diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 84d253f..a01b653 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -3,6 +3,8 @@ gost - GO Simple Tunnel
### GO语言实现的安全隧道
+[English README](README_en.md)
+
特性
------
* 可同时监听多端口
@@ -10,9 +12,10 @@ gost - GO Simple Tunnel
* 支持标准HTTP/HTTPS/SOCKS5代理协议
* SOCKS5代理支持TLS协商加密
* Tunnel UDP over TCP
-* 支持Shadowsocks协议,支持OTA (OTA功能需2.2及以上版本)
-* 支持端口转发 (2.1及以上版本)
-* 支持HTTP2.0 (2.2及以上版本)
+* 支持Shadowsocks协议,支持OTA (OTA: >=2.2)
+* 支持端口转发 (>=2.1)
+* 支持HTTP2.0 (>=2.2)
+* 实验性支持QUIC (>=2.3)
二进制文件下载:https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases
@@ -31,21 +34,23 @@ Google讨论组: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/go-gost
```
scheme分为两部分: protocol+transport
-protocol: 代理协议类型(http, socks5, shadowsocks), transport: 数据传输方式(ws, wss, tls, http2), 二者可以任意组合,或单独使用:
+protocol: 代理协议类型(http, socks5, shadowsocks), transport: 数据传输方式(ws, wss, tls, http2, quic), 二者可以任意组合,或单独使用:
> http - 作为HTTP代理: http://:8080
-> http+tls - 作为HTTPS代理(可能需要提供受信任的证书): http+tls://:8080
+> http+tls - 作为HTTPS代理(可能需要提供受信任的证书): http+tls://:443
> http2 - 作为HTTP2代理并向下兼容HTTPS代理: http2://:443
-> socks - 作为标准SOCKS5代理(支持tls协商加密): socks://:8080
+> socks - 作为标准SOCKS5代理(支持tls协商加密): socks://:1080
-> socks+ws - 作为SOCKS5代理,使用websocket传输数据: socks+ws://:8080
+> socks+wss - 作为SOCKS5代理,使用websocket传输数据: socks+wss://:1080
-> tls - 作为HTTPS/SOCKS5代理,使用tls传输数据: tls://:8080
+> tls - 作为HTTPS/SOCKS5代理,使用tls传输数据: tls://:443
-> ss - 作为Shadowsocks服务,ss://aes-256-cfb:123456@:8080
+> ss - 作为Shadowsocks服务,ss://aes-256-cfb:123456@:8338
+
+> quic - 作为QUIC代理,quic://:6121
#### 端口转发
@@ -66,7 +71,7 @@ scheme://[bind_address]:port/[host]:hostport
> -v=4 : 日志级别(1-5),级别越高,日志越详细(级别5将开启http2 debug)
-> -log_dir=. : 输出到目录
+> -log_dir=/log/dir/path : 输出到目录/log/dir/path
使用方法
@@ -108,7 +113,7 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
```bash
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
```
-gost按照-F设置顺序通过代理链将请求最终转发给a.b.c.d:NNNN处理,每一个转发代理可以是任意HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks类型代理。
+gost按照-F设置的顺序通过代理链将请求最终转发给a.b.c.d:NNNN处理,每一个转发代理可以是任意HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks类型代理。
#### 本地端口转发(TCP)
@@ -124,7 +129,7 @@ gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
```
将本地UDP端口5353上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:53上。
-**注: 转发UDP数据时,如果有代理链,则代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须支持gost SOCKS5类型代理。**
+**注:** 转发UDP数据时,如果有代理链,则代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须是gost SOCKS5类型代理。
#### 远程端口转发(TCP)
@@ -140,14 +145,29 @@ gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
```
将172.24.10.1:5353上的数据(通过代理链)转发到192.168.1.1:53上。
-**注: 若要使用远程端口转发功能,代理链不能为空(至少要设置一个-F参数),且代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须支持gost SOCKS5类型代理。**
+**注:** 若要使用远程端口转发功能,代理链不能为空(至少要设置一个-F参数),且代理链的末端(最后一个-F参数)必须是gost SOCKS5类型代理。
#### HTTP2
gost的HTTP2支持两种模式并自适应:
* 作为标准的HTTP2代理,并向下兼容HTTPS代理。
* 作为transport(类似于wss),传输其他协议。
-**注:gost的代理链仅支持一个HTTP2代理节点,采用就近原则,会将第一个遇到的HTTP2代理节点视为HTTP2代理,其他HTTP2代理节点则被视为HTTPS代理。**
+**注:** gost的代理链仅支持一个HTTP2代理节点,采用就近原则,会将第一个遇到的HTTP2代理节点视为HTTP2代理,其他HTTP2代理节点则被视为HTTPS代理。
+
+#### QUIC
+gost对QUIC的支持是基于[quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go)库。
+
+服务端:
+```bash
+gost -L=quic://:6121
+```
+
+客户端(Chrome):
+```bash
+chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
+```
+
+**注:** 由于Chrome自身的限制,目前只能通过QUIC访问HTTP网站,无法访问HTTPS网站。
加密机制
------
@@ -189,10 +209,10 @@ gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
如果两端都是gost(如上)则数据传输会被加密(协商使用tls或tls-auth方法),否则使用标准SOCKS5进行通讯(no-auth或user/pass方法)。
-注:如果transport已经支持加密(wss, tls, http2),则SOCKS5不会再使用加密方法,防止不必要的双重加密。
+**注:** 如果transport已经支持加密(wss, tls, http2),则SOCKS5不会再使用加密方法,防止不必要的双重加密。
