that case +// is the detail. +// +// As a special case, handleResponse may return (nil, nil) to skip the +// frame (currently only used for 100 expect continue). This special +// case is going away after Issue 13851 is fixed. +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) handleResponse(cs *clientStream, f *MetaHeadersFrame) (*http.Response, error) { + if f.Truncated { + return nil, errResponseHeaderListSize + } + + status := f.PseudoValue("status") + if status == "" { + return nil, errors.New("missing status pseudo header") + } + statusCode, err := strconv.Atoi(status) + if err != nil { + return nil, errors.New("malformed non-numeric status pseudo header") + } + + if statusCode == 100 { + traceGot100Continue(cs.trace) + if cs.on100 != nil { + cs.on100() // forces any write delay timer to fire + } + cs.pastHeaders = false // do it all again + return nil, nil + } + + header := make(http.Header) + res := &http.Response{ + Proto: "HTTP/2.0", + ProtoMajor: 2, + Header: header, + StatusCode: statusCode, + Status: status + " " + http.StatusText(statusCode), + } + for _, hf := range f.RegularFields() { + key := http.CanonicalHeaderKey(hf.Name) + if key == "Trailer" { + t := res.Trailer + if t == nil { + t = make(http.Header) + res.Trailer = t + } + foreachHeaderElement(hf.Value, func(v string) { + t[http.CanonicalHeaderKey(v)] = nil + }) + } else { + header[key] = append(header[key], hf.Value) + } + } + + streamEnded := f.StreamEnded() + isHead := cs.req.Method == "HEAD" + if !streamEnded || isHead { + res.ContentLength = -1 + if clens := res.Header["Content-Length"]; len(clens) == 1 { + if clen64, err := strconv.ParseInt(clens[0], 10, 64); err == nil { + res.ContentLength = clen64 + } else { + // TODO: care? unlike http/1, it won't mess up our framing, so it's + // more safe smuggling-wise to ignore. + } + } else if len(clens) > 1 { + // TODO: care? unlike http/1, it won't mess up our framing, so it's + // more safe smuggling-wise to ignore. + } + } + + if streamEnded || isHead { + res.Body = noBody + return res, nil + } + + buf := new(bytes.Buffer) // TODO(bradfitz): recycle this garbage + cs.bufPipe = pipe{b: buf} + cs.bytesRemain = res.ContentLength + res.Body = transportResponseBody{cs} + go cs.awaitRequestCancel(cs.req) + + if cs.requestedGzip && res.Header.Get("Content-Encoding") == "gzip" { + res.Header.Del("Content-Encoding") + res.Header.Del("Content-Length") + res.ContentLength = -1 + res.Body = &gzipReader{body: res.Body} + setResponseUncompressed(res) + } + return res, nil +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processTrailers(cs *clientStream, f *MetaHeadersFrame) error { + if cs.pastTrailers { + // Too many HEADERS frames for this stream. + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) + } + cs.pastTrailers = true + if !f.StreamEnded() { + // We expect that any headers for trailers also + // has END_STREAM. + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) + } + if len(f.PseudoFields()) > 0 { + // No pseudo header fields are defined for trailers. + // TODO: ConnectionError might be overly harsh? Check. + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) + } + + trailer := make(http.Header) + for _, hf := range f.RegularFields() { + key := http.CanonicalHeaderKey(hf.Name) + trailer[key] = append(trailer[key], hf.Value) + } + cs.trailer = trailer + + rl.endStream(cs) + return nil +} + +// transportResponseBody is the concrete type of Transport.RoundTrip's +// Response.Body. It is an io.ReadCloser. On Read, it reads from cs.body. +// On Close it sends RST_STREAM if EOF wasn't already seen. +type transportResponseBody struct { + cs *clientStream +} + +func (b transportResponseBody) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) { + cs := b.cs + cc := cs.cc + + if cs.readErr != nil { + return 0, cs.readErr + } + n, err = b.cs.bufPipe.Read(p) + if cs.bytesRemain != -1 { + if int64(n) > cs.bytesRemain { + n = int(cs.bytesRemain) + if err == nil { + err = errors.New("net/http: server replied with more than declared Content-Length; truncated") + cc.writeStreamReset(cs.ID, ErrCodeProtocol, err) + } + cs.readErr = err + return int(cs.bytesRemain), err + } + cs.bytesRemain -= int64(n) + if err == io.EOF && cs.bytesRemain > 0 { + err = io.ErrUnexpectedEOF + cs.readErr = err + return n, err + } + } + if n == 0 { + // No flow control tokens to send back. + return + } + + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + + var connAdd, streamAdd int32 + // Check the conn-level first, before the stream-level. + if v := cc.inflow.available(); v < transportDefaultConnFlow/2 { + connAdd = transportDefaultConnFlow - v + cc.inflow.add(connAdd) + } + if err == nil { // No need to refresh if the stream is over or failed. + // Consider any buffered body data (read from the conn but not + // consumed by the client) when computing flow control for this + // stream. + v := int(cs.inflow.available()) + cs.bufPipe.Len() + if v < transportDefaultStreamFlow-transportDefaultStreamMinRefresh { + streamAdd = int32(transportDefaultStreamFlow - v) + cs.inflow.add(streamAdd) + } + } + if connAdd != 0 || streamAdd != 0 { + cc.wmu.Lock() + defer cc.wmu.Unlock() + if connAdd != 0 { + cc.fr.WriteWindowUpdate(0, mustUint31(connAdd)) + } + if streamAdd != 0 { + cc.fr.WriteWindowUpdate(cs.ID, mustUint31(streamAdd)) + } + cc.bw.Flush() + } + return +} + +var errClosedResponseBody = errors.New("http2: response body closed") + +func (b transportResponseBody) Close() error { + cs := b.cs + cc := cs.cc + + serverSentStreamEnd := cs.bufPipe.Err() == io.EOF + unread := cs.bufPipe.Len() + + if unread > 0 || !serverSentStreamEnd { + cc.mu.Lock() + cc.wmu.Lock() + if !serverSentStreamEnd { + cc.fr.WriteRSTStream(cs.ID, ErrCodeCancel) + } + // Return connection-level flow control. + if unread > 0 { + cc.inflow.add(int32(unread)) + cc.fr.WriteWindowUpdate(0, uint32(unread)) + } + cc.bw.Flush() + cc.wmu.Unlock() + cc.mu.Unlock() + } + + cs.bufPipe.BreakWithError(errClosedResponseBody) + return nil +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processData(f *DataFrame) error { + cc := rl.cc + cs := cc.streamByID(f.StreamID, f.StreamEnded()) + data := f.Data() + if cs == nil { + cc.mu.Lock() + neverSent := cc.nextStreamID + cc.mu.Unlock() + if f.StreamID >= neverSent { + // We never asked for this. + cc.logf("http2: Transport received unsolicited DATA frame; closing connection") + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) + } + // We probably did ask for this, but canceled. Just ignore it. + // TODO: be stricter here? only silently ignore things which + // we canceled, but not things which were closed normally + // by the peer? Tough without accumulating too much state. + + // But at least return their flow control: + if f.Length > 0 { + cc.mu.Lock() + cc.inflow.add(int32(f.Length)) + cc.mu.Unlock() + + cc.wmu.Lock() + cc.fr.WriteWindowUpdate(0, uint32(f.Length)) + cc.bw.Flush() + cc.wmu.Unlock() + } + return nil + } + if f.Length > 0 { + if len(data) > 0 && cs.bufPipe.b == nil { + // Data frame after it's already closed? + cc.logf("http2: Transport received DATA frame for closed stream; closing connection") + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) + } + + // Check connection-level flow control. + cc.mu.Lock() + if cs.inflow.available() >= int32(f.Length) { + cs.inflow.take(int32(f.Length)) + } else { + cc.mu.Unlock() + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeFlowControl) + } + // Return any padded flow control now, since we won't + // refund it later on body reads. + if pad := int32(f.Length) - int32(len(data)); pad > 0 { + cs.inflow.add(pad) + cc.inflow.add(pad) + cc.wmu.Lock() + cc.fr.WriteWindowUpdate(0, uint32(pad)) + cc.fr.WriteWindowUpdate(cs.ID, uint32(pad)) + cc.bw.Flush() + cc.wmu.Unlock() + } + cc.mu.Unlock() + + if len(data) > 0 { + if _, err := cs.bufPipe.Write(data); err != nil { + rl.endStreamError(cs, err) + return err + } + } + } + + if f.StreamEnded() { + rl.endStream(cs) + } + return nil +} + +var errInvalidTrailers = errors.New("http2: invalid trailers") + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) endStream(cs *clientStream) { + // TODO: check that any declared content-length matches, like + // server.go's (*stream).endStream method. + rl.endStreamError(cs, nil) +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) endStreamError(cs *clientStream, err error) { + var code func() + if err == nil { + err = io.EOF + code = cs.copyTrailers + } + cs.bufPipe.closeWithErrorAndCode(err, code) + delete(rl.activeRes, cs.ID) + if isConnectionCloseRequest(cs.req) { + rl.closeWhenIdle = true + } + + select { + case cs.resc <- resAndError{err: err}: + default: + } +} + +func (cs *clientStream) copyTrailers() { + for k, vv := range cs.trailer { + t := cs.resTrailer + if *t == nil { + *t = make(http.Header) + } + (*t)[k] = vv + } +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processGoAway(f *GoAwayFrame) error { + cc := rl.cc + cc.t.connPool().MarkDead(cc) + if f.ErrCode != 0 { + // TODO: deal with GOAWAY more. particularly the error code + cc.vlogf("transport got GOAWAY with error code = %v", f.ErrCode) + } + cc.setGoAway(f) + return nil +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processSettings(f *SettingsFrame) error { + cc := rl.cc + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + + if f.IsAck() { + if cc.wantSettingsAck { + cc.wantSettingsAck = false + return nil + } + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) + } + + err := f.ForeachSetting(func(s Setting) error { + switch s.ID { + case SettingMaxFrameSize: + cc.maxFrameSize = s.Val + case SettingMaxConcurrentStreams: + cc.maxConcurrentStreams = s.Val + case SettingInitialWindowSize: + // Values above the maximum flow-control + // window size of 2^31-1 MUST be treated as a + // connection error (Section 5.4.1) of type + // FLOW_CONTROL_ERROR. + if s.Val > math.MaxInt32 { + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeFlowControl) + } + + // Adjust flow control of currently-open + // frames by the difference of the old initial + // window size and this one. + delta := int32(s.Val) - int32(cc.initialWindowSize) + for _, cs := range cc.streams { + cs.flow.add(delta) + } + cc.cond.Broadcast() + + cc.initialWindowSize = s.Val + default: + // TODO(bradfitz): handle more settings? SETTINGS_HEADER_TABLE_SIZE probably. + cc.vlogf("Unhandled Setting: %v", s) + } + return nil + }) + if err != nil { + return err + } + + cc.wmu.Lock() + defer cc.wmu.Unlock() + + cc.fr.WriteSettingsAck() + cc.bw.Flush() + return cc.werr +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processWindowUpdate(f *WindowUpdateFrame) error { + cc := rl.cc + cs := cc.streamByID(f.StreamID, false) + if f.StreamID != 0 && cs == nil { + return nil + } + + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + + fl := &cc.flow + if cs != nil { + fl = &cs.flow + } + if !fl.add(int32(f.Increment)) { + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeFlowControl) + } + cc.cond.Broadcast() + return nil +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processResetStream(f *RSTStreamFrame) error { + cs := rl.cc.streamByID(f.StreamID, true) + if cs == nil { + // TODO: return error if server tries to RST_STEAM an idle stream + return nil + } + select { + case <-cs.peerReset: + // Already reset. + // This is the only goroutine + // which closes this, so there + // isn't a race. + default: + err := streamError(cs.ID, f.ErrCode) + cs.resetErr = err + close(cs.peerReset) + cs.bufPipe.CloseWithError(err) + cs.cc.cond.Broadcast() // wake up checkResetOrDone via clientStream.awaitFlowControl + } + delete(rl.activeRes, cs.ID) + return nil +} + +// Ping sends a PING frame to the server and waits for the ack. +// Public implementation is in go17.go and not_go17.go +func (cc *ClientConn) ping(ctx contextContext) error { + c := make(chan struct{}) + // Generate a random payload + var p [8]byte + for { + if _, err := rand.Read(p[:]); err != nil { + return err + } + cc.mu.Lock() + // check for dup before insert + if _, found := cc.pings[p]; !found { + cc.pings[p] = c + cc.mu.Unlock() + break + } + cc.mu.Unlock() + } + cc.wmu.Lock() + if err := cc.fr.WritePing(false, p); err != nil { + cc.wmu.Unlock() + return err + } + if err := cc.bw.Flush(); err != nil { + cc.wmu.Unlock() + return err + } + cc.wmu.Unlock() + select { + case <-c: + return nil + case <-ctx.Done(): + return ctx.Err() + case <-cc.readerDone: + // connection closed + return cc.readerErr + } +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processPing(f *PingFrame) error { + if f.IsAck() { + cc := rl.cc + cc.mu.Lock() + defer cc.mu.Unlock() + // If ack, notify listener if any + if c, ok := cc.pings[f.Data]; ok { + close(c) + delete(cc.pings, f.Data) + } + return nil + } + cc := rl.cc + cc.wmu.Lock() + defer cc.wmu.Unlock() + if err := cc.fr.WritePing(true, f.Data); err != nil { + return err + } + return cc.bw.Flush() +} + +func (rl *clientConnReadLoop) processPushPromise(f *PushPromiseFrame) error { + // We told the peer we don't want them. + // Spec says: + // "PUSH_PROMISE MUST NOT be sent if the SETTINGS_ENABLE_PUSH + // setting of the peer endpoint is set to 0. An endpoint that + // has set this setting and has received acknowledgement MUST + // treat the receipt of a PUSH_PROMISE frame as a connection + // error (Section 5.4.1) of type PROTOCOL_ERROR." + return ConnectionError(ErrCodeProtocol) +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) writeStreamReset(streamID uint32, code ErrCode, err error) { + // TODO: map err to more interesting error codes, once the + // HTTP community comes up with some. But currently for + // RST_STREAM there's no equivalent to GOAWAY frame's debug + // data, and the error codes are all pretty vague ("cancel"). + cc.wmu.Lock() + cc.fr.WriteRSTStream(streamID, code) + cc.bw.Flush() + cc.wmu.Unlock() +} + +var ( + errResponseHeaderListSize = errors.New("http2: response header list larger than advertised limit") + errPseudoTrailers = errors.New("http2: invalid pseudo header in trailers") +) + +func (cc *ClientConn) logf(format string, args ...interface{}) { + cc.t.logf(format, args...) +} + +func (cc *ClientConn) vlogf(format string, args ...interface{}) { + cc.t.vlogf(format, args...) +} + +func (t *Transport) vlogf(format string, args ...interface{}) { + if VerboseLogs { + t.logf(format, args...) + } +} + +func (t *Transport) logf(format string, args ...interface{}) { + log.Printf(format, args...) +} + +var noBody io.ReadCloser = ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewReader(nil)) + +func strSliceContains(ss []string, s string) bool { + for _, v := range ss { + if v == s { + return true + } + } + return false +} + +type erringRoundTripper struct{ err error } + +func (rt erringRoundTripper) RoundTrip(*http.Request) (*http.Response, error) { return nil, rt.err } + +// gzipReader wraps a response body so it can lazily +// call gzip.NewReader on the first call to Read +type gzipReader struct { + body io.ReadCloser // underlying Response.Body + zr *gzip.Reader // lazily-initialized gzip reader + zerr error // sticky error +} + +func (gz *gzipReader) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) { + if gz.zerr != nil { + return 0, gz.zerr + } + if gz.zr == nil { + gz.zr, err = gzip.NewReader(gz.body) + if err != nil { + gz.zerr = err + return 0, err + } + } + return gz.zr.Read(p) +} + +func (gz *gzipReader) Close() error { + return gz.body.Close() +} + +type errorReader struct{ err error } + +func (r errorReader) Read(p []byte) (int, error) { return 0, r.err } + +// bodyWriterState encapsulates various state around the Transport's writing +// of the request body, particularly regarding doing delayed writes of the body +// when the request contains "Expect: 100-continue". +type bodyWriterState struct { + cs *clientStream + timer *time.Timer // if non-nil, we're doing a delayed write + fnonce *sync.Once // to call fn with + fn func() // the code to run in the goroutine, writing the body + resc chan error // result of fn's execution + delay time.Duration // how long we should delay a delayed write for +} + +func (t *Transport) getBodyWriterState(cs *clientStream, body io.Reader) (s bodyWriterState) { + s.cs = cs + if body == nil { + return + } + resc := make(chan error, 1) + s.resc = resc + s.fn = func() { + resc <- cs.writeRequestBody(body, cs.req.Body) + } + s.delay = t.expectContinueTimeout() + if s.delay == 0 || + !httplex.HeaderValuesContainsToken( + cs.req.Header["Expect"], + "100-continue") { + return + } + s.fnonce = new(sync.Once) + + // Arm the timer with a very large duration, which we'll + // intentionally lower later. It has to be large now because + // we need a handle to it before writing the headers, but the + // s.delay value is defined to not start until after the + // request headers were written. + const hugeDuration = 365 * 24 * time.Hour + s.timer = time.AfterFunc(hugeDuration, func() { + s.fnonce.Do(s.fn) + }) + return +} + +func (s bodyWriterState) cancel() { + if s.timer != nil { + s.timer.Stop() + } +} + +func (s bodyWriterState) on100() { + if s.timer == nil { + // If we didn't do a delayed write, ignore the server's + // bogus 100 continue response. + return + } + s.timer.Stop() + go func() { s.fnonce.Do(s.fn) }() +} + +// scheduleBodyWrite starts writing the body, either immediately (in +// the common case) or after the delay timeout. It should not be +// called until after the headers have been written. +func (s bodyWriterState) scheduleBodyWrite() { + if s.timer == nil { + // We're not doing a delayed write (see + // getBodyWriterState), so just start the writing + // goroutine immediately. + go s.fn() + return + } + traceWait100Continue(s.cs.trace) + if s.timer.Stop() { + s.timer.Reset(s.delay) + } +} + +// isConnectionCloseRequest reports whether req should use its own +// connection for a single request and then close the connection. +func isConnectionCloseRequest(req *http.Request) bool { + return req.Close || httplex.HeaderValuesContainsToken(req.Header["Connection"], "close") +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/write.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/write.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..a45d6de --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/write.go @@ -0,0 +1,309 @@ +// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +package http2 + +import ( + "bytes" + "fmt" + "log" + "net/http" + "time" + + "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack" + "golang.org/x/net/lex/httplex" +) + +// writeFramer is implemented by any type that is used to write frames. +type writeFramer interface { + writeFrame(writeContext) error + + // staysWithinBuffer reports whether this writer promises that + // it will only write less than or equal to size bytes, and it + // won't Flush the write context. + staysWithinBuffer(size int) bool +} + +// writeContext is the interface needed by the various frame writer +// types below. All the writeFrame methods below are scheduled via the +// frame writing scheduler (see writeScheduler in writesched.go). +// +// This interface is implemented by *serverConn. +// +// TODO: decide whether to a) use this in the client code (which didn't +// end up using this yet, because it has a simpler design, not +// currently implementing priorities), or b) delete this and +// make the server code a bit more concrete. +type writeContext interface { + Framer() *Framer + Flush() error + CloseConn() error + // HeaderEncoder returns an HPACK encoder that writes to the + // returned buffer. + HeaderEncoder() (*hpack.Encoder, *bytes.Buffer) +} + +// endsStream reports whether the given frame writer w will locally +// close the stream. +func endsStream(w writeFramer) bool { + switch v := w.(type) { + case *writeData: + return v.endStream + case *writeResHeaders: + return v.endStream + case nil: + // This can only happen if the caller reuses w after it's + // been intentionally nil'ed out to prevent use. Keep this + // here to catch future refactoring breaking it. + panic("endsStream called on nil writeFramer") + } + return false +} + +type flushFrameWriter struct{} + +func (flushFrameWriter) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Flush() +} + +func (flushFrameWriter) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { return false } + +type writeSettings []Setting + +func (s writeSettings) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { + const settingSize = 6 // uint16 + uint32 + return frameHeaderLen+settingSize*len(s) <= max + +} + +func (s writeSettings) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Framer().WriteSettings([]Setting(s)...) +} + +type writeGoAway struct { + maxStreamID uint32 + code ErrCode +} + +func (p *writeGoAway) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + err := ctx.Framer().WriteGoAway(p.maxStreamID, p.code, nil) + if p.code != 0 { + ctx.Flush() // ignore error: we're hanging up on them anyway + time.Sleep(50 * time.Millisecond) + ctx.CloseConn() + } + return err +} + +func (*writeGoAway) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { return false } // flushes + +type writeData struct { + streamID uint32 + p []byte + endStream bool +} + +func (w *writeData) String() string { + return fmt.Sprintf("writeData(stream=%d, p=%d, endStream=%v)", w.streamID, len(w.p), w.endStream) +} + +func (w *writeData) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Framer().WriteData(w.streamID, w.endStream, w.p) +} + +func (w *writeData) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { + return frameHeaderLen+len(w.p) <= max +} + +// handlerPanicRST is the message sent from handler goroutines when +// the handler panics. +type handlerPanicRST struct { + StreamID uint32 +} + +func (hp handlerPanicRST) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Framer().WriteRSTStream(hp.StreamID, ErrCodeInternal) +} + +func (hp handlerPanicRST) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { return frameHeaderLen+4 <= max } + +func (se StreamError) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Framer().WriteRSTStream(se.StreamID, se.Code) +} + +func (se StreamError) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { return frameHeaderLen+4 <= max } + +type writePingAck struct{ pf *PingFrame } + +func (w writePingAck) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Framer().WritePing(true, w.pf.Data) +} + +func (w writePingAck) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { return frameHeaderLen+len(w.pf.Data) <= max } + +type writeSettingsAck struct{} + +func (writeSettingsAck) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Framer().WriteSettingsAck() +} + +func (writeSettingsAck) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { return frameHeaderLen <= max } + +// writeResHeaders is a request to write a HEADERS and 0+ CONTINUATION frames +// for HTTP response headers or trailers from a server handler. +type writeResHeaders struct { + streamID uint32 + httpResCode int // 0 means no ":status" line + h http.Header // may be nil + trailers []string // if non-nil, which keys of h to write. nil means all. + endStream bool + + date string + contentType string + contentLength string +} + +func encKV(enc *hpack.Encoder, k, v string) { + if VerboseLogs { + log.Printf("http2: server encoding header %q = %q", k, v) + } + enc.WriteField(hpack.HeaderField{Name: k, Value: v}) +} + +func (w *writeResHeaders) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { + // TODO: this is a common one. It'd be nice to return true + // here and get into the fast path if we could be clever and + // calculate the size fast enough, or at least a conservative + // uppper bound that usually fires. (Maybe if w.h and + // w.trailers are nil, so we don't need to enumerate it.) + // Otherwise I'm afraid that just calculating the length to + // answer this question would be slower than the ~2µs benefit. + return false +} + +func (w *writeResHeaders) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + enc, buf := ctx.HeaderEncoder() + buf.Reset() + + if w.httpResCode != 0 { + encKV(enc, ":status", httpCodeString(w.httpResCode)) + } + + encodeHeaders(enc, w.h, w.trailers) + + if w.contentType != "" { + encKV(enc, "content-type", w.contentType) + } + if w.contentLength != "" { + encKV(enc, "content-length", w.contentLength) + } + if w.date != "" { + encKV(enc, "date", w.date) + } + + headerBlock := buf.Bytes() + if len(headerBlock) == 0 && w.trailers == nil { + panic("unexpected empty hpack") + } + + // For now we're lazy and just pick the minimum MAX_FRAME_SIZE + // that all peers must support (16KB). Later we could care + // more and send larger frames if the peer advertised it, but + // there's little point. Most headers are small anyway (so we + // generally won't have CONTINUATION frames), and extra frames + // only waste 9 bytes anyway. + const maxFrameSize = 16384 + + first := true + for len(headerBlock) > 0 { + frag := headerBlock + if len(frag) > maxFrameSize { + frag = frag[:maxFrameSize] + } + headerBlock = headerBlock[len(frag):] + endHeaders := len(headerBlock) == 0 + var err error + if first { + first = false + err = ctx.Framer().WriteHeaders(HeadersFrameParam{ + StreamID: w.streamID, + BlockFragment: frag, + EndStream: w.endStream, + EndHeaders: endHeaders, + }) + } else { + err = ctx.Framer().WriteContinuation(w.streamID, endHeaders, frag) + } + if err != nil { + return err + } + } + return nil +} + +type write100ContinueHeadersFrame struct { + streamID uint32 +} + +func (w write100ContinueHeadersFrame) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + enc, buf := ctx.HeaderEncoder() + buf.Reset() + encKV(enc, ":status", "100") + return ctx.Framer().WriteHeaders(HeadersFrameParam{ + StreamID: w.streamID, + BlockFragment: buf.Bytes(), + EndStream: false, + EndHeaders: true, + }) +} + +func (w write100ContinueHeadersFrame) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { + // Sloppy but conservative: + return 9+2*(len(":status")+len("100")) <= max +} + +type writeWindowUpdate struct { + streamID uint32 // or 0 for conn-level + n uint32 +} + +func (wu writeWindowUpdate) staysWithinBuffer(max int) bool { return frameHeaderLen+4 <= max } + +func (wu writeWindowUpdate) writeFrame(ctx writeContext) error { + return ctx.Framer().WriteWindowUpdate(wu.streamID, wu.n) +} + +func encodeHeaders(enc *hpack.Encoder, h http.Header, keys []string) { + if keys == nil { + sorter := sorterPool.Get().(*sorter) + // Using defer here, since the returned keys from the + // sorter.Keys method is only valid until the sorter + // is returned: + defer sorterPool.Put(sorter) + keys = sorter.Keys(h) + } + for _, k := range keys { + vv := h[k] + k = lowerHeader(k) + if !validWireHeaderFieldName(k) { + // Skip it as backup paranoia. Per + // golang.org/issue/14048, these should + // already be rejected at a higher level. + continue + } + isTE := k == "transfer-encoding" + for _, v := range vv { + if !httplex.ValidHeaderFieldValue(v) { + // TODO: return an error? golang.org/issue/14048 + // For now just omit it. + continue + } + // TODO: more of "8.1.2.2 Connection-Specific Header Fields" + if isTE && v != "trailers" { + continue + } + encKV(enc, k, v) + } + } +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..9f3e1b3 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched.go @@ -0,0 +1,223 @@ +// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +package http2 + +import "fmt" + +// WriteScheduler is the interface implemented by HTTP/2 write schedulers. +// Methods are never called concurrently. +type WriteScheduler interface { + // OpenStream opens a new stream in the write scheduler. + // It is illegal to call this with streamID=0 or with a streamID that is + // already open -- the call may panic. + OpenStream(streamID uint32, options OpenStreamOptions) + + // CloseStream closes a stream in the write scheduler. Any frames queued on + // this stream should be discarded. It is illegal to call this on a stream + // that is not open -- the call may panic. + CloseStream(streamID uint32) + + // AdjustStream adjusts the priority of the given stream. This may be called + // on a stream that has not yet been opened or has been closed. Note that + // RFC 7540 allows PRIORITY frames to be sent on streams in any state. See: + // https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7540#section-5.1 + AdjustStream(streamID uint32, priority PriorityParam) + + // Push queues a frame in the scheduler. + Push(wr FrameWriteRequest) + + // Pop dequeues the next frame to write. Returns false if no frames can + // be written. Frames with a given wr.StreamID() are Pop'd in the same + // order they are Push'd. + Pop() (wr FrameWriteRequest, ok bool) +} + +// OpenStreamOptions specifies extra options for WriteScheduler.OpenStream. +type OpenStreamOptions struct { + // PusherID is zero if the stream was initiated by the client. Otherwise, + // PusherID names the stream that pushed the newly opened stream. + PusherID uint32 +} + +// FrameWriteRequest is a request to write a frame. +type FrameWriteRequest struct { + // write is the interface value that does the writing, once the + // WriteScheduler has selected this frame to write. The write + // functions are all defined in write.go. + write writeFramer + + // stream is the stream on which this frame will be written. + // nil for non-stream frames like PING and SETTINGS. + stream *stream + + // done, if non-nil, must be a buffered channel with space for + // 1 message and is sent the return value from write (or an + // earlier error) when the frame has been written. + done chan error +} + +// StreamID returns the id of the stream this frame will be written to. +// 0 is used for non-stream frames such as PING and SETTINGS. +func (wr FrameWriteRequest) StreamID() uint32 { + if wr.stream == nil { + return 0 + } + return wr.stream.id +} + +// DataSize returns the number of flow control bytes that must be consumed +// to write this entire frame. This is 0 for non-DATA frames. +func (wr FrameWriteRequest) DataSize() int { + if wd, ok := wr.write.(*writeData); ok { + return len(wd.p) + } + return 0 +} + +// Consume consumes min(n, available) bytes from this frame, where available +// is the number of flow control bytes available on the stream. Consume returns +// 0, 1, or 2 frames, where the integer return value gives the number of frames +// returned. +// +// If flow control prevents consuming any bytes, this returns (_, _, 0). If +// the entire frame was consumed, this returns (wr, _, 1). Otherwise, this +// returns (consumed, rest, 2), where 'consumed' contains the consumed bytes and +// 'rest' contains the remaining bytes. The consumed bytes are deducted from the +// underlying stream's flow control budget. +func (wr FrameWriteRequest) Consume(n int32) (FrameWriteRequest, FrameWriteRequest, int) { + var empty FrameWriteRequest + + // Non-DATA frames are always consumed whole. + wd, ok := wr.write.(*writeData) + if !ok || len(wd.p) == 0 { + return wr, empty, 1 + } + + // Might need to split after applying limits. + allowed := wr.stream.flow.available() + if n < allowed { + allowed = n + } + if wr.stream.sc.maxFrameSize < allowed { + allowed = wr.stream.sc.maxFrameSize + } + if allowed <= 0 { + return empty, empty, 0 + } + if len(wd.p) > int(allowed) { + wr.stream.flow.take(allowed) + consumed := FrameWriteRequest{ + stream: wr.stream, + write: &writeData{ + streamID: wd.streamID, + p: wd.p[:allowed], + // Even if the original had endStream set, there + // are bytes remaining because len(wd.p) > allowed, + // so we know endStream is false. + endStream: false, + }, + // Our caller is blocking on the final DATA frame, not + // this intermediate frame, so no need to wait. + done: nil, + } + rest := FrameWriteRequest{ + stream: wr.stream, + write: &writeData{ + streamID: wd.streamID, + p: wd.p[allowed:], + endStream: wd.endStream, + }, + done: wr.done, + } + return consumed, rest, 2 + } + + // The frame is consumed whole. + // NB: This cast cannot overflow because allowed is <= math.MaxInt32. + wr.stream.flow.take(int32(len(wd.p))) + return wr, empty, 1 +} + +// String is for debugging only. +func (wr FrameWriteRequest) String() string { + var streamID uint32 + if wr.stream != nil { + streamID = wr.stream.id + } + var des string + if s, ok := wr.write.(fmt.Stringer); ok { + des = s.String() + } else { + des = fmt.Sprintf("%T", wr.write) + } + return fmt.Sprintf("[FrameWriteRequest stream=%d, ch=%v, writer=%v]", streamID, wr.done != nil, des) +} + +// writeQueue is used by implementations of WriteScheduler. +type writeQueue struct { + s []FrameWriteRequest +} + +func (q *writeQueue) empty() bool { return len(q.s) == 0 } + +func (q *writeQueue) push(wr FrameWriteRequest) { + q.s = append(q.s, wr) +} + +func (q *writeQueue) shift() FrameWriteRequest { + if len(q.s) == 0 { + panic("invalid use of queue") + } + wr := q.s[0] + // TODO: less copy-happy queue. + copy(q.s, q.s[1:]) + q.s[len(q.s)-1] = FrameWriteRequest{} + q.s = q.s[:len(q.s)-1] + return wr +} + +// consume consumes up to n bytes from q.s[0]. If the frame is +// entirely consumed, it is removed from the queue. If the frame +// is partially consumed, the frame is kept with the consumed +// bytes removed. Returns true iff any bytes were consumed. +func (q *writeQueue) consume(n int32) (FrameWriteRequest, bool) { + if len(q.s) == 0 { + return FrameWriteRequest{}, false + } + consumed, rest, numresult := q.s[0].Consume(n) + switch numresult { + case 0: + return FrameWriteRequest{}, false + case 1: + q.shift() + case 2: + q.s[0] = rest + } + return consumed, true +} + +type writeQueuePool []*writeQueue + +// put inserts an unused writeQueue into the pool. +func (p *writeQueuePool) put(q *writeQueue) { + for i := range q.s { + q.s[i] = FrameWriteRequest{} + } + q.s = q.s[:0] + *p = append(*p, q) +} + +// get returns an empty writeQueue. +func (p *writeQueuePool) get() *writeQueue { + ln := len(*p) + if ln == 0 { + return new(writeQueue) + } + x := ln - 1 + q := (*p)[x] + (*p)[x] = nil + *p = (*p)[:x] + return q +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched_priority.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched_priority.