diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 33b92f6..df417b2 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -18,9 +18,9 @@ gost - GO Simple Tunnel
* 可设置转发代理,支持多级转发(代理链)
* 支持标准HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4(A)/SOCKS5代理协议
* [支持多种隧道类型](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/configuration/)
-* SOCKS5代理支持TLS协商加密
-* Tunnel UDP over TCP
-* TCP透明代理
+* [SOCKS5代理支持TLS协商加密](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/socks/)
+* [Tunnel UDP over TCP](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/socks/)
+* [TCP透明代理](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/redirect/)
* [本地/远程TCP/UDP端口转发](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/port-forwarding/)
* [支持Shadowsocks(TCP/UDP)协议](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/ss/)
* [支持SNI代理](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/sni/)
@@ -241,31 +241,40 @@ gost -L=:8888 -F='obfs4://server_ip:443?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdV
加密机制
------
+
#### HTTP
+
对于HTTP可以使用TLS加密整个通讯过程,即HTTPS代理:
服务端:
+
```bash
gost -L=https://:443
```
客户端:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
```
#### HTTP2
+
gost的HTTP2代理模式仅支持使用TLS加密的HTTP2协议,不支持明文HTTP2传输。
gost的HTTP2通道模式支持加密(h2)和明文(h2c)两种模式。
#### SOCKS5
+
gost支持标准SOCKS5协议的no-auth(0x00)和user/pass(0x02)方法,并在此基础上扩展了两个:tls(0x80)和tls-auth(0x82),用于数据加密。
服务端:
+
```bash
gost -L=socks5://:1080
```
+
客户端:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks5://server_ip:1080
```
@@ -276,10 +285,12 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=socks5://server_ip:1080
gost对shadowsocks的支持是基于[shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go)库。
服务端:
+
```bash
gost -L=ss://chacha20:123456@:8338
```
客户端:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://chacha20:123456@server_ip:8338
```
@@ -289,6 +300,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://chacha20:123456@server_ip:8338
目前仅服务端支持UDP Relay。
服务端:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssu://chacha20:123456@:8338
```
diff --git a/README_en.md b/README_en.md
index 2213c53..d8d4f47 100644
--- a/README_en.md
+++ b/README_en.md
@@ -6,146 +6,55 @@ gost - GO Simple Tunnel
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/ginuerzh/gost)
[](https://travis-ci.org/ginuerzh/gost)
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/ginuerzh/gost)
-[](https://build.snapcraft.io/user/ginuerzh/gost)
+[](https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases/latest)
+[](https://build.snapcraft.io/user/ginuerzh/gost)
Features
------
* Listening on multiple ports
* Multi-level forward proxy - proxy chain
* Standard HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4(A)/SOCKS5 proxy protocols support
-* TLS encryption via negotiation support for SOCKS5 proxy
-* Tunnel UDP over TCP
-* Permission control
-* Local/remote TCP/UDP port forwarding (2.1+)
-* Shadowsocks protocol (UDP: 2.4+)
-* KCP protocol (2.3+)
-* Transparent TCP proxy (2.3+)
-* HTTP2 tunnel (2.4+)
-* SSH tunnel (2.4+)
-* QUIC tunnel (2.4+)
-* obfs4 tunnel (2.4+)
+* [Support multiple tunnel types](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/configuration/)
+* [TLS encryption via negotiation support for SOCKS5 proxy](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/socks/)
+* [Tunnel UDP over TCP](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/socks/)
+* [Transparent TCP proxy](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/redirect/)
+* [Local/remote TCP/UDP port forwarding](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/port-forwarding/)
+* [Shadowsocks protocol](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/ss/)
+* [SNI proxy](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/sni/)
+* [Permission control](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/permission/)
+* [Load balancing](https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/load-balancing/)
-Binary file download:https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases
+Wiki: https://docs.ginuerzh.xyz/gost/en/
Google group: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/go-gost
-Gost and other proxy services are considered to be proxy nodes,
-gost can handle the request itself, or forward the request to any one or more proxy nodes.