#### Shadowsocks
-gost对Shadowsocks加密方法的支持是基于[shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go)库。
+gost对shadowsocks的支持是基于[shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go)库。
服务端(可以通过ota参数开启OTA模式):
```bash
diff --git a/README_en.md b/README_en.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..98360d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/README_en.md
@@ -0,0 +1,263 @@
+gost - GO Simple Tunnel
+======
+
+### A simple security tunnel written in Golang
+
+Features
+------
+* Listening on multiple ports
+* Multi-level forward proxy - proxy chain
+* Standard HTTP/HTTPS/SOCKS5 proxy protocols
+* TLS encryption via negotiation support for SOCKS5 proxy
+* Tunnel UDP over TCP
+* Shadowsocks protocol with OTA supported (OTA: >=2.2)
+* Local/remote port forwarding (>=2.1)
+* HTTP2.0 (>=2.2)
+* Experimental QUIC support (>=2.3)
+
+Binary file download:https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases
+
+Google group: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/go-gost
+
+Gost and other proxy services are considered to be proxy nodes,
+gost can handle the request itself, or forward the request to any one or more proxy nodes.
+
+Parameter Description
+------
+#### Proxy and proxy chain
+
+Effective for the -L and -F parameters
+
+```bash
+[scheme://][user:pass@host]:port
+```
+scheme can be divided into two parts: protocol+transport
+
+protocol: proxy protocol types(http, socks5, shadowsocks),
+transport: data transmission mode(ws, wss, tls, http2, quic), may be used in any combination or individually:
+
+> http - standard HTTP proxy: http://:8080
+
+> http+tls - standard HTTPS proxy(may need to provide a trusted certificate): http+tls://:443
+
+> http2 - HTTP2 proxy and backwards-compatible with HTTPS proxy: http2://:443
+
+> socks - standard SOCKS5 proxy: socks://:1080
+
+> socks+wss - SOCKS5 over websocket: socks+wss://:1080
+
+> tls - HTTPS/SOCKS5 over tls: tls://:443
+
+> ss - standard shadowsocks proxy, ss://aes-256-cfb:123456@:8338
+
+> quic - standard QUIC proxy, quic://:6121
+
+#### Port forwarding
+
+Effective for the -L parameter
+
+```bash
+scheme://[bind_address]:port/[host]:hostport
+```
+> scheme - forward mode, local: tcp, udp; remote: rtcp, rudp
+
+> bind_address:port - local/remote binding address
+
+> host:hostport - target address
+
+#### Logging
+
+> -logtostderr : log to console
+
+> -v=4 : log level(1-5),The higher the level, the more detailed the log (level 5 will enable HTTP2 debug)
+
+> -log_dir=/log/dir/path : log to directory /log/dir/path
+
+Usage
+------
+#### No forward proxy
+
+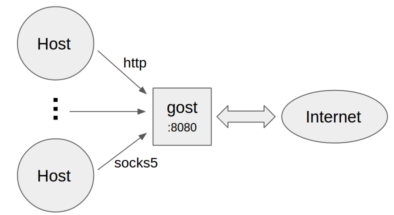 +
+* Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080
+```
+
+* Proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
+```
+
+* Listen on multiple ports
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
+```
+
+#### Forward proxy
+
+
+
+* Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080
+```
+
+* Proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
+```
+
+* Listen on multiple ports
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
+```
+
+#### Forward proxy
+
+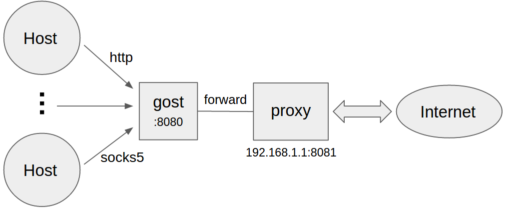 +```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+* Forward proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+* Forward proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+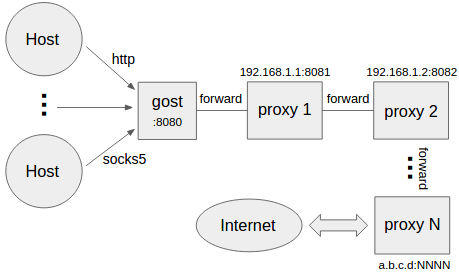 +```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
+```
+Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