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..40108b0 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched_priority.go @@ -0,0 +1,444 @@ +// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +package http2 + +import ( + "fmt" + "math" + "sort" +) + +// RFC 7540, Section 5.3.5: the default weight is 16. +const priorityDefaultWeight = 15 // 16 = 15 + 1 + +// PriorityWriteSchedulerConfig configures a priorityWriteScheduler. +type PriorityWriteSchedulerConfig struct { + // MaxClosedNodesInTree controls the maximum number of closed streams to + // retain in the priority tree. Setting this to zero saves a small amount + // of memory at the cost of performance. + // + // See RFC 7540, Section 5.3.4: + // "It is possible for a stream to become closed while prioritization + // information ... is in transit. ... This potentially creates suboptimal + // prioritization, since the stream could be given a priority that is + // different from what is intended. To avoid these problems, an endpoint + // SHOULD retain stream prioritization state for a period after streams + // become closed. The longer state is retained, the lower the chance that + // streams are assigned incorrect or default priority values." + MaxClosedNodesInTree int + + // MaxIdleNodesInTree controls the maximum number of idle streams to + // retain in the priority tree. Setting this to zero saves a small amount + // of memory at the cost of performance. + // + // See RFC 7540, Section 5.3.4: + // Similarly, streams that are in the "idle" state can be assigned + // priority or become a parent of other streams. This allows for the + // creation of a grouping node in the dependency tree, which enables + // more flexible expressions of priority. Idle streams begin with a + // default priority (Section 5.3.5). + MaxIdleNodesInTree int + + // ThrottleOutOfOrderWrites enables write throttling to help ensure that + // data is delivered in priority order. This works around a race where + // stream B depends on stream A and both streams are about to call Write + // to queue DATA frames. If B wins the race, a naive scheduler would eagerly + // write as much data from B as possible, but this is suboptimal because A + // is a higher-priority stream. With throttling enabled, we write a small + // amount of data from B to minimize the amount of bandwidth that B can + // steal from A. + ThrottleOutOfOrderWrites bool +} + +// NewPriorityWriteScheduler constructs a WriteScheduler that schedules +// frames by following HTTP/2 priorities as described in RFC 7340 Section 5.3. +// If cfg is nil, default options are used. +func NewPriorityWriteScheduler(cfg *PriorityWriteSchedulerConfig) WriteScheduler { + if cfg == nil { + // For justification of these defaults, see: + // https://docs.google.com/document/d/1oLhNg1skaWD4_DtaoCxdSRN5erEXrH-KnLrMwEpOtFY + cfg = &PriorityWriteSchedulerConfig{ + MaxClosedNodesInTree: 10, + MaxIdleNodesInTree: 10, + ThrottleOutOfOrderWrites: false, + } + } + + ws := &priorityWriteScheduler{ + nodes: make(map[uint32]*priorityNode), + maxClosedNodesInTree: cfg.MaxClosedNodesInTree, + maxIdleNodesInTree: cfg.MaxIdleNodesInTree, + enableWriteThrottle: cfg.ThrottleOutOfOrderWrites, + } + ws.nodes[0] = &ws.root + if cfg.ThrottleOutOfOrderWrites { + ws.writeThrottleLimit = 1024 + } else { + ws.writeThrottleLimit = math.MaxInt32 + } + return ws +} + +type priorityNodeState int + +const ( + priorityNodeOpen priorityNodeState = iota + priorityNodeClosed + priorityNodeIdle +) + +// priorityNode is a node in an HTTP/2 priority tree. +// Each node is associated with a single stream ID. +// See RFC 7540, Section 5.3. +type priorityNode struct { + q writeQueue // queue of pending frames to write + id uint32 // id of the stream, or 0 for the root of the tree + weight uint8 // the actual weight is weight+1, so the value is in [1,256] + state priorityNodeState // open | closed | idle + bytes int64 // number of bytes written by this node, or 0 if closed + subtreeBytes int64 // sum(node.bytes) of all nodes in this subtree + + // These links form the priority tree. + parent *priorityNode + kids *priorityNode // start of the kids list + prev, next *priorityNode // doubly-linked list of siblings +} + +func (n *priorityNode) setParent(parent *priorityNode) { + if n == parent { + panic("setParent to self") + } + if n.parent == parent { + return + } + // Unlink from current parent. + if parent := n.parent; parent != nil { + if n.prev == nil { + parent.kids = n.next + } else { + n.prev.next = n.next + } + if n.next != nil { + n.next.prev = n.prev + } + } + // Link to new parent. + // If parent=nil, remove n from the tree. + // Always insert at the head of parent.kids (this is assumed by walkReadyInOrder). + n.parent = parent + if parent == nil { + n.next = nil + n.prev = nil + } else { + n.next = parent.kids + n.prev = nil + if n.next != nil { + n.next.prev = n + } + parent.kids = n + } +} + +func (n *priorityNode) addBytes(b int64) { + n.bytes += b + for ; n != nil; n = n.parent { + n.subtreeBytes += b + } +} + +// walkReadyInOrder iterates over the tree in priority order, calling f for each node +// with a non-empty write queue. When f returns true, this funcion returns true and the +// walk halts. tmp is used as scratch space for sorting. +// +// f(n, openParent) takes two arguments: the node to visit, n, and a bool that is true +// if any ancestor p of n is still open (ignoring the root node). +func (n *priorityNode) walkReadyInOrder(openParent bool, tmp *[]*priorityNode, f func(*priorityNode, bool) bool) bool { + if !n.q.empty() && f(n, openParent) { + return true + } + if n.kids == nil { + return false + } + + // Don't consider the root "open" when updating openParent since + // we can't send data frames on the root stream (only control frames). + if n.id != 0 { + openParent = openParent || (n.state == priorityNodeOpen) + } + + // Common case: only one kid or all kids have the same weight. + // Some clients don't use weights; other clients (like web browsers) + // use mostly-linear priority trees. + w := n.kids.weight + needSort := false + for k := n.kids.next; k != nil; k = k.next { + if k.weight != w { + needSort = true + break + } + } + if !needSort { + for k := n.kids; k != nil; k = k.next { + if k.walkReadyInOrder(openParent, tmp, f) { + return true + } + } + return false + } + + // Uncommon case: sort the child nodes. We remove the kids from the parent, + // then re-insert after sorting so we can reuse tmp for future sort calls. + *tmp = (*tmp)[:0] + for n.kids != nil { + *tmp = append(*tmp, n.kids) + n.kids.setParent(nil) + } + sort.Sort(sortPriorityNodeSiblings(*tmp)) + for i := len(*tmp) - 1; i >= 0; i-- { + (*tmp)[i].setParent(n) // setParent inserts at the head of n.kids + } + for k := n.kids; k != nil; k = k.next { + if k.walkReadyInOrder(openParent, tmp, f) { + return true + } + } + return false +} + +type sortPriorityNodeSiblings []*priorityNode + +func (z sortPriorityNodeSiblings) Len() int { return len(z) } +func (z sortPriorityNodeSiblings) Swap(i, k int) { z[i], z[k] = z[k], z[i] } +func (z sortPriorityNodeSiblings) Less(i, k int) bool { + // Prefer the subtree that has sent fewer bytes relative to its weight. + // See sections 5.3.2 and 5.3.4. + wi, bi := float64(z[i].weight+1), float64(z[i].subtreeBytes) + wk, bk := float64(z[k].weight+1), float64(z[k].subtreeBytes) + if bi == 0 && bk == 0 { + return wi >= wk + } + if bk == 0 { + return false + } + return bi/bk <= wi/wk +} + +type priorityWriteScheduler struct { + // root is the root of the priority tree, where root.id = 0. + // The root queues control frames that are not associated with any stream. + root priorityNode + + // nodes maps stream ids to priority tree nodes. + nodes map[uint32]*priorityNode + + // maxID is the maximum stream id in nodes. + maxID uint32 + + // lists of nodes that have been closed or are idle, but are kept in + // the tree for improved prioritization. When the lengths exceed either + // maxClosedNodesInTree or maxIdleNodesInTree, old nodes are discarded. + closedNodes, idleNodes []*priorityNode + + // From the config. + maxClosedNodesInTree int + maxIdleNodesInTree int + writeThrottleLimit int32 + enableWriteThrottle bool + + // tmp is scratch space for priorityNode.walkReadyInOrder to reduce allocations. + tmp []*priorityNode + + // pool of empty queues for reuse. + queuePool writeQueuePool +} + +func (ws *priorityWriteScheduler) OpenStream(streamID uint32, options OpenStreamOptions) { + // The stream may be currently idle but cannot be opened or closed. + if curr := ws.nodes[streamID]; curr != nil { + if curr.state != priorityNodeIdle { + panic(fmt.Sprintf("stream %d already opened", streamID)) + } + curr.state = priorityNodeOpen + return + } + + // RFC 7540, Section 5.3.5: + // "All streams are initially assigned a non-exclusive dependency on stream 0x0. + // Pushed streams initially depend on their associated stream. In both cases, + // streams are assigned a default weight of 16." + parent := ws.nodes[options.PusherID] + if parent == nil { + parent = &ws.root + } + n := &priorityNode{ + q: *ws.queuePool.get(), + id: streamID, + weight: priorityDefaultWeight, + state: priorityNodeOpen, + } + n.setParent(parent) + ws.nodes[streamID] = n + if streamID > ws.maxID { + ws.maxID = streamID + } +} + +func (ws *priorityWriteScheduler) CloseStream(streamID uint32) { + if streamID == 0 { + panic("violation of WriteScheduler interface: cannot close stream 0") + } + if ws.nodes[streamID] == nil { + panic(fmt.Sprintf("violation of WriteScheduler interface: unknown stream %d", streamID)) + } + if ws.nodes[streamID].state != priorityNodeOpen { + panic(fmt.Sprintf("violation of WriteScheduler interface: stream %d already closed", streamID)) + } + + n := ws.nodes[streamID] + n.state = priorityNodeClosed + n.addBytes(-n.bytes) + + q := n.q + ws.queuePool.put(&q) + n.q.s = nil + if ws.maxClosedNodesInTree > 0 { + ws.addClosedOrIdleNode(&ws.closedNodes, ws.maxClosedNodesInTree, n) + } else { + ws.removeNode(n) + } +} + +func (ws *priorityWriteScheduler) AdjustStream(streamID uint32, priority PriorityParam) { + if streamID == 0 { + panic("adjustPriority on root") + } + + // If streamID does not exist, there are two cases: + // - A closed stream that has been removed (this will have ID <= maxID) + // - An idle stream that is being used for "grouping" (this will have ID > maxID) + n := ws.nodes[streamID] + if n == nil { + if streamID <= ws.maxID || ws.maxIdleNodesInTree == 0 { + return + } + ws.maxID = streamID + n = &priorityNode{ + q: *ws.queuePool.get(), + id: streamID, + weight: priorityDefaultWeight, + state: priorityNodeIdle, + } + n.setParent(&ws.root) + ws.nodes[streamID] = n + ws.addClosedOrIdleNode(&ws.idleNodes, ws.maxIdleNodesInTree, n) + } + + // Section 5.3.1: A dependency on a stream that is not currently in the tree + // results in that stream being given a default priority (Section 5.3.5). + parent := ws.nodes[priority.StreamDep] + if parent == nil { + n.setParent(&ws.root) + n.weight = priorityDefaultWeight + return + } + + // Ignore if the client tries to make a node its own parent. + if n == parent { + return + } + + // Section 5.3.3: + // "If a stream is made dependent on one of its own dependencies, the + // formerly dependent stream is first moved to be dependent on the + // reprioritized stream's previous parent. The moved dependency retains + // its weight." + // + // That is: if parent depends on n, move parent to depend on n.parent. + for x := parent.parent; x != nil; x = x.parent { + if x == n { + parent.setParent(n.parent) + break + } + } + + // Section 5.3.3: The exclusive flag causes the stream to become the sole + // dependency of its parent stream, causing other dependencies to become + // dependent on the exclusive stream. + if priority.Exclusive { + k := parent.kids + for k != nil { + next := k.next + if k != n { + k.setParent(n) + } + k = next + } + } + + n.setParent(parent) + n.weight = priority.Weight +} + +func (ws *priorityWriteScheduler) Push(wr FrameWriteRequest) { + var n *priorityNode + if id := wr.StreamID(); id == 0 { + n = &ws.root + } else { + n = ws.nodes[id] + if n == nil { + panic("add on non-open stream") + } + } + n.q.push(wr) +} + +func (ws *priorityWriteScheduler) Pop() (wr FrameWriteRequest, ok bool) { + ws.root.walkReadyInOrder(false, &ws.tmp, func(n *priorityNode, openParent bool) bool { + limit := int32(math.MaxInt32) + if openParent { + limit = ws.writeThrottleLimit + } + wr, ok = n.q.consume(limit) + if !ok { + return false + } + n.addBytes(int64(wr.DataSize())) + // If B depends on A and B continuously has data available but A + // does not, gradually increase the throttling limit to allow B to + // steal more and more bandwidth from A. + if openParent { + ws.writeThrottleLimit += 1024 + if ws.writeThrottleLimit < 0 { + ws.writeThrottleLimit = math.MaxInt32 + } + } else if ws.enableWriteThrottle { + ws.writeThrottleLimit = 1024 + } + return true + }) + return wr, ok +} + +func (ws *priorityWriteScheduler) addClosedOrIdleNode(list *[]*priorityNode, maxSize int, n *priorityNode) { + if maxSize == 0 { + return + } + if len(*list) == maxSize { + // Remove the oldest node, then shift left. + ws.removeNode((*list)[0]) + x := (*list)[1:] + copy(*list, x) + *list = (*list)[:len(x)] + } + *list = append(*list, n) +} + +func (ws *priorityWriteScheduler) removeNode(n *priorityNode) { + for k := n.kids; k != nil; k = k.next { + k.setParent(n.parent) + } + n.setParent(nil) + delete(ws.nodes, n.id) +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched_random.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched_random.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..36d7919 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/http2/writesched_random.go @@ -0,0 +1,72 @@ +// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +package http2 + +import "math" + +// NewRandomWriteScheduler constructs a WriteScheduler that ignores HTTP/2 +// priorities. Control frames like SETTINGS and PING are written before DATA +// frames, but if no control frames are queued and multiple streams have queued +// HEADERS or DATA frames, Pop selects a ready stream arbitrarily. +func NewRandomWriteScheduler() WriteScheduler { + return &randomWriteScheduler{sq: make(map[uint32]*writeQueue)} +} + +type randomWriteScheduler struct { + // zero are frames not associated with a specific stream. + zero writeQueue + + // sq contains the stream-specific queues, keyed by stream ID. + // When a stream is idle or closed, it's deleted from the map. + sq map[uint32]*writeQueue + + // pool of empty queues for reuse. + queuePool writeQueuePool +} + +func (ws *randomWriteScheduler) OpenStream(streamID uint32, options OpenStreamOptions) { + // no-op: idle streams are not tracked +} + +func (ws *randomWriteScheduler) CloseStream(streamID uint32) { + q, ok := ws.sq[streamID] + if !ok { + return + } + delete(ws.sq, streamID) + ws.queuePool.put(q) +} + +func (ws *randomWriteScheduler) AdjustStream(streamID uint32, priority PriorityParam) { + // no-op: priorities are ignored +} + +func (ws *randomWriteScheduler) Push(wr FrameWriteRequest) { + id := wr.StreamID() + if id == 0 { + ws.zero.push(wr) + return + } + q, ok := ws.sq[id] + if !ok { + q = ws.queuePool.get() + ws.sq[id] = q + } + q.push(wr) +} + +func (ws *randomWriteScheduler) Pop() (FrameWriteRequest, bool) { + // Control frames first. + if !ws.zero.empty() { + return ws.zero.shift(), true + } + // Iterate over all non-idle streams until finding one that can be consumed. + for _, q := range ws.sq { + if wr, ok := q.consume(math.MaxInt32); ok { + return wr, true + } + } + return FrameWriteRequest{}, false +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/idna/idna.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/idna/idna.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..3daa897 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/idna/idna.go @@ -0,0 +1,68 @@ +// Copyright 2012 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +// Package idna implements IDNA2008 (Internationalized Domain Names for +// Applications), defined in RFC 5890, RFC 5891, RFC 5892, RFC 5893 and +// RFC 5894. +package idna // import "golang.org/x/net/idna" + +import ( + "strings" + "unicode/utf8" +) + +// TODO(nigeltao): specify when errors occur. For example, is ToASCII(".") or +// ToASCII("foo\x00") an error? See also http://www.unicode.org/faq/idn.html#11 + +// acePrefix is the ASCII Compatible Encoding prefix. +const acePrefix = "xn--" + +// ToASCII converts a domain or domain label to its ASCII form. For example, +// ToASCII("bücher.example.com") is "xn--bcher-kva.example.com", and +// ToASCII("golang") is "golang". +func ToASCII(s string) (string, error) { + if ascii(s) { + return s, nil + } + labels := strings.Split(s, ".") + for i, label := range labels { + if !ascii(label) { + a, err := encode(acePrefix, label) + if err != nil { + return "", err + } + labels[i] = a + } + } + return strings.Join(labels, "."), nil +} + +// ToUnicode converts a domain or domain label to its Unicode form. For example, +// ToUnicode("xn--bcher-kva.example.com") is "bücher.example.com", and +// ToUnicode("golang") is "golang". +func ToUnicode(s string) (string, error) { + if !strings.Contains(s, acePrefix) { + return s, nil + } + labels := strings.Split(s, ".") + for i, label := range labels { + if strings.HasPrefix(label, acePrefix) { + u, err := decode(label[len(acePrefix):]) + if err != nil { + return "", err + } + labels[i] = u + } + } + return strings.Join(labels, "."), nil +} + +func ascii(s string) bool { + for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ { + if s[i] >= utf8.RuneSelf { + return false + } + } + return true +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/idna/punycode.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/idna/punycode.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..92e733f --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/idna/punycode.go @@ -0,0 +1,200 @@ +// Copyright 2012 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +package idna + +// This file implements the Punycode algorithm from RFC 3492. + +import ( + "fmt" + "math" + "strings" + "unicode/utf8" +) + +// These parameter values are specified in section 5. +// +// All computation is done with int32s, so that overflow behavior is identical +// regardless of whether int is 32-bit or 64-bit. +const ( + base int32 = 36 + damp int32 = 700 + initialBias int32 = 72 + initialN int32 = 128 + skew int32 = 38 + tmax int32 = 26 + tmin int32 = 1 +) + +// decode decodes a string as specified in section 6.2. +func decode(encoded string) (string, error) { + if encoded == "" { + return "", nil + } + pos := 1 + strings.LastIndex(encoded, "-") + if pos == 1 { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", encoded) + } + if pos == len(encoded) { + return encoded[:len(encoded)-1], nil + } + output := make([]rune, 0, len(encoded)) + if pos != 0 { + for _, r := range encoded[:pos-1] { + output = append(output, r) + } + } + i, n, bias := int32(0), initialN, initialBias + for pos < len(encoded) { + oldI, w := i, int32(1) + for k := base; ; k += base { + if pos == len(encoded) { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", encoded) + } + digit, ok := decodeDigit(encoded[pos]) + if !ok { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", encoded) + } + pos++ + i += digit * w + if i < 0 { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", encoded) + } + t := k - bias + if t < tmin { + t = tmin + } else if t > tmax { + t = tmax + } + if digit < t { + break + } + w *= base - t + if w >= math.MaxInt32/base { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", encoded) + } + } + x := int32(len(output) + 1) + bias = adapt(i-oldI, x, oldI == 0) + n += i / x + i %= x + if n > utf8.MaxRune || len(output) >= 1024 { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", encoded) + } + output = append(output, 0) + copy(output[i+1:], output[i:]) + output[i] = n + i++ + } + return string(output), nil +} + +// encode encodes a string as specified in section 6.3 and prepends prefix to +// the result. +// +// The "while h < length(input)" line in the specification becomes "for +// remaining != 0" in the Go code, because len(s) in Go is in bytes, not runes. +func encode(prefix, s string) (string, error) { + output := make([]byte, len(prefix), len(prefix)+1+2*len(s)) + copy(output, prefix) + delta, n, bias := int32(0), initialN, initialBias + b, remaining := int32(0), int32(0) + for _, r := range s { + if r < 0x80 { + b++ + output = append(output, byte(r)) + } else { + remaining++ + } + } + h := b + if b > 0 { + output = append(output, '-') + } + for remaining != 0 { + m := int32(0x7fffffff) + for _, r := range s { + if m > r && r >= n { + m = r + } + } + delta += (m - n) * (h + 1) + if delta < 0 { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", s) + } + n = m + for _, r := range s { + if r < n { + delta++ + if delta < 0 { + return "", fmt.Errorf("idna: invalid label %q", s) + } + continue + } + if r > n { + continue + } + q := delta + for k := base; ; k += base { + t := k - bias + if t < tmin { + t = tmin + } else if t > tmax { + t = tmax + } + if q < t { + break + } + output = append(output, encodeDigit(t+(q-t)%(base-t))) + q = (q - t) / (base - t) + } + output = append(output, encodeDigit(q)) + bias = adapt(delta, h+1, h == b) + delta = 0 + h++ + remaining-- + } + delta++ + n++ + } + return string(output), nil +} + +func decodeDigit(x byte) (digit int32, ok bool) { + switch { + case '0' <= x && x <= '9': + return int32(x - ('0' - 26)), true + case 'A' <= x && x <= 'Z': + return int32(x - 'A'), true + case 'a' <= x && x <= 'z': + return int32(x - 'a'), true + } + return 0, false +} + +func encodeDigit(digit int32) byte { + switch { + case 0 <= digit && digit < 26: + return byte(digit + 'a') + case 26 <= digit && digit < 36: + return byte(digit + ('0' - 26)) + } + panic("idna: internal error in punycode encoding") +} + +// adapt is the bias adaptation function specified in section 6.1. +func adapt(delta, numPoints int32, firstTime bool) int32 { + if firstTime { + delta /= damp + } else { + delta /= 2 + } + delta += delta / numPoints + k := int32(0) + for delta > ((base-tmin)*tmax)/2 { + delta /= base - tmin + k += base + } + return k + (base-tmin+1)*delta/(delta+skew) +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/iana/const.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/iana/const.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..3438a27 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/iana/const.go @@ -0,0 +1,180 @@ +// go generate gen.go +// GENERATED BY THE COMMAND ABOVE; DO NOT EDIT + +// Package iana provides protocol number resources managed by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). +package iana // import "golang.org/x/net/internal/iana" + +// Differentiated Services Field Codepoints (DSCP), Updated: 2013-06-25 +const ( + DiffServCS0 = 0x0 // CS0 + DiffServCS1 = 0x20 // CS1 + DiffServCS2 = 0x40 // CS2 + DiffServCS3 = 0x60 // CS3 + DiffServCS4 = 0x80 // CS4 + DiffServCS5 = 0xa0 // CS5 + DiffServCS6 = 0xc0 // CS6 + DiffServCS7 = 0xe0 // CS7 + DiffServAF11 = 0x28 // AF11 + DiffServAF12 = 0x30 // AF12 + DiffServAF13 = 0x38 // AF13 + DiffServAF21 = 0x48 // AF21 + DiffServAF22 = 0x50 // AF22 + DiffServAF23 = 0x58 // AF23 + DiffServAF31 = 0x68 // AF31 + DiffServAF32 = 0x70 // AF32 + DiffServAF33 = 0x78 // AF33 + DiffServAF41 = 0x88 // AF41 + DiffServAF42 = 0x90 // AF42 + DiffServAF43 = 0x98 // AF43 + DiffServEFPHB = 0xb8 // EF PHB + DiffServVOICEADMIT = 0xb0 // VOICE-ADMIT +) + +// IPv4 TOS Byte and IPv6 Traffic Class Octet, Updated: 2001-09-06 +const ( + NotECNTransport = 0x0 // Not-ECT (Not ECN-Capable Transport) + ECNTransport1 = 0x1 // ECT(1) (ECN-Capable Transport(1)) + ECNTransport0 = 0x2 // ECT(0) (ECN-Capable Transport(0)) + CongestionExperienced = 0x3 // CE (Congestion Experienced) +) + +// Protocol Numbers, Updated: 2015-10-06 +const ( + ProtocolIP = 0 // IPv4 encapsulation, pseudo protocol number + ProtocolHOPOPT = 0 // IPv6 Hop-by-Hop Option + ProtocolICMP = 1 // Internet Control Message + ProtocolIGMP = 2 // Internet Group Management + ProtocolGGP = 3 // Gateway-to-Gateway + ProtocolIPv4 = 4 // IPv4 encapsulation + ProtocolST = 5 // Stream + ProtocolTCP = 6 // Transmission Control + ProtocolCBT = 7 // CBT + ProtocolEGP = 8 // Exterior Gateway Protocol + ProtocolIGP = 9 // any private interior gateway (used by Cisco for their IGRP) + ProtocolBBNRCCMON = 10 // BBN RCC Monitoring + ProtocolNVPII = 11 // Network Voice Protocol + ProtocolPUP = 12 // PUP + ProtocolEMCON = 14 // EMCON + ProtocolXNET = 15 // Cross Net Debugger + ProtocolCHAOS = 16 // Chaos + ProtocolUDP = 17 // User Datagram + ProtocolMUX = 18 // Multiplexing + ProtocolDCNMEAS = 19 // DCN Measurement Subsystems + ProtocolHMP = 20 // Host Monitoring + ProtocolPRM = 21 // Packet Radio Measurement + ProtocolXNSIDP = 22 // XEROX NS IDP + ProtocolTRUNK1 = 23 // Trunk-1 + ProtocolTRUNK2 = 24 // Trunk-2 + ProtocolLEAF1 = 25 // Leaf-1 + ProtocolLEAF2 = 26 // Leaf-2 + ProtocolRDP = 27 // Reliable Data Protocol + ProtocolIRTP = 28 // Internet Reliable Transaction + ProtocolISOTP4 = 29 // ISO Transport Protocol Class 4 + ProtocolNETBLT = 30 // Bulk Data Transfer Protocol + ProtocolMFENSP = 31 // MFE Network Services Protocol + ProtocolMERITINP = 32 // MERIT Internodal Protocol + ProtocolDCCP = 33 // Datagram Congestion Control Protocol + Protocol3PC = 34 // Third Party Connect Protocol + ProtocolIDPR = 35 // Inter-Domain Policy Routing Protocol + ProtocolXTP = 36 // XTP + ProtocolDDP = 37 // Datagram Delivery Protocol + ProtocolIDPRCMTP = 38 // IDPR Control Message Transport Proto + ProtocolTPPP = 39 // TP++ Transport Protocol + ProtocolIL = 40 // IL Transport Protocol + ProtocolIPv6 = 41 // IPv6 encapsulation + ProtocolSDRP = 42 // Source Demand Routing Protocol + ProtocolIPv6Route = 43 // Routing Header for IPv6 + ProtocolIPv6Frag = 44 // Fragment Header for IPv6 + ProtocolIDRP = 45 // Inter-Domain Routing Protocol + ProtocolRSVP = 46 // Reservation Protocol + ProtocolGRE = 47 // Generic Routing Encapsulation + ProtocolDSR = 48 // Dynamic Source Routing Protocol + ProtocolBNA = 49 // BNA + ProtocolESP = 50 // Encap Security Payload + ProtocolAH = 51 // Authentication Header + ProtocolINLSP = 52 // Integrated Net Layer Security TUBA + ProtocolNARP = 54 // NBMA Address Resolution Protocol + ProtocolMOBILE = 55 // IP Mobility + ProtocolTLSP = 56 // Transport Layer Security Protocol using Kryptonet key management + ProtocolSKIP = 57 // SKIP + ProtocolIPv6ICMP = 58 // ICMP for IPv6 + ProtocolIPv6NoNxt = 59 // No Next Header for IPv6 + ProtocolIPv6Opts = 60 // Destination Options for IPv6 + ProtocolCFTP = 62 // CFTP + ProtocolSATEXPAK = 64 // SATNET and Backroom EXPAK + ProtocolKRYPTOLAN = 65 // Kryptolan + ProtocolRVD = 66 // MIT Remote Virtual Disk Protocol + ProtocolIPPC = 67 // Internet Pluribus Packet Core + ProtocolSATMON = 69 // SATNET Monitoring + ProtocolVISA = 70 // VISA Protocol + ProtocolIPCV = 71 // Internet Packet Core Utility + ProtocolCPNX = 72 // Computer Protocol Network Executive + ProtocolCPHB = 73 // Computer Protocol Heart Beat + ProtocolWSN = 74 // Wang Span Network + ProtocolPVP = 75 // Packet Video Protocol + ProtocolBRSATMON = 76 // Backroom SATNET Monitoring + ProtocolSUNND = 77 // SUN ND PROTOCOL-Temporary + ProtocolWBMON = 78 // WIDEBAND Monitoring + ProtocolWBEXPAK = 79 // WIDEBAND EXPAK + ProtocolISOIP = 80 // ISO Internet Protocol + ProtocolVMTP = 81 // VMTP + ProtocolSECUREVMTP = 82 // SECURE-VMTP + ProtocolVINES = 83 // VINES + ProtocolTTP = 84 // Transaction Transport Protocol + ProtocolIPTM = 84 // Internet Protocol Traffic Manager + ProtocolNSFNETIGP = 85 // NSFNET-IGP + ProtocolDGP = 86 // Dissimilar Gateway Protocol + ProtocolTCF = 87 // TCF + ProtocolEIGRP = 88 // EIGRP + ProtocolOSPFIGP = 89 // OSPFIGP + ProtocolSpriteRPC = 90 // Sprite RPC Protocol + ProtocolLARP = 91 // Locus Address Resolution Protocol + ProtocolMTP = 92 // Multicast Transport Protocol + ProtocolAX25 = 93 // AX.25 Frames + ProtocolIPIP = 94 // IP-within-IP Encapsulation Protocol + ProtocolSCCSP = 96 // Semaphore Communications Sec. Pro. + ProtocolETHERIP = 97 // Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation + ProtocolENCAP = 98 // Encapsulation Header + ProtocolGMTP = 100 // GMTP + ProtocolIFMP = 101 // Ipsilon Flow Management Protocol + ProtocolPNNI = 102 // PNNI over IP + ProtocolPIM = 103 // Protocol Independent Multicast + ProtocolARIS = 104 // ARIS + ProtocolSCPS = 105 // SCPS + ProtocolQNX = 106 // QNX + ProtocolAN = 107 // Active Networks + ProtocolIPComp = 108 // IP Payload Compression Protocol + ProtocolSNP = 109 // Sitara Networks Protocol + ProtocolCompaqPeer = 110 // Compaq Peer Protocol + ProtocolIPXinIP = 111 // IPX in IP + ProtocolVRRP = 112 // Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol + ProtocolPGM = 113 // PGM Reliable Transport Protocol + ProtocolL2TP = 115 // Layer Two Tunneling Protocol + ProtocolDDX = 116 // D-II Data Exchange (DDX) + ProtocolIATP = 117 // Interactive Agent Transfer Protocol + ProtocolSTP = 118 // Schedule Transfer Protocol + ProtocolSRP = 119 // SpectraLink Radio Protocol + ProtocolUTI = 120 // UTI + ProtocolSMP = 121 // Simple Message Protocol + ProtocolPTP = 123 // Performance Transparency Protocol + ProtocolISIS = 124 // ISIS over IPv4 + ProtocolFIRE = 125 // FIRE + ProtocolCRTP = 126 // Combat Radio Transport Protocol + ProtocolCRUDP = 127 // Combat Radio User Datagram + ProtocolSSCOPMCE = 128 // SSCOPMCE + ProtocolIPLT = 129 // IPLT + ProtocolSPS = 130 // Secure Packet Shield + ProtocolPIPE = 131 // Private IP Encapsulation within IP + ProtocolSCTP = 132 // Stream Control Transmission Protocol + ProtocolFC = 133 // Fibre Channel + ProtocolRSVPE2EIGNORE = 134 // RSVP-E2E-IGNORE + ProtocolMobilityHeader = 135 // Mobility Header + ProtocolUDPLite = 136 // UDPLite + ProtocolMPLSinIP = 137 // MPLS-in-IP + ProtocolMANET = 138 // MANET Protocols + ProtocolHIP = 139 // Host Identity Protocol + ProtocolShim6 = 140 // Shim6 Protocol + ProtocolWESP = 141 // Wrapped Encapsulating Security Payload + ProtocolROHC = 142 // Robust Header Compression + ProtocolReserved = 255 // Reserved +) diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/iana/gen.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/iana/gen.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..2d8c07c --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/iana/gen.go @@ -0,0 +1,293 @@ +// Copyright 2013 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +// +build ignore + +//go:generate go run gen.go + +// This program generates internet protocol constants and tables by +// reading IANA protocol registries. +package main + +import ( + "bytes" + "encoding/xml" + "fmt" + "go/format" + "io" + "io/ioutil" + "net/http" + "os" + "strconv" + "strings" +) + +var registries = []struct { + url string + parse func(io.Writer, io.Reader) error +}{ + { + "http://www.iana.org/assignments/dscp-registry/dscp-registry.xml", + parseDSCPRegistry, + }, + { + "http://www.iana.org/assignments/ipv4-tos-byte/ipv4-tos-byte.xml", + parseTOSTCByte, + }, + { + "http://www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers/protocol-numbers.xml", + parseProtocolNumbers, + }, +} + +func main() { + var bb bytes.Buffer + fmt.Fprintf(&bb, "// go generate gen.go\n") + fmt.Fprintf(&bb, "// GENERATED BY THE COMMAND ABOVE; DO NOT EDIT\n\n") + fmt.Fprintf(&bb, "// Package iana provides protocol number resources managed by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).\n") + fmt.Fprintf(&bb, `package iana // import "golang.org/x/net/internal/iana"`+"\n\n") + for _, r := range registries { + resp, err := http.Get(r.url) + if err != nil { + fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err) + os.Exit(1) + } + defer resp.Body.Close() + if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK { + fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "got HTTP status code %v for %v\n", resp.StatusCode, r.url) + os.Exit(1) + } + if err := r.parse(&bb, resp.Body); err != nil { + fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err) + os.Exit(1) + } + fmt.Fprintf(&bb, "\n") + } + b, err := format.Source(bb.Bytes()) + if err != nil { + fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err) + os.Exit(1) + } + if err := ioutil.WriteFile("const.go", b, 0644); err != nil { + fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err) + os.Exit(1) + } +} + +func parseDSCPRegistry(w io.Writer, r io.Reader) error { + dec := xml.NewDecoder(r) + var dr dscpRegistry + if err := dec.Decode(&dr); err != nil { + return err + } + drs := dr.escape() + fmt.Fprintf(w, "// %s, Updated: %s\n", dr.Title, dr.Updated) + fmt.Fprintf(w, "const (\n") + for _, dr := range drs { + fmt.Fprintf(w, "DiffServ%s = %#x", dr.Name, dr.Value) + fmt.Fprintf(w, "// %s\n", dr.OrigName) + } + fmt.Fprintf(w, ")\n") + return nil +} + +type dscpRegistry struct { + XMLName xml.Name `xml:"registry"` + Title string `xml:"title"` + Updated string `xml:"updated"` + Note string `xml:"note"` + RegTitle string `xml:"registry>title"` + PoolRecords []struct { + Name string `xml:"name"` + Space string `xml:"space"` + } `xml:"registry>record"` + Records []struct { + Name string `xml:"name"` + Space string `xml:"space"` + } `xml:"registry>registry>record"` +} + +type canonDSCPRecord struct { + OrigName string + Name string + Value int +} + +func (drr *dscpRegistry) escape() []canonDSCPRecord { + drs := make([]canonDSCPRecord, len(drr.Records)) + sr := strings.NewReplacer( + "+", "", + "-", "", + "/", "", + ".", "", + " ", "", + ) + for i, dr := range drr.Records { + s := strings.TrimSpace(dr.Name) + drs[i].OrigName = s + drs[i].Name = sr.Replace(s) + n, err := strconv.ParseUint(dr.Space, 2, 8) + if err != nil { + continue + } + drs[i].Value = int(n) << 2 + } + return drs +} + +func parseTOSTCByte(w io.Writer, r io.Reader) error { + dec := xml.NewDecoder(r) + var ttb tosTCByte + if err := dec.Decode(&ttb); err != nil { + return err + } + trs := ttb.escape() + fmt.Fprintf(w, "// %s, Updated: %s\n", ttb.Title, ttb.Updated) + fmt.Fprintf(w, "const (\n") + for _, tr := range trs { + fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s = %#x", tr.Keyword, tr.Value) + fmt.Fprintf(w, "// %s\n", tr.OrigKeyword) + } + fmt.Fprintf(w, ")\n") + return nil +} + +type tosTCByte struct { + XMLName xml.Name `xml:"registry"` + Title string `xml:"title"` + Updated string `xml:"updated"` + Note string `xml:"note"` + RegTitle string `xml:"registry>title"` + Records []struct { + Binary string `xml:"binary"` + Keyword string `xml:"keyword"` + } `xml:"registry>record"` +} + +type canonTOSTCByteRecord struct { + OrigKeyword string + Keyword string + Value int +} + +func (ttb *tosTCByte) escape() []canonTOSTCByteRecord { + trs := make([]canonTOSTCByteRecord, len(ttb.Records)) + sr := strings.NewReplacer( + "Capable", "", + "(", "", + ")", "", + "+", "", + "-", "", + "/", "", + ".", "", + " ", "", + ) + for i, tr := range ttb.Records { + s := strings.TrimSpace(tr.Keyword) + trs[i].OrigKeyword = s + ss := strings.Split(s, " ") + if len(ss) > 1 { + trs[i].Keyword = strings.Join(ss[1:], " ") + } else { + trs[i].Keyword = ss[0] + } + trs[i].Keyword = sr.Replace(trs[i].Keyword) + n, err := strconv.ParseUint(tr.Binary, 2, 8) + if err != nil { + continue + } + trs[i].Value = int(n) + } + return trs +} + +func parseProtocolNumbers(w io.Writer, r io.Reader) error { + dec := xml.NewDecoder(r) + var pn protocolNumbers + if err := dec.Decode(&pn); err != nil { + return err + } + prs := pn.escape() + prs = append([]canonProtocolRecord{{ + Name: "IP", + Descr: "IPv4 encapsulation, pseudo protocol number", + Value: 0, + }}, prs...) + fmt.Fprintf(w, "// %s, Updated: %s\n", pn.Title, pn.Updated) + fmt.Fprintf(w, "const (\n") + for _, pr := range prs { + if pr.Name == "" { + continue + } + fmt.Fprintf(w, "Protocol%s = %d", pr.Name, pr.Value) + s := pr.Descr + if s == "" { + s = pr.OrigName + } + fmt.Fprintf(w, "// %s\n", s) + } + fmt.Fprintf(w, ")\n") + return nil +} + +type protocolNumbers struct { + XMLName xml.Name `xml:"registry"` + Title string `xml:"title"` + Updated string `xml:"updated"` + RegTitle string `xml:"registry>title"` + Note string `xml:"registry>note"` + Records []struct { + Value string `xml:"value"` + Name string `xml:"name"` + Descr string `xml:"description"` + } `xml:"registry>record"` +} + +type canonProtocolRecord struct { + OrigName string + Name string + Descr string + Value int +} + +func (pn *protocolNumbers) escape() []canonProtocolRecord { + prs := make([]canonProtocolRecord, len(pn.Records)) + sr := strings.NewReplacer( + "-in-", "in", + "-within-", "within", + "-over-", "over", + "+", "P", + "-", "", + "/", "", + ".", "", + " ", "", + ) + for i, pr := range pn.Records { + if strings.Contains(pr.Name, "Deprecated") || + strings.Contains(pr.Name, "deprecated") { + continue + } + prs[i].OrigName = pr.Name + s := strings.TrimSpace(pr.Name) + switch pr.Name { + case "ISIS over IPv4": + prs[i].Name = "ISIS" + case "manet": + prs[i].Name = "MANET" + default: + prs[i].Name = sr.Replace(s) + } + ss := strings.Split(pr.Descr, "\n") + for i := range ss { + ss[i] = strings.TrimSpace(ss[i]) + } + if len(ss) > 1 { + prs[i].Descr = strings.Join(ss, " ") + } else { + prs[i].Descr = ss[0] + } + prs[i].Value, _ = strconv.Atoi(pr.Value) + } + return prs +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..e82e51c --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket.go @@ -0,0 +1,37 @@ +// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +// Package netreflect implements run-time reflection for the +// facilities of net package. +package netreflect + +import ( + "errors" + "net" +) + +var ( + errInvalidType = errors.New("invalid type") + errOpNoSupport = errors.New("operation not supported") +) + +// SocketOf returns the socket descriptor of c. +func SocketOf(c net.Conn) (uintptr, error) { + switch c.(type) { + case *net.TCPConn, *net.UDPConn, *net.IPConn, *net.UnixConn: + return socketOf(c) + default: + return 0, errInvalidType + } +} + +// PacketSocketOf returns the socket descriptor of c. +func PacketSocketOf(c net.PacketConn) (uintptr, error) { + switch c.(type) { + case *net.UDPConn, *net.IPConn, *net.UnixConn: + return socketOf(c.(net.Conn)) + default: + return 0, errInvalidType + } +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket_posix.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket_posix.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..df475a2 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket_posix.go @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ +// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +// +build darwin dragonfly freebsd linux netbsd openbsd solaris windows + +package netreflect + +import ( + "net" + "reflect" + "runtime" +) + +func socketOf(c net.Conn) (uintptr, error) { + v := reflect.ValueOf(c) + switch e := v.Elem(); e.Kind() { + case reflect.Struct: + fd := e.FieldByName("conn").FieldByName("fd") + switch e := fd.Elem(); e.Kind() { + case reflect.Struct: + sysfd := e.FieldByName("sysfd") + if runtime.GOOS == "windows" { + return uintptr(sysfd.Uint()), nil + } + return uintptr(sysfd.Int()), nil + } + } + return 0, errInvalidType +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket_stub.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket_stub.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..85adb4b --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect/socket_stub.go @@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ +// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +// +build !darwin,!dragonfly,!freebsd,!linux,!netbsd,!openbsd,!solaris,!windows + +package netreflect + +import "net" + +func socketOf(c net.Conn) (uintptr, error) { return 0, errOpNoSupport } diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/bpfopt_linux.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/bpfopt_linux.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..2d626d9 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/bpfopt_linux.go @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ +// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +package ipv4 + +import ( + "os" + "unsafe" + + "golang.org/x/net/bpf" + "golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect" +) + +// SetBPF attaches a BPF program to the connection. +// +// Only supported on Linux. +func (c *dgramOpt) SetBPF(filter []bpf.RawInstruction) error { + s, err := netreflect.PacketSocketOf(c.PacketConn) + if err != nil { + return err + } + prog := sockFProg{ + Len: uint16(len(filter)), + Filter: (*sockFilter)(unsafe.Pointer(&filter[0])), + } + return os.NewSyscallError("setsockopt", setsockopt(s, sysSOL_SOCKET, sysSO_ATTACH_FILTER, unsafe.Pointer(&prog), uint32(unsafe.Sizeof(prog)))) +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/bpfopt_stub.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/bpfopt_stub.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..c4a8481 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/bpfopt_stub.go @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ +// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +// +build !linux + +package ipv4 + +import "golang.org/x/net/bpf" + +// SetBPF attaches a BPF program to the connection. +// +// Only supported on Linux. +func (c *dgramOpt) SetBPF(filter []bpf.RawInstruction) error { + return errOpNoSupport +} diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/control.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/control.go new file mode 100644 index 0000000..8cadfd7 --- /dev/null +++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/golang.org/x/net/ipv4/control.go @@ -0,0 +1,70 @@ +// Copyright 2012 The Go Authors. All rights reserved. +// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style +// license that can be found in the LICENSE file. + +package ipv4 + +import ( + "fmt" + "net" + "sync" +) + +type rawOpt struct { + sync.RWMutex + cflags ControlFlags +} + +func (c *rawOpt) set(f ControlFlags) { c.cflags |= f } +func (c *rawOpt) clear(f ControlFlags) { c.cflags &^= f } +func (c *rawOpt) isset(f ControlFlags) bool { return c.cflags&f != 0 } + +type ControlFlags uint + +const ( + FlagTTL ControlFlags = 1 << iota // pass the TTL on the received packet + FlagSrc // pass the source address on the received packet + FlagDst // pass the destination address on the received packet + FlagInterface // pass the interface index on the received packet +) + +// A ControlMessage represents per packet basis IP-level socket options. +type ControlMessage struct { + // Receiving socket options: SetControlMessage allows to + // receive the options from the protocol stack using ReadFrom + // method of PacketConn or RawConn. + // + // Specifying socket options: ControlMessage for WriteTo + // method of PacketConn or RawConn allows to send the options + // to the protocol stack. + // + TTL int // time-to-live, receiving only + Src net.IP // source address, specifying only + Dst net.IP // destination address, receiving only + IfIndex int // interface index, must be 1 <= value when specifying +} + +func (cm *ControlMessage) String() string { + if cm == nil { + return "| + | github.com/gorilla | +golang.org/x/net | +
|---|---|---|
| RFC 6455 Features | ||
| Passes Autobahn Test Suite | Yes | No |
| Receive fragmented message | Yes | No, see note 1 |
| Send close message | Yes | No |
| Send pings and receive pongs | Yes | No |
| Get the type of a received data message | Yes | Yes, see note 2 |
| Other Features | ||
| Compression Extensions | Experimental | No |
| Read message using io.Reader | Yes | No, see note 3 |
| Write message using io.WriteCloser | Yes | No, see note 3 |
 +
+## Usage
+
+Client: [full demo](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun/blob/master/client/main.go#L231)
+```go
+kcpconn, err := kcp.DialWithOptions("192.168.0.1:10000", nil, 10, 3)
+```
+Server: [full demo](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun/blob/master/server/main.go#L235)
+```go
+lis, err := kcp.ListenWithOptions(":10000", nil, 10, 3)
+```
+
+## Performance
+```
+ 型号名称: MacBook Pro
+ 型号标识符: MacBookPro12,1
+ 处理器名称: Intel Core i5
+ 处理器速度: 2.7 GHz
+ 处理器数目: 1
+ 核总数: 2
+ L2 缓存(每个核): 256 KB
+ L3 缓存: 3 MB
+ 内存: 8 GB
+```
+```
+$ go test -run Speed
+new client 127.0.0.1:61165
+total recv: 16777216
+time for 16MB rtt with encryption 570.41176ms
+&{BytesSent:33554432 BytesReceived:33554432 MaxConn:2 ActiveOpens:1 PassiveOpens:1 CurrEstab:1 InErrs:0 InCsumErrors:0 InSegs:42577 OutSegs:42641 OutBytes:48111336 RetransSegs:92 FastRetransSegs:92 LostSegs:0 RepeatSegs:0 FECRecovered:1 FECErrs:0 FECSegs:8514}
+PASS
+ok github.com/xtaci/kcp-go 0.600s
+```
+
+## Links
+
+1. https://github.com/xtaci/libkcp -- Official client library for iOS/Android(C++11)
+2. https://github.com/skywind3000/kcp -- A Fast and Reliable ARQ Protocol
+3. https://github.com/klauspost/reedsolomon -- Reed-Solomon Erasure Coding in Go
+
+## Donation
+
+
+
+All donations on this project will be used to support the development of [gonet/2](http://gonet2.github.io/).