-
-
-Ubuntu Store
+Getting started
------
-Gost has been released in ubuntu store, and can be installed directly through the `snap` in ubuntu 16.04:
-```bash
-$ sudo snap install gost
-```
-
-
-Parameter Description
-------
-#### Proxy and proxy chain
-
-Effective for the -L and -F parameters
-
-```bash
-[scheme://][user:pass@host]:port
-```
-scheme can be divided into two parts: protocol+transport
-
-protocol: proxy protocol types (http, socks4(a), socks5, ss),
-transport: data transmission mode (ws, wss, tls, quic, kcp, ssh, h2, h2c, obfs4), may be used in any combination or individually:
-
-> http - standard HTTP proxy: http://:8080
-
-> https - standard HTTPS proxy (may need to provide a trusted certificate): http+tls://:443 or https://:443
-
-> http2 - HTTP2 proxy and backwards-compatible with HTTPS proxy: http2://:443
-
-> h2 - HTTP2 h2 tunnel: h2://:443
-
-> h2c - HTTP2 h2c tunnel: h2c://:443
-
-> socks4(a) - standard SOCKS4(A) proxy: socks4://:1080 or socks4a://:1080
-
-> socks5 - standard SOCKS5 proxy: socks5://:1080
-
-> socks5+wss - SOCKS5 over websocket: socks5+wss://:1080
-
-> tls - HTTPS/SOCKS5 over TLS: tls://:443
-
-> ss - standard shadowsocks proxy: ss://chacha20:123456@:8338
-
-> ssu - shadowsocks UDP relay server: ssu://chacha20:123456@:8338
-
-> quic - QUIC tunnel: quic://:6121
-
-> kcp - KCP tunnel: kcp://:8388
-
-> redirect - transparent proxy: redirect://:12345
-
-> ssh - SSH proxy tunnel: ssh://:2222, SSH forward tunnel: forward+ssh://:2222
-
-> obfs4 - obfs4 tunnel: obfs4://:8080
-
-#### Port forwarding
-
-Effective for the -L parameter
-
-```bash
-scheme://[bind_address]:port/[host]:hostport
-```
-> scheme - forward mode, local: tcp, udp; remote: rtcp, rudp
-
-> bind_address:port - local/remote binding address
-
-> host:hostport - target address
-
-#### Configuration file
-
-Contributed by [@septs](https://github.com/septs).
-
-> -C : specifies the configuration file path
-
-The configuration file is in standard JSON format:
-```json
-{
- "ServeNodes": [
- ":8080",
- "ss://chacha20:12345678@:8338"
- ],
- "ChainNodes": [
- "http://192.168.1.1:8080",
- "https://10.0.2.1:443"
- ],
- "Debug": true
-}
-```
-
-`ServeNodes` is equivalent to the `-L` parameter, `ChainNodes` is equivalent to the `-F` parameter, `Debug` is equivalent to the `-D` parameter.
-
-Usage
-------
#### No forward proxy
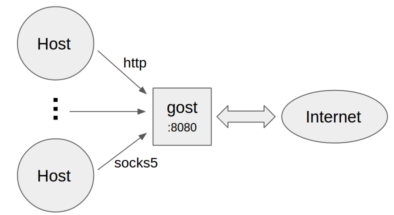 * Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080
```
* Proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
```
* Multiple sets of authentication information
+
```bash
gost -L=localhost:8080?secrets=secrets.txt
```
The secrets parameter allows you to set multiple authentication information for HTTP/SOCKS5 proxies, the format is:
+
```plain
# username password
@@ -154,6 +63,7 @@ test002 12345678
```
* Listen on multiple ports
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks5://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
@@ -167,6 +77,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
```
* Forward proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```
@@ -178,6 +89,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://192.168.1.1:6121 -F=socks5+wss://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=http2://192.168.1.3:443 ... -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
```
+
Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
@@ -186,6 +98,7 @@ each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
```bash
gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH forwad tunnel, then gost will use the local port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -197,6 +110,7 @@ gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
@@ -207,6 +121,7 @@ Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and the
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH tunnel, then gost will use the remote port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -218,44 +133,60 @@ gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy, gost will use UDP-over-TCP to forward data.