+each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+#### Local TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Local UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### Remote TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Remote UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** To use the remote port forwarding feature, the proxy chain can not be empty (at least one -F parameter is set)
+and the end of the chain (last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost HTTP2 supports two modes and self-adapting:
+* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+* As transport (similar to wss), tunnel other protocol.
+
+**NOTE:** The proxy chain of gost supports only one HTTP2 proxy node and the nearest rule applies,
+the first HTTP2 proxy node is treated as an HTTP2 proxy, and the other HTTP2 proxy nodes are treated as HTTPS proxies.
+
+#### QUIC
+Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=quic://:6121
+```
+
+Client(Chrome):
+```bash
+chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
+```
+
+**NOTE:** Due to Chrome's limitations, it is currently only possible to access the HTTP (but not HTTPS) site through QUIC.
+
+Encryption Mechanism
+------
+#### HTTP
+For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http+tls://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost supports only the HTTP2 protocol that uses TLS encryption (h2) and does not support plaintext HTTP2 (h2c) transport.
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### SOCKS5
+Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
+and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80)和tls-auth(0x82).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=socks://:1080
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
+```
+
+If both ends are gosts (as example above), the data transfer will be encrypted (using tls or tls-auth).
+Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
+
+**NOTE:** If transport already supports encryption (wss, tls, http2), SOCKS5 will no longer use the encryption method to prevent unnecessary double encryption.
+
+#### Shadowsocks
+Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
+
+Server (The OTA mode can be enabled by the ota parameter):
+```bash
+gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338?ota=1
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
+```
+
+#### TLS
+There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+```bash
+gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
+```
+
+SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
+------
+#### No forward proxy
+
+
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
+```
+Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
+each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+#### Local TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Local UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### Remote TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Remote UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** To use the remote port forwarding feature, the proxy chain can not be empty (at least one -F parameter is set)
+and the end of the chain (last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost HTTP2 supports two modes and self-adapting:
+* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+* As transport (similar to wss), tunnel other protocol.
+
+**NOTE:** The proxy chain of gost supports only one HTTP2 proxy node and the nearest rule applies,
+the first HTTP2 proxy node is treated as an HTTP2 proxy, and the other HTTP2 proxy nodes are treated as HTTPS proxies.
+
+#### QUIC
+Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=quic://:6121
+```
+
+Client(Chrome):
+```bash
+chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
+```
+
+**NOTE:** Due to Chrome's limitations, it is currently only possible to access the HTTP (but not HTTPS) site through QUIC.