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/crypt.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/crypt.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..df85278
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/crypt.go
@@ -0,0 +1,301 @@
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "crypto/aes"
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "crypto/des"
+ "crypto/sha1"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/blowfish"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/cast5"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/salsa20"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/tea"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/twofish"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/xtea"
+)
+
+var (
+ initialVector = []byte{167, 115, 79, 156, 18, 172, 27, 1, 164, 21, 242, 193, 252, 120, 230, 107}
+ saltxor = `sH3CIVoF#rWLtJo6`
+)
+
+// BlockCrypt defines encryption/decryption methods for a given byte slice
+type BlockCrypt interface {
+ // Encrypt encrypts the whole block in src into dst.
+ // Dst and src may point at the same memory.
+ Encrypt(dst, src []byte)
+
+ // Decrypt decrypts the whole block in src into dst.
+ // Dst and src may point at the same memory.
+ Decrypt(dst, src []byte)
+}
+
+// Salsa20BlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type Salsa20BlockCrypt struct {
+ key [32]byte
+}
+
+// NewSalsa20BlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewSalsa20BlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(Salsa20BlockCrypt)
+ copy(c.key[:], key)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *Salsa20BlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) {
+ salsa20.XORKeyStream(dst[8:], src[8:], src[:8], &c.key)
+ copy(dst[:8], src[:8])
+}
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *Salsa20BlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) {
+ salsa20.XORKeyStream(dst[8:], src[8:], src[:8], &c.key)
+ copy(dst[:8], src[:8])
+}
+
+// TwofishBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type TwofishBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewTwofishBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewTwofishBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(TwofishBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := twofish.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, twofish.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*twofish.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *TwofishBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *TwofishBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// TripleDESBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type TripleDESBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewTripleDESBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewTripleDESBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(TripleDESBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := des.NewTripleDESCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, des.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*des.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *TripleDESBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *TripleDESBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// Cast5BlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type Cast5BlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewCast5BlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewCast5BlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(Cast5BlockCrypt)
+ block, err := cast5.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, cast5.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*cast5.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *Cast5BlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *Cast5BlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// BlowfishBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type BlowfishBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewBlowfishBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewBlowfishBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(BlowfishBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := blowfish.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, blowfish.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*blowfish.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *BlowfishBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *BlowfishBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// AESBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type AESBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewAESBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewAESBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(AESBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, aes.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*aes.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *AESBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *AESBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// TEABlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type TEABlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewTEABlockCrypt initate BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewTEABlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(TEABlockCrypt)
+ block, err := tea.NewCipherWithRounds(key, 16)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, tea.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*tea.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *TEABlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *TEABlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// XTEABlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type XTEABlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewXTEABlockCrypt initate BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewXTEABlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(XTEABlockCrypt)
+ block, err := xtea.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, xtea.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*xtea.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *XTEABlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *XTEABlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// SimpleXORBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type SimpleXORBlockCrypt struct {
+ xortbl []byte
+}
+
+// NewSimpleXORBlockCrypt initate BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewSimpleXORBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(SimpleXORBlockCrypt)
+ c.xortbl = pbkdf2.Key(key, []byte(saltxor), 32, mtuLimit, sha1.New)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *SimpleXORBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { xorBytes(dst, src, c.xortbl) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *SimpleXORBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { xorBytes(dst, src, c.xortbl) }
+
+// NoneBlockCrypt simple returns the plaintext
+type NoneBlockCrypt struct{}
+
+// NewNoneBlockCrypt initate by the given key
+func NewNoneBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ return new(NoneBlockCrypt), nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *NoneBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { copy(dst, src) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *NoneBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { copy(dst, src) }
+
+// packet encryption with local CFB mode
+func encrypt(block cipher.Block, dst, src, buf []byte) {
+ blocksize := block.BlockSize()
+ tbl := buf[:blocksize]
+ block.Encrypt(tbl, initialVector)
+ n := len(src) / blocksize
+ base := 0
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ xorWords(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+ block.Encrypt(tbl, dst[base:])
+ base += blocksize
+ }
+ xorBytes(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+}
+
+func decrypt(block cipher.Block, dst, src, buf []byte) {
+ blocksize := block.BlockSize()
+ tbl := buf[:blocksize]
+ next := buf[blocksize:]
+ block.Encrypt(tbl, initialVector)
+ n := len(src) / blocksize
+ base := 0
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ block.Encrypt(next, src[base:])
+ xorWords(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+ tbl, next = next, tbl
+ base += blocksize
+ }
+ xorBytes(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/donate.png b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/donate.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0f353d9
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/donate.png differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/fec.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/fec.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..10ad1c0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/fec.go
@@ -0,0 +1,241 @@
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/klauspost/reedsolomon"
+)
+
+const (
+ fecHeaderSize = 6
+ fecHeaderSizePlus2 = fecHeaderSize + 2 // plus 2B data size
+ typeData = 0xf1
+ typeFEC = 0xf2
+ fecExpire = 30000 // 30s
+)
+
+type (
+ // FEC defines forward error correction for packets
+ FEC struct {
+ rx []fecPacket // ordered receive queue
+ rxlimit int // queue size limit
+ dataShards int
+ parityShards int
+ shardSize int
+ next uint32 // next seqid
+ enc reedsolomon.Encoder
+ shards [][]byte
+ shardsflag []bool
+ paws uint32 // Protect Against Wrapped Sequence numbers
+ lastCheck uint32
+ xmitBuf sync.Pool
+ }
+
+ fecPacket struct {
+ seqid uint32
+ flag uint16
+ data []byte
+ ts uint32
+ }
+)
+
+func newFEC(rxlimit, dataShards, parityShards int) *FEC {
+ if dataShards <= 0 || parityShards <= 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ if rxlimit < dataShards+parityShards {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ fec := new(FEC)
+ fec.rxlimit = rxlimit
+ fec.dataShards = dataShards
+ fec.parityShards = parityShards
+ fec.shardSize = dataShards + parityShards
+ fec.paws = (0xffffffff/uint32(fec.shardSize) - 1) * uint32(fec.shardSize)
+ enc, err := reedsolomon.New(dataShards, parityShards)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ fec.enc = enc
+ fec.shards = make([][]byte, fec.shardSize)
+ fec.shardsflag = make([]bool, fec.shardSize)
+ fec.xmitBuf.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+
+ return fec
+}
+
+// decode a fec packet
+func (fec *FEC) decode(data []byte) fecPacket {
+ var pkt fecPacket
+ pkt.seqid = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data)
+ pkt.flag = binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(data[4:])
+ pkt.ts = currentMs()
+ // allocate memory & copy
+ buf := fec.xmitBuf.Get().([]byte)
+ n := copy(buf, data[6:])
+ xorBytes(buf[n:], buf[n:], buf[n:])
+ pkt.data = buf
+ return pkt
+}
+
+func (fec *FEC) markData(data []byte) {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(data, fec.next)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(data[4:], typeData)
+ fec.next++
+}
+
+func (fec *FEC) markFEC(data []byte) {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(data, fec.next)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(data[4:], typeFEC)
+ fec.next++
+ if fec.next >= fec.paws { // paws would only occurs in markFEC
+ fec.next = 0
+ }
+}
+
+// input a fec packet
+func (fec *FEC) input(pkt fecPacket) (recovered [][]byte) {
+ // expiration
+ now := currentMs()
+ if now-fec.lastCheck >= fecExpire {
+ var rx []fecPacket
+ for k := range fec.rx {
+ if now-fec.rx[k].ts < fecExpire {
+ rx = append(rx, fec.rx[k])
+ } else {
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[k].data)
+ }
+ }
+ fec.rx = rx
+ fec.lastCheck = now
+ }
+
+ // insertion
+ n := len(fec.rx) - 1
+ insertIdx := 0
+ for i := n; i >= 0; i-- {
+ if pkt.seqid == fec.rx[i].seqid { // de-duplicate
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(pkt.data)
+ return nil
+ } else if pkt.seqid > fec.rx[i].seqid { // insertion
+ insertIdx = i + 1
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ // insert into ordered rx queue
+ if insertIdx == n+1 {
+ fec.rx = append(fec.rx, pkt)
+ } else {
+ fec.rx = append(fec.rx, fecPacket{})
+ copy(fec.rx[insertIdx+1:], fec.rx[insertIdx:])
+ fec.rx[insertIdx] = pkt
+ }
+
+ // shard range for current packet
+ shardBegin := pkt.seqid - pkt.seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize)
+ shardEnd := shardBegin + uint32(fec.shardSize) - 1
+
+ // max search range in ordered queue for current shard
+ searchBegin := insertIdx - int(pkt.seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize))
+ if searchBegin < 0 {
+ searchBegin = 0
+ }
+ searchEnd := searchBegin + fec.shardSize - 1
+ if searchEnd >= len(fec.rx) {
+ searchEnd = len(fec.rx) - 1
+ }
+
+ if searchEnd > searchBegin && searchEnd-searchBegin+1 >= fec.dataShards {
+ numshard := 0
+ numDataShard := 0
+ first := -1
+ maxlen := 0
+ shards := fec.shards
+ shardsflag := fec.shardsflag
+ for k := range fec.shards {
+ shards[k] = nil
+ shardsflag[k] = false
+ }
+
+ for i := searchBegin; i <= searchEnd; i++ {
+ seqid := fec.rx[i].seqid
+ if seqid > shardEnd {
+ break
+ } else if seqid >= shardBegin {
+ shards[seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize)] = fec.rx[i].data
+ shardsflag[seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize)] = true
+ numshard++
+ if fec.rx[i].flag == typeData {
+ numDataShard++
+ }
+ if numshard == 1 {
+ first = i
+ }
+ if len(fec.rx[i].data) > maxlen {
+ maxlen = len(fec.rx[i].data)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ if numDataShard == fec.dataShards { // no lost
+ for i := first; i < first+numshard; i++ { // free
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[i].data)
+ }
+ copy(fec.rx[first:], fec.rx[first+numshard:])
+ for i := 0; i < numshard; i++ { // dereference
+ fec.rx[len(fec.rx)-1-i] = fecPacket{}
+ }
+ fec.rx = fec.rx[:len(fec.rx)-numshard]
+ } else if numshard >= fec.dataShards { // recoverable
+ for k := range shards {
+ if shards[k] != nil {
+ shards[k] = shards[k][:maxlen]
+ }
+ }
+ if err := fec.enc.Reconstruct(shards); err == nil {
+ for k := range shards[:fec.dataShards] {
+ if !shardsflag[k] {
+ recovered = append(recovered, shards[k])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for i := first; i < first+numshard; i++ { // free
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[i].data)
+ }
+ copy(fec.rx[first:], fec.rx[first+numshard:])
+ for i := 0; i < numshard; i++ { // dereference
+ fec.rx[len(fec.rx)-1-i] = fecPacket{}
+ }
+ fec.rx = fec.rx[:len(fec.rx)-numshard]
+ }
+ }
+
+ // keep rxlimit
+ if len(fec.rx) > fec.rxlimit {
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[0].data) // free
+ fec.rx[0].data = nil
+ fec.rx = fec.rx[1:]
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+func (fec *FEC) calcECC(data [][]byte, offset, maxlen int) (ecc [][]byte) {
+ if len(data) != fec.shardSize {
+ return nil
+ }
+ shards := make([][]byte, fec.shardSize)
+ for k := range shards {
+ shards[k] = data[k][offset:maxlen]
+ }
+
+ if err := fec.enc.Encode(shards); err != nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return data[fec.dataShards:]
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/frame.png b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/frame.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7952e4a
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/frame.png differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/kcp.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/kcp.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..78ccf26
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/kcp.go
@@ -0,0 +1,961 @@
+// Package kcp - A Fast and Reliable ARQ Protocol
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "container/heap"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "sync/atomic"
+)
+
+const (
+ IKCP_RTO_NDL = 30 // no delay min rto
+ IKCP_RTO_MIN = 100 // normal min rto
+ IKCP_RTO_DEF = 200
+ IKCP_RTO_MAX = 60000
+ IKCP_CMD_PUSH = 81 // cmd: push data
+ IKCP_CMD_ACK = 82 // cmd: ack
+ IKCP_CMD_WASK = 83 // cmd: window probe (ask)
+ IKCP_CMD_WINS = 84 // cmd: window size (tell)
+ IKCP_ASK_SEND = 1 // need to send IKCP_CMD_WASK
+ IKCP_ASK_TELL = 2 // need to send IKCP_CMD_WINS
+ IKCP_WND_SND = 32
+ IKCP_WND_RCV = 32
+ IKCP_MTU_DEF = 1400
+ IKCP_ACK_FAST = 3
+ IKCP_INTERVAL = 100
+ IKCP_OVERHEAD = 24
+ IKCP_DEADLINK = 20
+ IKCP_THRESH_INIT = 2
+ IKCP_THRESH_MIN = 2
+ IKCP_PROBE_INIT = 7000 // 7 secs to probe window size
+ IKCP_PROBE_LIMIT = 120000 // up to 120 secs to probe window
+)
+
+// Output is a closure which captures conn and calls conn.Write
+type Output func(buf []byte, size int)
+
+/* encode 8 bits unsigned int */
+func ikcp_encode8u(p []byte, c byte) []byte {
+ p[0] = c
+ return p[1:]
+}
+
+/* decode 8 bits unsigned int */
+func ikcp_decode8u(p []byte, c *byte) []byte {
+ *c = p[0]
+ return p[1:]
+}
+
+/* encode 16 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_encode16u(p []byte, w uint16) []byte {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(p, w)
+ return p[2:]
+}
+
+/* decode 16 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_decode16u(p []byte, w *uint16) []byte {
+ *w = binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(p)
+ return p[2:]
+}
+
+/* encode 32 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_encode32u(p []byte, l uint32) []byte {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(p, l)
+ return p[4:]
+}
+
+/* decode 32 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_decode32u(p []byte, l *uint32) []byte {
+ *l = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(p)
+ return p[4:]
+}
+
+func _imin_(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a <= b {
+ return a
+ } else {
+ return b
+ }
+}
+
+func _imax_(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a >= b {
+ return a
+ } else {
+ return b
+ }
+}
+
+func _ibound_(lower, middle, upper uint32) uint32 {
+ return _imin_(_imax_(lower, middle), upper)
+}
+
+func _itimediff(later, earlier uint32) int32 {
+ return (int32)(later - earlier)
+}
+
+// Segment defines a KCP segment
+type Segment struct {
+ conv uint32
+ cmd uint32
+ frg uint32
+ wnd uint32
+ ts uint32
+ sn uint32
+ una uint32
+ resendts uint32
+ rto uint32
+ fastack uint32
+ xmit uint32
+ data []byte
+}
+
+// encode a segment into buffer
+func (seg *Segment) encode(ptr []byte) []byte {
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.conv)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode8u(ptr, uint8(seg.cmd))
+ ptr = ikcp_encode8u(ptr, uint8(seg.frg))
+ ptr = ikcp_encode16u(ptr, uint16(seg.wnd))
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.ts)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.sn)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.una)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, uint32(len(seg.data)))
+ return ptr
+}
+
+// NewSegment creates a KCP segment
+func NewSegment(size int) *Segment {
+ seg := new(Segment)
+ seg.data = make([]byte, size)
+ return seg
+}
+
+// KCP defines a single KCP connection
+type KCP struct {
+ conv, mtu, mss, state uint32
+ snd_una, snd_nxt, rcv_nxt uint32
+ ssthresh uint32
+ rx_rttval, rx_srtt, rx_rto, rx_minrto uint32
+ snd_wnd, rcv_wnd, rmt_wnd, cwnd, probe uint32
+ current, interval, ts_flush, xmit uint32
+ nodelay, updated uint32
+ ts_probe, probe_wait uint32
+ dead_link, incr uint32
+
+ fastresend int32
+ nocwnd, stream int32
+
+ snd_queue []Segment
+ rcv_queue []Segment
+ snd_buf []Segment
+ rcv_buf []Segment
+
+ acklist ACKList
+
+ buffer []byte
+ output Output
+}
+
+// ACK packet to return
+type ACK struct {
+ sn uint32
+ ts uint32
+}
+
+// ACKList is heapified
+type ACKList []ACK
+
+func (l ACKList) Len() int { return len(l) }
+func (l ACKList) Less(i, j int) bool { return l[i].sn < l[j].sn }
+func (l ACKList) Swap(i, j int) { l[i], l[j] = l[j], l[i] }
+func (l *ACKList) Push(x interface{}) { *l = append(*l, x.(ACK)) }
+func (l *ACKList) Pop() interface{} {
+ old := *l
+ n := len(old)
+ x := old[n-1]
+ *l = old[0 : n-1]
+ return x
+}
+
+// NewKCP create a new kcp control object, 'conv' must equal in two endpoint
+// from the same connection.
+func NewKCP(conv uint32, output Output) *KCP {
+ kcp := new(KCP)
+ kcp.conv = conv
+ kcp.snd_wnd = IKCP_WND_SND
+ kcp.rcv_wnd = IKCP_WND_RCV
+ kcp.rmt_wnd = IKCP_WND_RCV
+ kcp.mtu = IKCP_MTU_DEF
+ kcp.mss = kcp.mtu - IKCP_OVERHEAD
+ kcp.buffer = make([]byte, (kcp.mtu+IKCP_OVERHEAD)*3)
+ kcp.rx_rto = IKCP_RTO_DEF
+ kcp.rx_minrto = IKCP_RTO_MIN
+ kcp.interval = IKCP_INTERVAL
+ kcp.ts_flush = IKCP_INTERVAL
+ kcp.ssthresh = IKCP_THRESH_INIT
+ kcp.dead_link = IKCP_DEADLINK
+ kcp.output = output
+ return kcp
+}
+
+// PeekSize checks the size of next message in the recv queue
+func (kcp *KCP) PeekSize() (length int) {
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) == 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_queue[0]
+ if seg.frg == 0 {
+ return len(seg.data)
+ }
+
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(seg.frg+1) {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_queue {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_queue[k]
+ length += len(seg.data)
+ if seg.frg == 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+// Recv is user/upper level recv: returns size, returns below zero for EAGAIN
+func (kcp *KCP) Recv(buffer []byte) (n int) {
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) == 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ peeksize := kcp.PeekSize()
+ if peeksize < 0 {
+ return -2
+ }
+
+ if peeksize > len(buffer) {
+ return -3
+ }
+
+ var fast_recover bool
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) >= int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ fast_recover = true
+ }
+
+ // merge fragment
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_queue {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_queue[k]
+ copy(buffer, seg.data)
+ buffer = buffer[len(seg.data):]
+ n += len(seg.data)
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ if seg.frg == 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.rcv_queue = kcp.rcv_queue[count:]
+
+ // move available data from rcv_buf -> rcv_queue
+ count = 0
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_buf[k]
+ if seg.sn == kcp.rcv_nxt && len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ kcp.rcv_queue = append(kcp.rcv_queue, *seg)
+ kcp.rcv_nxt++
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.rcv_buf = kcp.rcv_buf[count:]
+
+ // fast recover
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) && fast_recover {
+ // ready to send back IKCP_CMD_WINS in ikcp_flush
+ // tell remote my window size
+ kcp.probe |= IKCP_ASK_TELL
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+// Send is user/upper level send, returns below zero for error
+func (kcp *KCP) Send(buffer []byte) int {
+ var count int
+ if len(buffer) == 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ // append to previous segment in streaming mode (if possible)
+ if kcp.stream != 0 {
+ n := len(kcp.snd_queue)
+ if n > 0 {
+ old := &kcp.snd_queue[n-1]
+ if len(old.data) < int(kcp.mss) {
+ capacity := int(kcp.mss) - len(old.data)
+ extend := capacity
+ if len(buffer) < capacity {
+ extend = len(buffer)
+ }
+ seg := NewSegment(len(old.data) + extend)
+ seg.frg = 0
+ copy(seg.data, old.data)
+ copy(seg.data[len(old.data):], buffer)
+ buffer = buffer[extend:]
+ kcp.snd_queue[n-1] = *seg
+ }
+ }
+
+ if len(buffer) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ }
+
+ if len(buffer) <= int(kcp.mss) {
+ count = 1
+ } else {
+ count = (len(buffer) + int(kcp.mss) - 1) / int(kcp.mss)
+ }
+
+ if count > 255 {
+ return -2
+ }
+
+ if count == 0 {
+ count = 1
+ }
+
+ for i := 0; i < count; i++ {
+ var size int
+ if len(buffer) > int(kcp.mss) {
+ size = int(kcp.mss)
+ } else {
+ size = len(buffer)
+ }
+ seg := NewSegment(size)
+ copy(seg.data, buffer[:size])
+ if kcp.stream == 0 { // message mode
+ seg.frg = uint32(count - i - 1)
+ } else { // stream mode
+ seg.frg = 0
+ }
+ kcp.snd_queue = append(kcp.snd_queue, *seg)
+ buffer = buffer[size:]
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6298
+func (kcp *KCP) update_ack(rtt int32) {
+ var rto uint32
+ if kcp.rx_srtt == 0 {
+ kcp.rx_srtt = uint32(rtt)
+ kcp.rx_rttval = uint32(rtt) / 2
+ } else {
+ delta := rtt - int32(kcp.rx_srtt)
+ if delta < 0 {
+ delta = -delta
+ }
+ kcp.rx_rttval = (3*kcp.rx_rttval + uint32(delta)) / 4
+ kcp.rx_srtt = (7*kcp.rx_srtt + uint32(rtt)) / 8
+ if kcp.rx_srtt < 1 {
+ kcp.rx_srtt = 1
+ }
+ }
+ rto = kcp.rx_srtt + _imax_(1, 4*kcp.rx_rttval)
+ kcp.rx_rto = _ibound_(kcp.rx_minrto, rto, IKCP_RTO_MAX)
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) shrink_buf() {
+ if len(kcp.snd_buf) > 0 {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[0]
+ kcp.snd_una = seg.sn
+ } else {
+ kcp.snd_una = kcp.snd_nxt
+ }
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_ack(sn uint32) {
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_una) < 0 || _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_nxt) >= 0 {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ if sn == seg.sn {
+ copy(kcp.snd_buf[k:], kcp.snd_buf[k+1:])
+ kcp.snd_buf[len(kcp.snd_buf)-1] = Segment{}
+ kcp.snd_buf = kcp.snd_buf[:len(kcp.snd_buf)-1]
+ break
+ }
+ if _itimediff(sn, seg.sn) < 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_fastack(sn uint32) {
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_una) < 0 || _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_nxt) >= 0 {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ if _itimediff(sn, seg.sn) < 0 {
+ break
+ } else if sn != seg.sn { // && kcp.current >= seg.ts+kcp.rx_srtt {
+ seg.fastack++
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_una(una uint32) {
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ if _itimediff(una, seg.sn) > 0 {
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.snd_buf = kcp.snd_buf[count:]
+}
+
+// ack append
+func (kcp *KCP) ack_push(sn, ts uint32) {
+ heap.Push(&kcp.acklist, ACK{sn, ts})
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_data(newseg *Segment) {
+ sn := newseg.sn
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt+kcp.rcv_wnd) >= 0 ||
+ _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt) < 0 {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.RepeatSegs, 1)
+ return
+ }
+
+ n := len(kcp.rcv_buf) - 1
+ insert_idx := 0
+ repeat := false
+ for i := n; i >= 0; i-- {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_buf[i]
+ if seg.sn == sn {
+ repeat = true
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.RepeatSegs, 1)
+ break
+ }
+ if _itimediff(sn, seg.sn) > 0 {
+ insert_idx = i + 1
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if !repeat {
+ if insert_idx == n+1 {
+ kcp.rcv_buf = append(kcp.rcv_buf, *newseg)
+ } else {
+ kcp.rcv_buf = append(kcp.rcv_buf, Segment{})
+ copy(kcp.rcv_buf[insert_idx+1:], kcp.rcv_buf[insert_idx:])
+ kcp.rcv_buf[insert_idx] = *newseg
+ }
+ }
+
+ // move available data from rcv_buf -> rcv_queue
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_buf[k]
+ if seg.sn == kcp.rcv_nxt && len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ kcp.rcv_queue = append(kcp.rcv_queue, kcp.rcv_buf[k])
+ kcp.rcv_nxt++
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.rcv_buf = kcp.rcv_buf[count:]
+}
+
+// Input when you received a low level packet (eg. UDP packet), call it
+func (kcp *KCP) Input(data []byte, update_ack bool) int {
+ una := kcp.snd_una
+ if len(data) < IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ var maxack uint32
+ var flag int
+ for {
+ var ts, sn, length, una, conv uint32
+ var wnd uint16
+ var cmd, frg uint8
+
+ if len(data) < int(IKCP_OVERHEAD) {
+ break
+ }
+
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &conv)
+ if conv != kcp.conv {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ data = ikcp_decode8u(data, &cmd)
+ data = ikcp_decode8u(data, &frg)
+ data = ikcp_decode16u(data, &wnd)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &ts)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &sn)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &una)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &length)
+ if len(data) < int(length) {
+ return -2
+ }
+
+ if cmd != IKCP_CMD_PUSH && cmd != IKCP_CMD_ACK &&
+ cmd != IKCP_CMD_WASK && cmd != IKCP_CMD_WINS {
+ return -3
+ }
+
+ kcp.rmt_wnd = uint32(wnd)
+ kcp.parse_una(una)
+ kcp.shrink_buf()
+
+ if cmd == IKCP_CMD_ACK {
+ if update_ack && _itimediff(kcp.current, ts) >= 0 {
+ kcp.update_ack(_itimediff(kcp.current, ts))
+ }
+ kcp.parse_ack(sn)
+ kcp.shrink_buf()
+ if flag == 0 {
+ flag = 1
+ maxack = sn
+ } else if _itimediff(sn, maxack) > 0 {
+ maxack = sn
+ }
+ } else if cmd == IKCP_CMD_PUSH {
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt+kcp.rcv_wnd) < 0 {
+ kcp.ack_push(sn, ts)
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt) >= 0 {
+ seg := NewSegment(int(length))
+ seg.conv = conv
+ seg.cmd = uint32(cmd)
+ seg.frg = uint32(frg)
+ seg.wnd = uint32(wnd)
+ seg.ts = ts
+ seg.sn = sn
+ seg.una = una
+ copy(seg.data, data[:length])
+ kcp.parse_data(seg)
+ }
+ }
+ } else if cmd == IKCP_CMD_WASK {
+ // ready to send back IKCP_CMD_WINS in Ikcp_flush
+ // tell remote my window size
+ kcp.probe |= IKCP_ASK_TELL
+ } else if cmd == IKCP_CMD_WINS {
+ // do nothing
+ } else {
+ return -3
+ }
+
+ data = data[length:]
+ }
+
+ if flag != 0 && update_ack {
+ kcp.parse_fastack(maxack)
+ }
+
+ if _itimediff(kcp.snd_una, una) > 0 {
+ if kcp.cwnd < kcp.rmt_wnd {
+ mss := kcp.mss
+ if kcp.cwnd < kcp.ssthresh {
+ kcp.cwnd++
+ kcp.incr += mss
+ } else {
+ if kcp.incr < mss {
+ kcp.incr = mss
+ }
+ kcp.incr += (mss*mss)/kcp.incr + (mss / 16)
+ if (kcp.cwnd+1)*mss <= kcp.incr {
+ kcp.cwnd++
+ }
+ }
+ if kcp.cwnd > kcp.rmt_wnd {
+ kcp.cwnd = kcp.rmt_wnd
+ kcp.incr = kcp.rmt_wnd * mss
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return 0
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) wnd_unused() int32 {
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ return int32(int(kcp.rcv_wnd) - len(kcp.rcv_queue))
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// flush pending data
+func (kcp *KCP) flush() {
+ current := kcp.current
+ buffer := kcp.buffer
+ change := 0
+ lost := false
+
+ if kcp.updated == 0 {
+ return
+ }
+ var seg Segment
+ seg.conv = kcp.conv
+ seg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_ACK
+ seg.wnd = uint32(kcp.wnd_unused())
+ seg.una = kcp.rcv_nxt
+
+ // flush acknowledges
+ ptr := buffer
+ for kcp.acklist.Len() > 0 {
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size+IKCP_OVERHEAD > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+ ack := heap.Pop(&kcp.acklist).(ACK)
+ seg.sn, seg.ts = ack.sn, ack.ts
+ ptr = seg.encode(ptr)
+ }
+ kcp.acklist = nil
+
+ // probe window size (if remote window size equals zero)
+ if kcp.rmt_wnd == 0 {
+ if kcp.probe_wait == 0 {
+ kcp.probe_wait = IKCP_PROBE_INIT
+ kcp.ts_probe = kcp.current + kcp.probe_wait
+ } else {
+ if _itimediff(kcp.current, kcp.ts_probe) >= 0 {
+ if kcp.probe_wait < IKCP_PROBE_INIT {
+ kcp.probe_wait = IKCP_PROBE_INIT
+ }
+ kcp.probe_wait += kcp.probe_wait / 2
+ if kcp.probe_wait > IKCP_PROBE_LIMIT {
+ kcp.probe_wait = IKCP_PROBE_LIMIT
+ }
+ kcp.ts_probe = kcp.current + kcp.probe_wait
+ kcp.probe |= IKCP_ASK_SEND
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ kcp.ts_probe = 0
+ kcp.probe_wait = 0
+ }
+
+ // flush window probing commands
+ if (kcp.probe & IKCP_ASK_SEND) != 0 {
+ seg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_WASK
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size+IKCP_OVERHEAD > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+ ptr = seg.encode(ptr)
+ }
+
+ // flush window probing commands
+ if (kcp.probe & IKCP_ASK_TELL) != 0 {
+ seg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_WINS
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size+IKCP_OVERHEAD > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+ ptr = seg.encode(ptr)
+ }
+
+ kcp.probe = 0
+
+ // calculate window size
+ cwnd := _imin_(kcp.snd_wnd, kcp.rmt_wnd)
+ if kcp.nocwnd == 0 {
+ cwnd = _imin_(kcp.cwnd, cwnd)
+ }
+
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.snd_queue {
+ if _itimediff(kcp.snd_nxt, kcp.snd_una+cwnd) >= 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ newseg := kcp.snd_queue[k]
+ newseg.conv = kcp.conv
+ newseg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_PUSH
+ newseg.wnd = seg.wnd
+ newseg.ts = current
+ newseg.sn = kcp.snd_nxt
+ newseg.una = kcp.rcv_nxt
+ newseg.resendts = current
+ newseg.rto = kcp.rx_rto
+ newseg.fastack = 0
+ newseg.xmit = 0
+ kcp.snd_buf = append(kcp.snd_buf, newseg)
+ kcp.snd_nxt++
+ count++
+ kcp.snd_queue[k].data = nil
+ }
+ kcp.snd_queue = kcp.snd_queue[count:]
+
+ // calculate resent
+ resent := uint32(kcp.fastresend)
+ if kcp.fastresend <= 0 {
+ resent = 0xffffffff
+ }
+ rtomin := (kcp.rx_rto >> 3)
+ if kcp.nodelay != 0 {
+ rtomin = 0
+ }
+
+ // flush data segments
+ nque := len(kcp.snd_queue)
+ var lostSegs, fastRetransSegs, earlyRetransSegs uint64
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ segment := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ needsend := false
+ if segment.xmit == 0 {
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ segment.rto = kcp.rx_rto
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto + rtomin
+ } else if _itimediff(current, segment.resendts) >= 0 {
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ kcp.xmit++
+ if kcp.nodelay == 0 {
+ segment.rto += kcp.rx_rto
+ } else {
+ segment.rto += kcp.rx_rto / 2
+ }
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto
+ lost = true
+ lostSegs++
+ } else if segment.fastack >= resent {
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ segment.fastack = 0
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto
+ change++
+ fastRetransSegs++
+ } else if segment.fastack > 0 && nque == 0 {
+ // early retransmit
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ segment.fastack = 0
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto
+ change++
+ earlyRetransSegs++
+ }
+
+ if needsend {
+ segment.ts = current
+ segment.wnd = seg.wnd
+ segment.una = kcp.rcv_nxt
+
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ need := IKCP_OVERHEAD + len(segment.data)
+
+ if size+need > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+
+ ptr = segment.encode(ptr)
+ copy(ptr, segment.data)
+ ptr = ptr[len(segment.data):]
+
+ if segment.xmit >= kcp.dead_link {
+ kcp.state = 0xFFFFFFFF
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.RetransSegs, lostSegs+fastRetransSegs+earlyRetransSegs)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.LostSegs, lostSegs)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.EarlyRetransSegs, earlyRetransSegs)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FastRetransSegs, fastRetransSegs)
+
+ // flash remain segments
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size > 0 {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ }
+
+ // update ssthresh
+ // rate halving, https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6937
+ if change != 0 {
+ inflight := kcp.snd_nxt - kcp.snd_una
+ kcp.ssthresh = inflight / 2
+ if kcp.ssthresh < IKCP_THRESH_MIN {
+ kcp.ssthresh = IKCP_THRESH_MIN
+ }
+ kcp.cwnd = kcp.ssthresh + resent
+ kcp.incr = kcp.cwnd * kcp.mss
+ }
+
+ // congestion control, https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5681
+ if lost {
+ kcp.ssthresh = cwnd / 2
+ if kcp.ssthresh < IKCP_THRESH_MIN {
+ kcp.ssthresh = IKCP_THRESH_MIN
+ }
+ kcp.cwnd = 1
+ kcp.incr = kcp.mss
+ }
+
+ if kcp.cwnd < 1 {
+ kcp.cwnd = 1
+ kcp.incr = kcp.mss
+ }
+}
+
+// Update updates state (call it repeatedly, every 10ms-100ms), or you can ask
+// ikcp_check when to call it again (without ikcp_input/_send calling).