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 supports two modes:
+
* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Standard proxy
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443?ping=30
```
##### Tunnel
-服务端:
+
+Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=h2://:443
```
-客户端:
+
+Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=h2://server_ip:443
```
#### QUIC
+
Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=quic://:6121
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
```
@@ -266,16 +197,20 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
Support for KCP is based on libraries [kcp-go](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go) and [kcptun](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388
```
Gost will automatically load kcp.json configuration file from current working directory if exists,
or you can use the parameter to specify the path to the file.
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
```
@@ -283,27 +218,36 @@ gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
**NOTE:** KCP node can only be used as the first node of the proxy chain.
#### SSH
+
Gost SSH supports two modes:
+
* As a forward tunnel, used by local/remote TCP port forwarding.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Forward tunnel
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=forward+ssh://:2222
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:1222/:22 -F=forward+ssh://server_ip:2222
```
##### Transport tunnel
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssh://:2222
```
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ssh://server_ip:2222?ping=60
```
@@ -322,48 +266,61 @@ gost -L=redirect://:12345 -F=http2://server_ip:443
Contributed by [@isofew](https://github.com/isofew).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=obfs4://:443
```
When the server is running normally, the console prints out the connection address for the client to use:
-```
+
+```bash
obfs4://:443/?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0
```
Client:
-```
+
+```bash
gost -L=:8888 -F='obfs4://server_ip:443?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0'
```
Encryption Mechanism
------
+
#### HTTP
+
For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http+tls://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
```
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 proxy mode only supports the use of TLS encrypted HTTP2 protocol, does not support plaintext HTTP2.
Gost HTTP2 tunnel mode supports both encryption (h2) and plaintext (h2c) modes.
#### SOCKS5
+
Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80) and tls-auth(0x82).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=socks://:1080
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
```
@@ -375,95 +332,48 @@ Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
```
##### Shadowsocks UDP relay
+
Currently, only the server supports UDP Relay.
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssu://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
#### TLS
There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+
* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+
* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+
```bash
gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
```
Client can specify `secure` parameter to perform server's certificate chain and host name verification:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://server_domain_name:443?secure=true"
```
Client can specify a CA certificate to allow for [Certificate Pinning](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Certificate_pinning):
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://:443?ca=ca.pem"
```
+
Certificate Pinning is contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
-------
-#### No forward proxy
-
-
* Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080
```
* Proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
```
* Multiple sets of authentication information
+
```bash
gost -L=localhost:8080?secrets=secrets.txt
```
The secrets parameter allows you to set multiple authentication information for HTTP/SOCKS5 proxies, the format is:
+
```plain
# username password
@@ -154,6 +63,7 @@ test002 12345678
```
* Listen on multiple ports
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks5://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
@@ -167,6 +77,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
```
* Forward proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```
@@ -178,6 +89,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://192.168.1.1:6121 -F=socks5+wss://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=http2://192.168.1.3:443 ... -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
```
+
Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
@@ -186,6 +98,7 @@ each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
```bash
gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH forwad tunnel, then gost will use the local port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -197,6 +110,7 @@ gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
@@ -207,6 +121,7 @@ Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and the
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH tunnel, then gost will use the remote port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -218,44 +133,60 @@ gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy, gost will use UDP-over-TCP to forward data.
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 supports two modes:
+
* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Standard proxy
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443?ping=30
```
##### Tunnel
-服务端:
+
+Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=h2://:443
```
-客户端:
+
+Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=h2://server_ip:443
```
#### QUIC
+
Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=quic://:6121
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
```
@@ -266,16 +197,20 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
Support for KCP is based on libraries [kcp-go](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go) and [kcptun](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388
```
Gost will automatically load kcp.json configuration file from current working directory if exists,
or you can use the parameter to specify the path to the file.
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
```
@@ -283,27 +218,36 @@ gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
**NOTE:** KCP node can only be used as the first node of the proxy chain.
#### SSH
+
Gost SSH supports two modes:
+
* As a forward tunnel, used by local/remote TCP port forwarding.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Forward tunnel
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=forward+ssh://:2222
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:1222/:22 -F=forward+ssh://server_ip:2222
```
##### Transport tunnel
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssh://:2222
```
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ssh://server_ip:2222?ping=60
```
@@ -322,48 +266,61 @@ gost -L=redirect://:12345 -F=http2://server_ip:443
Contributed by [@isofew](https://github.com/isofew).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=obfs4://:443
```
When the server is running normally, the console prints out the connection address for the client to use:
-```
+
+```bash
obfs4://:443/?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0
```
Client:
-```
+
+```bash
gost -L=:8888 -F='obfs4://server_ip:443?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0'
```
Encryption Mechanism
------
+
#### HTTP
+
For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http+tls://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
```
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 proxy mode only supports the use of TLS encrypted HTTP2 protocol, does not support plaintext HTTP2.