+
+Encryption Mechanism
+------
+#### HTTP
+For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http+tls://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost supports only the HTTP2 protocol that uses TLS encryption (h2) and does not support plaintext HTTP2 (h2c) transport.
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### SOCKS5
+Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
+and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80)和tls-auth(0x82).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=socks://:1080
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
+```
+
+If both ends are gosts (as example above), the data transfer will be encrypted (using tls or tls-auth).
+Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
+
+**NOTE:** If transport already supports encryption (wss, tls, http2), SOCKS5 will no longer use the encryption method to prevent unnecessary double encryption.
+
+#### Shadowsocks
+Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
+
+Server (The OTA mode can be enabled by the ota parameter):
+```bash
+gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338?ota=1
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
+```
+
+#### TLS
+There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+```bash
+gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
+```
+
+SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
+------
+#### No forward proxy
+
+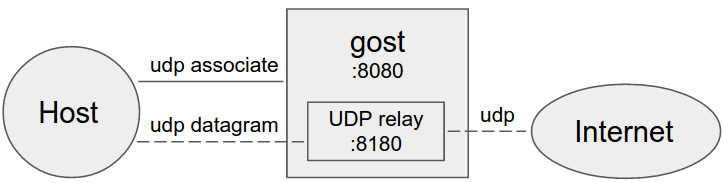 +
+Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
+
+#### Forward proxy
+
+
+
+Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
+
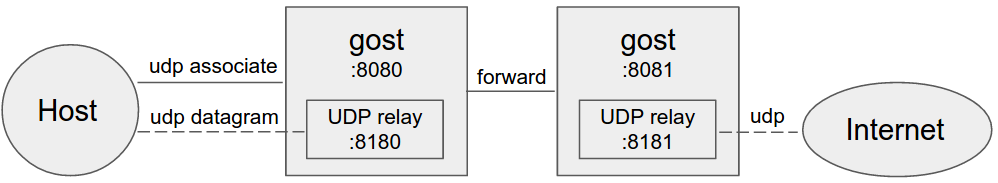
+#### Forward proxy
+
+ +
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+
+
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+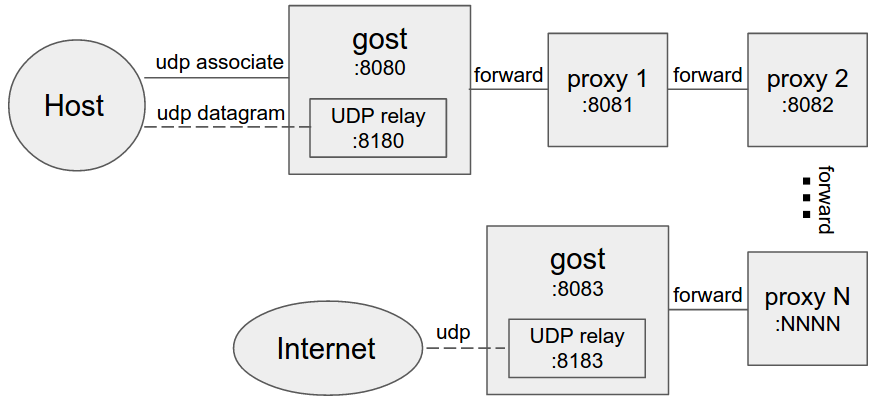 +
+When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+Limitation
+------
+The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
+
+If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+
+
+
+When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+Limitation
+------
+The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
+
+If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+
+
 +
+* Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080
+```
+
+* Proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
+```
+
+* Listen on multiple ports
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
+```
+
+#### Forward proxy
+
+
+
+* Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080
+```
+
+* Proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080
+```
+
+* Listen on multiple ports
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338
+```
+
+#### Forward proxy
+
+ +```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+* Forward proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+* Forward proxy authentication
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081
+```
+
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+ +```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
+```
+Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
+each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+#### Local TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Local UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### Remote TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Remote UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** To use the remote port forwarding feature, the proxy chain can not be empty (at least one -F parameter is set)
+and the end of the chain (last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost HTTP2 supports two modes and self-adapting:
+* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+* As transport (similar to wss), tunnel other protocol.