+// 'current' - current timestamp in millisec.
+func (kcp *KCP) Update(current uint32) {
+ var slap int32
+
+ kcp.current = current
+
+ if kcp.updated == 0 {
+ kcp.updated = 1
+ kcp.ts_flush = kcp.current
+ }
+
+ slap = _itimediff(kcp.current, kcp.ts_flush)
+
+ if slap >= 10000 || slap < -10000 {
+ kcp.ts_flush = kcp.current
+ slap = 0
+ }
+
+ if slap >= 0 {
+ kcp.ts_flush += kcp.interval
+ if _itimediff(kcp.current, kcp.ts_flush) >= 0 {
+ kcp.ts_flush = kcp.current + kcp.interval
+ }
+ kcp.flush()
+ }
+}
+
+// Check determines when should you invoke ikcp_update:
+// returns when you should invoke ikcp_update in millisec, if there
+// is no ikcp_input/_send calling. you can call ikcp_update in that
+// time, instead of call update repeatly.
+// Important to reduce unnacessary ikcp_update invoking. use it to
+// schedule ikcp_update (eg. implementing an epoll-like mechanism,
+// or optimize ikcp_update when handling massive kcp connections)
+func (kcp *KCP) Check(current uint32) uint32 {
+ ts_flush := kcp.ts_flush
+ tm_flush := int32(0x7fffffff)
+ tm_packet := int32(0x7fffffff)
+ minimal := uint32(0)
+ if kcp.updated == 0 {
+ return current
+ }
+
+ if _itimediff(current, ts_flush) >= 10000 ||
+ _itimediff(current, ts_flush) < -10000 {
+ ts_flush = current
+ }
+
+ if _itimediff(current, ts_flush) >= 0 {
+ return current
+ }
+
+ tm_flush = _itimediff(ts_flush, current)
+
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ diff := _itimediff(seg.resendts, current)
+ if diff <= 0 {
+ return current
+ }
+ if diff < tm_packet {
+ tm_packet = diff
+ }
+ }
+
+ minimal = uint32(tm_packet)
+ if tm_packet >= tm_flush {
+ minimal = uint32(tm_flush)
+ }
+ if minimal >= kcp.interval {
+ minimal = kcp.interval
+ }
+
+ return current + minimal
+}
+
+// SetMtu changes MTU size, default is 1400
+func (kcp *KCP) SetMtu(mtu int) int {
+ if mtu < 50 || mtu < IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ return -1
+ }
+ buffer := make([]byte, (mtu+IKCP_OVERHEAD)*3)
+ if buffer == nil {
+ return -2
+ }
+ kcp.mtu = uint32(mtu)
+ kcp.mss = kcp.mtu - IKCP_OVERHEAD
+ kcp.buffer = buffer
+ return 0
+}
+
+// NoDelay options
+// fastest: ikcp_nodelay(kcp, 1, 20, 2, 1)
+// nodelay: 0:disable(default), 1:enable
+// interval: internal update timer interval in millisec, default is 100ms
+// resend: 0:disable fast resend(default), 1:enable fast resend
+// nc: 0:normal congestion control(default), 1:disable congestion control
+func (kcp *KCP) NoDelay(nodelay, interval, resend, nc int) int {
+ if nodelay >= 0 {
+ kcp.nodelay = uint32(nodelay)
+ if nodelay != 0 {
+ kcp.rx_minrto = IKCP_RTO_NDL
+ } else {
+ kcp.rx_minrto = IKCP_RTO_MIN
+ }
+ }
+ if interval >= 0 {
+ if interval > 5000 {
+ interval = 5000
+ } else if interval < 10 {
+ interval = 10
+ }
+ kcp.interval = uint32(interval)
+ }
+ if resend >= 0 {
+ kcp.fastresend = int32(resend)
+ }
+ if nc >= 0 {
+ kcp.nocwnd = int32(nc)
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// WndSize sets maximum window size: sndwnd=32, rcvwnd=32 by default
+func (kcp *KCP) WndSize(sndwnd, rcvwnd int) int {
+ if sndwnd > 0 {
+ kcp.snd_wnd = uint32(sndwnd)
+ }
+ if rcvwnd > 0 {
+ kcp.rcv_wnd = uint32(rcvwnd)
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// WaitSnd gets how many packet is waiting to be sent
+func (kcp *KCP) WaitSnd() int {
+ return len(kcp.snd_buf) + len(kcp.snd_queue)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/sess.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/sess.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..737b99d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/sess.go
@@ -0,0 +1,901 @@
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "io"
+ "net"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+
+ "github.com/klauspost/crc32"
+
+ "golang.org/x/net/ipv4"
+)
+
+// Option defines extra options
+type Option interface{}
+
+// OptionWithConvId defines conversation id
+type OptionWithConvId struct {
+ Id uint32
+}
+
+type errTimeout struct {
+ error
+}
+
+func (errTimeout) Timeout() bool { return true }
+func (errTimeout) Temporary() bool { return true }
+func (errTimeout) Error() string { return "i/o timeout" }
+
+const (
+ defaultWndSize = 128 // default window size, in packet
+ nonceSize = 16 // magic number
+ crcSize = 4 // 4bytes packet checksum
+ cryptHeaderSize = nonceSize + crcSize
+ mtuLimit = 2048
+ txQueueLimit = 8192
+ rxFecLimit = 8192
+ defaultKeepAliveInterval = 10 * time.Second
+)
+
+type (
+ // UDPSession defines a KCP session implemented by UDP
+ UDPSession struct {
+ kcp *KCP // the core ARQ
+ l *Listener // point to server listener if it's a server socket
+ fec *FEC // forward error correction
+ conn net.PacketConn // the underlying packet socket
+ block BlockCrypt
+ remote net.Addr
+ rd time.Time // read deadline
+ wd time.Time // write deadline
+ sockbuff []byte // kcp receiving is based on packet, I turn it into stream
+ die chan struct{}
+ chReadEvent chan struct{}
+ chWriteEvent chan struct{}
+ chTicker chan time.Time
+ chUDPOutput chan []byte
+ headerSize int
+ ackNoDelay bool
+ isClosed bool
+ keepAliveInterval time.Duration
+ xmitBuf sync.Pool
+ mu sync.Mutex
+ }
+
+ setReadBuffer interface {
+ SetReadBuffer(bytes int) error
+ }
+
+ setWriteBuffer interface {
+ SetWriteBuffer(bytes int) error
+ }
+)
+
+// newUDPSession create a new udp session for client or server
+func newUDPSession(conv uint32, dataShards, parityShards int, l *Listener, conn net.PacketConn, remote net.Addr, block BlockCrypt) *UDPSession {
+ sess := new(UDPSession)
+ sess.chTicker = make(chan time.Time, 1)
+ sess.chUDPOutput = make(chan []byte, txQueueLimit)
+ sess.die = make(chan struct{})
+ sess.chReadEvent = make(chan struct{}, 1)
+ sess.chWriteEvent = make(chan struct{}, 1)
+ sess.remote = remote
+ sess.conn = conn
+ sess.keepAliveInterval = defaultKeepAliveInterval
+ sess.l = l
+ sess.block = block
+ sess.fec = newFEC(rxFecLimit, dataShards, parityShards)
+ sess.xmitBuf.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+ // calculate header size
+ if sess.block != nil {
+ sess.headerSize += cryptHeaderSize
+ }
+ if sess.fec != nil {
+ sess.headerSize += fecHeaderSizePlus2
+ }
+
+ sess.kcp = NewKCP(conv, func(buf []byte, size int) {
+ if size >= IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ ext := sess.xmitBuf.Get().([]byte)[:sess.headerSize+size]
+ copy(ext[sess.headerSize:], buf)
+ select {
+ case sess.chUDPOutput <- ext:
+ case <-sess.die:
+ }
+ }
+ })
+ sess.kcp.WndSize(defaultWndSize, defaultWndSize)
+ sess.kcp.SetMtu(IKCP_MTU_DEF - sess.headerSize)
+
+ go sess.updateTask()
+ go sess.outputTask()
+ if sess.l == nil { // it's a client connection
+ go sess.readLoop()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.ActiveOpens, 1)
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.PassiveOpens, 1)
+ }
+ currestab := atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.CurrEstab, 1)
+ maxconn := atomic.LoadUint64(&DefaultSnmp.MaxConn)
+ if currestab > maxconn {
+ atomic.CompareAndSwapUint64(&DefaultSnmp.MaxConn, maxconn, currestab)
+ }
+
+ return sess
+}
+
+// Read implements the Conn Read method.
+func (s *UDPSession) Read(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ for {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ if len(s.sockbuff) > 0 { // copy from buffer
+ n = copy(b, s.sockbuff)
+ s.sockbuff = s.sockbuff[n:]
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return n, nil
+ }
+
+ if s.isClosed {
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errors.New("broken pipe")
+ }
+
+ if !s.rd.IsZero() {
+ if time.Now().After(s.rd) { // timeout
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errTimeout{}
+ }
+ }
+
+ if n := s.kcp.PeekSize(); n > 0 { // data arrived
+ if len(b) >= n {
+ s.kcp.Recv(b)
+ } else {
+ buf := make([]byte, n)
+ s.kcp.Recv(buf)
+ n = copy(b, buf)
+ s.sockbuff = buf[n:] // store remaining bytes into sockbuff for next read
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.BytesReceived, uint64(n))
+ return n, nil
+ }
+
+ var timeout <-chan time.Time
+ if !s.rd.IsZero() {
+ delay := s.rd.Sub(time.Now())
+ timeout = time.After(delay)
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+
+ // wait for read event or timeout
+ select {
+ case <-s.chReadEvent:
+ case <-timeout:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// Write implements the Conn Write method.
+func (s *UDPSession) Write(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ for {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ if s.isClosed {
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errors.New("broken pipe")
+ }
+
+ if !s.wd.IsZero() {
+ if time.Now().After(s.wd) { // timeout
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errTimeout{}
+ }
+ }
+
+ if s.kcp.WaitSnd() < 2*int(s.kcp.snd_wnd) {
+ n = len(b)
+ max := s.kcp.mss << 8
+ for {
+ if len(b) <= int(max) { // in most cases
+ s.kcp.Send(b)
+ break
+ } else {
+ s.kcp.Send(b[:max])
+ b = b[max:]
+ }
+ }
+ s.kcp.current = currentMs()
+ s.kcp.flush()
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.BytesSent, uint64(n))
+ return n, nil
+ }
+
+ var timeout <-chan time.Time
+ if !s.wd.IsZero() {
+ delay := s.wd.Sub(time.Now())
+ timeout = time.After(delay)
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+
+ // wait for write event or timeout
+ select {
+ case <-s.chWriteEvent:
+ case <-timeout:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// Close closes the connection.
+func (s *UDPSession) Close() error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.isClosed {
+ return errors.New("broken pipe")
+ }
+ close(s.die)
+ s.isClosed = true
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.CurrEstab, ^uint64(0))
+ if s.l == nil { // client socket close
+ return s.conn.Close()
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// LocalAddr returns the local network address. The Addr returned is shared by all invocations of LocalAddr, so do not modify it.
+func (s *UDPSession) LocalAddr() net.Addr { return s.conn.LocalAddr() }
+
+// RemoteAddr returns the remote network address. The Addr returned is shared by all invocations of RemoteAddr, so do not modify it.
+func (s *UDPSession) RemoteAddr() net.Addr { return s.remote }
+
+// SetDeadline sets the deadline associated with the listener. A zero time value disables the deadline.
+func (s *UDPSession) SetDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.rd = t
+ s.wd = t
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetReadDeadline implements the Conn SetReadDeadline method.
+func (s *UDPSession) SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.rd = t
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteDeadline implements the Conn SetWriteDeadline method.
+func (s *UDPSession) SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.wd = t
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWindowSize set maximum window size
+func (s *UDPSession) SetWindowSize(sndwnd, rcvwnd int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.kcp.WndSize(sndwnd, rcvwnd)
+}
+
+// SetMtu sets the maximum transmission unit
+func (s *UDPSession) SetMtu(mtu int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.kcp.SetMtu(mtu - s.headerSize)
+}
+
+// SetStreamMode toggles the stream mode on/off
+func (s *UDPSession) SetStreamMode(enable bool) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if enable {
+ s.kcp.stream = 1
+ } else {
+ s.kcp.stream = 0
+ }
+}
+
+// SetACKNoDelay changes ack flush option, set true to flush ack immediately,
+func (s *UDPSession) SetACKNoDelay(nodelay bool) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.ackNoDelay = nodelay
+}
+
+// SetNoDelay calls nodelay() of kcp
+func (s *UDPSession) SetNoDelay(nodelay, interval, resend, nc int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.kcp.NoDelay(nodelay, interval, resend, nc)
+}
+
+// SetDSCP sets the 6bit DSCP field of IP header, no effect if it's accepted from Listener
+func (s *UDPSession) SetDSCP(dscp int) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(net.Conn); ok {
+ return ipv4.NewConn(nc).SetTOS(dscp << 2)
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetReadBuffer sets the socket read buffer, no effect if it's accepted from Listener
+func (s *UDPSession) SetReadBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(setReadBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetReadBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteBuffer sets the socket write buffer, no effect if it's accepted from Listener
+func (s *UDPSession) SetWriteBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(setWriteBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetWriteBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetKeepAlive changes per-connection NAT keepalive interval; 0 to disable, default to 10s
+func (s *UDPSession) SetKeepAlive(interval int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.keepAliveInterval = time.Duration(interval) * time.Second
+}
+
+// writeTo wraps write method for client & listener
+func (s *UDPSession) writeTo(b []byte, addr net.Addr) (int, error) {
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(io.Writer); ok {
+ return nc.Write(b)
+ }
+ }
+ return s.conn.WriteTo(b, addr)
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) outputTask() {
+ // offset pre-compute
+ fecOffset := 0
+ if s.block != nil {
+ fecOffset = cryptHeaderSize
+ }
+ szOffset := fecOffset + fecHeaderSize
+
+ // fec data group
+ var fecGroup [][]byte
+ var fecCnt int
+ var fecMaxSize int
+ if s.fec != nil {
+ fecGroup = make([][]byte, s.fec.shardSize)
+ for k := range fecGroup {
+ fecGroup[k] = make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+ }
+
+ // keepalive
+ var lastPing time.Time
+ ticker := time.NewTicker(5 * time.Second)
+ defer ticker.Stop()
+
+ for {
+ select {
+ case ext := <-s.chUDPOutput:
+ var ecc [][]byte
+ if s.fec != nil {
+ s.fec.markData(ext[fecOffset:])
+ // explicit size
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(ext[szOffset:], uint16(len(ext[szOffset:])))
+
+ // copy data to fec group
+ xorBytes(fecGroup[fecCnt], fecGroup[fecCnt], fecGroup[fecCnt])
+ copy(fecGroup[fecCnt], ext)
+ fecCnt++
+ if len(ext) > fecMaxSize {
+ fecMaxSize = len(ext)
+ }
+
+ // calculate Reed-Solomon Erasure Code
+ if fecCnt == s.fec.dataShards {
+ ecc = s.fec.calcECC(fecGroup, szOffset, fecMaxSize)
+ for k := range ecc {
+ s.fec.markFEC(ecc[k][fecOffset:])
+ ecc[k] = ecc[k][:fecMaxSize]
+ }
+ fecCnt = 0
+ fecMaxSize = 0
+ }
+ }
+
+ if s.block != nil {
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, ext[:nonceSize])
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(ext[cryptHeaderSize:])
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(ext[nonceSize:], checksum)
+ s.block.Encrypt(ext, ext)
+
+ if ecc != nil {
+ for k := range ecc {
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, ecc[k][:nonceSize])
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(ecc[k][cryptHeaderSize:])
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(ecc[k][nonceSize:], checksum)
+ s.block.Encrypt(ecc[k], ecc[k])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ //if rand.Intn(100) < 80 {
+ if n, err := s.writeTo(ext, s.remote); err == nil {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutSegs, 1)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutBytes, uint64(n))
+ }
+ //}
+
+ if ecc != nil {
+ for k := range ecc {
+ if n, err := s.writeTo(ecc[k], s.remote); err == nil {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutSegs, 1)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutBytes, uint64(n))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ xorBytes(ext, ext, ext)
+ s.xmitBuf.Put(ext)
+ case <-ticker.C: // NAT keep-alive
+ if len(s.chUDPOutput) == 0 {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ interval := s.keepAliveInterval
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ if interval > 0 && time.Now().After(lastPing.Add(interval)) {
+ buf := make([]byte, 2)
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, buf)
+ rnd := int(binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(buf))
+ sz := rnd%(IKCP_MTU_DEF-s.headerSize-IKCP_OVERHEAD) + s.headerSize + IKCP_OVERHEAD
+ ping := make([]byte, sz)
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, ping)
+ s.writeTo(ping, s.remote)
+ lastPing = time.Now()
+ }
+ }
+ case <-s.die:
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// kcp update, input loop
+func (s *UDPSession) updateTask() {
+ var tc <-chan time.Time
+ if s.l == nil { // client
+ ticker := time.NewTicker(10 * time.Millisecond)
+ tc = ticker.C
+ defer ticker.Stop()
+ } else {
+ tc = s.chTicker
+ }
+
+ for {
+ select {
+ case <-tc:
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ current := currentMs()
+ s.kcp.Update(current)
+ if s.kcp.WaitSnd() < 2*int(s.kcp.snd_wnd) {
+ s.notifyWriteEvent()
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ case <-s.die:
+ if s.l != nil { // has listener
+ select {
+ case s.l.chDeadlinks <- s.remote:
+ case <-s.l.die:
+ }
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// GetConv gets conversation id of a session
+func (s *UDPSession) GetConv() uint32 {
+ return s.kcp.conv
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) notifyReadEvent() {
+ select {
+ case s.chReadEvent <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) notifyWriteEvent() {
+ select {
+ case s.chWriteEvent <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) kcpInput(data []byte) {
+ current := currentMs()
+ if s.fec != nil {
+ f := s.fec.decode(data)
+ if f.flag == typeData || f.flag == typeFEC {
+ if f.flag == typeFEC {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FECSegs, 1)
+ }
+
+ if recovers := s.fec.input(f); recovers != nil {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ for k := range recovers {
+ sz := binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(recovers[k])
+ if int(sz) <= len(recovers[k]) && sz >= 2 {
+ s.kcp.Input(recovers[k][2:sz], false)
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FECErrs, 1)
+ }
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FECRecovered, uint64(len(recovers)))
+ }
+ }
+ if f.flag == typeData {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ s.kcp.Input(data[fecHeaderSizePlus2:], true)
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ }
+ } else {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ s.kcp.Input(data, true)
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ }
+
+ // notify reader
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ if n := s.kcp.PeekSize(); n > 0 {
+ s.notifyReadEvent()
+ }
+ if s.ackNoDelay {
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ s.kcp.flush()
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InSegs, 1)
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) receiver(ch chan []byte) {
+ for {
+ data := s.xmitBuf.Get().([]byte)[:mtuLimit]
+ if n, _, err := s.conn.ReadFrom(data); err == nil && n >= s.headerSize+IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ select {
+ case ch <- data[:n]:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ } else if err != nil {
+ return
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InErrs, 1)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// read loop for client session
+func (s *UDPSession) readLoop() {
+ chPacket := make(chan []byte, txQueueLimit)
+ go s.receiver(chPacket)
+
+ for {
+ select {
+ case data := <-chPacket:
+ raw := data
+ dataValid := false
+ if s.block != nil {
+ s.block.Decrypt(data, data)
+ data = data[nonceSize:]
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(data[crcSize:])
+ if checksum == binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data) {
+ data = data[crcSize:]
+ dataValid = true
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InCsumErrors, 1)
+ }
+ } else if s.block == nil {
+ dataValid = true
+ }
+
+ if dataValid {
+ s.kcpInput(data)
+ }
+ xorBytes(raw, raw, raw)
+ s.xmitBuf.Put(raw)
+ case <-s.die:
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+type (
+ // Listener defines a server listening for connections
+ Listener struct {
+ block BlockCrypt
+ dataShards, parityShards int
+ fec *FEC // for fec init test
+ conn net.PacketConn
+ sessions map[string]*UDPSession
+ chAccepts chan *UDPSession
+ chDeadlinks chan net.Addr
+ headerSize int
+ die chan struct{}
+ rxbuf sync.Pool
+ rd atomic.Value
+ wd atomic.Value
+ }
+
+ packet struct {
+ from net.Addr
+ data []byte
+ }
+)
+
+// monitor incoming data for all connections of server
+func (l *Listener) monitor() {
+ chPacket := make(chan packet, txQueueLimit)
+ go l.receiver(chPacket)
+ ticker := time.NewTicker(10 * time.Millisecond)
+ defer ticker.Stop()
+ for {
+ select {
+ case p := <-chPacket:
+ raw := p.data
+ data := p.data
+ from := p.from
+ dataValid := false
+ if l.block != nil {
+ l.block.Decrypt(data, data)
+ data = data[nonceSize:]
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(data[crcSize:])
+ if checksum == binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data) {
+ data = data[crcSize:]
+ dataValid = true
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InCsumErrors, 1)
+ }
+ } else if l.block == nil {
+ dataValid = true
+ }
+
+ if dataValid {
+ addr := from.String()
+ s, ok := l.sessions[addr]
+ if !ok { // new session
+ var conv uint32
+ convValid := false
+ if l.fec != nil {
+ isfec := binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(data[4:])
+ if isfec == typeData {
+ conv = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data[fecHeaderSizePlus2:])
+ convValid = true
+ }
+ } else {
+ conv = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data)
+ convValid = true
+ }
+
+ if convValid {
+ s := newUDPSession(conv, l.dataShards, l.parityShards, l, l.conn, from, l.block)
+ s.kcpInput(data)
+ l.sessions[addr] = s
+ l.chAccepts <- s
+ }
+ } else {
+ s.kcpInput(data)
+ }
+ }
+
+ xorBytes(raw, raw, raw)
+ l.rxbuf.Put(raw)
+ case deadlink := <-l.chDeadlinks:
+ delete(l.sessions, deadlink.String())
+ case <-l.die:
+ return
+ case <-ticker.C:
+ now := time.Now()
+ for _, s := range l.sessions {
+ select {
+ case s.chTicker <- now:
+ default:
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (l *Listener) receiver(ch chan packet) {
+ for {
+ data := l.rxbuf.Get().([]byte)[:mtuLimit]
+ if n, from, err := l.conn.ReadFrom(data); err == nil && n >= l.headerSize+IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ ch <- packet{from, data[:n]}
+ } else if err != nil {
+ return
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InErrs, 1)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// SetReadBuffer sets the socket read buffer for the Listener
+func (l *Listener) SetReadBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ if nc, ok := l.conn.(setReadBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetReadBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteBuffer sets the socket write buffer for the Listener
+func (l *Listener) SetWriteBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ if nc, ok := l.conn.(setWriteBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetWriteBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetDSCP sets the 6bit DSCP field of IP header
+func (l *Listener) SetDSCP(dscp int) error {
+ if nc, ok := l.conn.(net.Conn); ok {
+ return ipv4.NewConn(nc).SetTOS(dscp << 2)
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Accept implements the Accept method in the Listener interface; it waits for the next call and returns a generic Conn.
+func (l *Listener) Accept() (net.Conn, error) {
+ return l.AcceptKCP()
+}
+
+// AcceptKCP accepts a KCP connection
+func (l *Listener) AcceptKCP() (*UDPSession, error) {
+ var timeout <-chan time.Time
+ if tdeadline, ok := l.rd.Load().(time.Time); ok && !tdeadline.IsZero() {
+ timeout = time.After(tdeadline.Sub(time.Now()))
+ }
+
+ select {
+ case <-timeout:
+ return nil, &errTimeout{}
+ case c := <-l.chAccepts:
+ return c, nil
+ case <-l.die:
+ return nil, errors.New("listener stopped")
+ }
+}
+
+// SetDeadline sets the deadline associated with the listener. A zero time value disables the deadline.
+func (l *Listener) SetDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ l.SetReadDeadline(t)
+ l.SetWriteDeadline(t)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetReadDeadline implements the Conn SetReadDeadline method.
+func (l *Listener) SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ l.rd.Store(t)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteDeadline implements the Conn SetWriteDeadline method.
+func (l *Listener) SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ l.wd.Store(t)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Close stops listening on the UDP address. Already Accepted connections are not closed.
+func (l *Listener) Close() error {
+ close(l.die)
+ return l.conn.Close()
+}
+
+// Addr returns the listener's network address, The Addr returned is shared by all invocations of Addr, so do not modify it.
+func (l *Listener) Addr() net.Addr {
+ return l.conn.LocalAddr()
+}
+
+// Listen listens for incoming KCP packets addressed to the local address laddr on the network "udp",
+func Listen(laddr string) (*Listener, error) {
+ return ListenWithOptions(laddr, nil, 0, 0)
+}
+
+// ListenWithOptions listens for incoming KCP packets addressed to the local address laddr on the network "udp" with packet encryption,
+// dataShards, parityShards defines Reed-Solomon Erasure Coding parameters
+func ListenWithOptions(laddr string, block BlockCrypt, dataShards, parityShards int) (*Listener, error) {
+ udpaddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", laddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.ResolveUDPAddr")
+ }
+ conn, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", udpaddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.ListenUDP")
+ }
+
+ l := new(Listener)
+ l.conn = conn
+ l.sessions = make(map[string]*UDPSession)
+ l.chAccepts = make(chan *UDPSession, 1024)
+ l.chDeadlinks = make(chan net.Addr, 1024)
+ l.die = make(chan struct{})
+ l.dataShards = dataShards
+ l.parityShards = parityShards
+ l.block = block
+ l.fec = newFEC(rxFecLimit, dataShards, parityShards)
+ l.rxbuf.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+
+ // calculate header size
+ if l.block != nil {
+ l.headerSize += cryptHeaderSize
+ }
+ if l.fec != nil {
+ l.headerSize += fecHeaderSizePlus2
+ }
+
+ go l.monitor()
+ return l, nil
+}
+
+// Dial connects to the remote address "raddr" on the network "udp"
+func Dial(raddr string) (*UDPSession, error) {
+ return DialWithOptions(raddr, nil, 0, 0)
+}
+
+// DialWithOptions connects to the remote address "raddr" on the network "udp" with packet encryption
+func DialWithOptions(raddr string, block BlockCrypt, dataShards, parityShards int, opts ...Option) (*UDPSession, error) {
+ udpaddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", raddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.ResolveUDPAddr")
+ }
+
+ udpconn, err := net.DialUDP("udp", nil, udpaddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.DialUDP")
+ }
+
+ buf := make([]byte, 4)
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, buf)
+ convid := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buf)
+ for k := range opts {
+ switch opt := opts[k].(type) {
+ case OptionWithConvId:
+ convid = opt.Id
+ default:
+ return nil, errors.New("unrecognized option")
+ }
+ }
+ return newUDPSession(convid, dataShards, parityShards, nil, udpconn, udpaddr, block), nil
+}
+
+func currentMs() uint32 {
+ return uint32(time.Now().UnixNano() / int64(time.Millisecond))
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/shannon.jpg b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/shannon.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..055236a
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/shannon.jpg differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/snmp.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/snmp.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..997b163
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/snmp.go
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+package kcp
+
+import "sync/atomic"
+
+// Snmp defines network statistics indicator
+type Snmp struct {
+ BytesSent uint64 // payload bytes sent
+ BytesReceived uint64
+ MaxConn uint64
+ ActiveOpens uint64
+ PassiveOpens uint64
+ CurrEstab uint64
+ InErrs uint64
+ InCsumErrors uint64 // checksum errors
+ InSegs uint64
+ OutSegs uint64
+ OutBytes uint64 // udp bytes sent
+ RetransSegs uint64
+ FastRetransSegs uint64
+ EarlyRetransSegs uint64
+ LostSegs uint64
+ RepeatSegs uint64
+ FECRecovered uint64
+ FECErrs uint64
+ FECSegs uint64 // fec segments received
+}
+
+func newSnmp() *Snmp {
+ return new(Snmp)
+}
+
+// Copy make a copy of current snmp snapshot
+func (s *Snmp) Copy() *Snmp {
+ d := newSnmp()
+ d.BytesSent = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.BytesSent)
+ d.BytesReceived = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.BytesReceived)
+ d.MaxConn = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.MaxConn)
+ d.ActiveOpens = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.ActiveOpens)
+ d.PassiveOpens = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.PassiveOpens)
+ d.CurrEstab = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.CurrEstab)
+ d.InErrs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.InErrs)
+ d.InCsumErrors = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.InCsumErrors)
+ d.InSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.InSegs)
+ d.OutSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.OutSegs)
+ d.OutBytes = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.OutBytes)
+ d.RetransSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.RetransSegs)
+ d.FastRetransSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FastRetransSegs)
+ d.EarlyRetransSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.EarlyRetransSegs)
+ d.LostSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.LostSegs)
+ d.RepeatSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.RepeatSegs)
+ d.FECSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FECSegs)
+ d.FECErrs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FECErrs)
+ d.FECRecovered = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FECRecovered)
+ return d
+}
+
+// DefaultSnmp is the global KCP connection statistics collector
+var DefaultSnmp *Snmp
+
+func init() {
+ DefaultSnmp = newSnmp()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/xor.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/xor.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5d21095
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/xor.go
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+// Copyright 2013 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "runtime"
+ "unsafe"
+)
+
+const wordSize = int(unsafe.Sizeof(uintptr(0)))
+const supportsUnaligned = runtime.GOARCH == "386" || runtime.GOARCH == "amd64" || runtime.GOARCH == "ppc64" || runtime.GOARCH == "ppc64le" || runtime.GOARCH == "s390x"
+
+// fastXORBytes xors in bulk. It only works on architectures that
+// support unaligned read/writes.