Gost HTTP2 tunnel mode supports both encryption (h2) and plaintext (h2c) modes.
#### SOCKS5
+
Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80) and tls-auth(0x82).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=socks://:1080
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
```
@@ -375,95 +332,48 @@ Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
```
##### Shadowsocks UDP relay
+
Currently, only the server supports UDP Relay.
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssu://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
#### TLS
There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+
* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+
* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+
```bash
gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
```
Client can specify `secure` parameter to perform server's certificate chain and host name verification:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://server_domain_name:443?secure=true"
```
Client can specify a CA certificate to allow for [Certificate Pinning](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Certificate_pinning):
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://:443?ca=ca.pem"
```
+
Certificate Pinning is contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
-------
-#### No forward proxy
-
-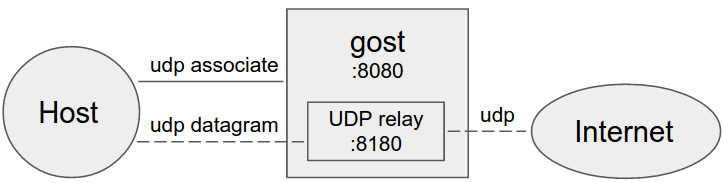 -
-Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
-
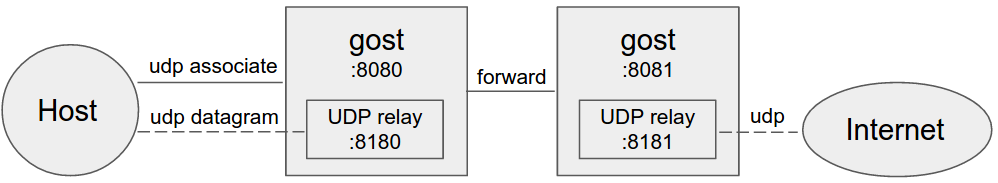
-#### Forward proxy
-
-
-
-Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
-
-#### Forward proxy
-
- -
-#### Multi-level forward proxy
-
-
-
-#### Multi-level forward proxy
-
-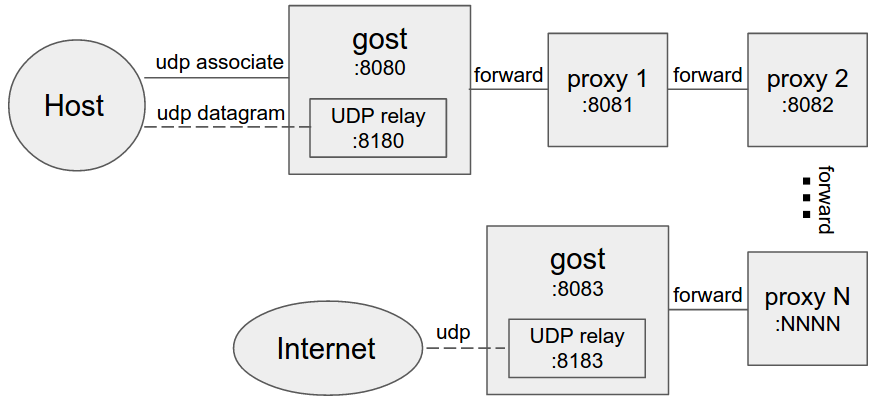 -
-When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
-
-Permission control
-------
-Contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-One can pass available permissions with `whitelist` and `blacklist` values when starting a socks and ssh server. The format for each rule is as follows: `[actions]:[hosts]:[ports]`.
-
-`[actions]` are comma-separted list of allowed actions: `rtcp`, `rudp`, `tcp`, `udp`. can be `*` to encompass all actions.
-
-`[hosts]` are comma-separated list of allowed hosts that one can bind on (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`). hosts support globs, like `*.google.com`. can be `*` to encompass all hosts.