+
+**NOTE:** The proxy chain of gost supports only one HTTP2 proxy node and the nearest rule applies,
+the first HTTP2 proxy node is treated as an HTTP2 proxy, and the other HTTP2 proxy nodes are treated as HTTPS proxies.
+
+#### QUIC
+Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=quic://:6121
+```
+
+Client(Chrome):
+```bash
+chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
+```
+
+**NOTE:** Due to Chrome's limitations, it is currently only possible to access the HTTP (but not HTTPS) site through QUIC.
+
+Encryption Mechanism
+------
+#### HTTP
+For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http+tls://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost supports only the HTTP2 protocol that uses TLS encryption (h2) and does not support plaintext HTTP2 (h2c) transport.
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### SOCKS5
+Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
+and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80)和tls-auth(0x82).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=socks://:1080
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
+```
+
+If both ends are gosts (as example above), the data transfer will be encrypted (using tls or tls-auth).
+Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
+
+**NOTE:** If transport already supports encryption (wss, tls, http2), SOCKS5 will no longer use the encryption method to prevent unnecessary double encryption.
+
+#### Shadowsocks
+Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
+
+Server (The OTA mode can be enabled by the ota parameter):
+```bash
+gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338?ota=1
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
+```
+
+#### TLS
+There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+```bash
+gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
+```
+
+SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
+------
+#### No forward proxy
+
+
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://192.168.1.1:443 -F=socks+ws://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@192.168.1.3:8338 -F=a.b.c.d:NNNN
+```
+Gost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F,
+each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+#### Local TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Local UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=...
+```
+The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### Remote TCP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain).
+
+#### Remote UDP port forwarding
+
+```bash
+gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53 -F=... -F=socks://172.24.10.1:1080
+```
+The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
+
+**NOTE:** To use the remote port forwarding feature, the proxy chain can not be empty (at least one -F parameter is set)
+and the end of the chain (last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost HTTP2 supports two modes and self-adapting:
+* As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
+* As transport (similar to wss), tunnel other protocol.
+
+**NOTE:** The proxy chain of gost supports only one HTTP2 proxy node and the nearest rule applies,
+the first HTTP2 proxy node is treated as an HTTP2 proxy, and the other HTTP2 proxy nodes are treated as HTTPS proxies.
+
+#### QUIC
+Support for QUIC is based on library [quic-go](https://github.com/lucas-clemente/quic-go).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=quic://:6121
+```
+
+Client(Chrome):
+```bash
+chrome --enable-quic --proxy-server=quic://server_ip:6121
+```
+
+**NOTE:** Due to Chrome's limitations, it is currently only possible to access the HTTP (but not HTTPS) site through QUIC.
+
+Encryption Mechanism
+------
+#### HTTP
+For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http+tls://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### HTTP2
+Gost supports only the HTTP2 protocol that uses TLS encryption (h2) and does not support plaintext HTTP2 (h2c) transport.
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=http2://:443
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443
+```
+
+#### SOCKS5
+Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02),
+and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80)和tls-auth(0x82).
+
+Server:
+```bash
+gost -L=socks://:1080
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080
+```
+
+If both ends are gosts (as example above), the data transfer will be encrypted (using tls or tls-auth).
+Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
+
+**NOTE:** If transport already supports encryption (wss, tls, http2), SOCKS5 will no longer use the encryption method to prevent unnecessary double encryption.
+
+#### Shadowsocks
+Support for shadowsocks is based on library [shadowsocks-go](https://github.com/shadowsocks/shadowsocks-go).
+
+Server (The OTA mode can be enabled by the ota parameter):
+```bash
+gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338?ota=1
+```
+Client:
+```bash
+gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338
+```
+
+#### TLS
+There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
+* Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
+* Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
+```bash
+gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"
+```
+
+SOCKS5 UDP Data Processing
+------
+#### No forward proxy
+
+ +
+Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
+
+#### Forward proxy
+
+
+
+Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
+
+#### Forward proxy
+
+ +
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+
+
+#### Multi-level forward proxy
+
+ +
+When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+Limitation
+------
+The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
+
+If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+
+
+
+When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
+
+Limitation
+------
+The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
+
+If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.
+
+
+