+func fastXORBytes(dst, a, b []byte) int {
+ n := len(a)
+ if len(b) < n {
+ n = len(b)
+ }
+
+ w := n / wordSize
+ if w > 0 {
+ wordBytes := w * wordSize
+ fastXORWords(dst[:wordBytes], a[:wordBytes], b[:wordBytes])
+ }
+
+ for i := (n - n%wordSize); i < n; i++ {
+ dst[i] = a[i] ^ b[i]
+ }
+
+ return n
+}
+
+func safeXORBytes(dst, a, b []byte) int {
+ n := len(a)
+ if len(b) < n {
+ n = len(b)
+ }
+ ex := n % 8
+ for i := 0; i < ex; i++ {
+ dst[i] = a[i] ^ b[i]
+ }
+
+ for i := ex; i < n; i += 8 {
+ dst[i] = a[i] ^ b[i]
+ dst[i+1] = a[i+1] ^ b[i+1]
+ dst[i+2] = a[i+2] ^ b[i+2]
+ dst[i+3] = a[i+3] ^ b[i+3]
+
+ dst[i+4] = a[i+4] ^ b[i+4]
+ dst[i+5] = a[i+5] ^ b[i+5]
+ dst[i+6] = a[i+6] ^ b[i+6]
+ dst[i+7] = a[i+7] ^ b[i+7]
+ }
+ return n
+}
+
+// xorBytes xors the bytes in a and b. The destination is assumed to have enough
+// space. Returns the number of bytes xor'd.
+func xorBytes(dst, a, b []byte) int {
+ if supportsUnaligned {
+ return fastXORBytes(dst, a, b)
+ } else {
+ // TODO(hanwen): if (dst, a, b) have common alignment
+ // we could still try fastXORBytes. It is not clear
+ // how often this happens, and it's only worth it if
+ // the block encryption itself is hardware
+ // accelerated.
+ return safeXORBytes(dst, a, b)
+ }
+}
+
+// fastXORWords XORs multiples of 4 or 8 bytes (depending on architecture.)
+// The arguments are assumed to be of equal length.
+func fastXORWords(dst, a, b []byte) {
+ dw := *(*[]uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&dst))
+ aw := *(*[]uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&a))
+ bw := *(*[]uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&b))
+ n := len(b) / wordSize
+ ex := n % 8
+ for i := 0; i < ex; i++ {
+ dw[i] = aw[i] ^ bw[i]
+ }
+
+ for i := ex; i < n; i += 8 {
+ dw[i] = aw[i] ^ bw[i]
+ dw[i+1] = aw[i+1] ^ bw[i+1]
+ dw[i+2] = aw[i+2] ^ bw[i+2]
+ dw[i+3] = aw[i+3] ^ bw[i+3]
+ dw[i+4] = aw[i+4] ^ bw[i+4]
+ dw[i+5] = aw[i+5] ^ bw[i+5]
+ dw[i+6] = aw[i+6] ^ bw[i+6]
+ dw[i+7] = aw[i+7] ^ bw[i+7]
+ }
+}
+
+func xorWords(dst, a, b []byte) {
+ if supportsUnaligned {
+ fastXORWords(dst, a, b)
+ } else {
+ safeXORBytes(dst, a, b)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/LICENSE b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/LICENSE
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..37c57a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/LICENSE
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+MIT License
+
+Copyright (c) 2016 xtaci
+
+Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
+of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
+in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
+to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
+copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
+furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
+
+The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
+copies or substantial portions of the Software.
+
+THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
+IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
+FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
+AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
+LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
+OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
+SOFTWARE.
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/README.md b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..15e9871
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+# SMUX
+[![GoDoc][1]][2] [![MIT licensed][3]][4] [![Build Status][5]][6] [![Go Report Card][7]][8] [![Coverage Statusd][9]][10]
+
+
+
+## Usage
+
+Client: [full demo](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun/blob/master/client/main.go#L231)
+```go
+kcpconn, err := kcp.DialWithOptions("192.168.0.1:10000", nil, 10, 3)
+```
+Server: [full demo](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun/blob/master/server/main.go#L235)
+```go
+lis, err := kcp.ListenWithOptions(":10000", nil, 10, 3)
+```
+
+## Performance
+```
+ 型号名称: MacBook Pro
+ 型号标识符: MacBookPro12,1
+ 处理器名称: Intel Core i5
+ 处理器速度: 2.7 GHz
+ 处理器数目: 1
+ 核总数: 2
+ L2 缓存(每个核): 256 KB
+ L3 缓存: 3 MB
+ 内存: 8 GB
+```
+```
+$ go test -run Speed
+new client 127.0.0.1:61165
+total recv: 16777216
+time for 16MB rtt with encryption 570.41176ms
+&{BytesSent:33554432 BytesReceived:33554432 MaxConn:2 ActiveOpens:1 PassiveOpens:1 CurrEstab:1 InErrs:0 InCsumErrors:0 InSegs:42577 OutSegs:42641 OutBytes:48111336 RetransSegs:92 FastRetransSegs:92 LostSegs:0 RepeatSegs:0 FECRecovered:1 FECErrs:0 FECSegs:8514}
+PASS
+ok github.com/xtaci/kcp-go 0.600s
+```
+
+## Links
+
+1. https://github.com/xtaci/libkcp -- Official client library for iOS/Android(C++11)
+2. https://github.com/skywind3000/kcp -- A Fast and Reliable ARQ Protocol
+3. https://github.com/klauspost/reedsolomon -- Reed-Solomon Erasure Coding in Go
+
+## Donation
+
+
+
+All donations on this project will be used to support the development of [gonet/2](http://gonet2.github.io/).
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/crypt.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/crypt.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..df85278
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/crypt.go
@@ -0,0 +1,301 @@
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "crypto/aes"
+ "crypto/cipher"
+ "crypto/des"
+ "crypto/sha1"
+
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/blowfish"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/cast5"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/salsa20"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/tea"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/twofish"
+ "golang.org/x/crypto/xtea"
+)
+
+var (
+ initialVector = []byte{167, 115, 79, 156, 18, 172, 27, 1, 164, 21, 242, 193, 252, 120, 230, 107}
+ saltxor = `sH3CIVoF#rWLtJo6`
+)
+
+// BlockCrypt defines encryption/decryption methods for a given byte slice
+type BlockCrypt interface {
+ // Encrypt encrypts the whole block in src into dst.
+ // Dst and src may point at the same memory.
+ Encrypt(dst, src []byte)
+
+ // Decrypt decrypts the whole block in src into dst.
+ // Dst and src may point at the same memory.
+ Decrypt(dst, src []byte)
+}
+
+// Salsa20BlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type Salsa20BlockCrypt struct {
+ key [32]byte
+}
+
+// NewSalsa20BlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewSalsa20BlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(Salsa20BlockCrypt)
+ copy(c.key[:], key)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *Salsa20BlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) {
+ salsa20.XORKeyStream(dst[8:], src[8:], src[:8], &c.key)
+ copy(dst[:8], src[:8])
+}
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *Salsa20BlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) {
+ salsa20.XORKeyStream(dst[8:], src[8:], src[:8], &c.key)
+ copy(dst[:8], src[:8])
+}
+
+// TwofishBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type TwofishBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewTwofishBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewTwofishBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(TwofishBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := twofish.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, twofish.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*twofish.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *TwofishBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *TwofishBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// TripleDESBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type TripleDESBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewTripleDESBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewTripleDESBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(TripleDESBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := des.NewTripleDESCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, des.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*des.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *TripleDESBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *TripleDESBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// Cast5BlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type Cast5BlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewCast5BlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewCast5BlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(Cast5BlockCrypt)
+ block, err := cast5.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, cast5.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*cast5.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *Cast5BlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *Cast5BlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// BlowfishBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type BlowfishBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewBlowfishBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewBlowfishBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(BlowfishBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := blowfish.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, blowfish.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*blowfish.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *BlowfishBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *BlowfishBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// AESBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type AESBlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewAESBlockCrypt initates BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewAESBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(AESBlockCrypt)
+ block, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, aes.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*aes.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *AESBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *AESBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// TEABlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type TEABlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewTEABlockCrypt initate BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewTEABlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(TEABlockCrypt)
+ block, err := tea.NewCipherWithRounds(key, 16)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, tea.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*tea.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *TEABlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *TEABlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// XTEABlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type XTEABlockCrypt struct {
+ encbuf []byte
+ decbuf []byte
+ block cipher.Block
+}
+
+// NewXTEABlockCrypt initate BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewXTEABlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(XTEABlockCrypt)
+ block, err := xtea.NewCipher(key)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ c.block = block
+ c.encbuf = make([]byte, xtea.BlockSize)
+ c.decbuf = make([]byte, 2*xtea.BlockSize)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *XTEABlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { encrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.encbuf) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *XTEABlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { decrypt(c.block, dst, src, c.decbuf) }
+
+// SimpleXORBlockCrypt implements BlockCrypt
+type SimpleXORBlockCrypt struct {
+ xortbl []byte
+}
+
+// NewSimpleXORBlockCrypt initate BlockCrypt by the given key
+func NewSimpleXORBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ c := new(SimpleXORBlockCrypt)
+ c.xortbl = pbkdf2.Key(key, []byte(saltxor), 32, mtuLimit, sha1.New)
+ return c, nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *SimpleXORBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { xorBytes(dst, src, c.xortbl) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *SimpleXORBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { xorBytes(dst, src, c.xortbl) }
+
+// NoneBlockCrypt simple returns the plaintext
+type NoneBlockCrypt struct{}
+
+// NewNoneBlockCrypt initate by the given key
+func NewNoneBlockCrypt(key []byte) (BlockCrypt, error) {
+ return new(NoneBlockCrypt), nil
+}
+
+// Encrypt implements Encrypt interface
+func (c *NoneBlockCrypt) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) { copy(dst, src) }
+
+// Decrypt implements Decrypt interface
+func (c *NoneBlockCrypt) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) { copy(dst, src) }
+
+// packet encryption with local CFB mode
+func encrypt(block cipher.Block, dst, src, buf []byte) {
+ blocksize := block.BlockSize()
+ tbl := buf[:blocksize]
+ block.Encrypt(tbl, initialVector)
+ n := len(src) / blocksize
+ base := 0
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ xorWords(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+ block.Encrypt(tbl, dst[base:])
+ base += blocksize
+ }
+ xorBytes(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+}
+
+func decrypt(block cipher.Block, dst, src, buf []byte) {
+ blocksize := block.BlockSize()
+ tbl := buf[:blocksize]
+ next := buf[blocksize:]
+ block.Encrypt(tbl, initialVector)
+ n := len(src) / blocksize
+ base := 0
+ for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
+ block.Encrypt(next, src[base:])
+ xorWords(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+ tbl, next = next, tbl
+ base += blocksize
+ }
+ xorBytes(dst[base:], src[base:], tbl)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/donate.png b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/donate.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0f353d9
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/donate.png differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/fec.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/fec.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..10ad1c0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/fec.go
@@ -0,0 +1,241 @@
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "sync"
+
+ "github.com/klauspost/reedsolomon"
+)
+
+const (
+ fecHeaderSize = 6
+ fecHeaderSizePlus2 = fecHeaderSize + 2 // plus 2B data size
+ typeData = 0xf1
+ typeFEC = 0xf2
+ fecExpire = 30000 // 30s
+)
+
+type (
+ // FEC defines forward error correction for packets
+ FEC struct {
+ rx []fecPacket // ordered receive queue
+ rxlimit int // queue size limit
+ dataShards int
+ parityShards int
+ shardSize int
+ next uint32 // next seqid
+ enc reedsolomon.Encoder
+ shards [][]byte
+ shardsflag []bool
+ paws uint32 // Protect Against Wrapped Sequence numbers
+ lastCheck uint32
+ xmitBuf sync.Pool
+ }
+
+ fecPacket struct {
+ seqid uint32
+ flag uint16
+ data []byte
+ ts uint32
+ }
+)
+
+func newFEC(rxlimit, dataShards, parityShards int) *FEC {
+ if dataShards <= 0 || parityShards <= 0 {
+ return nil
+ }
+ if rxlimit < dataShards+parityShards {
+ return nil
+ }
+
+ fec := new(FEC)
+ fec.rxlimit = rxlimit
+ fec.dataShards = dataShards
+ fec.parityShards = parityShards
+ fec.shardSize = dataShards + parityShards
+ fec.paws = (0xffffffff/uint32(fec.shardSize) - 1) * uint32(fec.shardSize)
+ enc, err := reedsolomon.New(dataShards, parityShards)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ fec.enc = enc
+ fec.shards = make([][]byte, fec.shardSize)
+ fec.shardsflag = make([]bool, fec.shardSize)
+ fec.xmitBuf.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+
+ return fec
+}
+
+// decode a fec packet
+func (fec *FEC) decode(data []byte) fecPacket {
+ var pkt fecPacket
+ pkt.seqid = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data)
+ pkt.flag = binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(data[4:])
+ pkt.ts = currentMs()
+ // allocate memory & copy
+ buf := fec.xmitBuf.Get().([]byte)
+ n := copy(buf, data[6:])
+ xorBytes(buf[n:], buf[n:], buf[n:])
+ pkt.data = buf
+ return pkt
+}
+
+func (fec *FEC) markData(data []byte) {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(data, fec.next)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(data[4:], typeData)
+ fec.next++
+}
+
+func (fec *FEC) markFEC(data []byte) {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(data, fec.next)
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(data[4:], typeFEC)
+ fec.next++
+ if fec.next >= fec.paws { // paws would only occurs in markFEC
+ fec.next = 0
+ }
+}
+
+// input a fec packet
+func (fec *FEC) input(pkt fecPacket) (recovered [][]byte) {
+ // expiration
+ now := currentMs()
+ if now-fec.lastCheck >= fecExpire {
+ var rx []fecPacket
+ for k := range fec.rx {
+ if now-fec.rx[k].ts < fecExpire {
+ rx = append(rx, fec.rx[k])
+ } else {
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[k].data)
+ }
+ }
+ fec.rx = rx
+ fec.lastCheck = now
+ }
+
+ // insertion
+ n := len(fec.rx) - 1
+ insertIdx := 0
+ for i := n; i >= 0; i-- {
+ if pkt.seqid == fec.rx[i].seqid { // de-duplicate
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(pkt.data)
+ return nil
+ } else if pkt.seqid > fec.rx[i].seqid { // insertion
+ insertIdx = i + 1
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ // insert into ordered rx queue
+ if insertIdx == n+1 {
+ fec.rx = append(fec.rx, pkt)
+ } else {
+ fec.rx = append(fec.rx, fecPacket{})
+ copy(fec.rx[insertIdx+1:], fec.rx[insertIdx:])
+ fec.rx[insertIdx] = pkt
+ }
+
+ // shard range for current packet
+ shardBegin := pkt.seqid - pkt.seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize)
+ shardEnd := shardBegin + uint32(fec.shardSize) - 1
+
+ // max search range in ordered queue for current shard
+ searchBegin := insertIdx - int(pkt.seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize))
+ if searchBegin < 0 {
+ searchBegin = 0
+ }
+ searchEnd := searchBegin + fec.shardSize - 1
+ if searchEnd >= len(fec.rx) {
+ searchEnd = len(fec.rx) - 1
+ }
+
+ if searchEnd > searchBegin && searchEnd-searchBegin+1 >= fec.dataShards {
+ numshard := 0
+ numDataShard := 0
+ first := -1
+ maxlen := 0
+ shards := fec.shards
+ shardsflag := fec.shardsflag
+ for k := range fec.shards {
+ shards[k] = nil
+ shardsflag[k] = false
+ }
+
+ for i := searchBegin; i <= searchEnd; i++ {
+ seqid := fec.rx[i].seqid
+ if seqid > shardEnd {
+ break
+ } else if seqid >= shardBegin {
+ shards[seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize)] = fec.rx[i].data
+ shardsflag[seqid%uint32(fec.shardSize)] = true
+ numshard++
+ if fec.rx[i].flag == typeData {
+ numDataShard++
+ }
+ if numshard == 1 {
+ first = i
+ }
+ if len(fec.rx[i].data) > maxlen {
+ maxlen = len(fec.rx[i].data)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ if numDataShard == fec.dataShards { // no lost
+ for i := first; i < first+numshard; i++ { // free
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[i].data)
+ }
+ copy(fec.rx[first:], fec.rx[first+numshard:])
+ for i := 0; i < numshard; i++ { // dereference
+ fec.rx[len(fec.rx)-1-i] = fecPacket{}
+ }
+ fec.rx = fec.rx[:len(fec.rx)-numshard]
+ } else if numshard >= fec.dataShards { // recoverable
+ for k := range shards {
+ if shards[k] != nil {
+ shards[k] = shards[k][:maxlen]
+ }
+ }
+ if err := fec.enc.Reconstruct(shards); err == nil {
+ for k := range shards[:fec.dataShards] {
+ if !shardsflag[k] {
+ recovered = append(recovered, shards[k])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ for i := first; i < first+numshard; i++ { // free
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[i].data)
+ }
+ copy(fec.rx[first:], fec.rx[first+numshard:])
+ for i := 0; i < numshard; i++ { // dereference
+ fec.rx[len(fec.rx)-1-i] = fecPacket{}
+ }
+ fec.rx = fec.rx[:len(fec.rx)-numshard]
+ }
+ }
+
+ // keep rxlimit
+ if len(fec.rx) > fec.rxlimit {
+ fec.xmitBuf.Put(fec.rx[0].data) // free
+ fec.rx[0].data = nil
+ fec.rx = fec.rx[1:]
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+func (fec *FEC) calcECC(data [][]byte, offset, maxlen int) (ecc [][]byte) {
+ if len(data) != fec.shardSize {
+ return nil
+ }
+ shards := make([][]byte, fec.shardSize)
+ for k := range shards {
+ shards[k] = data[k][offset:maxlen]
+ }
+
+ if err := fec.enc.Encode(shards); err != nil {
+ return nil
+ }
+ return data[fec.dataShards:]
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/frame.png b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/frame.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7952e4a
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/frame.png differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/kcp.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/kcp.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..78ccf26
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/kcp.go
@@ -0,0 +1,961 @@
+// Package kcp - A Fast and Reliable ARQ Protocol
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "container/heap"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "sync/atomic"
+)
+
+const (
+ IKCP_RTO_NDL = 30 // no delay min rto
+ IKCP_RTO_MIN = 100 // normal min rto
+ IKCP_RTO_DEF = 200
+ IKCP_RTO_MAX = 60000
+ IKCP_CMD_PUSH = 81 // cmd: push data
+ IKCP_CMD_ACK = 82 // cmd: ack
+ IKCP_CMD_WASK = 83 // cmd: window probe (ask)
+ IKCP_CMD_WINS = 84 // cmd: window size (tell)
+ IKCP_ASK_SEND = 1 // need to send IKCP_CMD_WASK
+ IKCP_ASK_TELL = 2 // need to send IKCP_CMD_WINS
+ IKCP_WND_SND = 32
+ IKCP_WND_RCV = 32
+ IKCP_MTU_DEF = 1400
+ IKCP_ACK_FAST = 3
+ IKCP_INTERVAL = 100
+ IKCP_OVERHEAD = 24
+ IKCP_DEADLINK = 20
+ IKCP_THRESH_INIT = 2
+ IKCP_THRESH_MIN = 2
+ IKCP_PROBE_INIT = 7000 // 7 secs to probe window size
+ IKCP_PROBE_LIMIT = 120000 // up to 120 secs to probe window
+)
+
+// Output is a closure which captures conn and calls conn.Write
+type Output func(buf []byte, size int)
+
+/* encode 8 bits unsigned int */
+func ikcp_encode8u(p []byte, c byte) []byte {
+ p[0] = c
+ return p[1:]
+}
+
+/* decode 8 bits unsigned int */
+func ikcp_decode8u(p []byte, c *byte) []byte {
+ *c = p[0]
+ return p[1:]
+}
+
+/* encode 16 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_encode16u(p []byte, w uint16) []byte {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(p, w)
+ return p[2:]
+}
+
+/* decode 16 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_decode16u(p []byte, w *uint16) []byte {
+ *w = binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(p)
+ return p[2:]
+}
+
+/* encode 32 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_encode32u(p []byte, l uint32) []byte {
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(p, l)
+ return p[4:]
+}
+
+/* decode 32 bits unsigned int (lsb) */
+func ikcp_decode32u(p []byte, l *uint32) []byte {
+ *l = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(p)
+ return p[4:]
+}
+
+func _imin_(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a <= b {
+ return a
+ } else {
+ return b
+ }
+}
+
+func _imax_(a, b uint32) uint32 {
+ if a >= b {
+ return a
+ } else {
+ return b
+ }
+}
+
+func _ibound_(lower, middle, upper uint32) uint32 {
+ return _imin_(_imax_(lower, middle), upper)
+}
+
+func _itimediff(later, earlier uint32) int32 {
+ return (int32)(later - earlier)
+}
+
+// Segment defines a KCP segment
+type Segment struct {
+ conv uint32
+ cmd uint32
+ frg uint32
+ wnd uint32
+ ts uint32
+ sn uint32
+ una uint32
+ resendts uint32
+ rto uint32
+ fastack uint32
+ xmit uint32
+ data []byte
+}
+
+// encode a segment into buffer
+func (seg *Segment) encode(ptr []byte) []byte {
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.conv)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode8u(ptr, uint8(seg.cmd))
+ ptr = ikcp_encode8u(ptr, uint8(seg.frg))
+ ptr = ikcp_encode16u(ptr, uint16(seg.wnd))
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.ts)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.sn)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, seg.una)
+ ptr = ikcp_encode32u(ptr, uint32(len(seg.data)))
+ return ptr
+}
+
+// NewSegment creates a KCP segment
+func NewSegment(size int) *Segment {
+ seg := new(Segment)
+ seg.data = make([]byte, size)
+ return seg
+}
+
+// KCP defines a single KCP connection
+type KCP struct {
+ conv, mtu, mss, state uint32
+ snd_una, snd_nxt, rcv_nxt uint32
+ ssthresh uint32
+ rx_rttval, rx_srtt, rx_rto, rx_minrto uint32
+ snd_wnd, rcv_wnd, rmt_wnd, cwnd, probe uint32
+ current, interval, ts_flush, xmit uint32
+ nodelay, updated uint32
+ ts_probe, probe_wait uint32
+ dead_link, incr uint32
+
+ fastresend int32
+ nocwnd, stream int32
+
+ snd_queue []Segment
+ rcv_queue []Segment
+ snd_buf []Segment
+ rcv_buf []Segment
+
+ acklist ACKList
+
+ buffer []byte
+ output Output
+}
+
+// ACK packet to return
+type ACK struct {
+ sn uint32
+ ts uint32
+}
+
+// ACKList is heapified
+type ACKList []ACK
+
+func (l ACKList) Len() int { return len(l) }
+func (l ACKList) Less(i, j int) bool { return l[i].sn < l[j].sn }
+func (l ACKList) Swap(i, j int) { l[i], l[j] = l[j], l[i] }
+func (l *ACKList) Push(x interface{}) { *l = append(*l, x.(ACK)) }
+func (l *ACKList) Pop() interface{} {
+ old := *l
+ n := len(old)
+ x := old[n-1]
+ *l = old[0 : n-1]
+ return x
+}
+
+// NewKCP create a new kcp control object, 'conv' must equal in two endpoint
+// from the same connection.
+func NewKCP(conv uint32, output Output) *KCP {
+ kcp := new(KCP)
+ kcp.conv = conv
+ kcp.snd_wnd = IKCP_WND_SND
+ kcp.rcv_wnd = IKCP_WND_RCV
+ kcp.rmt_wnd = IKCP_WND_RCV
+ kcp.mtu = IKCP_MTU_DEF
+ kcp.mss = kcp.mtu - IKCP_OVERHEAD
+ kcp.buffer = make([]byte, (kcp.mtu+IKCP_OVERHEAD)*3)
+ kcp.rx_rto = IKCP_RTO_DEF
+ kcp.rx_minrto = IKCP_RTO_MIN
+ kcp.interval = IKCP_INTERVAL
+ kcp.ts_flush = IKCP_INTERVAL
+ kcp.ssthresh = IKCP_THRESH_INIT
+ kcp.dead_link = IKCP_DEADLINK
+ kcp.output = output
+ return kcp
+}
+
+// PeekSize checks the size of next message in the recv queue
+func (kcp *KCP) PeekSize() (length int) {
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) == 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_queue[0]
+ if seg.frg == 0 {
+ return len(seg.data)
+ }
+
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(seg.frg+1) {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_queue {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_queue[k]
+ length += len(seg.data)
+ if seg.frg == 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+// Recv is user/upper level recv: returns size, returns below zero for EAGAIN
+func (kcp *KCP) Recv(buffer []byte) (n int) {
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) == 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ peeksize := kcp.PeekSize()
+ if peeksize < 0 {
+ return -2
+ }
+
+ if peeksize > len(buffer) {
+ return -3
+ }
+
+ var fast_recover bool
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) >= int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ fast_recover = true
+ }
+
+ // merge fragment
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_queue {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_queue[k]
+ copy(buffer, seg.data)
+ buffer = buffer[len(seg.data):]
+ n += len(seg.data)
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ if seg.frg == 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.rcv_queue = kcp.rcv_queue[count:]
+
+ // move available data from rcv_buf -> rcv_queue
+ count = 0
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_buf[k]
+ if seg.sn == kcp.rcv_nxt && len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ kcp.rcv_queue = append(kcp.rcv_queue, *seg)
+ kcp.rcv_nxt++
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.rcv_buf = kcp.rcv_buf[count:]
+
+ // fast recover
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) && fast_recover {
+ // ready to send back IKCP_CMD_WINS in ikcp_flush
+ // tell remote my window size
+ kcp.probe |= IKCP_ASK_TELL
+ }
+ return
+}
+
+// Send is user/upper level send, returns below zero for error
+func (kcp *KCP) Send(buffer []byte) int {
+ var count int
+ if len(buffer) == 0 {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ // append to previous segment in streaming mode (if possible)
+ if kcp.stream != 0 {
+ n := len(kcp.snd_queue)
+ if n > 0 {
+ old := &kcp.snd_queue[n-1]
+ if len(old.data) < int(kcp.mss) {
+ capacity := int(kcp.mss) - len(old.data)
+ extend := capacity
+ if len(buffer) < capacity {
+ extend = len(buffer)
+ }
+ seg := NewSegment(len(old.data) + extend)
+ seg.frg = 0
+ copy(seg.data, old.data)
+ copy(seg.data[len(old.data):], buffer)
+ buffer = buffer[extend:]
+ kcp.snd_queue[n-1] = *seg
+ }
+ }
+
+ if len(buffer) == 0 {
+ return 0
+ }
+ }
+
+ if len(buffer) <= int(kcp.mss) {
+ count = 1
+ } else {
+ count = (len(buffer) + int(kcp.mss) - 1) / int(kcp.mss)
+ }
+
+ if count > 255 {
+ return -2
+ }
+
+ if count == 0 {
+ count = 1
+ }
+
+ for i := 0; i < count; i++ {
+ var size int
+ if len(buffer) > int(kcp.mss) {
+ size = int(kcp.mss)
+ } else {
+ size = len(buffer)
+ }
+ seg := NewSegment(size)
+ copy(seg.data, buffer[:size])
+ if kcp.stream == 0 { // message mode
+ seg.frg = uint32(count - i - 1)
+ } else { // stream mode
+ seg.frg = 0
+ }
+ kcp.snd_queue = append(kcp.snd_queue, *seg)
+ buffer = buffer[size:]
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6298
+func (kcp *KCP) update_ack(rtt int32) {
+ var rto uint32
+ if kcp.rx_srtt == 0 {
+ kcp.rx_srtt = uint32(rtt)
+ kcp.rx_rttval = uint32(rtt) / 2
+ } else {
+ delta := rtt - int32(kcp.rx_srtt)
+ if delta < 0 {
+ delta = -delta
+ }
+ kcp.rx_rttval = (3*kcp.rx_rttval + uint32(delta)) / 4
+ kcp.rx_srtt = (7*kcp.rx_srtt + uint32(rtt)) / 8
+ if kcp.rx_srtt < 1 {
+ kcp.rx_srtt = 1
+ }
+ }
+ rto = kcp.rx_srtt + _imax_(1, 4*kcp.rx_rttval)
+ kcp.rx_rto = _ibound_(kcp.rx_minrto, rto, IKCP_RTO_MAX)
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) shrink_buf() {
+ if len(kcp.snd_buf) > 0 {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[0]
+ kcp.snd_una = seg.sn
+ } else {
+ kcp.snd_una = kcp.snd_nxt
+ }
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_ack(sn uint32) {
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_una) < 0 || _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_nxt) >= 0 {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ if sn == seg.sn {
+ copy(kcp.snd_buf[k:], kcp.snd_buf[k+1:])
+ kcp.snd_buf[len(kcp.snd_buf)-1] = Segment{}
+ kcp.snd_buf = kcp.snd_buf[:len(kcp.snd_buf)-1]
+ break
+ }
+ if _itimediff(sn, seg.sn) < 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_fastack(sn uint32) {
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_una) < 0 || _itimediff(sn, kcp.snd_nxt) >= 0 {
+ return
+ }
+
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ if _itimediff(sn, seg.sn) < 0 {
+ break
+ } else if sn != seg.sn { // && kcp.current >= seg.ts+kcp.rx_srtt {
+ seg.fastack++
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_una(una uint32) {
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ if _itimediff(una, seg.sn) > 0 {
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.snd_buf = kcp.snd_buf[count:]
+}
+
+// ack append
+func (kcp *KCP) ack_push(sn, ts uint32) {
+ heap.Push(&kcp.acklist, ACK{sn, ts})
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) parse_data(newseg *Segment) {
+ sn := newseg.sn
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt+kcp.rcv_wnd) >= 0 ||
+ _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt) < 0 {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.RepeatSegs, 1)
+ return
+ }
+
+ n := len(kcp.rcv_buf) - 1
+ insert_idx := 0
+ repeat := false
+ for i := n; i >= 0; i-- {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_buf[i]
+ if seg.sn == sn {
+ repeat = true
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.RepeatSegs, 1)
+ break
+ }
+ if _itimediff(sn, seg.sn) > 0 {
+ insert_idx = i + 1
+ break
+ }
+ }
+
+ if !repeat {
+ if insert_idx == n+1 {
+ kcp.rcv_buf = append(kcp.rcv_buf, *newseg)
+ } else {
+ kcp.rcv_buf = append(kcp.rcv_buf, Segment{})
+ copy(kcp.rcv_buf[insert_idx+1:], kcp.rcv_buf[insert_idx:])
+ kcp.rcv_buf[insert_idx] = *newseg
+ }
+ }
+
+ // move available data from rcv_buf -> rcv_queue
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.rcv_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.rcv_buf[k]
+ if seg.sn == kcp.rcv_nxt && len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ kcp.rcv_queue = append(kcp.rcv_queue, kcp.rcv_buf[k])
+ kcp.rcv_nxt++
+ count++
+ seg.data = nil
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ kcp.rcv_buf = kcp.rcv_buf[count:]
+}
+
+// Input when you received a low level packet (eg. UDP packet), call it
+func (kcp *KCP) Input(data []byte, update_ack bool) int {
+ una := kcp.snd_una
+ if len(data) < IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ var maxack uint32
+ var flag int
+ for {
+ var ts, sn, length, una, conv uint32
+ var wnd uint16
+ var cmd, frg uint8
+
+ if len(data) < int(IKCP_OVERHEAD) {
+ break
+ }
+
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &conv)
+ if conv != kcp.conv {
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ data = ikcp_decode8u(data, &cmd)
+ data = ikcp_decode8u(data, &frg)
+ data = ikcp_decode16u(data, &wnd)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &ts)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &sn)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &una)
+ data = ikcp_decode32u(data, &length)
+ if len(data) < int(length) {
+ return -2
+ }
+
+ if cmd != IKCP_CMD_PUSH && cmd != IKCP_CMD_ACK &&
+ cmd != IKCP_CMD_WASK && cmd != IKCP_CMD_WINS {
+ return -3
+ }
+
+ kcp.rmt_wnd = uint32(wnd)
+ kcp.parse_una(una)
+ kcp.shrink_buf()
+
+ if cmd == IKCP_CMD_ACK {
+ if update_ack && _itimediff(kcp.current, ts) >= 0 {
+ kcp.update_ack(_itimediff(kcp.current, ts))
+ }
+ kcp.parse_ack(sn)
+ kcp.shrink_buf()
+ if flag == 0 {
+ flag = 1
+ maxack = sn
+ } else if _itimediff(sn, maxack) > 0 {
+ maxack = sn
+ }
+ } else if cmd == IKCP_CMD_PUSH {
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt+kcp.rcv_wnd) < 0 {
+ kcp.ack_push(sn, ts)
+ if _itimediff(sn, kcp.rcv_nxt) >= 0 {
+ seg := NewSegment(int(length))
+ seg.conv = conv
+ seg.cmd = uint32(cmd)
+ seg.frg = uint32(frg)
+ seg.wnd = uint32(wnd)
+ seg.ts = ts
+ seg.sn = sn
+ seg.una = una
+ copy(seg.data, data[:length])
+ kcp.parse_data(seg)
+ }
+ }
+ } else if cmd == IKCP_CMD_WASK {
+ // ready to send back IKCP_CMD_WINS in Ikcp_flush
+ // tell remote my window size
+ kcp.probe |= IKCP_ASK_TELL
+ } else if cmd == IKCP_CMD_WINS {
+ // do nothing
+ } else {
+ return -3
+ }
+
+ data = data[length:]
+ }
+
+ if flag != 0 && update_ack {
+ kcp.parse_fastack(maxack)
+ }
+
+ if _itimediff(kcp.snd_una, una) > 0 {
+ if kcp.cwnd < kcp.rmt_wnd {
+ mss := kcp.mss
+ if kcp.cwnd < kcp.ssthresh {
+ kcp.cwnd++
+ kcp.incr += mss
+ } else {
+ if kcp.incr < mss {
+ kcp.incr = mss
+ }
+ kcp.incr += (mss*mss)/kcp.incr + (mss / 16)
+ if (kcp.cwnd+1)*mss <= kcp.incr {
+ kcp.cwnd++
+ }
+ }
+ if kcp.cwnd > kcp.rmt_wnd {
+ kcp.cwnd = kcp.rmt_wnd
+ kcp.incr = kcp.rmt_wnd * mss
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ return 0
+}
+
+func (kcp *KCP) wnd_unused() int32 {
+ if len(kcp.rcv_queue) < int(kcp.rcv_wnd) {
+ return int32(int(kcp.rcv_wnd) - len(kcp.rcv_queue))
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// flush pending data
+func (kcp *KCP) flush() {
+ current := kcp.current
+ buffer := kcp.buffer
+ change := 0
+ lost := false
+
+ if kcp.updated == 0 {
+ return
+ }
+ var seg Segment
+ seg.conv = kcp.conv
+ seg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_ACK
+ seg.wnd = uint32(kcp.wnd_unused())
+ seg.una = kcp.rcv_nxt
+
+ // flush acknowledges
+ ptr := buffer
+ for kcp.acklist.Len() > 0 {
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size+IKCP_OVERHEAD > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+ ack := heap.Pop(&kcp.acklist).(ACK)
+ seg.sn, seg.ts = ack.sn, ack.ts
+ ptr = seg.encode(ptr)
+ }
+ kcp.acklist = nil
+
+ // probe window size (if remote window size equals zero)
+ if kcp.rmt_wnd == 0 {
+ if kcp.probe_wait == 0 {
+ kcp.probe_wait = IKCP_PROBE_INIT
+ kcp.ts_probe = kcp.current + kcp.probe_wait
+ } else {
+ if _itimediff(kcp.current, kcp.ts_probe) >= 0 {
+ if kcp.probe_wait < IKCP_PROBE_INIT {
+ kcp.probe_wait = IKCP_PROBE_INIT
+ }
+ kcp.probe_wait += kcp.probe_wait / 2
+ if kcp.probe_wait > IKCP_PROBE_LIMIT {
+ kcp.probe_wait = IKCP_PROBE_LIMIT
+ }
+ kcp.ts_probe = kcp.current + kcp.probe_wait
+ kcp.probe |= IKCP_ASK_SEND
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ kcp.ts_probe = 0
+ kcp.probe_wait = 0
+ }
+
+ // flush window probing commands
+ if (kcp.probe & IKCP_ASK_SEND) != 0 {
+ seg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_WASK
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size+IKCP_OVERHEAD > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+ ptr = seg.encode(ptr)
+ }
+
+ // flush window probing commands
+ if (kcp.probe & IKCP_ASK_TELL) != 0 {
+ seg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_WINS
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size+IKCP_OVERHEAD > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+ ptr = seg.encode(ptr)
+ }
+
+ kcp.probe = 0
+
+ // calculate window size
+ cwnd := _imin_(kcp.snd_wnd, kcp.rmt_wnd)
+ if kcp.nocwnd == 0 {
+ cwnd = _imin_(kcp.cwnd, cwnd)
+ }
+
+ count := 0
+ for k := range kcp.snd_queue {
+ if _itimediff(kcp.snd_nxt, kcp.snd_una+cwnd) >= 0 {
+ break
+ }
+ newseg := kcp.snd_queue[k]
+ newseg.conv = kcp.conv
+ newseg.cmd = IKCP_CMD_PUSH
+ newseg.wnd = seg.wnd
+ newseg.ts = current
+ newseg.sn = kcp.snd_nxt
+ newseg.una = kcp.rcv_nxt
+ newseg.resendts = current
+ newseg.rto = kcp.rx_rto
+ newseg.fastack = 0
+ newseg.xmit = 0
+ kcp.snd_buf = append(kcp.snd_buf, newseg)
+ kcp.snd_nxt++
+ count++
+ kcp.snd_queue[k].data = nil
+ }
+ kcp.snd_queue = kcp.snd_queue[count:]
+
+ // calculate resent
+ resent := uint32(kcp.fastresend)
+ if kcp.fastresend <= 0 {
+ resent = 0xffffffff
+ }
+ rtomin := (kcp.rx_rto >> 3)
+ if kcp.nodelay != 0 {
+ rtomin = 0
+ }
+
+ // flush data segments
+ nque := len(kcp.snd_queue)
+ var lostSegs, fastRetransSegs, earlyRetransSegs uint64
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ segment := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ needsend := false
+ if segment.xmit == 0 {
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ segment.rto = kcp.rx_rto
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto + rtomin
+ } else if _itimediff(current, segment.resendts) >= 0 {
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ kcp.xmit++
+ if kcp.nodelay == 0 {
+ segment.rto += kcp.rx_rto
+ } else {
+ segment.rto += kcp.rx_rto / 2
+ }
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto
+ lost = true
+ lostSegs++
+ } else if segment.fastack >= resent {
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ segment.fastack = 0
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto
+ change++
+ fastRetransSegs++
+ } else if segment.fastack > 0 && nque == 0 {
+ // early retransmit
+ needsend = true
+ segment.xmit++
+ segment.fastack = 0
+ segment.resendts = current + segment.rto
+ change++
+ earlyRetransSegs++
+ }
+
+ if needsend {
+ segment.ts = current
+ segment.wnd = seg.wnd
+ segment.una = kcp.rcv_nxt
+
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ need := IKCP_OVERHEAD + len(segment.data)
+
+ if size+need > int(kcp.mtu) {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ ptr = buffer
+ }
+
+ ptr = segment.encode(ptr)
+ copy(ptr, segment.data)
+ ptr = ptr[len(segment.data):]
+
+ if segment.xmit >= kcp.dead_link {
+ kcp.state = 0xFFFFFFFF
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.RetransSegs, lostSegs+fastRetransSegs+earlyRetransSegs)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.LostSegs, lostSegs)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.EarlyRetransSegs, earlyRetransSegs)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FastRetransSegs, fastRetransSegs)
+
+ // flash remain segments
+ size := len(buffer) - len(ptr)
+ if size > 0 {
+ kcp.output(buffer, size)
+ }
+
+ // update ssthresh
+ // rate halving, https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6937
+ if change != 0 {
+ inflight := kcp.snd_nxt - kcp.snd_una
+ kcp.ssthresh = inflight / 2
+ if kcp.ssthresh < IKCP_THRESH_MIN {
+ kcp.ssthresh = IKCP_THRESH_MIN
+ }
+ kcp.cwnd = kcp.ssthresh + resent
+ kcp.incr = kcp.cwnd * kcp.mss
+ }
+
+ // congestion control, https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5681
+ if lost {
+ kcp.ssthresh = cwnd / 2
+ if kcp.ssthresh < IKCP_THRESH_MIN {
+ kcp.ssthresh = IKCP_THRESH_MIN
+ }
+ kcp.cwnd = 1
+ kcp.incr = kcp.mss
+ }
+
+ if kcp.cwnd < 1 {
+ kcp.cwnd = 1
+ kcp.incr = kcp.mss
+ }
+}
+
+// Update updates state (call it repeatedly, every 10ms-100ms), or you can ask
+// ikcp_check when to call it again (without ikcp_input/_send calling).