-
-`[ports]` are comma-separated list of ports that one can bind to (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`), can be `*` to encompass all ports.
-
-Multiple permissions can be passed if seperated with `+`:
-
-`rtcp,rudp:localhost,127.0.0.1:2222,8000-9000+udp:8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4:53` (allow for reverse tcp and udp binding on localhost and 127.0.0.1 on ports 2222 and 8000-9000 port range, plus allow for udp forwarding to 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 on port 53)
-
-SSH remote port forwarding can only bind on 127.0.0.1:8000
-```bash
-gost -L=forward+ssh://localhost:8389?whitelist=rtcp:127.0.0.1:8000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 TCP/UDP remote port forwarding can only bind on ports greater than 1000
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?blacklist=rtcp,rudp:*:0-1000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 UDP forwading can only forward to 8.8.8.8:53
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?whitelist=udp:8.8.8.8:53
-```
-
-Limitation
-------
-The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
-
-If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
-
-
-
-
-When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
-
-Permission control
-------
-Contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-One can pass available permissions with `whitelist` and `blacklist` values when starting a socks and ssh server. The format for each rule is as follows: `[actions]:[hosts]:[ports]`.
-
-`[actions]` are comma-separted list of allowed actions: `rtcp`, `rudp`, `tcp`, `udp`. can be `*` to encompass all actions.
-
-`[hosts]` are comma-separated list of allowed hosts that one can bind on (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`). hosts support globs, like `*.google.com`. can be `*` to encompass all hosts.
-
-`[ports]` are comma-separated list of ports that one can bind to (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`), can be `*` to encompass all ports.
-
-Multiple permissions can be passed if seperated with `+`:
-
-`rtcp,rudp:localhost,127.0.0.1:2222,8000-9000+udp:8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4:53` (allow for reverse tcp and udp binding on localhost and 127.0.0.1 on ports 2222 and 8000-9000 port range, plus allow for udp forwarding to 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 on port 53)
-
-SSH remote port forwarding can only bind on 127.0.0.1:8000
-```bash
-gost -L=forward+ssh://localhost:8389?whitelist=rtcp:127.0.0.1:8000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 TCP/UDP remote port forwarding can only bind on ports greater than 1000
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?blacklist=rtcp,rudp:*:0-1000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 UDP forwading can only forward to 8.8.8.8:53
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?whitelist=udp:8.8.8.8:53
-```
-
-Limitation
-------
-The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
-
-If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
-
-
-
 * Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080
```
* Proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
```
* Multiple sets of authentication information
+
```bash
gost -L=localhost:8080?secrets=secrets.txt
```
The secrets parameter allows you to set multiple authentication information for HTTP/SOCKS5 proxies, the format is:
+
```plain
# username password
@@ -154,6 +63,7 @@ test002 12345678
```
* Listen on multiple ports
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks5://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
@@ -167,6 +77,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
```
* Forward proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```
@@ -178,6 +89,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://192.168.1.1:6121 -F=socks5+wss://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=http2://192.168.1.3:443 ... -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
```
+
Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
@@ -186,6 +98,7 @@ each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
```bash
gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH forwad tunnel, then gost will use the local port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -197,6 +110,7 @@ gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
@@ -207,6 +121,7 @@ Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and the
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH tunnel, then gost will use the remote port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -218,44 +133,60 @@ gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy, gost will use UDP-over-TCP to forward data.
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 supports two modes:
+
* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Standard proxy
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443?ping=30
```
##### Tunnel
-服务端:
+
+Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=h2://:443
```
-客户端:
+
+Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=h2://server_ip:443
```
#### QUIC
+
Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=quic://:6121
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
```
@@ -266,16 +197,20 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
Support for KCP is based on libraries [kcp-go](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go) and [kcptun](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388
```
Gost will automatically load kcp.json configuration file from current working directory if exists,
or you can use the parameter to specify the path to the file.