+// 'current' - current timestamp in millisec.
+func (kcp *KCP) Update(current uint32) {
+ var slap int32
+
+ kcp.current = current
+
+ if kcp.updated == 0 {
+ kcp.updated = 1
+ kcp.ts_flush = kcp.current
+ }
+
+ slap = _itimediff(kcp.current, kcp.ts_flush)
+
+ if slap >= 10000 || slap < -10000 {
+ kcp.ts_flush = kcp.current
+ slap = 0
+ }
+
+ if slap >= 0 {
+ kcp.ts_flush += kcp.interval
+ if _itimediff(kcp.current, kcp.ts_flush) >= 0 {
+ kcp.ts_flush = kcp.current + kcp.interval
+ }
+ kcp.flush()
+ }
+}
+
+// Check determines when should you invoke ikcp_update:
+// returns when you should invoke ikcp_update in millisec, if there
+// is no ikcp_input/_send calling. you can call ikcp_update in that
+// time, instead of call update repeatly.
+// Important to reduce unnacessary ikcp_update invoking. use it to
+// schedule ikcp_update (eg. implementing an epoll-like mechanism,
+// or optimize ikcp_update when handling massive kcp connections)
+func (kcp *KCP) Check(current uint32) uint32 {
+ ts_flush := kcp.ts_flush
+ tm_flush := int32(0x7fffffff)
+ tm_packet := int32(0x7fffffff)
+ minimal := uint32(0)
+ if kcp.updated == 0 {
+ return current
+ }
+
+ if _itimediff(current, ts_flush) >= 10000 ||
+ _itimediff(current, ts_flush) < -10000 {
+ ts_flush = current
+ }
+
+ if _itimediff(current, ts_flush) >= 0 {
+ return current
+ }
+
+ tm_flush = _itimediff(ts_flush, current)
+
+ for k := range kcp.snd_buf {
+ seg := &kcp.snd_buf[k]
+ diff := _itimediff(seg.resendts, current)
+ if diff <= 0 {
+ return current
+ }
+ if diff < tm_packet {
+ tm_packet = diff
+ }
+ }
+
+ minimal = uint32(tm_packet)
+ if tm_packet >= tm_flush {
+ minimal = uint32(tm_flush)
+ }
+ if minimal >= kcp.interval {
+ minimal = kcp.interval
+ }
+
+ return current + minimal
+}
+
+// SetMtu changes MTU size, default is 1400
+func (kcp *KCP) SetMtu(mtu int) int {
+ if mtu < 50 || mtu < IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ return -1
+ }
+ buffer := make([]byte, (mtu+IKCP_OVERHEAD)*3)
+ if buffer == nil {
+ return -2
+ }
+ kcp.mtu = uint32(mtu)
+ kcp.mss = kcp.mtu - IKCP_OVERHEAD
+ kcp.buffer = buffer
+ return 0
+}
+
+// NoDelay options
+// fastest: ikcp_nodelay(kcp, 1, 20, 2, 1)
+// nodelay: 0:disable(default), 1:enable
+// interval: internal update timer interval in millisec, default is 100ms
+// resend: 0:disable fast resend(default), 1:enable fast resend
+// nc: 0:normal congestion control(default), 1:disable congestion control
+func (kcp *KCP) NoDelay(nodelay, interval, resend, nc int) int {
+ if nodelay >= 0 {
+ kcp.nodelay = uint32(nodelay)
+ if nodelay != 0 {
+ kcp.rx_minrto = IKCP_RTO_NDL
+ } else {
+ kcp.rx_minrto = IKCP_RTO_MIN
+ }
+ }
+ if interval >= 0 {
+ if interval > 5000 {
+ interval = 5000
+ } else if interval < 10 {
+ interval = 10
+ }
+ kcp.interval = uint32(interval)
+ }
+ if resend >= 0 {
+ kcp.fastresend = int32(resend)
+ }
+ if nc >= 0 {
+ kcp.nocwnd = int32(nc)
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// WndSize sets maximum window size: sndwnd=32, rcvwnd=32 by default
+func (kcp *KCP) WndSize(sndwnd, rcvwnd int) int {
+ if sndwnd > 0 {
+ kcp.snd_wnd = uint32(sndwnd)
+ }
+ if rcvwnd > 0 {
+ kcp.rcv_wnd = uint32(rcvwnd)
+ }
+ return 0
+}
+
+// WaitSnd gets how many packet is waiting to be sent
+func (kcp *KCP) WaitSnd() int {
+ return len(kcp.snd_buf) + len(kcp.snd_queue)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/sess.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/sess.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..737b99d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/sess.go
@@ -0,0 +1,901 @@
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "crypto/rand"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "io"
+ "net"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+
+ "github.com/klauspost/crc32"
+
+ "golang.org/x/net/ipv4"
+)
+
+// Option defines extra options
+type Option interface{}
+
+// OptionWithConvId defines conversation id
+type OptionWithConvId struct {
+ Id uint32
+}
+
+type errTimeout struct {
+ error
+}
+
+func (errTimeout) Timeout() bool { return true }
+func (errTimeout) Temporary() bool { return true }
+func (errTimeout) Error() string { return "i/o timeout" }
+
+const (
+ defaultWndSize = 128 // default window size, in packet
+ nonceSize = 16 // magic number
+ crcSize = 4 // 4bytes packet checksum
+ cryptHeaderSize = nonceSize + crcSize
+ mtuLimit = 2048
+ txQueueLimit = 8192
+ rxFecLimit = 8192
+ defaultKeepAliveInterval = 10 * time.Second
+)
+
+type (
+ // UDPSession defines a KCP session implemented by UDP
+ UDPSession struct {
+ kcp *KCP // the core ARQ
+ l *Listener // point to server listener if it's a server socket
+ fec *FEC // forward error correction
+ conn net.PacketConn // the underlying packet socket
+ block BlockCrypt
+ remote net.Addr
+ rd time.Time // read deadline
+ wd time.Time // write deadline
+ sockbuff []byte // kcp receiving is based on packet, I turn it into stream
+ die chan struct{}
+ chReadEvent chan struct{}
+ chWriteEvent chan struct{}
+ chTicker chan time.Time
+ chUDPOutput chan []byte
+ headerSize int
+ ackNoDelay bool
+ isClosed bool
+ keepAliveInterval time.Duration
+ xmitBuf sync.Pool
+ mu sync.Mutex
+ }
+
+ setReadBuffer interface {
+ SetReadBuffer(bytes int) error
+ }
+
+ setWriteBuffer interface {
+ SetWriteBuffer(bytes int) error
+ }
+)
+
+// newUDPSession create a new udp session for client or server
+func newUDPSession(conv uint32, dataShards, parityShards int, l *Listener, conn net.PacketConn, remote net.Addr, block BlockCrypt) *UDPSession {
+ sess := new(UDPSession)
+ sess.chTicker = make(chan time.Time, 1)
+ sess.chUDPOutput = make(chan []byte, txQueueLimit)
+ sess.die = make(chan struct{})
+ sess.chReadEvent = make(chan struct{}, 1)
+ sess.chWriteEvent = make(chan struct{}, 1)
+ sess.remote = remote
+ sess.conn = conn
+ sess.keepAliveInterval = defaultKeepAliveInterval
+ sess.l = l
+ sess.block = block
+ sess.fec = newFEC(rxFecLimit, dataShards, parityShards)
+ sess.xmitBuf.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+ // calculate header size
+ if sess.block != nil {
+ sess.headerSize += cryptHeaderSize
+ }
+ if sess.fec != nil {
+ sess.headerSize += fecHeaderSizePlus2
+ }
+
+ sess.kcp = NewKCP(conv, func(buf []byte, size int) {
+ if size >= IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ ext := sess.xmitBuf.Get().([]byte)[:sess.headerSize+size]
+ copy(ext[sess.headerSize:], buf)
+ select {
+ case sess.chUDPOutput <- ext:
+ case <-sess.die:
+ }
+ }
+ })
+ sess.kcp.WndSize(defaultWndSize, defaultWndSize)
+ sess.kcp.SetMtu(IKCP_MTU_DEF - sess.headerSize)
+
+ go sess.updateTask()
+ go sess.outputTask()
+ if sess.l == nil { // it's a client connection
+ go sess.readLoop()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.ActiveOpens, 1)
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.PassiveOpens, 1)
+ }
+ currestab := atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.CurrEstab, 1)
+ maxconn := atomic.LoadUint64(&DefaultSnmp.MaxConn)
+ if currestab > maxconn {
+ atomic.CompareAndSwapUint64(&DefaultSnmp.MaxConn, maxconn, currestab)
+ }
+
+ return sess
+}
+
+// Read implements the Conn Read method.
+func (s *UDPSession) Read(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ for {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ if len(s.sockbuff) > 0 { // copy from buffer
+ n = copy(b, s.sockbuff)
+ s.sockbuff = s.sockbuff[n:]
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return n, nil
+ }
+
+ if s.isClosed {
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errors.New("broken pipe")
+ }
+
+ if !s.rd.IsZero() {
+ if time.Now().After(s.rd) { // timeout
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errTimeout{}
+ }
+ }
+
+ if n := s.kcp.PeekSize(); n > 0 { // data arrived
+ if len(b) >= n {
+ s.kcp.Recv(b)
+ } else {
+ buf := make([]byte, n)
+ s.kcp.Recv(buf)
+ n = copy(b, buf)
+ s.sockbuff = buf[n:] // store remaining bytes into sockbuff for next read
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.BytesReceived, uint64(n))
+ return n, nil
+ }
+
+ var timeout <-chan time.Time
+ if !s.rd.IsZero() {
+ delay := s.rd.Sub(time.Now())
+ timeout = time.After(delay)
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+
+ // wait for read event or timeout
+ select {
+ case <-s.chReadEvent:
+ case <-timeout:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// Write implements the Conn Write method.
+func (s *UDPSession) Write(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ for {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ if s.isClosed {
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errors.New("broken pipe")
+ }
+
+ if !s.wd.IsZero() {
+ if time.Now().After(s.wd) { // timeout
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ return 0, errTimeout{}
+ }
+ }
+
+ if s.kcp.WaitSnd() < 2*int(s.kcp.snd_wnd) {
+ n = len(b)
+ max := s.kcp.mss << 8
+ for {
+ if len(b) <= int(max) { // in most cases
+ s.kcp.Send(b)
+ break
+ } else {
+ s.kcp.Send(b[:max])
+ b = b[max:]
+ }
+ }
+ s.kcp.current = currentMs()
+ s.kcp.flush()
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.BytesSent, uint64(n))
+ return n, nil
+ }
+
+ var timeout <-chan time.Time
+ if !s.wd.IsZero() {
+ delay := s.wd.Sub(time.Now())
+ timeout = time.After(delay)
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+
+ // wait for write event or timeout
+ select {
+ case <-s.chWriteEvent:
+ case <-timeout:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// Close closes the connection.
+func (s *UDPSession) Close() error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.isClosed {
+ return errors.New("broken pipe")
+ }
+ close(s.die)
+ s.isClosed = true
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.CurrEstab, ^uint64(0))
+ if s.l == nil { // client socket close
+ return s.conn.Close()
+ }
+
+ return nil
+}
+
+// LocalAddr returns the local network address. The Addr returned is shared by all invocations of LocalAddr, so do not modify it.
+func (s *UDPSession) LocalAddr() net.Addr { return s.conn.LocalAddr() }
+
+// RemoteAddr returns the remote network address. The Addr returned is shared by all invocations of RemoteAddr, so do not modify it.
+func (s *UDPSession) RemoteAddr() net.Addr { return s.remote }
+
+// SetDeadline sets the deadline associated with the listener. A zero time value disables the deadline.
+func (s *UDPSession) SetDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.rd = t
+ s.wd = t
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetReadDeadline implements the Conn SetReadDeadline method.
+func (s *UDPSession) SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.rd = t
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteDeadline implements the Conn SetWriteDeadline method.
+func (s *UDPSession) SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.wd = t
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWindowSize set maximum window size
+func (s *UDPSession) SetWindowSize(sndwnd, rcvwnd int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.kcp.WndSize(sndwnd, rcvwnd)
+}
+
+// SetMtu sets the maximum transmission unit
+func (s *UDPSession) SetMtu(mtu int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.kcp.SetMtu(mtu - s.headerSize)
+}
+
+// SetStreamMode toggles the stream mode on/off
+func (s *UDPSession) SetStreamMode(enable bool) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if enable {
+ s.kcp.stream = 1
+ } else {
+ s.kcp.stream = 0
+ }
+}
+
+// SetACKNoDelay changes ack flush option, set true to flush ack immediately,
+func (s *UDPSession) SetACKNoDelay(nodelay bool) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.ackNoDelay = nodelay
+}
+
+// SetNoDelay calls nodelay() of kcp
+func (s *UDPSession) SetNoDelay(nodelay, interval, resend, nc int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.kcp.NoDelay(nodelay, interval, resend, nc)
+}
+
+// SetDSCP sets the 6bit DSCP field of IP header, no effect if it's accepted from Listener
+func (s *UDPSession) SetDSCP(dscp int) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(net.Conn); ok {
+ return ipv4.NewConn(nc).SetTOS(dscp << 2)
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetReadBuffer sets the socket read buffer, no effect if it's accepted from Listener
+func (s *UDPSession) SetReadBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(setReadBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetReadBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteBuffer sets the socket write buffer, no effect if it's accepted from Listener
+func (s *UDPSession) SetWriteBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(setWriteBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetWriteBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetKeepAlive changes per-connection NAT keepalive interval; 0 to disable, default to 10s
+func (s *UDPSession) SetKeepAlive(interval int) {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ defer s.mu.Unlock()
+ s.keepAliveInterval = time.Duration(interval) * time.Second
+}
+
+// writeTo wraps write method for client & listener
+func (s *UDPSession) writeTo(b []byte, addr net.Addr) (int, error) {
+ if s.l == nil {
+ if nc, ok := s.conn.(io.Writer); ok {
+ return nc.Write(b)
+ }
+ }
+ return s.conn.WriteTo(b, addr)
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) outputTask() {
+ // offset pre-compute
+ fecOffset := 0
+ if s.block != nil {
+ fecOffset = cryptHeaderSize
+ }
+ szOffset := fecOffset + fecHeaderSize
+
+ // fec data group
+ var fecGroup [][]byte
+ var fecCnt int
+ var fecMaxSize int
+ if s.fec != nil {
+ fecGroup = make([][]byte, s.fec.shardSize)
+ for k := range fecGroup {
+ fecGroup[k] = make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+ }
+
+ // keepalive
+ var lastPing time.Time
+ ticker := time.NewTicker(5 * time.Second)
+ defer ticker.Stop()
+
+ for {
+ select {
+ case ext := <-s.chUDPOutput:
+ var ecc [][]byte
+ if s.fec != nil {
+ s.fec.markData(ext[fecOffset:])
+ // explicit size
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(ext[szOffset:], uint16(len(ext[szOffset:])))
+
+ // copy data to fec group
+ xorBytes(fecGroup[fecCnt], fecGroup[fecCnt], fecGroup[fecCnt])
+ copy(fecGroup[fecCnt], ext)
+ fecCnt++
+ if len(ext) > fecMaxSize {
+ fecMaxSize = len(ext)
+ }
+
+ // calculate Reed-Solomon Erasure Code
+ if fecCnt == s.fec.dataShards {
+ ecc = s.fec.calcECC(fecGroup, szOffset, fecMaxSize)
+ for k := range ecc {
+ s.fec.markFEC(ecc[k][fecOffset:])
+ ecc[k] = ecc[k][:fecMaxSize]
+ }
+ fecCnt = 0
+ fecMaxSize = 0
+ }
+ }
+
+ if s.block != nil {
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, ext[:nonceSize])
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(ext[cryptHeaderSize:])
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(ext[nonceSize:], checksum)
+ s.block.Encrypt(ext, ext)
+
+ if ecc != nil {
+ for k := range ecc {
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, ecc[k][:nonceSize])
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(ecc[k][cryptHeaderSize:])
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(ecc[k][nonceSize:], checksum)
+ s.block.Encrypt(ecc[k], ecc[k])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ //if rand.Intn(100) < 80 {
+ if n, err := s.writeTo(ext, s.remote); err == nil {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutSegs, 1)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutBytes, uint64(n))
+ }
+ //}
+
+ if ecc != nil {
+ for k := range ecc {
+ if n, err := s.writeTo(ecc[k], s.remote); err == nil {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutSegs, 1)
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.OutBytes, uint64(n))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ xorBytes(ext, ext, ext)
+ s.xmitBuf.Put(ext)
+ case <-ticker.C: // NAT keep-alive
+ if len(s.chUDPOutput) == 0 {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ interval := s.keepAliveInterval
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ if interval > 0 && time.Now().After(lastPing.Add(interval)) {
+ buf := make([]byte, 2)
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, buf)
+ rnd := int(binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(buf))
+ sz := rnd%(IKCP_MTU_DEF-s.headerSize-IKCP_OVERHEAD) + s.headerSize + IKCP_OVERHEAD
+ ping := make([]byte, sz)
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, ping)
+ s.writeTo(ping, s.remote)
+ lastPing = time.Now()
+ }
+ }
+ case <-s.die:
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// kcp update, input loop
+func (s *UDPSession) updateTask() {
+ var tc <-chan time.Time
+ if s.l == nil { // client
+ ticker := time.NewTicker(10 * time.Millisecond)
+ tc = ticker.C
+ defer ticker.Stop()
+ } else {
+ tc = s.chTicker
+ }
+
+ for {
+ select {
+ case <-tc:
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ current := currentMs()
+ s.kcp.Update(current)
+ if s.kcp.WaitSnd() < 2*int(s.kcp.snd_wnd) {
+ s.notifyWriteEvent()
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ case <-s.die:
+ if s.l != nil { // has listener
+ select {
+ case s.l.chDeadlinks <- s.remote:
+ case <-s.l.die:
+ }
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// GetConv gets conversation id of a session
+func (s *UDPSession) GetConv() uint32 {
+ return s.kcp.conv
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) notifyReadEvent() {
+ select {
+ case s.chReadEvent <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) notifyWriteEvent() {
+ select {
+ case s.chWriteEvent <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) kcpInput(data []byte) {
+ current := currentMs()
+ if s.fec != nil {
+ f := s.fec.decode(data)
+ if f.flag == typeData || f.flag == typeFEC {
+ if f.flag == typeFEC {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FECSegs, 1)
+ }
+
+ if recovers := s.fec.input(f); recovers != nil {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ for k := range recovers {
+ sz := binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(recovers[k])
+ if int(sz) <= len(recovers[k]) && sz >= 2 {
+ s.kcp.Input(recovers[k][2:sz], false)
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FECErrs, 1)
+ }
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.FECRecovered, uint64(len(recovers)))
+ }
+ }
+ if f.flag == typeData {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ s.kcp.Input(data[fecHeaderSizePlus2:], true)
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ }
+ } else {
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ s.kcp.Input(data, true)
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ }
+
+ // notify reader
+ s.mu.Lock()
+ if n := s.kcp.PeekSize(); n > 0 {
+ s.notifyReadEvent()
+ }
+ if s.ackNoDelay {
+ s.kcp.current = current
+ s.kcp.flush()
+ }
+ s.mu.Unlock()
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InSegs, 1)
+}
+
+func (s *UDPSession) receiver(ch chan []byte) {
+ for {
+ data := s.xmitBuf.Get().([]byte)[:mtuLimit]
+ if n, _, err := s.conn.ReadFrom(data); err == nil && n >= s.headerSize+IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ select {
+ case ch <- data[:n]:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ } else if err != nil {
+ return
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InErrs, 1)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// read loop for client session
+func (s *UDPSession) readLoop() {
+ chPacket := make(chan []byte, txQueueLimit)
+ go s.receiver(chPacket)
+
+ for {
+ select {
+ case data := <-chPacket:
+ raw := data
+ dataValid := false
+ if s.block != nil {
+ s.block.Decrypt(data, data)
+ data = data[nonceSize:]
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(data[crcSize:])
+ if checksum == binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data) {
+ data = data[crcSize:]
+ dataValid = true
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InCsumErrors, 1)
+ }
+ } else if s.block == nil {
+ dataValid = true
+ }
+
+ if dataValid {
+ s.kcpInput(data)
+ }
+ xorBytes(raw, raw, raw)
+ s.xmitBuf.Put(raw)
+ case <-s.die:
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+type (
+ // Listener defines a server listening for connections
+ Listener struct {
+ block BlockCrypt
+ dataShards, parityShards int
+ fec *FEC // for fec init test
+ conn net.PacketConn
+ sessions map[string]*UDPSession
+ chAccepts chan *UDPSession
+ chDeadlinks chan net.Addr
+ headerSize int
+ die chan struct{}
+ rxbuf sync.Pool
+ rd atomic.Value
+ wd atomic.Value
+ }
+
+ packet struct {
+ from net.Addr
+ data []byte
+ }
+)
+
+// monitor incoming data for all connections of server
+func (l *Listener) monitor() {
+ chPacket := make(chan packet, txQueueLimit)
+ go l.receiver(chPacket)
+ ticker := time.NewTicker(10 * time.Millisecond)
+ defer ticker.Stop()
+ for {
+ select {
+ case p := <-chPacket:
+ raw := p.data
+ data := p.data
+ from := p.from
+ dataValid := false
+ if l.block != nil {
+ l.block.Decrypt(data, data)
+ data = data[nonceSize:]
+ checksum := crc32.ChecksumIEEE(data[crcSize:])
+ if checksum == binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data) {
+ data = data[crcSize:]
+ dataValid = true
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InCsumErrors, 1)
+ }
+ } else if l.block == nil {
+ dataValid = true
+ }
+
+ if dataValid {
+ addr := from.String()
+ s, ok := l.sessions[addr]
+ if !ok { // new session
+ var conv uint32
+ convValid := false
+ if l.fec != nil {
+ isfec := binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(data[4:])
+ if isfec == typeData {
+ conv = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data[fecHeaderSizePlus2:])
+ convValid = true
+ }
+ } else {
+ conv = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(data)
+ convValid = true
+ }
+
+ if convValid {
+ s := newUDPSession(conv, l.dataShards, l.parityShards, l, l.conn, from, l.block)
+ s.kcpInput(data)
+ l.sessions[addr] = s
+ l.chAccepts <- s
+ }
+ } else {
+ s.kcpInput(data)
+ }
+ }
+
+ xorBytes(raw, raw, raw)
+ l.rxbuf.Put(raw)
+ case deadlink := <-l.chDeadlinks:
+ delete(l.sessions, deadlink.String())
+ case <-l.die:
+ return
+ case <-ticker.C:
+ now := time.Now()
+ for _, s := range l.sessions {
+ select {
+ case s.chTicker <- now:
+ default:
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (l *Listener) receiver(ch chan packet) {
+ for {
+ data := l.rxbuf.Get().([]byte)[:mtuLimit]
+ if n, from, err := l.conn.ReadFrom(data); err == nil && n >= l.headerSize+IKCP_OVERHEAD {
+ ch <- packet{from, data[:n]}
+ } else if err != nil {
+ return
+ } else {
+ atomic.AddUint64(&DefaultSnmp.InErrs, 1)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// SetReadBuffer sets the socket read buffer for the Listener
+func (l *Listener) SetReadBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ if nc, ok := l.conn.(setReadBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetReadBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteBuffer sets the socket write buffer for the Listener
+func (l *Listener) SetWriteBuffer(bytes int) error {
+ if nc, ok := l.conn.(setWriteBuffer); ok {
+ return nc.SetWriteBuffer(bytes)
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetDSCP sets the 6bit DSCP field of IP header
+func (l *Listener) SetDSCP(dscp int) error {
+ if nc, ok := l.conn.(net.Conn); ok {
+ return ipv4.NewConn(nc).SetTOS(dscp << 2)
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Accept implements the Accept method in the Listener interface; it waits for the next call and returns a generic Conn.
+func (l *Listener) Accept() (net.Conn, error) {
+ return l.AcceptKCP()
+}
+
+// AcceptKCP accepts a KCP connection
+func (l *Listener) AcceptKCP() (*UDPSession, error) {
+ var timeout <-chan time.Time
+ if tdeadline, ok := l.rd.Load().(time.Time); ok && !tdeadline.IsZero() {
+ timeout = time.After(tdeadline.Sub(time.Now()))
+ }
+
+ select {
+ case <-timeout:
+ return nil, &errTimeout{}
+ case c := <-l.chAccepts:
+ return c, nil
+ case <-l.die:
+ return nil, errors.New("listener stopped")
+ }
+}
+
+// SetDeadline sets the deadline associated with the listener. A zero time value disables the deadline.
+func (l *Listener) SetDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ l.SetReadDeadline(t)
+ l.SetWriteDeadline(t)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetReadDeadline implements the Conn SetReadDeadline method.
+func (l *Listener) SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ l.rd.Store(t)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// SetWriteDeadline implements the Conn SetWriteDeadline method.
+func (l *Listener) SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error {
+ l.wd.Store(t)
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Close stops listening on the UDP address. Already Accepted connections are not closed.
+func (l *Listener) Close() error {
+ close(l.die)
+ return l.conn.Close()
+}
+
+// Addr returns the listener's network address, The Addr returned is shared by all invocations of Addr, so do not modify it.
+func (l *Listener) Addr() net.Addr {
+ return l.conn.LocalAddr()
+}
+
+// Listen listens for incoming KCP packets addressed to the local address laddr on the network "udp",
+func Listen(laddr string) (*Listener, error) {
+ return ListenWithOptions(laddr, nil, 0, 0)
+}
+
+// ListenWithOptions listens for incoming KCP packets addressed to the local address laddr on the network "udp" with packet encryption,
+// dataShards, parityShards defines Reed-Solomon Erasure Coding parameters
+func ListenWithOptions(laddr string, block BlockCrypt, dataShards, parityShards int) (*Listener, error) {
+ udpaddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", laddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.ResolveUDPAddr")
+ }
+ conn, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", udpaddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.ListenUDP")
+ }
+
+ l := new(Listener)
+ l.conn = conn
+ l.sessions = make(map[string]*UDPSession)
+ l.chAccepts = make(chan *UDPSession, 1024)
+ l.chDeadlinks = make(chan net.Addr, 1024)
+ l.die = make(chan struct{})
+ l.dataShards = dataShards
+ l.parityShards = parityShards
+ l.block = block
+ l.fec = newFEC(rxFecLimit, dataShards, parityShards)
+ l.rxbuf.New = func() interface{} {
+ return make([]byte, mtuLimit)
+ }
+
+ // calculate header size
+ if l.block != nil {
+ l.headerSize += cryptHeaderSize
+ }
+ if l.fec != nil {
+ l.headerSize += fecHeaderSizePlus2
+ }
+
+ go l.monitor()
+ return l, nil
+}
+
+// Dial connects to the remote address "raddr" on the network "udp"
+func Dial(raddr string) (*UDPSession, error) {
+ return DialWithOptions(raddr, nil, 0, 0)
+}
+
+// DialWithOptions connects to the remote address "raddr" on the network "udp" with packet encryption
+func DialWithOptions(raddr string, block BlockCrypt, dataShards, parityShards int, opts ...Option) (*UDPSession, error) {
+ udpaddr, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp", raddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.ResolveUDPAddr")
+ }
+
+ udpconn, err := net.DialUDP("udp", nil, udpaddr)
+ if err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "net.DialUDP")
+ }
+
+ buf := make([]byte, 4)
+ io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, buf)
+ convid := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buf)
+ for k := range opts {
+ switch opt := opts[k].(type) {
+ case OptionWithConvId:
+ convid = opt.Id
+ default:
+ return nil, errors.New("unrecognized option")
+ }
+ }
+ return newUDPSession(convid, dataShards, parityShards, nil, udpconn, udpaddr, block), nil
+}
+
+func currentMs() uint32 {
+ return uint32(time.Now().UnixNano() / int64(time.Millisecond))
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/shannon.jpg b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/shannon.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..055236a
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/shannon.jpg differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/snmp.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/snmp.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..997b163
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/snmp.go
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+package kcp
+
+import "sync/atomic"
+
+// Snmp defines network statistics indicator
+type Snmp struct {
+ BytesSent uint64 // payload bytes sent
+ BytesReceived uint64
+ MaxConn uint64
+ ActiveOpens uint64
+ PassiveOpens uint64
+ CurrEstab uint64
+ InErrs uint64
+ InCsumErrors uint64 // checksum errors
+ InSegs uint64
+ OutSegs uint64
+ OutBytes uint64 // udp bytes sent
+ RetransSegs uint64
+ FastRetransSegs uint64
+ EarlyRetransSegs uint64
+ LostSegs uint64
+ RepeatSegs uint64
+ FECRecovered uint64
+ FECErrs uint64
+ FECSegs uint64 // fec segments received
+}
+
+func newSnmp() *Snmp {
+ return new(Snmp)
+}
+
+// Copy make a copy of current snmp snapshot
+func (s *Snmp) Copy() *Snmp {
+ d := newSnmp()
+ d.BytesSent = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.BytesSent)
+ d.BytesReceived = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.BytesReceived)
+ d.MaxConn = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.MaxConn)
+ d.ActiveOpens = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.ActiveOpens)
+ d.PassiveOpens = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.PassiveOpens)
+ d.CurrEstab = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.CurrEstab)
+ d.InErrs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.InErrs)
+ d.InCsumErrors = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.InCsumErrors)
+ d.InSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.InSegs)
+ d.OutSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.OutSegs)
+ d.OutBytes = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.OutBytes)
+ d.RetransSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.RetransSegs)
+ d.FastRetransSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FastRetransSegs)
+ d.EarlyRetransSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.EarlyRetransSegs)
+ d.LostSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.LostSegs)
+ d.RepeatSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.RepeatSegs)
+ d.FECSegs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FECSegs)
+ d.FECErrs = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FECErrs)
+ d.FECRecovered = atomic.LoadUint64(&s.FECRecovered)
+ return d
+}
+
+// DefaultSnmp is the global KCP connection statistics collector
+var DefaultSnmp *Snmp
+
+func init() {
+ DefaultSnmp = newSnmp()
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/xor.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/xor.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5d21095
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2/xor.go
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+// Copyright 2013 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
+// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
+
+package kcp
+
+import (
+ "runtime"
+ "unsafe"
+)
+
+const wordSize = int(unsafe.Sizeof(uintptr(0)))
+const supportsUnaligned = runtime.GOARCH == "386" || runtime.GOARCH == "amd64" || runtime.GOARCH == "ppc64" || runtime.GOARCH == "ppc64le" || runtime.GOARCH == "s390x"
+
+// fastXORBytes xors in bulk. It only works on architectures that
+// support unaligned read/writes.
+func fastXORBytes(dst, a, b []byte) int {
+ n := len(a)
+ if len(b) < n {
+ n = len(b)
+ }
+
+ w := n / wordSize
+ if w > 0 {
+ wordBytes := w * wordSize
+ fastXORWords(dst[:wordBytes], a[:wordBytes], b[:wordBytes])
+ }
+
+ for i := (n - n%wordSize); i < n; i++ {
+ dst[i] = a[i] ^ b[i]
+ }
+
+ return n
+}
+
+func safeXORBytes(dst, a, b []byte) int {
+ n := len(a)
+ if len(b) < n {
+ n = len(b)
+ }
+ ex := n % 8
+ for i := 0; i < ex; i++ {
+ dst[i] = a[i] ^ b[i]
+ }
+
+ for i := ex; i < n; i += 8 {
+ dst[i] = a[i] ^ b[i]
+ dst[i+1] = a[i+1] ^ b[i+1]
+ dst[i+2] = a[i+2] ^ b[i+2]
+ dst[i+3] = a[i+3] ^ b[i+3]
+
+ dst[i+4] = a[i+4] ^ b[i+4]
+ dst[i+5] = a[i+5] ^ b[i+5]
+ dst[i+6] = a[i+6] ^ b[i+6]
+ dst[i+7] = a[i+7] ^ b[i+7]
+ }
+ return n
+}
+
+// xorBytes xors the bytes in a and b. The destination is assumed to have enough
+// space. Returns the number of bytes xor'd.
+func xorBytes(dst, a, b []byte) int {
+ if supportsUnaligned {
+ return fastXORBytes(dst, a, b)
+ } else {
+ // TODO(hanwen): if (dst, a, b) have common alignment
+ // we could still try fastXORBytes. It is not clear
+ // how often this happens, and it's only worth it if
+ // the block encryption itself is hardware
+ // accelerated.
+ return safeXORBytes(dst, a, b)
+ }
+}
+
+// fastXORWords XORs multiples of 4 or 8 bytes (depending on architecture.)
+// The arguments are assumed to be of equal length.
+func fastXORWords(dst, a, b []byte) {
+ dw := *(*[]uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&dst))
+ aw := *(*[]uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&a))
+ bw := *(*[]uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&b))
+ n := len(b) / wordSize
+ ex := n % 8
+ for i := 0; i < ex; i++ {
+ dw[i] = aw[i] ^ bw[i]
+ }
+
+ for i := ex; i < n; i += 8 {
+ dw[i] = aw[i] ^ bw[i]
+ dw[i+1] = aw[i+1] ^ bw[i+1]
+ dw[i+2] = aw[i+2] ^ bw[i+2]
+ dw[i+3] = aw[i+3] ^ bw[i+3]
+ dw[i+4] = aw[i+4] ^ bw[i+4]
+ dw[i+5] = aw[i+5] ^ bw[i+5]
+ dw[i+6] = aw[i+6] ^ bw[i+6]
+ dw[i+7] = aw[i+7] ^ bw[i+7]
+ }
+}
+
+func xorWords(dst, a, b []byte) {
+ if supportsUnaligned {
+ fastXORWords(dst, a, b)
+ } else {
+ safeXORBytes(dst, a, b)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/LICENSE b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/LICENSE
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..37c57a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/LICENSE
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+MIT License
+
+Copyright (c) 2016 xtaci
+
+Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
+of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
+in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
+to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
+copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
+furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
+
+The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
+copies or substantial portions of the Software.
+
+THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
+IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
+FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
+AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
+LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
+OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
+SOFTWARE.
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/README.md b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..15e9871
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+# SMUX
+[![GoDoc][1]][2] [![MIT licensed][3]][4] [![Build Status][5]][6] [![Go Report Card][7]][8] [![Coverage Statusd][9]][10]
+
+ +
+[1]: https://godoc.org/github.com/xtaci/smux?status.svg
+[2]: https://godoc.org/github.com/xtaci/smux
+[3]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-MIT-blue.svg
+[4]: LICENSE
+[5]: https://travis-ci.org/xtaci/smux.svg?branch=master
+[6]: https://travis-ci.org/xtaci/smux
+[7]: https://goreportcard.com/badge/github.com/xtaci/smux
+[8]: https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/xtaci/smux
+[9]: https://codecov.io/gh/xtaci/smux/branch/master/graph/badge.svg
+[10]: https://codecov.io/gh/xtaci/smux
+
+## Introduction
+
+Smux (***S***imple ***MU***ltiple***X***ing) is a multiplexing library for Golang. It relies on an underlying connection to provide reliability and ordering, such as TCP or [KCP](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go), and provides stream-oriented multiplexing.
+
+## Features
+
+1. Tiny, less than 600 LOC.
+2. ***Token bucket*** controlled receiving, which provides smoother bandwidth graph(see picture below).
+3. Session-wide receive buffer, which is shared among streams.
+4. Minimized header(8Bytes), maximized payload.
+
+
+
+## Documentation
+
+For complete documentation, see the associated [Godoc](https://godoc.org/github.com/xtaci/smux).
+
+## Specification
+
+```
+VERSION(1B) | CMD(1B) | LENGTH(2B) | STREAMID(4B) | DATA(LENGTH)
+```
+
+## Usage
+
+The API of smux are mostly taken from [yamux](https://github.com/hashicorp/yamux)
+
+```go
+
+func client() {
+ // Get a TCP connection
+ conn, err := net.Dial(...)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Setup client side of smux
+ session, err := smux.Client(conn, nil)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Open a new stream
+ stream, err := session.OpenStream()
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Stream implements net.Conn
+ stream.Write([]byte("ping"))
+}
+
+func server() {
+ // Accept a TCP connection
+ conn, err := listener.Accept()
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Setup server side of smux
+ session, err := smux.Server(conn, nil)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Accept a stream
+ stream, err := session.AcceptStream()
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Listen for a message
+ buf := make([]byte, 4)
+ stream.Read(buf)
+}
+
+```
+
+## Status
+
+Beta
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/curve.jpg b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/curve.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3fc4863
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/curve.jpg differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..334fea3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "fmt"
+)
+
+const (
+ version = 1
+)
+
+const ( // cmds
+ cmdSYN byte = iota // stream open
+ cmdRST // stream close
+ cmdPSH // data push
+ cmdNOP // no operation
+)
+
+const (
+ sizeOfVer = 1
+ sizeOfCmd = 1
+ sizeOfLength = 2
+ sizeOfSid = 4
+ headerSize = sizeOfVer + sizeOfCmd + sizeOfSid + sizeOfLength
+)
+
+// Frame defines a packet from or to be multiplexed into a single connection
+type Frame struct {
+ ver byte
+ cmd byte
+ sid uint32
+ data []byte
+}
+
+func newFrame(cmd byte, sid uint32) Frame {
+ return Frame{ver: version, cmd: cmd, sid: sid}
+}
+
+type rawHeader []byte
+
+func (h rawHeader) Version() byte {
+ return h[0]
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) Cmd() byte {
+ return h[1]
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) Length() uint16 {
+ return binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(h[2:])
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) StreamID() uint32 {
+ return binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(h[4:])
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) String() string {
+ return fmt.Sprintf("Version:%d Cmd:%d StreamID:%d Length:%d",
+ h.Version(), h.Cmd(), h.StreamID(), h.Length())
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..afcf58b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.go
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+)
+
+// Config is used to tune the Smux session
+type Config struct {
+ // KeepAliveInterval is how often to send a NOP command to the remote
+ KeepAliveInterval time.Duration
+
+ // KeepAliveTimeout is how long the session
+ // will be closed if no data has arrived
+ KeepAliveTimeout time.Duration
+
+ // MaxFrameSize is used to control the maximum
+ // frame size to sent to the remote
+ MaxFrameSize int
+
+ // MaxReceiveBuffer is used to control the maximum
+ // number of data in the buffer pool
+ MaxReceiveBuffer int
+}
+
+// DefaultConfig is used to return a default configuration
+func DefaultConfig() *Config {
+ return &Config{
+ KeepAliveInterval: 10 * time.Second,
+ KeepAliveTimeout: 30 * time.Second,
+ MaxFrameSize: 4096,
+ MaxReceiveBuffer: 4194304,
+ }
+}
+
+// VerifyConfig is used to verify the sanity of configuration
+func VerifyConfig(config *Config) error {
+ if config.KeepAliveInterval == 0 {
+ return errors.New("keep-alive interval must be positive")
+ }
+ if config.KeepAliveTimeout < config.KeepAliveInterval {
+ return fmt.Errorf("keep-alive timeout must be larger than keep-alive interval")
+ }
+ if config.MaxFrameSize <= 0 {
+ return errors.New("max frame size must be positive")
+ }
+ if config.MaxFrameSize > 65535 {
+ return errors.New("max frame size must not be larger than 65535")
+ }
+ if config.MaxReceiveBuffer <= 0 {
+ return errors.New("max receive buffer must be positive")
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Server is used to initialize a new server-side connection.
+func Server(conn io.ReadWriteCloser, config *Config) (*Session, error) {
+ if config == nil {
+ config = DefaultConfig()
+ }
+ if err := VerifyConfig(config); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return newSession(config, conn, false), nil
+}
+
+// Client is used to initialize a new client-side connection.
+func Client(conn io.ReadWriteCloser, config *Config) (*Session, error) {
+ if config == nil {
+ config = DefaultConfig()
+ }
+
+ if err := VerifyConfig(config); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return newSession(config, conn, true), nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.jpg b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dde2e11
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.jpg differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/session.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/session.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a06f2ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/session.go
@@ -0,0 +1,275 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "io"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+)
+
+const (
+ defaultAcceptBacklog = 1024
+)
+
+const (
+ errBrokenPipe = "broken pipe"
+ errConnReset = "connection reset by peer"
+ errInvalidProtocol = "invalid protocol version"
+)
+
+// Session defines a multiplexed connection for streams
+type Session struct {
+ conn io.ReadWriteCloser
+ writeLock sync.Mutex
+
+ config *Config
+ nextStreamID uint32 // next stream identifier
+
+ bucket int32 // token bucket
+ bucketCond *sync.Cond // used for waiting for tokens
+
+ streams map[uint32]*Stream // all streams in this session
+ streamLock sync.Mutex // locks streams
+
+ die chan struct{} // flag session has died
+ dieLock sync.Mutex
+ chAccepts chan *Stream
+
+ dataReady int32 // flag data has arrived
+}
+
+func newSession(config *Config, conn io.ReadWriteCloser, client bool) *Session {
+ s := new(Session)
+ s.die = make(chan struct{})
+ s.conn = conn
+ s.config = config
+ s.streams = make(map[uint32]*Stream)
+ s.chAccepts = make(chan *Stream, defaultAcceptBacklog)
+ s.bucket = int32(config.MaxReceiveBuffer)
+ s.bucketCond = sync.NewCond(&sync.Mutex{})
+ if client {
+ s.nextStreamID = 1
+ } else {
+ s.nextStreamID = 2
+ }
+ go s.recvLoop()
+ go s.keepalive()
+ return s
+}
+
+// OpenStream is used to create a new stream
+func (s *Session) OpenStream() (*Stream, error) {
+ if s.IsClosed() {
+ return nil, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ }
+
+ sid := atomic.AddUint32(&s.nextStreamID, 2)
+ stream := newStream(sid, s.config.MaxFrameSize, s)
+
+ if _, err := s.writeFrame(newFrame(cmdSYN, sid)); err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "writeFrame")
+ }
+
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ s.streams[sid] = stream
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ return stream, nil
+}
+
+// AcceptStream is used to block until the next available stream
+// is ready to be accepted.
+func (s *Session) AcceptStream() (*Stream, error) {
+ select {
+ case stream := <-s.chAccepts:
+ return stream, nil
+ case <-s.die:
+ return nil, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ }
+}
+
+// Close is used to close the session and all streams.
+func (s *Session) Close() (err error) {
+ s.dieLock.Lock()
+ defer s.dieLock.Unlock()
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ close(s.die)
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ for k := range s.streams {
+ s.streams[k].sessionClose()
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ s.bucketCond.Signal()
+ return s.conn.Close()
+ }
+}
+
+// IsClosed does a safe check to see if we have shutdown
+func (s *Session) IsClosed() bool {
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return true
+ default:
+ return false
+ }
+}
+
+// NumStreams returns the number of currently open streams
+func (s *Session) NumStreams() int {
+ if s.IsClosed() {
+ return 0
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ defer s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ return len(s.streams)
+}
+
+// notify the session that a stream has closed
+func (s *Session) streamClosed(sid uint32) {
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if n := s.streams[sid].recycleTokens(); n > 0 { // return remaining tokens to the bucket
+ if atomic.AddInt32(&s.bucket, int32(n)) > 0 {
+ s.bucketCond.Signal()
+ }
+ }
+ delete(s.streams, sid)
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+}
+
+// returnTokens is called by stream to return token after read
+func (s *Session) returnTokens(n int) {
+ if atomic.AddInt32(&s.bucket, int32(n)) > 0 {
+ s.bucketCond.Signal()
+ }
+}
+
+// session read a frame from underlying connection
+// it's data is pointed to the input buffer
+func (s *Session) readFrame(buffer []byte) (f Frame, err error) {
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(s.conn, buffer[:headerSize]); err != nil {
+ return f, errors.Wrap(err, "readFrame")
+ }
+
+ dec := rawHeader(buffer)
+ if dec.Version() != version {
+ return f, errors.New(errInvalidProtocol)
+ }
+
+ f.ver = dec.Version()
+ f.cmd = dec.Cmd()
+ f.sid = dec.StreamID()
+ if length := dec.Length(); length > 0 {
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(s.conn, buffer[headerSize:headerSize+length]); err != nil {
+ return f, errors.Wrap(err, "readFrame")
+ }
+ f.data = buffer[headerSize : headerSize+length]
+ }
+ return f, nil
+}
+
+// recvLoop keeps on reading from underlying connection if tokens are available
+func (s *Session) recvLoop() {
+ buffer := make([]byte, (1<<16)+headerSize)
+ for {
+ s.bucketCond.L.Lock()
+ for atomic.LoadInt32(&s.bucket) <= 0 && !s.IsClosed() {
+ s.bucketCond.Wait()
+ }
+ s.bucketCond.L.Unlock()
+
+ if s.IsClosed() {
+ return
+ }
+
+ if f, err := s.readFrame(buffer); err == nil {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.dataReady, 1)
+
+ switch f.cmd {
+ case cmdNOP:
+ case cmdSYN:
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if _, ok := s.streams[f.sid]; !ok {
+ stream := newStream(f.sid, s.config.MaxFrameSize, s)
+ s.streams[f.sid] = stream
+ select {
+ case s.chAccepts <- stream:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ case cmdRST:
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if stream, ok := s.streams[f.sid]; ok {
+ stream.markRST()
+ stream.notifyReadEvent()
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ case cmdPSH:
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if stream, ok := s.streams[f.sid]; ok {
+ atomic.AddInt32(&s.bucket, -int32(len(f.data)))
+ stream.pushBytes(f.data)
+ stream.notifyReadEvent()
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ default:
+ s.Close()
+ return
+ }
+ } else {
+ s.Close()
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) keepalive() {
+ tickerPing := time.NewTicker(s.config.KeepAliveInterval)
+ tickerTimeout := time.NewTicker(s.config.KeepAliveTimeout)
+ defer tickerPing.Stop()
+ defer tickerTimeout.Stop()
+ for {
+ select {
+ case <-tickerPing.C:
+ s.writeFrame(newFrame(cmdNOP, 0))
+ s.bucketCond.Signal() // force a signal to the recvLoop
+ case <-tickerTimeout.C:
+ if !atomic.CompareAndSwapInt32(&s.dataReady, 1, 0) {
+ s.Close()
+ return
+ }
+ case <-s.die:
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// writeFrame writes the frame to the underlying connection
+// and returns the number of bytes written if successful
+func (s *Session) writeFrame(f Frame) (n int, err error) {
+ buf := make([]byte, headerSize+len(f.data))
+ buf[0] = f.ver
+ buf[1] = f.cmd
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(buf[2:], uint16(len(f.data)))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(buf[4:], f.sid)
+ copy(buf[headerSize:], f.data)
+
+ s.writeLock.Lock()
+ n, err = s.conn.Write(buf)
+ s.writeLock.Unlock()
+ return n, err
+}
+
+// writeBinary writes the byte slice to the underlying connection
+func (s *Session) writeBinary(bts []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ s.writeLock.Lock()
+ n, err = s.conn.Write(bts)
+ s.writeLock.Unlock()
+ return n, err
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/stream.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/stream.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8c44dd8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/stream.go
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+)
+
+// Stream implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+type Stream struct {
+ id uint32
+ rstflag int32
+ sess *Session
+ buffer bytes.Buffer
+ bufferLock sync.Mutex
+ frameSize int
+ chReadEvent chan struct{} // notify a read event
+ die chan struct{} // flag the stream has closed
+ dieLock sync.Mutex
+}
+
+// newStream initiates a Stream struct
+func newStream(id uint32, frameSize int, sess *Session) *Stream {
+ s := new(Stream)
+ s.id = id
+ s.chReadEvent = make(chan struct{}, 1)
+ s.frameSize = frameSize
+ s.sess = sess
+ s.die = make(chan struct{})
+ return s
+}
+
+// Read implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+func (s *Stream) Read(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+READ:
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return 0, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ }
+
+ s.bufferLock.Lock()
+ n, err = s.buffer.Read(b)
+ s.bufferLock.Unlock()
+
+ if n > 0 {
+ s.sess.returnTokens(n)
+ return n, nil
+ } else if atomic.LoadInt32(&s.rstflag) == 1 {
+ _ = s.Close()
+ return 0, errors.New(errConnReset)
+ }
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.chReadEvent:
+ goto READ
+ case <-s.die:
+ return 0, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ }
+}
+
+// Write implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+func (s *Stream) Write(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return 0, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ }
+
+ frames := s.split(b, cmdPSH, s.id)
+ // preallocate buffer
+ buffer := make([]byte, len(frames)*headerSize+len(b))
+ bts := buffer
+
+ // combine frames into a large blob
+ for k := range frames {
+ bts[0] = version
+ bts[1] = frames[k].cmd
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(bts[2:], uint16(len(frames[k].data)))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(bts[4:], frames[k].sid)
+ copy(bts[headerSize:], frames[k].data)
+ bts = bts[len(frames[k].data)+headerSize:]
+ }
+
+ if _, err = s.sess.writeBinary(buffer); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return len(b), nil
+}
+
+// Close implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+func (s *Stream) Close() error {
+ s.dieLock.Lock()
+ defer s.dieLock.Unlock()
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ close(s.die)
+ s.sess.streamClosed(s.id)
+ _, err := s.sess.writeFrame(newFrame(cmdRST, s.id))
+ return err
+ }
+}
+
+// session closes the stream
+func (s *Stream) sessionClose() {
+ s.dieLock.Lock()
+ defer s.dieLock.Unlock()
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ default:
+ close(s.die)
+ }
+}
+
+// pushBytes a slice into buffer
+func (s *Stream) pushBytes(p []byte) {
+ s.bufferLock.Lock()
+ s.buffer.Write(p)
+ s.bufferLock.Unlock()
+}
+
+// recycleTokens transform remaining bytes to tokens(will truncate buffer)
+func (s *Stream) recycleTokens() (n int) {
+ s.bufferLock.Lock()
+ n = s.buffer.Len()
+ s.buffer.Reset()
+ s.bufferLock.Unlock()
+ return
+}
+
+// split large byte buffer into smaller frames, reference only
+func (s *Stream) split(bts []byte, cmd byte, sid uint32) []Frame {
+ var frames []Frame
+ for len(bts) > s.frameSize {
+ frame := newFrame(cmd, sid)
+ frame.data = bts[:s.frameSize]
+ bts = bts[s.frameSize:]
+ frames = append(frames, frame)
+ }
+ if len(bts) > 0 {
+ frame := newFrame(cmd, sid)
+ frame.data = bts
+ frames = append(frames, frame)
+ }
+ return frames
+}
+
+// notify read event
+func (s *Stream) notifyReadEvent() {
+ select {
+ case s.chReadEvent <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+// mark this stream has been reset
+func (s *Stream) markRST() {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.rstflag, 1)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/vendor.json b/cmd/gost/vendor/vendor.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1a173ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/vendor.json
@@ -0,0 +1,289 @@
+{
+ "comment": "",
+ "ignore": "test",
+ "package": [
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "QPs3L3mjPoi+a9GJCjW8HhyJczM=",
+ "path": "github.com/codahale/chacha20",
+ "revision": "ec07b4f69a3f70b1dd2a8ad77230deb1ba5d6953",
+ "revisionTime": "2015-11-07T02:50:05Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "rcgVHpPL/iNmph28KP67c1UVmuM=",
+ "path": "github.com/ginuerzh/gosocks5",
+ "revision": "bc931b305d59cdf3d068eacff3c8d81536d3a39f",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-03T01:06:34Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "QooLgOqsl0ivXxYygSepzSRAtjQ=",
+ "path": "github.com/ginuerzh/gost",
+ "revision": "15a5d74b563e644a471fa42aab0a2876da6b1bb0",
+ "revisionTime": "2017-01-09T03:39:18Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "URsJa4y/sUUw/STmbeYx9EKqaYE=",
+ "path": "github.com/golang/glog",
+ "revision": "44145f04b68cf362d9c4df2182967c2275eaefed",
+ "revisionTime": "2014-09-23T20:47:00Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "d9PxF1XQGLMJZRct2R8qVM/eYlE=",
+ "path": "github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru",
+ "revision": "0a025b7e63adc15a622f29b0b2c4c3848243bbf6",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-13T22:13:03Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "9hffs0bAIU6CquiRhKQdzjHnKt0=",
+ "path": "github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru/simplelru",
+ "revision": "0a025b7e63adc15a622f29b0b2c4c3848243bbf6",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-13T22:13:03Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "/EgCTbjJkJh2yi9lqEgzmau8O4I=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/compress/snappy",
+ "revision": "1e658061989f47658e69492cf63a839630a25eba",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-20T15:14:30Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "iKPMvbAueGfdyHcWCgzwKzm8WVo=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/cpuid",
+ "revision": "09cded8978dc9e80714c4d85b0322337b0a1e5e0",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-03-02T07:53:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "BM6ZlNJmtKy3GBoWwg2X55gnZ4A=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/crc32",
+ "revision": "cb6bfca970f6908083f26f39a79009d608efd5cd",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-16T15:41:25Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "dwSGkUfh3A2h0VkXndzBX/27hVc=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/reedsolomon",
+ "revision": "c54154da9e35cab25232314cf69ab9d78447f9a5",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-12T19:31:07Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "fbae4URna3lp8RtTOutiXIO1JS0=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/aes12",
+ "revision": "8ee5b5610baca43b60ecfad586b3c40d92a96e0c",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-23T09:51:02Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "ne1X+frkx5fJcpz9FaZPuUZ7amM=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/fnv128a",
+ "revision": "393af48d391698c6ae4219566bfbdfef67269997",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-05-04T15:23:51Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "xbX/mARowOKpW3S1G8hmaDlWdp8=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "OA9E+y7g05x/mWJJHmA7oPxWKQo=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go-certificates",
+ "revision": "d2f86524cced5186554df90d92529757d22c1cb6",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-23T09:51:56Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "1+iOTf/w8VXGqQao0FMNEE2RFFg=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "8zoU6uLKP2Czs96VgmNMubNcWKk=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "vzBxE7JViWonmrSndgmRuye8ntA=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "CaOt7EZEuyWQ073FITB8qQfFswA=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "VvhIOTKtMkPZ7pdrCPHlDQI2wIw=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "IJDUjsrJP5dtHvxVNT32x4SQQVk=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "1DQTvvwcUUrmMKkN4ASjX5+iGqs=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "qp5LXpuvIAgW3BffRzHVZQk1WfE=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "ss57bkTclCnmt9fVosYie/ehkoo=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "j/A6Rfz4BWpt5rsR2j5kR0H2ZTI=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "ynJSWoF6v+3zMnh9R0QmmG6iGV8=",
+ "path": "github.com/pkg/errors",
+ "revision": "839d9e913e063e28dfd0e6c7b7512793e0a48be9",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-02T05:25:12Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "VrDrpS/tpn8nfuFCY51U4eH/Jg0=",
+ "path": "github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go/shadowsocks",
+ "revision": "5c9897ecdf623f385ccb8c2c78e32c5256961b41",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-06-15T15:25:08Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "JsJdKXhz87gWenMwBeejTOeNE7k=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/blowfish",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "TT1rac6kpQp2vz24m5yDGUNQ/QQ=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/cast5",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "dwOedwBJ1EIK9+S3t108Bx054Y8=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/curve25519",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "4D8hxMIaSDEW5pCQk22Xj4DcDh4=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/hkdf",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "1MGpGDQqnUoRpv7VEcQrXOBydXE=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "o5QDZYQhyiEt2jg1Fot34mR1rBg=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/salsa20",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "w8PESKJweP+BCAxCYPU1QC08qUU=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/salsa20/salsa",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "Iwv89z1aXYKaB936lnsmE2NcfqA=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/tea",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "/qXTeb4Dp6W5qlttwaN+Yur36+A=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/twofish",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "d37eTFvbbuPQcKt5vkgsx+6C4c0=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/xtea",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "tK8eFmQ0JeKpR3P0TjiGobzlIh0=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/bpf",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "UovsbmfW33+DGfUh1geZpGzIoVo=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/http2",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "HzuGD7AwgC0p1az1WAQnEFnEk98=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "GIGmSrYACByf5JDIP9ByBZksY80=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/idna",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "yRuyntx9a59ugMi5NlN4ST0XRcI=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/internal/iana",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "LVY0kRV5iwxDS3XQaBWxdzPemyc=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "yzxKtJnG6O34n0gsbnoceGhASdQ=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/ipv4",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "3xyuaSNmClqG4YWC7g0isQIbUTc=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/lex/httplex",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "G/v7O8ukxRnqPUrKYmf+niQ+JNU=",
+ "path": "gopkg.in/gorilla/websocket.v1",
+ "revision": "3ab3a8b8831546bd18fd182c20687ca853b2bb13",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-12-15T22:53:35Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "nkIlj9QTxHQ78Vb+VgjhXZ4rZ3E=",
+ "path": "gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2",
+ "revision": "6610d527ea5c4890cf593796ff8ff1f10486bb68",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-08T14:44:41Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "aIqXwA82JxLOXcgmuVSgcRqdJvU=",
+ "path": "gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1",
+ "revision": "9f2b528a60917e6446273926f4c676cac759d2b0",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-22T10:26:45Z"
+ }
+ ],
+ "rootPath": "github.com/ginuerzh/gost/cmd/gost"
+}
+
+[1]: https://godoc.org/github.com/xtaci/smux?status.svg
+[2]: https://godoc.org/github.com/xtaci/smux
+[3]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-MIT-blue.svg
+[4]: LICENSE
+[5]: https://travis-ci.org/xtaci/smux.svg?branch=master
+[6]: https://travis-ci.org/xtaci/smux
+[7]: https://goreportcard.com/badge/github.com/xtaci/smux
+[8]: https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/xtaci/smux
+[9]: https://codecov.io/gh/xtaci/smux/branch/master/graph/badge.svg
+[10]: https://codecov.io/gh/xtaci/smux
+
+## Introduction
+
+Smux (***S***imple ***MU***ltiple***X***ing) is a multiplexing library for Golang. It relies on an underlying connection to provide reliability and ordering, such as TCP or [KCP](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go), and provides stream-oriented multiplexing.
+
+## Features
+
+1. Tiny, less than 600 LOC.
+2. ***Token bucket*** controlled receiving, which provides smoother bandwidth graph(see picture below).
+3. Session-wide receive buffer, which is shared among streams.
+4. Minimized header(8Bytes), maximized payload.
+
+
+
+## Documentation
+
+For complete documentation, see the associated [Godoc](https://godoc.org/github.com/xtaci/smux).
+
+## Specification
+
+```
+VERSION(1B) | CMD(1B) | LENGTH(2B) | STREAMID(4B) | DATA(LENGTH)
+```
+
+## Usage
+
+The API of smux are mostly taken from [yamux](https://github.com/hashicorp/yamux)
+
+```go
+
+func client() {
+ // Get a TCP connection
+ conn, err := net.Dial(...)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Setup client side of smux
+ session, err := smux.Client(conn, nil)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Open a new stream
+ stream, err := session.OpenStream()
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Stream implements net.Conn
+ stream.Write([]byte("ping"))
+}
+
+func server() {
+ // Accept a TCP connection
+ conn, err := listener.Accept()
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Setup server side of smux
+ session, err := smux.Server(conn, nil)
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Accept a stream
+ stream, err := session.AcceptStream()
+ if err != nil {
+ panic(err)
+ }
+
+ // Listen for a message
+ buf := make([]byte, 4)
+ stream.Read(buf)
+}
+
+```
+
+## Status
+
+Beta
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/curve.jpg b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/curve.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3fc4863
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/curve.jpg differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/frame.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/frame.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..334fea3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/frame.go
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "fmt"
+)
+
+const (
+ version = 1
+)
+
+const ( // cmds
+ cmdSYN byte = iota // stream open
+ cmdRST // stream close
+ cmdPSH // data push
+ cmdNOP // no operation
+)
+
+const (
+ sizeOfVer = 1
+ sizeOfCmd = 1
+ sizeOfLength = 2
+ sizeOfSid = 4
+ headerSize = sizeOfVer + sizeOfCmd + sizeOfSid + sizeOfLength
+)
+
+// Frame defines a packet from or to be multiplexed into a single connection
+type Frame struct {
+ ver byte
+ cmd byte
+ sid uint32
+ data []byte
+}
+
+func newFrame(cmd byte, sid uint32) Frame {
+ return Frame{ver: version, cmd: cmd, sid: sid}
+}
+
+type rawHeader []byte
+
+func (h rawHeader) Version() byte {
+ return h[0]
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) Cmd() byte {
+ return h[1]
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) Length() uint16 {
+ return binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(h[2:])
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) StreamID() uint32 {
+ return binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(h[4:])
+}
+
+func (h rawHeader) String() string {
+ return fmt.Sprintf("Version:%d Cmd:%d StreamID:%d Length:%d",
+ h.Version(), h.Cmd(), h.StreamID(), h.Length())
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..afcf58b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.go
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "io"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+)
+
+// Config is used to tune the Smux session
+type Config struct {
+ // KeepAliveInterval is how often to send a NOP command to the remote
+ KeepAliveInterval time.Duration
+
+ // KeepAliveTimeout is how long the session
+ // will be closed if no data has arrived
+ KeepAliveTimeout time.Duration
+
+ // MaxFrameSize is used to control the maximum
+ // frame size to sent to the remote
+ MaxFrameSize int
+
+ // MaxReceiveBuffer is used to control the maximum
+ // number of data in the buffer pool
+ MaxReceiveBuffer int
+}
+
+// DefaultConfig is used to return a default configuration
+func DefaultConfig() *Config {
+ return &Config{
+ KeepAliveInterval: 10 * time.Second,
+ KeepAliveTimeout: 30 * time.Second,
+ MaxFrameSize: 4096,
+ MaxReceiveBuffer: 4194304,
+ }
+}
+
+// VerifyConfig is used to verify the sanity of configuration
+func VerifyConfig(config *Config) error {
+ if config.KeepAliveInterval == 0 {
+ return errors.New("keep-alive interval must be positive")
+ }
+ if config.KeepAliveTimeout < config.KeepAliveInterval {
+ return fmt.Errorf("keep-alive timeout must be larger than keep-alive interval")
+ }
+ if config.MaxFrameSize <= 0 {
+ return errors.New("max frame size must be positive")
+ }
+ if config.MaxFrameSize > 65535 {
+ return errors.New("max frame size must not be larger than 65535")
+ }
+ if config.MaxReceiveBuffer <= 0 {
+ return errors.New("max receive buffer must be positive")
+ }
+ return nil
+}
+
+// Server is used to initialize a new server-side connection.
+func Server(conn io.ReadWriteCloser, config *Config) (*Session, error) {
+ if config == nil {
+ config = DefaultConfig()
+ }
+ if err := VerifyConfig(config); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return newSession(config, conn, false), nil
+}
+
+// Client is used to initialize a new client-side connection.
+func Client(conn io.ReadWriteCloser, config *Config) (*Session, error) {
+ if config == nil {
+ config = DefaultConfig()
+ }
+
+ if err := VerifyConfig(config); err != nil {
+ return nil, err
+ }
+ return newSession(config, conn, true), nil
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.jpg b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dde2e11
Binary files /dev/null and b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/mux.jpg differ
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/session.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/session.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a06f2ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/session.go
@@ -0,0 +1,275 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "io"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+ "time"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+)
+
+const (
+ defaultAcceptBacklog = 1024
+)
+
+const (
+ errBrokenPipe = "broken pipe"
+ errConnReset = "connection reset by peer"
+ errInvalidProtocol = "invalid protocol version"
+)
+
+// Session defines a multiplexed connection for streams
+type Session struct {
+ conn io.ReadWriteCloser
+ writeLock sync.Mutex
+
+ config *Config
+ nextStreamID uint32 // next stream identifier
+
+ bucket int32 // token bucket
+ bucketCond *sync.Cond // used for waiting for tokens
+
+ streams map[uint32]*Stream // all streams in this session
+ streamLock sync.Mutex // locks streams
+
+ die chan struct{} // flag session has died
+ dieLock sync.Mutex
+ chAccepts chan *Stream
+
+ dataReady int32 // flag data has arrived
+}
+
+func newSession(config *Config, conn io.ReadWriteCloser, client bool) *Session {
+ s := new(Session)
+ s.die = make(chan struct{})
+ s.conn = conn
+ s.config = config
+ s.streams = make(map[uint32]*Stream)
+ s.chAccepts = make(chan *Stream, defaultAcceptBacklog)
+ s.bucket = int32(config.MaxReceiveBuffer)
+ s.bucketCond = sync.NewCond(&sync.Mutex{})
+ if client {
+ s.nextStreamID = 1
+ } else {
+ s.nextStreamID = 2
+ }
+ go s.recvLoop()
+ go s.keepalive()
+ return s
+}
+
+// OpenStream is used to create a new stream
+func (s *Session) OpenStream() (*Stream, error) {
+ if s.IsClosed() {
+ return nil, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ }
+
+ sid := atomic.AddUint32(&s.nextStreamID, 2)
+ stream := newStream(sid, s.config.MaxFrameSize, s)
+
+ if _, err := s.writeFrame(newFrame(cmdSYN, sid)); err != nil {
+ return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "writeFrame")
+ }
+
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ s.streams[sid] = stream
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ return stream, nil
+}
+
+// AcceptStream is used to block until the next available stream
+// is ready to be accepted.
+func (s *Session) AcceptStream() (*Stream, error) {
+ select {
+ case stream := <-s.chAccepts:
+ return stream, nil
+ case <-s.die:
+ return nil, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ }
+}
+
+// Close is used to close the session and all streams.