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
```
@@ -283,27 +218,36 @@ gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
**NOTE:** KCP node can only be used as the first node of the proxy chain.
#### SSH
+
Gost SSH supports two modes:
+
* As a forward tunnel, used by local/remote TCP port forwarding.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Forward tunnel
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=forward+ssh://:2222
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:1222/:22 -F=forward+ssh://server_ip:2222
```
##### Transport tunnel
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssh://:2222
```
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ssh://server_ip:2222?ping=60
```
@@ -322,48 +266,61 @@ gost -L=redirect://:12345 -F=http2://server_ip:443
Contributed by [@isofew](https://github.com/isofew).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=obfs4://:443
```
When the server is running normally, the console prints out the connection address for the client to use:
-```
+
+```bash
obfs4://:443/?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0
```
Client:
-```
+
+```bash
gost -L=:8888 -F='obfs4://server_ip:443?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0'
```
Encryption Mechanism
------
+
#### HTTP
+
For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http+tls://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
```
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 proxy mode only supports the use of TLS encrypted HTTP2 protocol, does not support plaintext HTTP2.
Gost HTTP2 tunnel mode supports both encryption (h2) and plaintext (h2c) modes.
#### SOCKS5
+
Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80) and tls-auth(0x82).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=socks://:1080
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
```
@@ -375,95 +332,48 @@ Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
```
##### Shadowsocks UDP relay
+
Currently, only the server supports UDP Relay.
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssu://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
#### TLS
There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+
* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+
* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+
```bash
gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
```
Client can specify `secure` parameter to perform server's certificate chain and host name verification:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://server_domain_name:443?secure=true"
```
Client can specify a CA certificate to allow for [Certificate Pinning](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Certificate_pinning):
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://:443?ca=ca.pem"
```
+
Certificate Pinning is contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
-------
-#### No forward proxy
-
-
* Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080
```
* Proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
```
* Multiple sets of authentication information
+
```bash
gost -L=localhost:8080?secrets=secrets.txt
```
The secrets parameter allows you to set multiple authentication information for HTTP/SOCKS5 proxies, the format is:
+
```plain
# username password
@@ -154,6 +63,7 @@ test002 12345678
```
* Listen on multiple ports
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks5://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
@@ -167,6 +77,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
```
* Forward proxy authentication
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```
@@ -178,6 +89,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://192.168.1.1:6121 -F=socks5+wss://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=http2://192.168.1.3:443 ... -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
```
+
Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
@@ -186,6 +98,7 @@ each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
```bash
gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH forwad tunnel, then gost will use the local port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -197,6 +110,7 @@ gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=...]
```
+
The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
@@ -207,6 +121,7 @@ Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and the
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH tunnel, then gost will use the remote port forwarding function of SSH directly:
```bash
@@ -218,44 +133,60 @@ gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222
```bash
gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]
```
+
The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the `ttl` parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy, gost will use UDP-over-TCP to forward data.
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 supports two modes:
+
* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Standard proxy
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http2://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443?ping=30
```
##### Tunnel
-服务端:
+
+Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=h2://:443
```
-客户端:
+
+Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=h2://server_ip:443
```
#### QUIC
+
Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=quic://:6121
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
```
@@ -266,16 +197,20 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121
Support for KCP is based on libraries [kcp-go](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go) and [kcptun](https://github.com/xtaci/kcptun).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388
```
Gost will automatically load kcp.json configuration file from current working directory if exists,
or you can use the parameter to specify the path to the file.
+
```bash
gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
```
@@ -283,27 +218,36 @@ gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/file
**NOTE:** KCP node can only be used as the first node of the proxy chain.
#### SSH
+
Gost SSH supports two modes:
+
* As a forward tunnel, used by local/remote TCP port forwarding.
+
* As a transport tunnel.
##### Forward tunnel
+
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=forward+ssh://:2222
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=rtcp://:1222/:22 -F=forward+ssh://server_ip:2222
```
##### Transport tunnel
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssh://:2222
```
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ssh://server_ip:2222?ping=60
```
@@ -322,48 +266,61 @@ gost -L=redirect://:12345 -F=http2://server_ip:443
Contributed by [@isofew](https://github.com/isofew).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=obfs4://:443
```
When the server is running normally, the console prints out the connection address for the client to use:
-```
+
+```bash
obfs4://:443/?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0
```
Client:
-```
+
+```bash
gost -L=:8888 -F='obfs4://server_ip:443?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0'
```
Encryption Mechanism
------
+
#### HTTP
+
For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=http+tls://:443
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
```
#### HTTP2
+
Gost HTTP2 proxy mode only supports the use of TLS encrypted HTTP2 protocol, does not support plaintext HTTP2.