+func (s *Session) Close() (err error) {
+ s.dieLock.Lock()
+ defer s.dieLock.Unlock()
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ close(s.die)
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ for k := range s.streams {
+ s.streams[k].sessionClose()
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ s.bucketCond.Signal()
+ return s.conn.Close()
+ }
+}
+
+// IsClosed does a safe check to see if we have shutdown
+func (s *Session) IsClosed() bool {
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return true
+ default:
+ return false
+ }
+}
+
+// NumStreams returns the number of currently open streams
+func (s *Session) NumStreams() int {
+ if s.IsClosed() {
+ return 0
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ defer s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ return len(s.streams)
+}
+
+// notify the session that a stream has closed
+func (s *Session) streamClosed(sid uint32) {
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if n := s.streams[sid].recycleTokens(); n > 0 { // return remaining tokens to the bucket
+ if atomic.AddInt32(&s.bucket, int32(n)) > 0 {
+ s.bucketCond.Signal()
+ }
+ }
+ delete(s.streams, sid)
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+}
+
+// returnTokens is called by stream to return token after read
+func (s *Session) returnTokens(n int) {
+ if atomic.AddInt32(&s.bucket, int32(n)) > 0 {
+ s.bucketCond.Signal()
+ }
+}
+
+// session read a frame from underlying connection
+// it's data is pointed to the input buffer
+func (s *Session) readFrame(buffer []byte) (f Frame, err error) {
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(s.conn, buffer[:headerSize]); err != nil {
+ return f, errors.Wrap(err, "readFrame")
+ }
+
+ dec := rawHeader(buffer)
+ if dec.Version() != version {
+ return f, errors.New(errInvalidProtocol)
+ }
+
+ f.ver = dec.Version()
+ f.cmd = dec.Cmd()
+ f.sid = dec.StreamID()
+ if length := dec.Length(); length > 0 {
+ if _, err := io.ReadFull(s.conn, buffer[headerSize:headerSize+length]); err != nil {
+ return f, errors.Wrap(err, "readFrame")
+ }
+ f.data = buffer[headerSize : headerSize+length]
+ }
+ return f, nil
+}
+
+// recvLoop keeps on reading from underlying connection if tokens are available
+func (s *Session) recvLoop() {
+ buffer := make([]byte, (1<<16)+headerSize)
+ for {
+ s.bucketCond.L.Lock()
+ for atomic.LoadInt32(&s.bucket) <= 0 && !s.IsClosed() {
+ s.bucketCond.Wait()
+ }
+ s.bucketCond.L.Unlock()
+
+ if s.IsClosed() {
+ return
+ }
+
+ if f, err := s.readFrame(buffer); err == nil {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.dataReady, 1)
+
+ switch f.cmd {
+ case cmdNOP:
+ case cmdSYN:
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if _, ok := s.streams[f.sid]; !ok {
+ stream := newStream(f.sid, s.config.MaxFrameSize, s)
+ s.streams[f.sid] = stream
+ select {
+ case s.chAccepts <- stream:
+ case <-s.die:
+ }
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ case cmdRST:
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if stream, ok := s.streams[f.sid]; ok {
+ stream.markRST()
+ stream.notifyReadEvent()
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ case cmdPSH:
+ s.streamLock.Lock()
+ if stream, ok := s.streams[f.sid]; ok {
+ atomic.AddInt32(&s.bucket, -int32(len(f.data)))
+ stream.pushBytes(f.data)
+ stream.notifyReadEvent()
+ }
+ s.streamLock.Unlock()
+ default:
+ s.Close()
+ return
+ }
+ } else {
+ s.Close()
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+func (s *Session) keepalive() {
+ tickerPing := time.NewTicker(s.config.KeepAliveInterval)
+ tickerTimeout := time.NewTicker(s.config.KeepAliveTimeout)
+ defer tickerPing.Stop()
+ defer tickerTimeout.Stop()
+ for {
+ select {
+ case <-tickerPing.C:
+ s.writeFrame(newFrame(cmdNOP, 0))
+ s.bucketCond.Signal() // force a signal to the recvLoop
+ case <-tickerTimeout.C:
+ if !atomic.CompareAndSwapInt32(&s.dataReady, 1, 0) {
+ s.Close()
+ return
+ }
+ case <-s.die:
+ return
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// writeFrame writes the frame to the underlying connection
+// and returns the number of bytes written if successful
+func (s *Session) writeFrame(f Frame) (n int, err error) {
+ buf := make([]byte, headerSize+len(f.data))
+ buf[0] = f.ver
+ buf[1] = f.cmd
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(buf[2:], uint16(len(f.data)))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(buf[4:], f.sid)
+ copy(buf[headerSize:], f.data)
+
+ s.writeLock.Lock()
+ n, err = s.conn.Write(buf)
+ s.writeLock.Unlock()
+ return n, err
+}
+
+// writeBinary writes the byte slice to the underlying connection
+func (s *Session) writeBinary(bts []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ s.writeLock.Lock()
+ n, err = s.conn.Write(bts)
+ s.writeLock.Unlock()
+ return n, err
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/stream.go b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/stream.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8c44dd8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1/stream.go
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
+package smux
+
+import (
+ "bytes"
+ "encoding/binary"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+
+ "github.com/pkg/errors"
+)
+
+// Stream implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+type Stream struct {
+ id uint32
+ rstflag int32
+ sess *Session
+ buffer bytes.Buffer
+ bufferLock sync.Mutex
+ frameSize int
+ chReadEvent chan struct{} // notify a read event
+ die chan struct{} // flag the stream has closed
+ dieLock sync.Mutex
+}
+
+// newStream initiates a Stream struct
+func newStream(id uint32, frameSize int, sess *Session) *Stream {
+ s := new(Stream)
+ s.id = id
+ s.chReadEvent = make(chan struct{}, 1)
+ s.frameSize = frameSize
+ s.sess = sess
+ s.die = make(chan struct{})
+ return s
+}
+
+// Read implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+func (s *Stream) Read(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+READ:
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return 0, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ }
+
+ s.bufferLock.Lock()
+ n, err = s.buffer.Read(b)
+ s.bufferLock.Unlock()
+
+ if n > 0 {
+ s.sess.returnTokens(n)
+ return n, nil
+ } else if atomic.LoadInt32(&s.rstflag) == 1 {
+ _ = s.Close()
+ return 0, errors.New(errConnReset)
+ }
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.chReadEvent:
+ goto READ
+ case <-s.die:
+ return 0, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ }
+}
+
+// Write implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+func (s *Stream) Write(b []byte) (n int, err error) {
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return 0, errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ }
+
+ frames := s.split(b, cmdPSH, s.id)
+ // preallocate buffer
+ buffer := make([]byte, len(frames)*headerSize+len(b))
+ bts := buffer
+
+ // combine frames into a large blob
+ for k := range frames {
+ bts[0] = version
+ bts[1] = frames[k].cmd
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(bts[2:], uint16(len(frames[k].data)))
+ binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(bts[4:], frames[k].sid)
+ copy(bts[headerSize:], frames[k].data)
+ bts = bts[len(frames[k].data)+headerSize:]
+ }
+
+ if _, err = s.sess.writeBinary(buffer); err != nil {
+ return 0, err
+ }
+ return len(b), nil
+}
+
+// Close implements io.ReadWriteCloser
+func (s *Stream) Close() error {
+ s.dieLock.Lock()
+ defer s.dieLock.Unlock()
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ return errors.New(errBrokenPipe)
+ default:
+ close(s.die)
+ s.sess.streamClosed(s.id)
+ _, err := s.sess.writeFrame(newFrame(cmdRST, s.id))
+ return err
+ }
+}
+
+// session closes the stream
+func (s *Stream) sessionClose() {
+ s.dieLock.Lock()
+ defer s.dieLock.Unlock()
+
+ select {
+ case <-s.die:
+ default:
+ close(s.die)
+ }
+}
+
+// pushBytes a slice into buffer
+func (s *Stream) pushBytes(p []byte) {
+ s.bufferLock.Lock()
+ s.buffer.Write(p)
+ s.bufferLock.Unlock()
+}
+
+// recycleTokens transform remaining bytes to tokens(will truncate buffer)
+func (s *Stream) recycleTokens() (n int) {
+ s.bufferLock.Lock()
+ n = s.buffer.Len()
+ s.buffer.Reset()
+ s.bufferLock.Unlock()
+ return
+}
+
+// split large byte buffer into smaller frames, reference only
+func (s *Stream) split(bts []byte, cmd byte, sid uint32) []Frame {
+ var frames []Frame
+ for len(bts) > s.frameSize {
+ frame := newFrame(cmd, sid)
+ frame.data = bts[:s.frameSize]
+ bts = bts[s.frameSize:]
+ frames = append(frames, frame)
+ }
+ if len(bts) > 0 {
+ frame := newFrame(cmd, sid)
+ frame.data = bts
+ frames = append(frames, frame)
+ }
+ return frames
+}
+
+// notify read event
+func (s *Stream) notifyReadEvent() {
+ select {
+ case s.chReadEvent <- struct{}{}:
+ default:
+ }
+}
+
+// mark this stream has been reset
+func (s *Stream) markRST() {
+ atomic.StoreInt32(&s.rstflag, 1)
+}
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/vendor.json b/cmd/gost/vendor/vendor.json
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1a173ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/vendor.json
@@ -0,0 +1,289 @@
+{
+ "comment": "",
+ "ignore": "test",
+ "package": [
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "QPs3L3mjPoi+a9GJCjW8HhyJczM=",
+ "path": "github.com/codahale/chacha20",
+ "revision": "ec07b4f69a3f70b1dd2a8ad77230deb1ba5d6953",
+ "revisionTime": "2015-11-07T02:50:05Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "rcgVHpPL/iNmph28KP67c1UVmuM=",
+ "path": "github.com/ginuerzh/gosocks5",
+ "revision": "bc931b305d59cdf3d068eacff3c8d81536d3a39f",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-03T01:06:34Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "QooLgOqsl0ivXxYygSepzSRAtjQ=",
+ "path": "github.com/ginuerzh/gost",
+ "revision": "15a5d74b563e644a471fa42aab0a2876da6b1bb0",
+ "revisionTime": "2017-01-09T03:39:18Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "URsJa4y/sUUw/STmbeYx9EKqaYE=",
+ "path": "github.com/golang/glog",
+ "revision": "44145f04b68cf362d9c4df2182967c2275eaefed",
+ "revisionTime": "2014-09-23T20:47:00Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "d9PxF1XQGLMJZRct2R8qVM/eYlE=",
+ "path": "github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru",
+ "revision": "0a025b7e63adc15a622f29b0b2c4c3848243bbf6",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-13T22:13:03Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "9hffs0bAIU6CquiRhKQdzjHnKt0=",
+ "path": "github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru/simplelru",
+ "revision": "0a025b7e63adc15a622f29b0b2c4c3848243bbf6",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-13T22:13:03Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "/EgCTbjJkJh2yi9lqEgzmau8O4I=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/compress/snappy",
+ "revision": "1e658061989f47658e69492cf63a839630a25eba",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-20T15:14:30Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "iKPMvbAueGfdyHcWCgzwKzm8WVo=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/cpuid",
+ "revision": "09cded8978dc9e80714c4d85b0322337b0a1e5e0",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-03-02T07:53:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "BM6ZlNJmtKy3GBoWwg2X55gnZ4A=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/crc32",
+ "revision": "cb6bfca970f6908083f26f39a79009d608efd5cd",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-16T15:41:25Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "dwSGkUfh3A2h0VkXndzBX/27hVc=",
+ "path": "github.com/klauspost/reedsolomon",
+ "revision": "c54154da9e35cab25232314cf69ab9d78447f9a5",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-12T19:31:07Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "fbae4URna3lp8RtTOutiXIO1JS0=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/aes12",
+ "revision": "8ee5b5610baca43b60ecfad586b3c40d92a96e0c",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-23T09:51:02Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "ne1X+frkx5fJcpz9FaZPuUZ7amM=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/fnv128a",
+ "revision": "393af48d391698c6ae4219566bfbdfef67269997",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-05-04T15:23:51Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "xbX/mARowOKpW3S1G8hmaDlWdp8=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "OA9E+y7g05x/mWJJHmA7oPxWKQo=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go-certificates",
+ "revision": "d2f86524cced5186554df90d92529757d22c1cb6",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-08-23T09:51:56Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "1+iOTf/w8VXGqQao0FMNEE2RFFg=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/ackhandler",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "8zoU6uLKP2Czs96VgmNMubNcWKk=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/congestion",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "vzBxE7JViWonmrSndgmRuye8ntA=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/crypto",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "CaOt7EZEuyWQ073FITB8qQfFswA=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/flowcontrol",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "VvhIOTKtMkPZ7pdrCPHlDQI2wIw=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/frames",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "IJDUjsrJP5dtHvxVNT32x4SQQVk=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/h2quic",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "1DQTvvwcUUrmMKkN4ASjX5+iGqs=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/handshake",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "qp5LXpuvIAgW3BffRzHVZQk1WfE=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/protocol",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "ss57bkTclCnmt9fVosYie/ehkoo=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/qerr",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "j/A6Rfz4BWpt5rsR2j5kR0H2ZTI=",
+ "path": "github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go/utils",
+ "revision": "ef977ee0591f72543f8323cd12a585f5406ff971",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-14T09:35:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "ynJSWoF6v+3zMnh9R0QmmG6iGV8=",
+ "path": "github.com/pkg/errors",
+ "revision": "839d9e913e063e28dfd0e6c7b7512793e0a48be9",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-02T05:25:12Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "VrDrpS/tpn8nfuFCY51U4eH/Jg0=",
+ "path": "github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go/shadowsocks",
+ "revision": "5c9897ecdf623f385ccb8c2c78e32c5256961b41",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-06-15T15:25:08Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "JsJdKXhz87gWenMwBeejTOeNE7k=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/blowfish",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "TT1rac6kpQp2vz24m5yDGUNQ/QQ=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/cast5",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "dwOedwBJ1EIK9+S3t108Bx054Y8=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/curve25519",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "4D8hxMIaSDEW5pCQk22Xj4DcDh4=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/hkdf",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "1MGpGDQqnUoRpv7VEcQrXOBydXE=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/pbkdf2",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "o5QDZYQhyiEt2jg1Fot34mR1rBg=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/salsa20",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "w8PESKJweP+BCAxCYPU1QC08qUU=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/salsa20/salsa",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "Iwv89z1aXYKaB936lnsmE2NcfqA=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/tea",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "/qXTeb4Dp6W5qlttwaN+Yur36+A=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/twofish",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "d37eTFvbbuPQcKt5vkgsx+6C4c0=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/crypto/xtea",
+ "revision": "1150b8bd09e53aea1d415621adae9bad665061a1",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-21T22:59:10Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "tK8eFmQ0JeKpR3P0TjiGobzlIh0=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/bpf",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "UovsbmfW33+DGfUh1geZpGzIoVo=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/http2",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "HzuGD7AwgC0p1az1WAQnEFnEk98=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/http2/hpack",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "GIGmSrYACByf5JDIP9ByBZksY80=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/idna",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "yRuyntx9a59ugMi5NlN4ST0XRcI=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/internal/iana",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "LVY0kRV5iwxDS3XQaBWxdzPemyc=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/internal/netreflect",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "yzxKtJnG6O34n0gsbnoceGhASdQ=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/ipv4",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "3xyuaSNmClqG4YWC7g0isQIbUTc=",
+ "path": "golang.org/x/net/lex/httplex",
+ "revision": "65dfc08770ce66f74becfdff5f8ab01caef4e946",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-10-24T22:38:16Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "G/v7O8ukxRnqPUrKYmf+niQ+JNU=",
+ "path": "gopkg.in/gorilla/websocket.v1",
+ "revision": "3ab3a8b8831546bd18fd182c20687ca853b2bb13",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-12-15T22:53:35Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "nkIlj9QTxHQ78Vb+VgjhXZ4rZ3E=",
+ "path": "gopkg.in/xtaci/kcp-go.v2",
+ "revision": "6610d527ea5c4890cf593796ff8ff1f10486bb68",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-08T14:44:41Z"
+ },
+ {
+ "checksumSHA1": "aIqXwA82JxLOXcgmuVSgcRqdJvU=",
+ "path": "gopkg.in/xtaci/smux.v1",
+ "revision": "9f2b528a60917e6446273926f4c676cac759d2b0",
+ "revisionTime": "2016-09-22T10:26:45Z"
+ }
+ ],
+ "rootPath": "github.com/ginuerzh/gost/cmd/gost"
+}
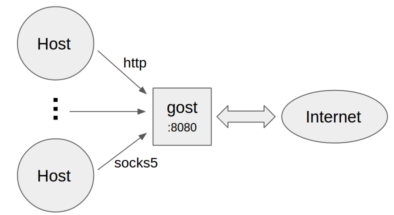 +
+* 作为标准HTTP/SOCKS5代理
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080
+```
+
+* 设置代理认证信息
+```bash
+gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
+```
+
+* 多组认证信息
+```bash
+gost -L=localhost:8080?secrets=secrets.txt
+```
+
+通过secrets参数可以为HTTP/SOCKS5代理设置多组认证信息,格式为:
+```plain
+# username password
+
+test001 123456
+test002 12345678
+```
+
+* 多端口监听
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
+```
+
+#### 设置转发代理
+
+
+
+* 作为标准HTTP/SOCKS5代理
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080
+```
+
+* 设置代理认证信息
+```bash
+gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
+```
+
+* 多组认证信息
+```bash
+gost -L=localhost:8080?secrets=secrets.txt
+```
+
+通过secrets参数可以为HTTP/SOCKS5代理设置多组认证信息,格式为:
+```plain
+# username password
+
+test001 123456
+test002 12345678
+```
+
+* 多端口监听
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
+```
+
+#### 设置转发代理
+
+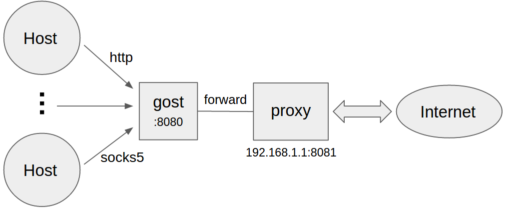 +```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+* 转发代理认证
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+#### 设置多级转发代理(代理链)
+
+
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+* 转发代理认证
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+#### 设置多级转发代理(代理链)
+
+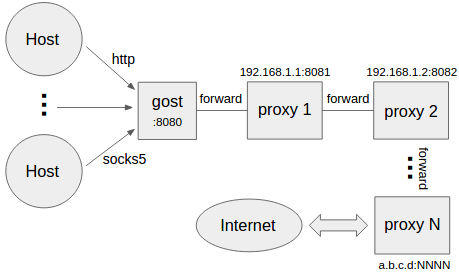 +```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
+```
+gost按照-F设置的顺序通过代理链将请求最终转发给a.b.c.d:NNNN处理,每一个转发代理可以是任意HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks类型代理。
+
+#### 本地端口转发(TCP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=...
+```
+将本地TCP端口2222上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:22上。
+
+#### 本地端口转发(UDP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
+```
+将本地UDP端口5353上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:53上。
+
+**注:** 转发UDP数据时,如果有代理链,则代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须是gost SOCKS5类型代理。
+
+#### 远程端口转发(TCP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+将172.24.10.1:2222上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:22上。
+
+#### 远程端口转发(UDP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+将172.24.10.1:5353上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:53上。
+
+**注:** 若要使用远程端口转发功能,代理链不能为空(至少要设置一个-F参数),且代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须是gost SOCKS5类型代理。
+
+#### HTTP2
+gost的HTTP2支持两种模式并自适应:
+* 作为标准的HTTP2代理,并向下兼容HTTPS代理。
+* 作为transport(类似于wss),传输其他协议。
+
+**注:** gost的代理链仅支持一个HTTP2代理节点,采用就近原则,会将第一个遇到的HTTP2代理节点视为HTTP2代理,其他HTTP2代理节点则被视为HTTPS代理。
+
+#### QUIC
+gost对QUIC的支持是基于[quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go)库。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=quic://:6121
+```
+
+客户端(Chrome):
+```bash
+chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
+```
+
+**注:** 由于Chrome自身的限制,目前只能通过QUIC访问HTTP网站,无法访问HTTPS网站。
+
+#### KCP
+gost对KCP的支持是基于[kcp-go](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go)和[kcptun](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun)库。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=kcp://:8388
+```
+
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388
+```
+
+或者手动指定加密方法和密码(手动指定的加密方法和密码会覆盖配置文件中的相应值)
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=kcp://aes:123456@:8388
+```
+
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://aes:123456@server_ip:8388
+```
+
+gost会自动加载当前工作目录中的kcp.json(如果存在)配置文件,或者可以手动通过参数指定配置文件路径:
+```bash
+gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
+```
+
+**注:** 客户端若要开启KCP转发,当且仅当代理链不为空且首个代理节点(第一个-F参数)为kcp类型。
+当KCP转发开启,代理链中的其他代理节点将被忽略。
+
+#### 透明代理
+基于iptables的透明代理。
+
+```bash
+gost -L=redirect://:12345 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+加密机制
+------
+#### HTTP
+对于HTTP可以使用TLS加密整个通讯过程,即HTTPS代理:
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=http+tls://:443
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### HTTP2
+gost仅支持使用TLS加密的HTTP2协议,不支持明文HTTP2传输。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### SOCKS5
+gost支持标准SOCKS5协议的no-auth(0x00)和user/pass(0x02)方法,并在此基础上扩展了两个:tls(0x80)和tls-auth(0x82),用于数据加密。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=socks://:1080
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
+```
+
+如果两端都是gost(如上)则数据传输会被加密(协商使用tls或tls-auth方法),否则使用标准SOCKS5进行通讯(no-auth或user/pass方法)。
+
+**注:** 如果transport已经支持加密(wss, tls, http2),则SOCKS5不会再使用加密方法,防止不必要的双重加密。
+
+#### Shadowsocks
+gost对shadowsocks的支持是基于[shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go)库。
+
+服务端(可以通过ota参数开启OTA模式):
+```bash
+gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338?ota=1
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
+```
+
+#### TLS
+gost内置了TLS证书,如果需要使用其他TLS证书,有两种方法:
+* 在gost运行目录放置cert.pem(公钥)和key.pem(私钥)两个文件即可,gost会自动加载运行目录下的cert.pem和key.pem文件。
+* 使用参数指定证书文件路径:
+```bash
+gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
+```
+
+SOCKS5 UDP数据处理
+------
+#### 不设置转发代理
+
+
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
+```
+gost按照-F设置的顺序通过代理链将请求最终转发给a.b.c.d:NNNN处理,每一个转发代理可以是任意HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks类型代理。
+
+#### 本地端口转发(TCP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=...
+```
+将本地TCP端口2222上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:22上。
+
+#### 本地端口转发(UDP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
+```
+将本地UDP端口5353上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:53上。
+
+**注:** 转发UDP数据时,如果有代理链,则代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须是gost SOCKS5类型代理。
+
+#### 远程端口转发(TCP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+将172.24.10.1:2222上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:22上。
+
+#### 远程端口转发(UDP)
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+将172.24.10.1:5353上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:53上。
+
+**注:** 若要使用远程端口转发功能,代理链不能为空(至少要设置一个-F参数),且代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须是gost SOCKS5类型代理。
+
+#### HTTP2
+gost的HTTP2支持两种模式并自适应:
+* 作为标准的HTTP2代理,并向下兼容HTTPS代理。
+* 作为transport(类似于wss),传输其他协议。
+
+**注:** gost的代理链仅支持一个HTTP2代理节点,采用就近原则,会将第一个遇到的HTTP2代理节点视为HTTP2代理,其他HTTP2代理节点则被视为HTTPS代理。
+
+#### QUIC
+gost对QUIC的支持是基于[quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go)库。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=quic://:6121
+```
+
+客户端(Chrome):
+```bash
+chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
+```
+
+**注:** 由于Chrome自身的限制,目前只能通过QUIC访问HTTP网站,无法访问HTTPS网站。
+
+#### KCP
+gost对KCP的支持是基于[kcp-go](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go)和[kcptun](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun)库。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=kcp://:8388
+```
+
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388
+```
+
+或者手动指定加密方法和密码(手动指定的加密方法和密码会覆盖配置文件中的相应值)
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=kcp://aes:123456@:8388
+```
+
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://aes:123456@server_ip:8388
+```
+
+gost会自动加载当前工作目录中的kcp.json(如果存在)配置文件,或者可以手动通过参数指定配置文件路径:
+```bash
+gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
+```
+
+**注:** 客户端若要开启KCP转发,当且仅当代理链不为空且首个代理节点(第一个-F参数)为kcp类型。
+当KCP转发开启,代理链中的其他代理节点将被忽略。
+
+#### 透明代理
+基于iptables的透明代理。
+
+```bash
+gost -L=redirect://:12345 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+加密机制
+------
+#### HTTP
+对于HTTP可以使用TLS加密整个通讯过程,即HTTPS代理:
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=http+tls://:443
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### HTTP2
+gost仅支持使用TLS加密的HTTP2协议,不支持明文HTTP2传输。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### SOCKS5
+gost支持标准SOCKS5协议的no-auth(0x00)和user/pass(0x02)方法,并在此基础上扩展了两个:tls(0x80)和tls-auth(0x82),用于数据加密。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=socks://:1080
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
+```
+
+如果两端都是gost(如上)则数据传输会被加密(协商使用tls或tls-auth方法),否则使用标准SOCKS5进行通讯(no-auth或user/pass方法)。
+
+**注:** 如果transport已经支持加密(wss, tls, http2),则SOCKS5不会再使用加密方法,防止不必要的双重加密。
+
+#### Shadowsocks
+gost对shadowsocks的支持是基于[shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go)库。
+
+服务端(可以通过ota参数开启OTA模式):
+```bash
+gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338?ota=1
+```
+客户端:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
+```
+
+#### TLS
+gost内置了TLS证书,如果需要使用其他TLS证书,有两种方法:
+* 在gost运行目录放置cert.pem(公钥)和key.pem(私钥)两个文件即可,gost会自动加载运行目录下的cert.pem和key.pem文件。
+* 使用参数指定证书文件路径:
+```bash
+gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
+```
+
+SOCKS5 UDP数据处理
+------
+#### 不设置转发代理
+
+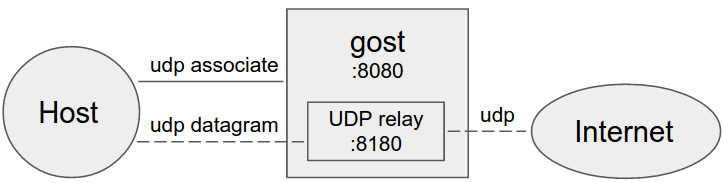 +
+gost作为标准SOCKS5代理处理UDP数据
+
+#### 设置转发代理
+
+
+
+gost作为标准SOCKS5代理处理UDP数据
+
+#### 设置转发代理
+
+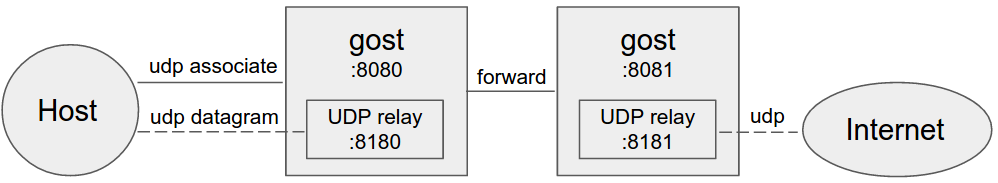 +
+#### 设置多个转发代理(代理链)
+
+
+
+#### 设置多个转发代理(代理链)
+
+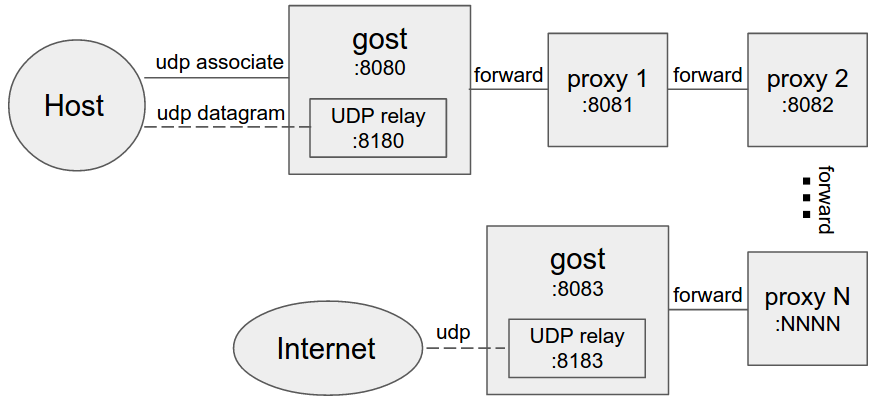 +
+当设置转发代理时,gost会使用UDP-over-TCP方式转发UDP数据。proxy1 - proxyN可以为任意HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks类型代理。
+
+限制条件
+------
+代理链中的HTTP代理节点必须支持CONNECT方法。
+
+如果要转发SOCKS5的BIND和UDP请求,代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须支持gost SOCKS5类型代理。
+
+
+
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/ginuerzh/gost/README_en.md b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/ginuerzh/gost/README_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..42c00ac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/ginuerzh/gost/README_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,341 @@
+gost - GO Simple Tunnel
+======
+
+### A simple security tunnel written in Golang
+
+Features
+------
+* Listening on multiple ports
+* Multi-level forward proxy - proxy chain
+* Standard HTTP/HTTPS/SOCKS5 proxy protocols support
+* TLS encryption via negotiation support for SOCKS5 proxy
+* Tunnel UDP over TCP
+* Shadowsocks protocol support (OTA: 2.2+)
+* Local/remote port forwarding (2.1+)
+* HTTP 2.0 support (2.2+)
+* Experimental QUIC support (2.3+)
+* KCP protocol support (2.3+)
+* Transparent proxy (2.3+)
+
+Binary file download:https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases
+
+Google group: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/go-gost
+
+Gost and other proxy services are considered to be proxy nodes,
+gost can handle the request itself, or forward the request to any one or more proxy nodes.
+
+Parameter Description
+------
+#### Proxy and proxy chain
+
+Effective for the -L and -F parameters
+
+```bash
+[scheme://][user:pass@host]:port
+```
+scheme can be divided into two parts: protocol+transport
+
+protocol: proxy protocol types (http, socks5, shadowsocks),
+transport: data transmission mode (ws, wss, tls, http2, quic, kcp), may be used in any combination or individually:
+
+> http - standard HTTP proxy: http://:8080
+
+> http+tls - standard HTTPS proxy (may need to provide a trusted certificate): http+tls://:443
+
+> http2 - HTTP2 proxy and backwards-compatible with HTTPS proxy: http2://:443
+
+> socks - standard SOCKS5 proxy: socks://:1080
+
+> socks+wss - SOCKS5 over websocket: socks+wss://:1080
+
+> tls - HTTPS/SOCKS5 over tls: tls://:443
+
+> ss - standard shadowsocks proxy, ss://aes-256-cfb:123456@:8338
+
+> quic - standard QUIC proxy, quic://:6121
+
+> kcp - standard KCP tunnel,kcp://:8388 or kcp://aes:123456@:8388
+
+> redirect - transparent proxy,redirect://:12345
+
+#### Port forwarding
+
+Effective for the -L parameter
+
+```bash
+scheme://[bind_address]:port/[host]:hostport
+```
+> scheme - forward mode, local: tcp, udp; remote: rtcp, rudp
+
+> bind_address:port - local/remote binding address
+
+> host:hostport - target address
+
+#### Configuration file
+
+> -C : specifies the configuration file path
+
+The configuration file is in standard JSON format:
+```json
+{
+ "ServeNodes": [
+ ":8080",
+ "ss://chacha20:12345678@:8338"
+ ],
+ "ChainNodes": [
+ "http://192.168.1.1:8080",
+ "https://10.0.2.1:443"
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+ServeNodes is equivalent to the -L parameter, ChainNodes is equivalent to the -F parameter.
+
+#### Logging
+
+> -logtostderr : log to console
+
+> -v=3 : log level (1-5),The higher the level, the more detailed the log (level 5 will enable HTTP2 debug)
+
+> -log_dir=/log/dir/path : log to directory /log/dir/path
+
+Usage
+------
+#### No forward proxy
+
+
+
+当设置转发代理时,gost会使用UDP-over-TCP方式转发UDP数据。proxy1 - proxyN可以为任意HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks类型代理。
+
+限制条件
+------
+代理链中的HTTP代理节点必须支持CONNECT方法。
+
+如果要转发SOCKS5的BIND和UDP请求,代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须支持gost SOCKS5类型代理。
+
+
+
diff --git a/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/ginuerzh/gost/README_en.md b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/ginuerzh/gost/README_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..42c00ac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/cmd/gost/vendor/github.com/ginuerzh/gost/README_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,341 @@
+gost - GO Simple Tunnel
+======
+
+### A simple security tunnel written in Golang
+
+Features
+------
+* Listening on multiple ports
+* Multi-level forward proxy - proxy chain
+* Standard HTTP/HTTPS/SOCKS5 proxy protocols support
+* TLS encryption via negotiation support for SOCKS5 proxy
+* Tunnel UDP over TCP
+* Shadowsocks protocol support (OTA: 2.2+)
+* Local/remote port forwarding (2.1+)
+* HTTP 2.0 support (2.2+)
+* Experimental QUIC support (2.3+)
+* KCP protocol support (2.3+)
+* Transparent proxy (2.3+)
+
+Binary file download:https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases
+
+Google group: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/go-gost
+
+Gost and other proxy services are considered to be proxy nodes,
+gost can handle the request itself, or forward the request to any one or more proxy nodes.
+
+Parameter Description
+------
+#### Proxy and proxy chain
+
+Effective for the -L and -F parameters
+
+```bash
+[scheme://][user:pass@host]:port
+```
+scheme can be divided into two parts: protocol+transport
+
+protocol: proxy protocol types (http, socks5, shadowsocks),
+transport: data transmission mode (ws, wss, tls, http2, quic, kcp), may be used in any combination or individually:
+
+> http - standard HTTP proxy: http://:8080
+
+> http+tls - standard HTTPS proxy (may need to provide a trusted certificate): http+tls://:443
+
+> http2 - HTTP2 proxy and backwards-compatible with HTTPS proxy: http2://:443
+
+> socks - standard SOCKS5 proxy: socks://:1080
+
+> socks+wss - SOCKS5 over websocket: socks+wss://:1080
+
+> tls - HTTPS/SOCKS5 over tls: tls://:443
+
+> ss - standard shadowsocks proxy, ss://aes-256-cfb:123456@:8338
+
+> quic - standard QUIC proxy, quic://:6121
+
+> kcp - standard KCP tunnel,kcp://:8388 or kcp://aes:123456@:8388
+
+> redirect - transparent proxy,redirect://:12345
+
+#### Port forwarding
+
+Effective for the -L parameter
+
+```bash
+scheme://[bind_address]:port/[host]:hostport
+```
+> scheme - forward mode, local: tcp, udp; remote: rtcp, rudp
+
+> bind_address:port - local/remote binding address
+
+> host:hostport - target address
+
+#### Configuration file
+
+> -C : specifies the configuration file path
+
+The configuration file is in standard JSON format:
+```json
+{
+ "ServeNodes": [
+ ":8080",
+ "ss://chacha20:12345678@:8338"
+ ],
+ "ChainNodes": [
+ "http://192.168.1.1:8080",
+ "https://10.0.2.1:443"
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+ServeNodes is equivalent to the -L parameter, ChainNodes is equivalent to the -F parameter.
+
+#### Logging
+
+> -logtostderr : log to console
+
+> -v=3 : log level (1-5),The higher the level, the more detailed the log (level 5 will enable HTTP2 debug)
+
+> -log_dir=/log/dir/path : log to directory /log/dir/path
+
+Usage
+------
+#### No forward proxy
+
+