Gost HTTP2 tunnel mode supports both encryption (h2) and plaintext (h2c) modes.
#### SOCKS5
+
Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80) and tls-auth(0x82).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=socks://:1080
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
```
@@ -375,95 +332,48 @@ Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
+
Client:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
```
##### Shadowsocks UDP relay
+
Currently, only the server supports UDP Relay.
Server:
+
```bash
gost -L=ssu://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
```
#### TLS
There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+
* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+
* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+
```bash
gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
```
Client can specify `secure` parameter to perform server's certificate chain and host name verification:
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://server_domain_name:443?secure=true"
```
Client can specify a CA certificate to allow for [Certificate Pinning](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Certificate_pinning):
+
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://:443?ca=ca.pem"
```
+
Certificate Pinning is contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
-------
-#### No forward proxy
-
- -
-Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
-
-#### Forward proxy
-
-
-
-Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
-
-#### Forward proxy
-
- -
-#### Multi-level forward proxy
-
-
-
-#### Multi-level forward proxy
-
- -
-When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
-
-Permission control
-------
-Contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-One can pass available permissions with `whitelist` and `blacklist` values when starting a socks and ssh server. The format for each rule is as follows: `[actions]:[hosts]:[ports]`.
-
-`[actions]` are comma-separted list of allowed actions: `rtcp`, `rudp`, `tcp`, `udp`. can be `*` to encompass all actions.
-
-`[hosts]` are comma-separated list of allowed hosts that one can bind on (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`). hosts support globs, like `*.google.com`. can be `*` to encompass all hosts.
-
-`[ports]` are comma-separated list of ports that one can bind to (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`), can be `*` to encompass all ports.
-
-Multiple permissions can be passed if seperated with `+`:
-
-`rtcp,rudp:localhost,127.0.0.1:2222,8000-9000+udp:8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4:53` (allow for reverse tcp and udp binding on localhost and 127.0.0.1 on ports 2222 and 8000-9000 port range, plus allow for udp forwarding to 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 on port 53)
-
-SSH remote port forwarding can only bind on 127.0.0.1:8000
-```bash
-gost -L=forward+ssh://localhost:8389?whitelist=rtcp:127.0.0.1:8000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 TCP/UDP remote port forwarding can only bind on ports greater than 1000
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?blacklist=rtcp,rudp:*:0-1000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 UDP forwading can only forward to 8.8.8.8:53
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?whitelist=udp:8.8.8.8:53
-```
-
-Limitation
-------
-The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
-
-If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
-
-
-
-
-When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
-
-Permission control
-------
-Contributed by [@sheerun](https://github.com/sheerun).
-
-One can pass available permissions with `whitelist` and `blacklist` values when starting a socks and ssh server. The format for each rule is as follows: `[actions]:[hosts]:[ports]`.
-
-`[actions]` are comma-separted list of allowed actions: `rtcp`, `rudp`, `tcp`, `udp`. can be `*` to encompass all actions.
-
-`[hosts]` are comma-separated list of allowed hosts that one can bind on (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`). hosts support globs, like `*.google.com`. can be `*` to encompass all hosts.
-
-`[ports]` are comma-separated list of ports that one can bind to (in case of `rtcp` and `rudp`), or forward to (incase of `tcp` and `udp`), can be `*` to encompass all ports.
-
-Multiple permissions can be passed if seperated with `+`:
-
-`rtcp,rudp:localhost,127.0.0.1:2222,8000-9000+udp:8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4:53` (allow for reverse tcp and udp binding on localhost and 127.0.0.1 on ports 2222 and 8000-9000 port range, plus allow for udp forwarding to 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 on port 53)
-
-SSH remote port forwarding can only bind on 127.0.0.1:8000
-```bash
-gost -L=forward+ssh://localhost:8389?whitelist=rtcp:127.0.0.1:8000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 TCP/UDP remote port forwarding can only bind on ports greater than 1000
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?blacklist=rtcp,rudp:*:0-1000
-```
-
-SOCKS5 UDP forwading can only forward to 8.8.8.8:53
-```bash
-gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?whitelist=udp:8.8.8.8:53
-```
-
-Limitation
-------
-The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
-
-If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
-
-
-